- published: 27 Aug 2015
- views: 5867
-
remove the playlistSoft Palate
- remove the playlistSoft Palate
- published: 19 Aug 2012
- views: 41029
- published: 08 May 2014
- views: 98164
- published: 08 Oct 2013
- views: 44648
- published: 01 Apr 2012
- views: 31448
- published: 24 Oct 2015
- views: 1704
- published: 11 Apr 2013
- views: 15189
- published: 13 Apr 2011
- views: 15979
- published: 05 Nov 2015
- views: 1067
- published: 31 Jan 2015
- views: 1792

The soft palate (also known as velum or muscular palate) is the soft tissue constituting the back of the roof of the mouth. The soft palate is distinguished from the hard palate at the front of the mouth in that it does not contain bone.
The soft palate is movable, consisting of muscle fibers sheathed in mucous membrane. It is responsible for closing off the nasal passages during the act of swallowing, and also for closing off the airway. During sneezing, it protects the nasal passage by diverting a portion of the excreted substance to the mouth.
The uvula hangs from the end of the soft palate. Research shows that the uvula is not actually involved in snoring processes. This has been shown through inconsistent results from uvula removal surgery. Snoring is more closely associated with fat deposition in the pharynx, enlarged tonsils of Waldeyer's Ring, or deviated septum problems. Touching the uvula or the end of the soft palate evokes a strong gag reflex in most people.
A speech sound made with the middle part of the tongue (dorsum) touching the soft palate is known as a velar consonant.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
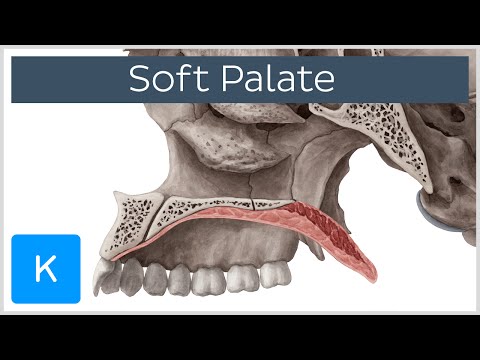 3:11
3:11Soft palate - Function, Definition & Anatomy - Human Anatomy | Kenhub
Soft palate - Function, Definition & Anatomy - Human Anatomy | KenhubSoft palate - Function, Definition & Anatomy - Human Anatomy | Kenhub
Find more videos at: https://www.kenhub.com Subscribe to our YouTube channel: http://bit.ly/VOEG2I The soft palate is the posterior muscular extension of the hard palate which together make up the palate of the oral cavity and the floor of the nasal cavity. This article will discuss the soft palate in detail including its borders, its function, its general anatomy, its musculature and its possible pathology. For more Human Anatomy video tutorials, interactive quizzes, articles and an atlas of Human Anatomy, go to https://www.kenhub.com ! Or subscribe to our Youtube channel: http://bit.ly/VOEG2I Like us on facebook: https://www.facebook.com/kenhubcom Follow us on twitter: https://twitter.com/kenHub_com Articles related to this video ============================= Soft Palate https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/the-soft-palate Atlas related to this video ============================= Palatum molle https://www.kenhub.com/en/atlas/palatum-molle -
 2:58
2:58How to Lift Soft Palate and Tongue while Singing - Felicia Ricci
How to Lift Soft Palate and Tongue while Singing - Felicia RicciHow to Lift Soft Palate and Tongue while Singing - Felicia Ricci
How to Lift Soft Palate and Tongue while Singing - Open Singing / http://www.BeltingCrashCourse.com / Learn what happens to your tongue and soft palate while you sing, crucial for creating an open space for resonance as well clear vocal tone. A raised palate and relaxed or lowered tongue are non-negotiable in order to sing well! As a professional voice finder, it's my sworn duty to teach you how to find your singing voice! Learning how to improve your singing voice is all about simple, achievable steps that make SENSE to you. All of us learn how to sing on our own timeline, and certain things will click more than others. But it's important that YOU understand your voice more than anyone else -- learning how to be a good singer is, in many ways, getting to know yourself :) If you feel you don't yet know how to sing like a pro, be patient -- every baby step and daily practice session helps. (And I'll keep posting new vids to help you!) xo Fel *~*~*~*~*~*~*~ For more singing tips videos, lessons on how to improve your singing, song breakdowns and other goodies, please don't forget to subscribe! http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=madameunreality -
