Prince is a general term for a ruler, monarch or member of a monarch's or former monarch's family, and is a hereditary title in the nobility of some European states. The feminine equivalent is a princess. The English word derives, via the French word ''prince'', from the Latin noun ''princeps'', from ''primus''(first) + ''capio''(to seize), meaning "the chief, most distinguished, ruler, prince".
Historical background
The
Latin word ''prīnceps'' (older Latin *prīsmo-kaps, literally "the one who takes the first [place/position]"), became the usual title of the informal leader of the
Roman senate some centuries before the transition to
empire, the ''
princeps senatus''.
Emperor Augustus established the formal position of monarch on the basis of ''principate'', not ''dominion''. He also tasked his grandsons as summer rulers of the city when most of the government were on holiday in the country or attending religious rituals, and, for that task, granted them the title of ''princeps''.
The title has generic and substantive meanings:
generically, ''prince'' refers to members of a family that ruled by hereditary right, the title being used to refer either to sovereigns or to cadets of a sovereign's family. The term may be broadly used of persons in various cultures, continents or eras. In Europe, it is the title legally borne by dynastic cadets in monarchies, and borne by courtesy by members of formerly reigning dynasties.
as a substantive title, a ''prince'' was a monarch of the lowest rank in post-Napoleonic Europe, e.g. Princes of, respectively, Andorra, Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen, Mingrelia, Monaco, Waldeck and Pyrmont, Wallachia, etc.
also substantively, the title was granted by popes and secular monarchs to specific individuals and to the heads of some high-ranking European families who, however, never exercised dynastic sovereignty and whose cadets are not entitled to share the princely title, e.g. de Beauvau-Craon, Colonna, von Bismarck, von Dohna-Schlobitten, von Eulenburg, de Faucigny-Lucinge, von Lichnowsky, von Pless, Ruffo di Calabria, (de Talleyrand) von Sagan, van Ursel, etc.
generically, cadets of some non-sovereign families whose head bears the non-dynastic title of prince (or, less commonly, duke) were sometimes also authorized to use the princely title, e.g. von Carolath-Beuthen, de Broglie, Demidoff di San Donato, Lieven, de Mérode, Pignatelli, Radziwill, von Wrede, Yussopov, etc.
substantively, the heirs apparent in some monarchies use a specific princely title associated with a territory within the monarch's realm, e.g. the Princes of, respectively, Asturias (Spain), Grão Pará (Brazil, formerly), Orange (Netherlands), Viana (Navarre, formerly), Wales (UK), etc.
substantively, it became the fashion from the 17th century for the heirs apparent of the leading ducal families to assume a princely title, associated with a ''seigneurie'' in the family's possession. These titles were borne by courtesy and preserved by tradition, not law, e.g. the ''princes de'', respectively, Bidache (Gramont), Marcillac (La Rochefoucauld), Tonnay-Charente (Mortemart), Poix (Noailles), Léon (Rohan-Chabot),
Prince as generic for ruler
The original, but now less common use of the word, originated in the application of the Latin word ''
princeps'', from
Roman, more precisely
Byzantine law, and the classical system of government that was the European
feudal society. In this sense, a prince is a ruler of a territory which is
sovereign, or
quasi-sovereign, i.e., exercising substantial (though not all) prerogatives associated with monarchs of independent nations, as was common, for instance, within the historical boundaries of the
Holy Roman Empire. In
medieval and
Early Modern Europe, there were as many as two hundred such territories, especially in Italy, Germany, and
Gaelic Ireland. In this sense, "prince" is used of any and all rulers, regardless of actual title or precise rank. This is the
Renaissance use of the term found in
Niccolò Machiavelli's famous work, ''
Il Principe''.
As a title, by the end of the medieval era, ''prince'' was borne by rulers of territories that were either substantially smaller than or exercised fewer of the rights of sovereignty than did emperors and kings. A lord of even a quite small territory might come to be referred to as a ''prince'' before the 13th century, either from translations of a native title into the Latin ''princeps'' (as for the hereditary ruler of Wales), or when the lord's territory was allodial. The lord of an allodium owned his lands and exercised prerogatives over the subjects in his territory absolutely, owing no feudal homage or duty as a vassal to a liege lord, nor being subject to any higher jurisdiction. Most small territories designated as principalities during feudal eras were allodial, e.g. the Princedom of Dombes.
