- published: 06 Dec 2014
- views: 832925
-
remove the playlistHoly Roman Empire
- remove the playlistHoly Roman Empire
- published: 21 Oct 2015
- views: 37550
- published: 26 Apr 2015
- views: 79702
- published: 02 Nov 2014
- views: 4105
- published: 05 Jun 2014
- views: 41061
- published: 11 Mar 2016
- views: 20
- published: 15 Dec 2015
- views: 114
- published: 24 Mar 2016
- views: 388
- published: 22 Mar 2016
- views: 552
- published: 01 May 2015
- views: 25242
- published: 30 Apr 2014
- views: 8231

The Holy Roman Empire (HRE; German: Heiliges Römisches Reich (HRR), Latin: Imperium Romanum Sacrum (IRS), Italian: Sacro Romano Impero (SRI)) was a German empire that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe. It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes. In its last centuries, its character became quite close to a union of territories.
The empire's territory was centered on the Kingdom of Germany, and included neighboring territories, which at its peak included the Kingdom of Italy and the Kingdom of Burgundy. For much of its history, the Empire consisted of hundreds of smaller sub-units, principalities, duchies, counties, Free Imperial Cities and other domains.
In 962 Otto I was crowned Holy Roman Emperor (German: Römisch-Deutscher Kaiser), although the Roman imperial title was first restored to Charlemagne in 800. Otto was the first emperor of the realm who was not a member of the earlier Carolingian dynasty. The last Holy Roman Emperor was Francis II, who abdicated and dissolved the Empire in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars. In a decree following the 1512 Diet of Cologne, the name was officially changed to Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation (German: Heiliges Römisches Reich Deutscher Nation, Latin: Imperium Romanum Sacrum Nationis Germanicæ).
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

The Roman Empire (Latin: IMPERIVM ROMANVM) was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean.
The 500-year-old Roman Republic, which preceded it, had been weakened and subverted through several civil wars. Several events are commonly proposed to mark the transition from Republic to Empire, including Julius Caesar's appointment as perpetual dictator (44 BC), the Battle of Actium (2 September 31 BC), and the Roman Senate's granting to Octavian the honorific Augustus (16 January 27 BC).
Roman expansion began in the days of the Republic, but the Empire reached its greatest extent under Emperor Trajan: during his reign (98 to 117 AD) the Roman Empire controlled approximately 6.5 million km2 of land surface. Because of the Empire's vast extent and long endurance, the institutions and culture of Rome had a profound and lasting influence on the development of language, religion, architecture, philosophy, law, and forms of government in the territory it governed, particularly Europe, and by means of European expansionism throughout the modern world.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 13:16
13:16Charles V and the Holy Roman Empire: Crash Course World History #219
Charles V and the Holy Roman Empire: Crash Course World History #219Charles V and the Holy Roman Empire: Crash Course World History #219
Get the new Crash Course World History Character poster here: http://store.dftba.com/products/crashcourse-characters-poster In which John Green teaches you about the Holy Roman Empire by teaching you about Charles V. Charles Hapsburg was the holy Roman Emperor, but he was also the King of Spain. And the King of Germany. And the King of Italy and the Lord of the Netherlands and Count Palatine of Burgundy. In short, Charles was runnin' thangs in much of the world during his reign. Charles ruled a lot of countries, and he was also known for encouraging intellectual discourse and he even spoke out against slavery, in a limited. So why did he consider himself a failure, and why did he break up the Empire when he abdicated in 1556? Mainly because the Holy Roman Empire didn't work