 12:59
12:59Ep 60 "The Soft Palate - The Return of The Ring"
Ep 60 "The Soft Palate - The Return of The Ring"Ep 60 "The Soft Palate - The Return of The Ring"
Should you raise the soft palate to sing high notes? The answer to this ancient question is truly EPIC. In Ep. 60, Voice Teacher Justin Stoney gives one answer to rule them all! And, restores health and good fortune to singers all across the vocal kingdom. You won't want to miss THIS truly royal episode! Enjoy Voice Lessons To The World! -
 4:46
4:46SOFT PALATE EXERCISES (6 of 6) -- Vocal Exercises -- American English Pronunciation
SOFT PALATE EXERCISES (6 of 6) -- Vocal Exercises -- American English PronunciationSOFT PALATE EXERCISES (6 of 6) -- Vocal Exercises -- American English Pronunciation
SUBSCRIBE!: http://bit.ly/RE_sub, Fan! http://bit.ly/RE_FB ESL: learn about the soft palate and how it can affect your voice in this American English pronunciation video. See the transcript for this video: http://www.rachelsenglish.com/videos/soft-palate-exercises Improve your American Accent / spoken English at Rachel's English with video-based lessons and exercises. Cải thiện nói tiếng Anh Mỹ / 미국 영어 발음 향상 / 話されているアメリカ英語を向上させる / Улучши разговорный американский английский / Meningkatkan berbicara bahasa Inggris Amerika / Melhore sua pronúncia do inglês americano / Mejora tu pronunciación en Inglés Americano / 美語 / تحسين لهجتك الأمريكية الإنجليزية / שפר את המבטא האמריקאי שלך ...with Rachel's English! subscribe: http://www.YouTube.com/subscription_center?add_user=RachelsEnglish website: http://www.RachelsEnglish.com -
 4:16
4:16Lifting the Soft Palate
Lifting the Soft PalateLifting the Soft Palate
AccentHelp coach Jim Johnson talks further about how the velum/soft palate works, including ways of lifting it. -
 12:20
12:20Soft palate anatomy
Soft palate anatomy -
 5:32
5:32Vocal Genie 1: Soft Palate
Vocal Genie 1: Soft Palate -
 7:20
7:20Voice Lessons: Your Soft Palate - Bring More Ease And Freedom To Your Singing and Speaking
Voice Lessons: Your Soft Palate - Bring More Ease And Freedom To Your Singing and SpeakingVoice Lessons: Your Soft Palate - Bring More Ease And Freedom To Your Singing and Speaking
(Download your free vocal warm-up video on my website... www.RejoiceInYourVoice.com) Do you want more ease in your sound? Do you desire a richness to your tone? Do you long to sing and speak with more resonance and freedom? This lesson may unlock your authentic voice and make sharing your passion easier... Last week one of my youtube viewers asked some questions about the soft palate and I thought all of you would enjoy a teaching around this very important team aspect of your vocal instrument. Whether you are a singer, actor, or speaker putting the soft palate to work for you can bring more ease, freedom, and richness to your tone. Enjoy the video... Until next time... always Rejoice In Your Voice™! xoxox, Tricia -
 4:23
4:23How To Sing - Soft Palate and TONE (the EQUALIZER) part 1
How To Sing - Soft Palate and TONE (the EQUALIZER) part 1How To Sing - Soft Palate and TONE (the EQUALIZER) part 1
How to sing Raising the soft palate reduces nasal sounds while engaging it with the back of the tongue is responsible for pharyngeal resonance. The soft palate can be manipulated and moved. How to sing how to sing how to sing how to sing -
 2:14
2:14Soft Palate Resection -- Resección Paladar Blando
Soft Palate Resection -- Resección Paladar BlandoSoft Palate Resection -- Resección Paladar Blando
Sutures in Veterinary Surgery -- Suturas en Medicina Veterinaria http://goo.gl/gQXDh -
 6:17