Lords who exercised lawful authority over territories and people within a feudal hierarchy were also sometimes regarded as ''princes'' in the general sense, especially if they held the rank of count or higher. This is attested in some surviving styles for e.g., British earls, marquesses, and dukes are still addressed by the Crown on ceremonial occasions as ''high and noble princes'' (cf. Royal and noble styles).
In parts of the Holy Roman Empire in which primogeniture did not prevail (i.e. Germany), all legitimate agnates had an equal right to the family's hereditary titles. While this meant that offices, such as emperor, king, and elector could only be legally occupied by one dynast at a time, holders of such other titles as duke, margrave, landgrave, count palatine, and prince could only differentiate themselves by adding the name of their appanage to the family's original title. Not only did this tend to proliferate unwieldy titles (e.g. Princess Katherine of Anhalt-Zerbst ane Karl, Count Palatine of Zweibrücken-Neukastell-Kleeburg), but as agnatic primogeniture gradually became the norm in the Holy Roman Empire by the end of the 18th century, another means of distinguishing the monarch from other members of his dynasty became necessary. Gradual substitution of the title of ''Prinz'' for the monarch's title of ''Fürst'' occurred, and became customary in all German dynasties except in the grand duchies of Mecklenburg and Oldenburg. Both ''Prinz'' and ''Fürst'' are translated into English as "prince", but they reflect not only different but mutually exclusive terms.
This distinction had evolved before the 18th century (in most families: Liechtenstein long remained an exception, cadets and females using ''Fürst/Fürstin'' into the 19th century) for dynasties headed by a ''Fürst'' in Germany. The custom spread through the Continent to such an extent that a renowned imperial general who belonged to a cadet branch of a reigning ducal family, remains best known to history by the generic dynastic title, ''Prince Eugene of Savoy''. Note that the princely title was used as a prefix to his Christian name, which also became customary.
Cadets of France's ''princes étrangers'' began to affect similar usage but when, for example, the House of La Tour d'Auvergne's ruling dukes of Bouillon, attempted to use the same style, it was initially resisted by historians such as Père Anselme – who, however, willingly recognized use of territorial titles, i.e. he accepts that the ducal heir apparent is known as ''prince de Bouillon'', but would record in 1728 only that the heir's cousin, the comte d'Oliergues was "''known as'' the Prince Frederick" ("''dit'' le prince Frédéric").
The post-medieval rank of ''gefürsteter Graf'' (princely count) embraced but elevated the German equivalent of the intermediate French, English and Spanish nobles. In Germany, these nobles rose to dynastic status by preserving from the Imperial crown (''de jure'' after the Peace of Westphalia in 1648) the exercise of such sovereign prerogatives as the minting of money; the muster of military troops and the right to wage war and contract treaties; local judicial authority and constabular enforcement; and the habit of inter-marrying with sovereign dynasties. Eventually, these titles came to be more highly valued than that of ''Fürst'' itself, and by the 19th century, their cadets would become known as ''Prinzen''.
Prince of the blood
Currently, the husband of a queen regnant is usually titled prince or prince consort, whereas the wives of male monarchs take the female equivalent of their husbands' title—the same as is used when a female mounts the throne in her own right, such as empress or queen. In Brazil, Spain and Portugal, however, the husband of a female monarch was accorded the masculine equivalent of her title—at least after she bore him a child. In previous epochs, husbands of queens regnant often shared their consorts' regnal title and rank.
But in cultures which allow the ruler to have several wives (e.g. four in Islam) and/or official concubines, for these women sometimes collectively referred to as harem there are often specific rules determining their hierarchy and a variety of titles, which may distinguish between those whose offspring can be in line for the succeesion or not, or specifically who is mother to the heir to the throne. (E.g. in English language the title "The Prince/Princess" refers to sons/daughters of the ruling monarch)
To complicate matters, the style ''His Royal Highness'', a prefix normally accompanying the title of a dynastic prince, of royal or imperial rank, that is, can be awarded separately (as a compromise or consolation prize, in some sense).
Although the definition above is the one that is most commonly understood, there are also different systems. Depending on country, epoch, and translation, other meanings of prince are possible.