very well. It was huge, and it didn't have any means of directly raising taxes. Plus, it was a pretty crazy time in Europe anyway, and Charles found himself in charge of the Catholic-Church-Endorsed Empire in the time of Martin Luther and the Protestant Reformation. John will teach you a bit about how Charles put the Empire together, and how it fell apart, and even talk a bit about the Diet of Worms. This episode was written by Neal Schulz, but we messed up the onscreen credits. Thanks, and great work, Neal. You can directly support Crash Course at https://www.patreon.com/crashcourse Subscribe for as little as $0 to keep up with everything we're doing. Free is nice, but if you can afford to pay a little every month, it really helps us to continue producing this content. -
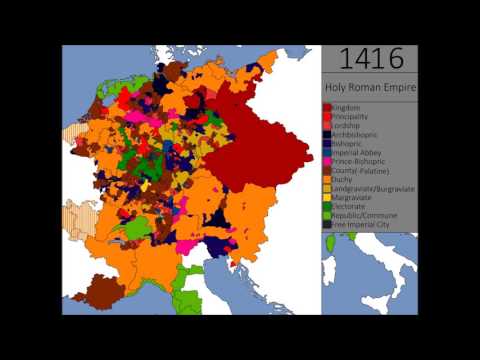 6:39
6:39The Holy Roman Empire: Every State, Every Year
The Holy Roman Empire: Every State, Every YearThe Holy Roman Empire: Every State, Every Year
The Kingdom of East Francia was created in 843 as a partition of the Frankish Empire and result of the Treaty of Verdun. Through Crusades, conquests, and inheritance, it expanded significantly thought the next 200 years, becoming the Holy Roman Empire in 962 after the conquest of Rome. After this point, the Empire began to divide to the point where it was more of the union than a state, allowing foreign powers to control large swaths of imperial territory. It shrank to the benefit of France during the Renaissance, whilst other states, such as the Netherlands and Switzerland, broke off in 1648 due to the Peace of Westphalia. As Prussia and Austria became increasingly dominant through the 1700s, it finally came to an end when they were defeat at the hands of Napoleon in 1806. After Napoleon, a similar state was set up, the German Confederation, which would last almost until German Unification in 1871. --KEY-- Colour = State in the HRE White = Not in HRE Colour-Colour = States within the HRE controlled by state outside HRE Colour-White = Territory outside HRE controlled by state in HRE Coloured Border = Within a March but not controlled (States in HRE controlled by other states in HRE are coluored) --MUSIC-- Alliance - Stand United Aaron Wilde - Together We Rise Anthem of Austria Hungary (1867-1918) -
 6:59
6:59The Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman EmpireThe Holy Roman Empire
See the history of the Holy Roman Empire from its birth 962 to the fall of the empire in 1806. -
 56:56
56:56The Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman EmpireThe Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation. Originally established in A.D. 800. Continuous existence from A.D. 926-1806. -
 90:40
90:40The Dark Ages... Christ Conquers Rome
The Dark Ages... Christ Conquers RomeThe Dark Ages... Christ Conquers Rome
United Preterist Church... https://www.facebook.com/groups/alliancepreterists/ From the fall of Rome to the rise of the Holy Roman Empire...The Kingdom Of God moves forward in history. From The History Channel documentary. -
 12:44
12:44Peter H. Wilson: "The Holy Roman Empire: 1000 Years of Europe's History" (Free Thinking, 10/3/16)
Peter H. Wilson: "The Holy Roman Empire: 1000 Years of Europe's History" (Free Thinking, 10/3/16)Peter H. Wilson: "The Holy Roman Empire: 1000 Years of Europe's History" (Free Thinking, 10/3/16)
*** Rana Mitter reads a new history of the Holy Roman Empire written by Chichele Professor of History Peter H. Wilson. *** -
 7:12
7:12Charlemagne's Holy Roman Empire and the Divine Right to Rule Video Lesson Transcript Study com
Charlemagne's Holy Roman Empire and the Divine Right to Rule Video Lesson Transcript Study comCharlemagne's Holy Roman Empire and the Divine Right to Rule Video Lesson Transcript Study com
Material taken from Study.com A helpful video on Charlemagne and his accomplishments/conquests, especially the massacre of verden. -
 29:30
29:30CHASING A KING! Total War: Attila - Age of Charlemagne - Holy Roman Empire Campaign #45