6:17Voice Lessons: Keeping Your Tongue Relaxed While Lifting Your Soft Palate
Voice Lessons: Keeping Your Tongue Relaxed While Lifting Your Soft PalateVoice Lessons: Keeping Your Tongue Relaxed While Lifting Your Soft Palate
(Download your FREE vocal warm-up video on my website www.RejoiceInYourVoice.com) Now that you are exploring some of your soft palate resonance from last week's lesson, you may find your tongue showing some signs of rebellion… It may be bunching up or pressing down in the back of the throat, or even tightening as you create sound. Here is a mini-voice lesson sharing some tools to help the tongue relax as you work your soft palate awareness into your speaking and singing…. Play with these concepts. Don’t force anything. Feel your way through the motions and find the ease in creating the tone. And until next time, Always Rejoice In Your Voice™! Xoxoxo, Tricia -
 11:05
11:05Soft Palate Surgery in Sleep Apnea : Dr.K.O.Paulose FRCS
Soft Palate Surgery in Sleep Apnea : Dr.K.O.Paulose FRCSSoft Palate Surgery in Sleep Apnea : Dr.K.O.Paulose FRCS
Treatment for snoring and sleep apnea is directed at the soft palate too. Removing excess of tissue including trimming of elongated uvula and stiffening procedures help mild to moderate caeses of sleep apnea. This is done in Jubilee Christian Mission Hospital Trivandrum Kerala South India. For more videos and details, go to http://drpaulose.com For more details and free updates you may subscribe to : http://drpaulose.com For Email Consultation, Please visit:http://drpaulose.com/consult -
 3:30
3:30How to practice keeping an open throat. Ep. #18
How to practice keeping an open throat. Ep. #18How to practice keeping an open throat. Ep. #18
In this episode of SInging Television, Sara Leib shows you a way raise your soft palate, to keep an open throat. -
 1:15
1:15Soft Palate Affects Snoring - Atlanta Snoring Institute
Soft Palate Affects Snoring - Atlanta Snoring InstituteSoft Palate Affects Snoring - Atlanta Snoring Institute
http://atlantasnoring.com Atlanta Snoring Institute can treat your snoring with simple and effective office procedures in about 20 minutes, allowing you to return to work right away. These procedures are effective in reducing or eliminating snoring in most patients. Snoring can be caused by different areas in the airway including the nose, soft palate, uvula, or the tonsils. Atlanta Snoring Institute will work with you to determine the cause of your snoring and the right treatment that will work for you. Call us today to schedule your free evaluation! Atlanta Snoring Institute 770-389-0000
- Artery
- ATC code A
- Biological tissue
- Birth defect
- Buccal fat pad
- Cementum
- Cheek
- Cleft palate
- Cleft uvula
- Deviated septum
- Digestive system
- EMedicine
- Fauces (anatomy)
- Fellatio
- Free gingival margin
- Frenulum of tongue
- Gingiva
- Gingival fibers
- Gingival margin
- Gingival sulcus
- Hard palate
- Herpangina
- Human pharynx
- Human tooth
- Incisive papilla
- Interdental papilla
- Latin
- Lingual septum
- Lingual tonsils
- Lip
- Lower lip
- Migratory stomatitis
- Mouth
- Mucosa
- Mucous membrane
- Muscle
- Musculus uvulae
- Nasalization
- Nerve
- Oral cavity proper
- Oral mucosa
- Oral pathology
- Oropharynx
- Palate
- Palatine raphe
- Palatine tonsil
- Palatine uvula
- Palato pharyngeal
- Palato-glossal
- Palatoglossal arch
- Parotid duct
- Parotid gland
- Pemphigus vulgaris
- Periodontal ligament
- Periodontium
- Petechiae
- Pharyngeal reflex
- Pharynx
- Philtrum
- Posterior tongue
- PubMed Identifier
- Respiratory system
- Salivary gland
- Soft palate
- Sublingual caruncle
- Sublingual gland
- Submandibular duct
- Submandibular gland
- Sulcular epithelium
- Swallowing
- Talk Soft palate
- Taste bud
- Tensor veli palatini
- Tongue
- Tonsil
- Tonsillar fossa
- Tonsillectomy
- Upper lip
- Velar consonant
- Vermilion border
- Vestibule of mouth
- Wikipedia Merging
-