Over the centuries foreign-language titles such as Italian ''principe'', French ''prince'', German ''Prinz'' (son of a king or emperor) ''Fürst'' (peer), Russian ''kniaz'', etc., are usually translated as prince in English.
Some princely titles are derived from that of national rulers, such as tsarevich from tsar. Other examples are (e)mirza(da), khanzada, nawabzada, sahibzada, shahzada, sultanzada (all using the Persian patronymic suffix ''-zada'', meaning ''son, descendant'').
However, some princely titles develop in unusual ways, such as adoption of a style for dynasts which is not pegged to the ruler's title, but rather continues an old tradition (e.g. ''grand duke'' in Romanov Russia), claims dynastic succession to a lost monarchy (e.g. ''prince de Tarente'' for the La Trémoïlle heirs to the Neapolitan throne, or is simply assumed by fiat (e.g. ''prince Français'' by the House of Bonaparte).
Specific titles
In some dynasties, a specific style other than prince has become customary for dynasts, such as ''
fils de France'' in the
House of Capet, and ''
infante'' in Spain, Portugal, and Brazil (''infante'' was borne by children of the monarch other than the
heir apparent, for whom each realm did use a unique princely title, viz, "Prince Imperial" in Brazil, "Prince of Brazil" in Portugal until 1822, and "Prince of Asturias" in Spain).
Sometimes a specific title is commonly used by various dynasties in a region, e.g. Mian in various of the Punjabi princely Hill States (lower Himalayan region in British India).
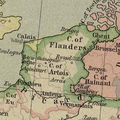
European dynasties usually awarded apanages to princes of the blood, typically attached to a feudal noble title, such as Britain's royal dukes, the ''Dauphin'' in France, the Count of Flanders in Belgium, and the Count of Syracuse in Sicily. Sometimes appanage titles were princely, e.g. Prince of Achaia (Courtenay), ''prince de Condé'' (Bourbon), Prince of Carignan (Savoy), but it was the fact that their owners were of princely ''rank'' rather than that they held a princely ''title'' which ensured their prominence.
:*''For the often specific terminology concerning a probable heir apparent, see Crown Prince and links there.''
Prince as a substantive title
Other princes derive their title not from dynastic membership as such, but from inheritance of a title named for a specific and historical territory, although the family's possession of prerogatives or properties in that territory may be long past. Such are most of the "princedoms" of France's ''
ancien régime'' so resented for their pretentiousness by
St-Simon. These include the princedoms of
Arches-Charleville, Boisbelle-Henrichemont, Chalais, Château-Regnault, Guéméné, Martigues, Mercœur, Sedan, Talmond, Tingrey, and the "kingship'' of Yvetot, among others.
===Prince as a reigning monarch===
A prince or princess who is the head of state of a territory that has a monarchy as a form of government is a reigning prince.
Nominal principalities
The current princely monarchies include:
the co-principality of Andorra (current reigning princes are the French President Nicolas Sarkozy and HE Joan Enric Vives Sicília)
The emirate of Kuwait (current reigning emir is Sabah Al-Ahmad Al-Jaber Al-Sabah)
The principality of Liechtenstein (current reigning prince is Hans-Adam II)
The principality of Monaco (current reigning prince is Albert II)
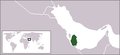
The Emirate of Qatar (Emir Hamad bin Khalifa)
The member emirates of the federation in the United Arab Emirates (''United Arab Principalities''):
* Abu Dhabi (Emir Khalifa bin Zayed Al Nahyan, also president of the UAE.)
* Ajman (Emir Humaid bin Rashid Al Nuaimi)
* Dubai (Emir Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum, also Vice President and Prime Minister of the UAE)
* Fujairah (Emir Hamad bin Mohammed Al Sharqi)
* Ras al-Khaimah (Emir Saqr bin Mohammad al-Qassimi)
* Sharjah (Emir Sultan III bin Muhammad al-Qasimi)
* Umm al-Quwain (Emir Saud bin Rashid Al Mu'alla)
Micronations
In the same tradition some self-proclaimed monarchs of so-called
micronations establish themselves as virtual princes:
Roy Bates calls himself Prince Roy of the Principality of Sealand
Leonard George Casley calls himself Prince Leonard I of the Principality of Hutt River (enclave in Australia)
Princes as representants of a reigning monarch
Various monarchies provide for different modes in which princes of the dynasty can temporarily or permanently share in the style and / or office of the Monarch, e.g. as
Regent or
Viceroy.