Soft palate - Function, Definition & Anatomy - Human Anatomy | Kenhub
Find more videos at: https://www.kenhub.com Subscribe to our YouTube channel: http://bit.ly/VOEG2I The soft palate is the posterior muscular extension of the hard palate which together make up the palate of the oral cavity and the floor of the nasal cavity. This article will discuss the soft palate in detail including its borders, its function, its general anatomy, its musculature and its possible pathology. For more Human Anatomy video tutorials, interactive quizzes, articles and an atlas of Human Anatomy, go to https://www.kenhub.com ! Or subscribe to our Youtube channel: http://bit.ly/VOEG2I Like us on facebook: https://www.facebook.com/kenhubcom Follow us on twitter: https://twitter.com/kenHub_com Articles related to this video ============================= Soft Palate https://www... -

How to Lift Soft Palate and Tongue while Singing - Felicia Ricci
How to Lift Soft Palate and Tongue while Singing - Open Singing / http://www.BeltingCrashCourse.com / Learn what happens to your tongue and soft palate while you sing, crucial for creating an open space for resonance as well clear vocal tone. A raised palate and relaxed or lowered tongue are non-negotiable in order to sing well! As a professional voice finder, it's my sworn duty to teach you how to find your singing voice! Learning how to improve your singing voice is all about simple, achievable steps that make SENSE to you. All of us learn how to sing on our own timeline, and certain things will click more than others. But it's important that YOU understand your voice more than anyone else -- learning how to be a good singer is, in many ways, getting to know yourself :) If you feel you d... -

Ep 60 "The Soft Palate - The Return of The Ring"
Should you raise the soft palate to sing high notes? The answer to this ancient question is truly EPIC. In Ep. 60, Voice Teacher Justin Stoney gives one answer to rule them all! And, restores health and good fortune to singers all across the vocal kingdom. You won't want to miss THIS truly royal episode! Enjoy Voice Lessons To The World! -

SOFT PALATE EXERCISES (6 of 6) -- Vocal Exercises -- American English Pronunciation
SUBSCRIBE!: http://bit.ly/RE_sub, Fan! http://bit.ly/RE_FB ESL: learn about the soft palate and how it can affect your voice in this American English pronunciation video. See the transcript for this video: http://www.rachelsenglish.com/videos/soft-palate-exercises Improve your American Accent / spoken English at Rachel's English with video-based lessons and exercises. Cải thiện nói tiếng Anh Mỹ / 미국 영어 발음 향상 / 話されているアメリカ英語を向上させる / Улучши разговорный американский английский / Meningkatkan berbicara bahasa Inggris Amerika / Melhore sua pronúncia do inglês americano / Mejora tu pronunciación en Inglés Americano / 美語 / تحسين لهجتك الأمريكية الإنجليزية / שפר את המבטא האמריקאי שלך ...with Rachel's English! subscribe: http://www.YouTube.com/subscription_ce... -

Lifting the Soft Palate
AccentHelp coach Jim Johnson talks further about how the velum/soft palate works, including ways of lifting it. -

-

-

Voice Lessons: Your Soft Palate - Bring More Ease And Freedom To Your Singing and Speaking
(Download your free vocal warm-up video on my website... www.RejoiceInYourVoice.com) Do you want more ease in your sound? Do you desire a richness to your tone? Do you long to sing and speak with more resonance and freedom? This lesson may unlock your authentic voice and make sharing your passion easier... Last week one of my youtube viewers asked some questions about the soft palate and I thought all of you would enjoy a teaching around this very important team aspect of your vocal instrument. Whether you are a singer, actor, or speaker putting the soft palate to work for you can bring more ease, freedom, and richness to your tone. Enjoy the video... Until next time... always Rejoice In Your Voice™! xoxox, Tricia -

How To Sing - Soft Palate and TONE (the EQUALIZER) part 1
How to sing Raising the soft palate reduces nasal sounds while engaging it with the back of the tongue is responsible for pharyngeal resonance. The soft palate can be manipulated and moved. How to sing how to sing how to sing how to sing -

Soft Palate Resection -- Resección Paladar Blando
Sutures in Veterinary Surgery -- Suturas en Medicina Veterinaria http://goo.gl/gQXDh -

Voice Lessons: Keeping Your Tongue Relaxed While Lifting Your Soft Palate
(Download your FREE vocal warm-up video on my website www.RejoiceInYourVoice.com) Now that you are exploring some of your soft palate resonance from last week's lesson, you may find your tongue showing some signs of rebellion… It may be bunching up or pressing down in the back of the throat, or even tightening as you create sound. Here is a mini-voice lesson sharing some tools to help the tongue relax as you work your soft palate awareness into your speaking and singing…. Play with these concepts. Don’t force anything. Feel your way through the motions and find the ease in creating the tone. And until next time, Always Rejoice In Your Voice™! Xoxoxo, Tricia -

Soft Palate Surgery in Sleep Apnea : Dr.K.O.Paulose FRCS
Treatment for snoring and sleep apnea is directed at the soft palate too. Removing excess of tissue including trimming of elongated uvula and stiffening procedures help mild to moderate caeses of sleep apnea. This is done in Jubilee Christian Mission Hospital Trivandrum Kerala South India. For more videos and details, go to http://drpaulose.com For more details and free updates you may subscribe to : http://drpaulose.com For Email Consultation, Please visit:http://drpaulose.com/consult -

How to practice keeping an open throat. Ep. #18
In this episode of SInging Television, Sara Leib shows you a way raise your soft palate, to keep an open throat. -

Soft Palate Affects Snoring - Atlanta Snoring Institute
http://atlantasnoring.com Atlanta Snoring Institute can treat your snoring with simple and effective office procedures in about 20 minutes, allowing you to return to work right away. These procedures are effective in reducing or eliminating snoring in most patients. Snoring can be caused by different areas in the airway including the nose, soft palate, uvula, or the tonsils. Atlanta Snoring Institute will work with you to determine the cause of your snoring and the right treatment that will work for you. Call us today to schedule your free evaluation! Atlanta Snoring Institute 770-389-0000 -

-

Soft palate - Inside the Voice - Sing Up
Exercises to help make sure all the air goes through your mouth, with none escaping through your nose, as you sing. This video is part of Sing Up's Inside the voice resources, created by Stuart Barr and Jenevora Williams. To find the resources, visit www.singup.org. -

Soft Palate Tutorial #1
Brief description on raising the soft palate for a better quality of sound while singing! Enjoy! www.vocalproof.com mnstring2nations@yahoo.com -

Laser Surgery - Elongated Soft Palate
Cutting Edge Surgical Laser application. -

soft palate
-

The Basics of the Soft Palate (Velum)
www.AccentHelp.com coach Jim Johnson walks you through how the soft palate - also known as the velum - works, and how it is related to nasality and nasal sounds. -

Exercise 8 soft palate awareness
-

Sing Out Saturday Q&A;: When and Why Should I Lift My Soft Palate?
This week's SOS talks you through the use of the soft palate: how to find it, how to lift it and when you may want to use this technique (and when maybe you shouldn't). -