Though these offices must not be reserved for members of the ruling dynasty, in some traditions they are, possibly even reflected in the style of the office, e.g. prince-lieutenant in Luxembourg repeatedly filled by the Crown prince before the grand duke's abdication, or in form of consortium imperii.
Some monarchies even have a practice in which the Monarch can formally abdicate in favor of his heir, and yet retain a kingly title with executive power, e.g. ''Maha Upayuvaraja'' (Sanskrit for ''Great Joint King'' in Cambodia), though sometimes also conferred on powerful regents who exercised executive powers.
Non-dynastic princes
France and the Holy Roman Empire
In several countries of the European continent, e.g. in France, prince can be an aristocratic title of someone having a high rank of
nobility in chief of a geographical place, but no actual territory and without any necessary link to the
royal family, which makes comparing it with e.g. the British system of royal princes difficult.
The kings of France started to bestow the style of prince, as a title among the nobility, from the 16th century onwards. These titles were created by elevating a ''seigneurie'' to the nominal status of a principality—although prerogatives of sovereignty were never conceded in the letters patent. These titles held no official place in the hierarchy of the nobility, but were often treated as ranking just below dukedoms, since they were often inherited (or assumed) by ducal heirs:
French titles of prince recognized by the king
* Holy Roman Empire States annexed by France
** Arches-Charleville: in the Ardennes region, near the border with the Empire.
** Château-Renaud: near Arches-Charleville.
** Dombes: on the east bank of the Rhône.
** Orange.
** Sedan: principality part of the Duchy of Bouillon.
* Ancient principalities seated in the Kingdom of France
** Boisbelle, later Henrichemont: in the Berry region, a sovereign principality recognized in 1598.
** Luxe: in the Béarn region, also styled Sovereign Count.
** Yvetot: in the Normandy region, recognized as King of Yvetot.
* Principalities created by the King
** Château-Porcien: in the Ardennes region, created in 1561 in the House of Croÿ.
** Guéméné: in Brittany, created in 1667 in the House of Rohan. Used at times for the heir of the Duke of Montbazon or form the Duke himself.
** Joinville: in the Champagne region, created in 1552 in the house of Lorraine.
** Martigues: in the Provence region, created 16th century in the House of Lorraine.
** Mercœur: in the Auvergne region, created in 1563 in the House of Lorraine, later a duchy. Recreated in 1719.
** Tingry: in the Nord-Pas-de-Calais region, created in 1587 in the House of Luxemburg.
* The princes of Condé and Conti, cadets of the French royal house, used recognized princely titles, but the lordships of Condé and Conti were never formally created principalities by the King.
Unrecognized titles of Prince
* Aigremont
* Anet: used by the Dukes of Vendôme, then the Dukes of Penthièvre.
* Antibes: claimed by the de Grasse family.
* Bédeille: in Béarn.
* Bidache: in Béarn used by the House of Gramont, but the heir was usually styled Count of Guiche rather than Prince of Bidache.
* Carency: in Artois. Originally a lordship of the House of Bourbon. It was inherited by the Counts of La Vauguyon, who used the style of Prince of Carency for the heir.
* Chabanais: in Angoumois. Reduced to a marquessate in 1702
* Chalais: in Périgord. Inherited by the elder branch of the House of Talleyrand. Grandeeship of Sapin annexed to the title in 1714.
* Commercy: lordship of Lorraine. Younger sons of the House of Lorraine used the style of Prince of Commercy.
* Courtenay: the House of Courtenay descended from Louis VI of France but was never recognized as Princes of the Blood by the King. The last branch of the house used the style of Prince of Courtenay from the 17th century. The style passed to the Dukes of Bauffremont.
* Elbeuf: lordship of Normandy. Younger sons of the House of Lorraine used the style of Prince of Elbeuf ; later a duchy.
* Lamballe: in Brittany, used by the heir of the Duke of Penthièvre.
* Lambesc: in Provence, used by various cadets of the House of Lorraine, notably by the heirs of the Dukes of Elbeuf.
* Léon: viscountcy of Brittany. The heirs of the Dukes of Rohan used the style of Prince of Léon.