Overground endoscope: dorsal displacement of soft palate in a horse
Video shows a dorsal displacement of the soft palate (DDSP) in a horse. WCVM clinicians collected the video using the WCVM's new overground video endoscope that will be used to examine a horse's upper airway during exercise and to diagnose upper airway dysfunctions such as DDSP..
Soft palate - Function, Definition & Anatomy - Human Anatomy | Kenhub
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:11
- Updated: 27 Aug 2015
- views: 5867
- published: 27 Aug 2015
- views: 5867
How to Lift Soft Palate and Tongue while Singing - Felicia Ricci
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:58
- Updated: 19 Aug 2012
- views: 41029
- published: 19 Aug 2012
- views: 41029
Ep 60 "The Soft Palate - The Return of The Ring"
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 12:59
- Updated: 08 May 2014
- views: 98164
- published: 08 May 2014
- views: 98164
SOFT PALATE EXERCISES (6 of 6) -- Vocal Exercises -- American English Pronunciation
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:46
- Updated: 08 Oct 2013
- views: 44648
- published: 08 Oct 2013
- views: 44648
Lifting the Soft Palate
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:16
- Updated: 01 Apr 2012
- views: 31448
- published: 01 Apr 2012
- views: 31448
Soft palate anatomy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 12:20
- Updated: 22 Nov 2015
- views: 1712
Vocal Genie 1: Soft Palate
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:32
- Updated: 21 Aug 2013
- views: 11761
Voice Lessons: Your Soft Palate - Bring More Ease And Freedom To Your Singing and Speaking
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:20
- Updated: 24 Oct 2015
- views: 1704
- published: 24 Oct 2015
- views: 1704
How To Sing - Soft Palate and TONE (the EQUALIZER) part 1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:23
- Updated: 11 Apr 2013
- views: 15189
- published: 11 Apr 2013
- views: 15189
Soft Palate Resection -- Resección Paladar Blando
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:14
- Updated: 13 Apr 2011
- views: 15979
- published: 13 Apr 2011
- views: 15979
Voice Lessons: Keeping Your Tongue Relaxed While Lifting Your Soft Palate
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:17
- Updated: 05 Nov 2015
- views: 1067
- published: 05 Nov 2015
- views: 1067
Soft Palate Surgery in Sleep Apnea : Dr.K.O.Paulose FRCS
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 11:05
- Updated: 31 Jan 2015
- views: 1792
- published: 31 Jan 2015
- views: 1792
How to practice keeping an open throat. Ep. #18
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:30
- Updated: 07 Apr 2010
- views: 86643
- published: 07 Apr 2010
- views: 86643
Soft Palate Affects Snoring - Atlanta Snoring Institute
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:15
- Updated: 14 Sep 2009
- views: 16407
- published: 14 Sep 2009
- views: 16407
Gross Anatomy: Hard and Soft Palate and Fauces
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:39
- Updated: 04 Sep 2009
- views: 13824
Soft palate - Inside the Voice - Sing Up
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:53
- Updated: 23 Mar 2011
- views: 9972
- published: 23 Mar 2011
- views: 9972
Soft Palate Tutorial #1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:21
- Updated: 30 Jan 2014
- views: 1114
- published: 30 Jan 2014
- views: 1114
Laser Surgery - Elongated Soft Palate
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:23
- Updated: 28 Jul 2009
- views: 17233
soft palate
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:19
- Updated: 13 Jul 2013
- views: 1251
- published: 13 Jul 2013
- views: 1251
The Basics of the Soft Palate (Velum)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:55
- Updated: 28 Mar 2012
- views: 11607
- published: 28 Mar 2012
- views: 11607
Exercise 8 soft palate awareness
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:48
- Updated: 30 Sep 2014
- views: 576
- published: 30 Sep 2014
- views: 576
Sing Out Saturday Q&A;: When and Why Should I Lift My Soft Palate?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:44
- Updated: 10 Aug 2013
- views: 2591
- published: 10 Aug 2013
- views: 2591
Overground endoscope: dorsal displacement of soft palate in a horse
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:36
- Updated: 30 Apr 2011
- views: 10026
- published: 30 Apr 2011
- views: 10026
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

Soft palate - Function, Definition & Anatomy - Human Anatomy | Kenhub
- Report rights infringement
- published: 27 Aug 2015
- views: 5867

How to Lift Soft Palate and Tongue while Singing - Felicia Ricci
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Aug 2012
- views: 41029

Ep 60 "The Soft Palate - The Return of The Ring"
- Report rights infringement
- published: 08 May 2014
- views: 98164

SOFT PALATE EXERCISES (6 of 6) -- Vocal Exercises -- American English Pronunciation
- Report rights infringement
- published: 08 Oct 2013
- views: 44648

Lifting the Soft Palate
- Report rights infringement
- published: 01 Apr 2012
- views: 31448

Soft palate anatomy
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 Nov 2015
- views: 1712

Vocal Genie 1: Soft Palate
- Report rights infringement
- published: 21 Aug 2013
- views: 11761

Voice Lessons: Your Soft Palate - Bring More Ease And Freedom To Your Singing and Speaking
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 Oct 2015
- views: 1704

How To Sing - Soft Palate and TONE (the EQUALIZER) part 1
- Report rights infringement
- published: 11 Apr 2013
- views: 15189

Soft Palate Resection -- Resección Paladar Blando
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 Apr 2011
- views: 15979

Voice Lessons: Keeping Your Tongue Relaxed While Lifting Your Soft Palate
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Nov 2015
- views: 1067

Soft Palate Surgery in Sleep Apnea : Dr.K.O.Paulose FRCS
- Report rights infringement
- published: 31 Jan 2015
- views: 1792

How to practice keeping an open throat. Ep. #18
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Apr 2010
- views: 86643

Soft Palate Affects Snoring - Atlanta Snoring Institute
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Sep 2009
- views: 16407