* Listenois: in Franche-Comté, used by the Dukes of Bauffremont after the Courtenay inheritance.
* Marsillac: in Angoumois, used by the heir of the Duke of La Rochefoucauld.
* Maubuisson: in Île-de-France, used by the Dukes of Rohan-Rohan.
* Montauban: in Brittany, used by various cadets of the House of Rohan.
* Montbazon: a duchy of the House of Rohan, style of Prince of Montbazon used by various cadets of the House.
* Mortagne: in Aquitaine, used by the Dukes of Richelieu.
* Poix: in Picardy, used by various houses, raised two times to a duchy.
* Pons: in Saintonge, used by cadets of the House of Lorraine.
* Rochefort: used by cadets of the House of Rohan.
* Soubise: used by cadets of the House of Rohan, also Dukes of Rohan-Rohan.
* Soyons: in Dauphiné, used by cadets of the Dukes of Uzès.
* Talmond: in Vendée, used by the Dukes of La Trémoïlle.
* Tonnay-Charente: used by the heirs of the Dukes of Mortemart.
* Turenne: sovereign viscountcy on the House of La Tour d'Auvergne, style of Prince of Turenne used by cadets of the house.
This can even occur in a monarchy within which an identical but real and substantive feudal title exists, such as Fürst in German. An example of this is:
Otto von Bismarck was called Prince of Bismarck in the empire of reunited Germany, under the Hohenzollern dynasty.
Spain and France
In other cases, such titular princedoms are created in chief of an event, such as a treaty of a victory. An example of this is:
The Spanish minister Manuel Godoy was created ''Principe de la Paz'' or ''Prince of Peace'' by his king for negotiating the 1795 double peace-treaty of Basilea, by which the revolutionary French republic made peace with Prussia and with Spain.
The triumphant generals who led their troops to victory often received a victory title from Napoleon, both princely and ducal.
King William I of the Netherlands bestowed the victory title of prince of Waterloo upon Arthur Wellesley, Duke of Wellington after his victory over Napoleon I Bonaparte at Waterloo in 1815.
Poland and Russia
In Poland specifically, the titles of prince dated either to the times before the Union of Lublin or were granted to Polish nobles by foreign kings, as the law in Poland forbade the king from dividing nobility by granting them hereditary titles. For more information, see The Princely Houses of Poland.
In the Russian system, ''knyaz'', translated as "prince", is the highest degree of official nobility. Members of older dynasties that were eventually subjected to the Russian imperial dynasty were also accorded the title of ''knyaz'' -- sometimes after first being allowed to use the higher title of tsarevich (e.g. the Princes Gruzinsky and Sibirsky. Rurikid branches used the ''knyaz'' title also after they were succeeded by the Romanovs as the Russian imperial dynasty. An example of this is:
Grigori Aleksandrovich Potemkin who was made Prince Potemkin
The title of prince in various Western traditions and languages
In each case, the title is followed (when available) by the female form and then (not always available, and obviously rarely applicable to a prince of the blood without a principality) the name of the territorial associated with it, each separated by a slash. If a second title (or set) is also given, then that one is for a Prince of the blood, the first for a principality. Be aware that the absence of a separate title for a prince of the blood may not always mean no such title exists; alternatively, the existence of a word does not imply there is also a reality in the linguistic territory concerned; it may very well be used exclusively to render titles in other languages, regardless whether there is a historical link with any (which often means that linguistic tradition is adopted)
Etymologically, we can discern the following traditions (some languages followed a historical link, e.g. within the Holy Roman Empire, not their language family; some even fail to follow the same logic for certain other aristocratic titles):
Romance languages
Languages (mostly Romance) only using the Latin root ''princeps'':
*Catalan: Príncep /Princesa – Príncep /Princesa
*French: Prince /Princesse – Prince /Princesse
*Friulian: Princip /Principesse – Princip /Principesse
*Italian: Principe /Principessa – Principe /Principessa
*Latin (post-Roman): Princeps/*Princeps/*
*Monegasque: Principu /Principessa – Principu /Principessa
*Occitan: Prince /Princessa – Prince /Princessa
*Portuguese: Príncipe /Princesa – Príncipe /Princesa
*Rhaeto-Romansh: Prinzi /Prinzessa – Prinzi /Prinzessa
*Romanian: Prinţ /Prinţesă – Principe /Principesă
*Spanish: Príncipe /Princesa – Príncipe /Princesa
*Venetian: Principe /Principessa – Principe /Principessa
Celtic languages
*Breton: Priñs /Priñsez
*Irish: Prionsa /Banphrionsa – Flaith /Banfhlaith
*Scottish Gaelic: Prionnsa /Bana-phrionnsa – Flath /Ban-fhlath
*Welsh: Tywysog /Tywysoges – Prins /Prinses
Germanic languages
Languages (mainly Germanic) that use (generally alongside a princeps-derivate for princes of the blood) an equivalent of the German ''Fürst'':
*English:Prince /Princess – Prince /Princess
*Afrikaans: Prins
*Danish: Fyrste /Fyrstinde – Prins /Prinsesse
*Dutch: Vorst /Vorstin- Prins /Prinses
*Faroese: Fúrsti /Fúrstafrúa, Fúrstinna – Prinsur /Prinsessa
*Frisian: Foarst /Foarstinne – Prins /Prinsesse
*German: Fürst /Fürstin – Prinz /Prinzessin
*Icelandic: Fursti /Furstynja – Prins /Prinsessa
*Luxembourgish: Fürst /Fürstin – Prënz /Prinzessin
*Norwegian: Fyrste /Fyrstinne – Prins /Prinsesse
*Old English: Ǣðeling /Hlæfdiġe
*Swedish: Furste /Furstinna – Prins /Prinsessa
Slavic and Baltic languages
Slavic and Baltic languages:
*Belarusian: Tsarevich, Karalevich, Prynts /Tsarewna, Karalewna, Pryntsesa
*Bulgarian: (phonetically pronounced) Knyaz /Knaginya, Kral, Prints /Printsesa
*Bosnian: Кнез/Књегиња or Knez/Kneginja, Краљевић/Краљевна or Kraljević/Kraljevna, Принц/Принцеза or Princ/Princeza
*Croatian: Knez/Kneginja, Kraljević/Kraljevna, Princ/Princeza
*Czech: Kníže /Kněžna, Princ/Princezna
*Latvian: Firsts /Firstiene – Princis /Princese
*Lithuanian: Kunigaikštis /Kunigaikštiene – Princas /Princese
*Macedonian: Knez /Knezhina, Tsarevich, Kralevich, Prints /Tsarevna, Kralevna, Printsesa
*Polish: Książę /Księżna, Książę, Królewicz /Księżna, Królewna
*Russian: Knyaz /Knyagina Knyazhyna, Tsarevich, Korolyevich, Prints /Tsarevna, Korolyevna, Printsessa
*Serbian: Кнез/Књегиња or Knez/Kneginja, Краљевић/Краљевна or Kraljević/Kraljevna, Принц/Принцеза or Princ/Princeza
*Slovak: Knieža /Kňažná, Kráľovič, Princ /Princezná
*Slovene: Knez /Kneginja, Kraljevič, Princ /Kraljična, Princesa
*Ukrainian: Knyaz /Knyazhnya, Tsarenko, Korolenko, Prints /Tsarivna, Korolivna, Printsizna
Other languages
Albanian: Princ /Princeshë – Princ /Princeshë
Arabic: Emir /Emira – Prince /Princess
Estonian: Vürst /Vürstinna – Prints /Printsess
Filipino: Prínsipe / Prinsesa – Prince / Princess
Finnish: Ruhtinas /Ruhtinatar – Prinssi /Prinsessa
Georgian: თავადი / ''Tavadi''
Greek (Medieval, formal): Prigkips, ''Πρίγκηψ''/Prigkipissa, ''Πριγκήπισσα''
Greek (Modern, colloquial): Prigkipas, ''Πρίγκηπας''/Prigkipissa, ''Πριγκήπισσα''
Hindi: ''Rājkumār'' (राजकुमार), ''Kũwar'' (कुँवर), both from Sanskrit ''rāj'' (royal) + ''kumāra'' (a boy)
Tamil: Ilavarasar/Ilavarasi-Prince/Princess
Hungarian (Magyar): ''Herceg'' / ''Hercegnő'', or ''Fejedelem'' / ''Fejedelemnő'' if head of state.
Maltese: Prinċep /Prinċipessa – Prinċep /Prinċipessa
Turkish: Prens /Prenses
Indonesian: Pangeran / Putri
Malaysian: Putera / Puteri
Urdu: Shahzada / Shahzadi – Prince /Princess
The title of prince in other traditions and languages
The above is essentially the story of European, Christian dynasties and other nobility, also 'exported' to their colonial and other overseas territories and otherwise adopted by rather westernized societies elsewhere (e.g. Haiti).
Applying these essentially western concepts, and terminology, to other cultures even when they don't do so, is common but in many respects rather dubious. Different (historical, religious...) backgrounds have also begot significantly different dynastic and nobiliary systems, which are poorly represented by the 'closest' western analogy.
It therefore makes sense to treat these per civilization.
Islamic traditions
Arabian tradition since the caliphate – in several monarchies it remains customary to use the title Sheikh (in itself below princely rank) for all members of the royal family. In families (often reigning dynasties) which claim descent from Muhammad, this is expressed in either of a number of titles (supposing different exact relations): sayid, sharif; these are retained even when too remote from any line of succession to be a member of any dynasty.
Malay countries
In the Ottoman empire, the sovereign of imperial rank (incorrectly known in the west as ''(Great) sultan'') was styled padishah with a host of additional titles, reflecting his claim as political successor to the various conquered states. Princes of the blood, male and female, were given the style sultan (normally reserved for Muslim rulers)
Persia (Iran) – Princes as members of a royal family, are referred to by the title ''Shahzadeh'', meaning "descendant of the king". Since the word ''zadeh'' could refer to either a male or female descendant, ''Shahzadeh'' had the parallel meaning of "princess" as well. Princes can also be sons of provincial kings (Khan) and the title referring to them would be the title of Khanzadeh. Princes as people who got a title from the King are called "Mirza", diminutive of "Amir Zadeh" (King's Son).
In Indian Muslim dynasties, the most common titles were Mirza (from ''Amirzada'') and Shahzada; while Nawabzada and Sahibzada were also given to younger blood princes.
East Asian traditions
China
In ancient China, the title of prince developed from being the highest title of
nobility (synonymous with
duke) in the
Zhou Dynasty, to five grades of princes (not counting the sons and grandsons of the emperor) by the time of the fall of the
Qing Dynasty.The Chinese word for prince ''Wang'' (, literally, King) as Chinese believe the emperor ''Huang Di'' () is the ruler of all kings. The most accurate translations of the English word "prince" are ''Huang Zi'' (, lit. Son of the Emperor) or ''Wang Zi'' (, lit. Son of the King).
Japan
In Japan, the title ''Kōshaku'' () was used as the highest title of ''
Kazoku'' ( Japanese modern nobility) before the present constitution. ''Kōshaku'', however, is more commonly translated as "Duke" to avoid confusion with the following royal ranks in the Imperial Household: ''Shinnō'' ( literally, King of the Blood); female ''Naishinnō'' ( lit., Queen (by herself) of the Blood); and ''Shinnōhi'' lit., Consort of King of the Blood); or ''Ō'' ( lit., King); female, ''Jyo-Ō'' ( lit., Queen (by herself)); and ''Ōhi'' ( lit., Consort of King). The former is the higher title of a male member of the Imperial family while the latter is the lower.
Korea
The title "Prince" was used for the king's male-line descendant. Prince translated generally into three divisions. In
Jo-seon, the king's legitimate son used title 대군 (Dae-goun). A son born of a concubine and king's great-great-grandson used 군. Presently, it is usually translated as 왕자.
India
''See''
princely states for the often particular, mainly
Hindu titles in former
British India, including modern
Pakistan,
Bangladesh,
Burma, and
Nepal.
Indochina
''See''
Cambodia,
Vietnam, and
Laos
Philippines
''See''
Principalia, the sultanates of
Maguindanao and
Sulu.
Thailand
In
Thailand (formerly Siam), the title of Prince was divided into three classes depending on the rank of their mothers. Those who were born of a King and had a royal mother (a Queen or a Princess consort) are titled ''
Chaofa Chai'' (: literally, "Male Celestial Lord"). Those born of a King and a commoner or children of Chaofas are tilted ''
Phra Ong Chao'' (พระองค์เจ้า). The children of Phra Ong Chaos are titled ''
Mom Chao'' (หม่อมเจ้า), abbreviated as M.C. (or ม.จ.).
African traditions
A Western model was sometimes copied by emancipated colonial regimes (e.g. Bokassa I's short-lived
Central-African Empire in Napoleonic fashion). Otherwise, most of the styles for members of ruling families do not lend themselves well to English translation. Nonetheless, in general the princely style has gradually replaced the
colonialist title of
chief, which does not particularly connote dynastic rank to Westerners, e.g.
Swazi Royal Family and
Zulu Royal Family.
The title of prince in religion
In states with an element of theocracy, this can affect princehood in several ways, such as the style of the ruler (e.g. with a secondary title meaning son or servant of a named divinity), but also the mode of succession (even reincarnation and recognition).
Furthermore, certain religious offices may be considered of princely rank, and/or imply comparable temporal rights.
The Pope, Cardinals, Prince Bishops, Lord Bishops, Prince-Provost, and Prince-abbots are referred to as Princes of the Church. Also in Christianity, Jesus Christ is sometimes referred to as the ''Prince of Peace''. Other titles for Jesus Christ are ''Prince of Princes'', ''Prince of the Covenant'', and ''Prince of the Kings of the Earth''. Further, Satan is often titled the ''Prince of Darkness''; and in the Christian faith he is also referred to as the ''Prince of this World'' and the ''Prince of the Power of the Air''. Another title for Satan, not as common today but apparently so in approximately 30 A.D. by the Pharisees of the day, was the title ''Prince of the Devils''. ''Prince of Israel'', ''Prince of the Angels'', and ''Prince of Light'' are titles given to the Archangel Michael. Some Christian churches also believe that since all Christians, like Jesus Christ, are children of God, then they too are princes and princesses of Heaven. Saint Peter, a disciple of Jesus, is also known as the Prince of the Apostles.
See also
Auctoritas, Dominate, Potestas and Imperium
Crown Prince, Grand Prince and Infante
Fils de France and Petit-Fils de France
First Prince of the Blood
Fürst
Grand Duchy, Grand duke and Grand duchess
Infante and Infanta
Heir apparent and Heir presumptive
King consort and Queen consort
King regnant and Queen regnant
List of British princes and List of British princesses
Monsieur and Madame Royale
Nobility, Royalty and Royal and noble ranks
Prince of the Apostles
Prince consort and Princess consort
Prince du Sang
Prince-elector and Prince Regent
Prince of the Church: Pope, Cardinal (Roman Catholic), Crown-cardinal, Prince-Bishop, Lord Bishop, Prince-Provost, and Prince-abbot
Princess
Principality and Princely state
References
External links
Princely States in British India and talaqdars in Oudh.
RoyalArk thorough on a limited number of dynasties.
World Statesmen select the present state, often navigate within for a former polity.
Category:Court titles
Category:Feudalism
Category:Heads of state
Category:Royal titles
Category:Noble titles
Category:Positions of authority
Category:Men's social titles
am:ልዑል
ar:برينس
zh-min-nan:Thâu-lâng
be:Прынц
be-x-old:Прынц
bg:Принц
ca:Príncep
cs:Princ
cy:Tywysog
da:Prins
de:Fürst
es:Príncipe
eo:Princo
fa:شاهزاده
fr:Prince (titre)
ko:왕자
hr:Princ
id:Pangeran
it:Principe
he:נסיך
ka:უფლისწული
lv:Princis
ms:Putera
nl:Prins
ja:プリンス
no:Prins
nn:Prins
pt:Príncipe
ro:Prinț
ru:Принц
scn:Prìncipi
simple:Prince
sk:Princ
sl:Princ
fi:Prinssi
sv:Prins
tr:Prens (unvan)
uk:Принц
vec:Principe
vi:Hoàng tử
zh:亲王
































































![[HD] Completion - MJ tribute Prince and Paris Jackson at 52 Grammys [HD] Completion - MJ tribute Prince and Paris Jackson at 52 Grammys](http://web.archive.org./web/20120420205436im_/http://i.ytimg.com/vi/hY4GzOLBPxg/0.jpg)