CHASING A KING! Total War: Attila - Age of Charlemagne - Holy Roman Empire Campaign #45CHASING A KING! Total War: Attila - Age of Charlemagne - Holy Roman Empire Campaign #45
#45 of My Total War: Attila - Age of Charlemagne - Kingdom of The Franks Campaign! Leave a Like For Charlemagne?! Timestamps: Feel Free To Suggest More! 15:05 - Night Sally Out! Battle ----------------------------------------------------------------------- Green Man Gaming Link: http://www.greenmangaming.com/?tap_a=1964-996bbb&tap;_s=2555-b18801 Green Man Gaming Discount Code 20% Off: LIONHE-ARTG20-GAMING ----------------------------------------------------------------------- Check Out EPIC Gaming Laptops from XMG: http://mysn.co.uk/shop?acc=c4ca4238a0b923820dcc509a6f75849b Get £30 OFF XMG Orders with this code: XMG-LIONHEART (Note these cannot be used in conjunction with any monthly special offers nor any other affiliate schemes) ----------------------------------------------------------------------- Get an Great Gaming Chair from GT Omega Here: UK: http://www.gtomegaracing.com/gt-omega-evo-racing-office-chair-black-and-red-leather?tracking=55aa19ed38756 USA: http://usa.gtomegaracing.com/?tracking=55aa19ed38756 For 5% Off At Checkout Use Code: lionheart ----------------------------------------------------------------------- Steamwork shop Attila Mods I'm using: http://steamcommunity.com/sharedfiles/filedetails/?id=434870578 ----------------------------------------------------------------------- Check out my First Impressions of Total War: Attila here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Z-3nX5UlQfg New Upload Schedule: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zJkmsxEoAHQ Check Out My New PS4 Gaming Channel - Deadly Duo Gaming: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC54GEeD-46UtFzK6ZHaqY9Q Missing My Uploads - Subscribe to Email Updates everytime I upload a new Video: http://www.youtube.com/subscription_manager?feature=feed How To Use the New Google+ Comment System on YouTube: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LdKNk-tSbhw&feature;=c4-overview&list;=UUIeaxRCoSLFLHvrCInghqcw ----------------------------------------------------------------------- Please Comment, Thumb UP and Subscribe! ----------------------------------------------------------------------- Connect with me! Email: contact@lionheartx10.co.uk Twitch: http://www.twitch.tv/lionheartx10 Twitter: https://twitter.com/#!/lionheartx10 Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/Lionheartx10 Steam: http://steamcommunity.com/groups/LionheartsLegion 2nd Channel: http://www.youtube.com/user/LionheartsDen Donate: http://tinyurl.com/a7mlfuz -
 27:36
27:36CHARGE POWER! Total War: Attila - Age of Charlemagne - Holy Roman Empire Campaign #44
CHARGE POWER! Total War: Attila - Age of Charlemagne - Holy Roman Empire Campaign #44CHARGE POWER! Total War: Attila - Age of Charlemagne - Holy Roman Empire Campaign #44
#44 of My Total War: Attila - Age of Charlemagne - Kingdom of The Franks Campaign! Leave a Like For Charlemagne?! Timestamps: Feel Free To Suggest More! Coming Soon! ----------------------------------------------------------------------- Green Man Gaming Link: http://www.greenmangaming.com/?tap_a=1964-996bbb&tap;_s=2555-b18801 Green Man Gaming Discount Code 20% Off: LIONHE-ARTG20-GAMING ----------------------------------------------------------------------- Check Out EPIC Gaming Laptops from XMG: http://mysn.co.uk/shop?acc=c4ca4238a0b923820dcc509a6f75849b Get £30 OFF XMG Orders with this code: XMG-LIONHEART (Note these cannot be used in conjunction with any monthly special offers nor any other affiliate schemes) ----------------------------------------------------------------------- Get an Great Gaming Chair from GT Omega Here: UK: http://www.gtomegaracing.com/gt-omega-evo-racing-office-chair-black-and-red-leather?tracking=55aa19ed38756 USA: http://usa.gtomegaracing.com/?tracking=55aa19ed38756 For 5% Off At Checkout Use Code: lionheart ----------------------------------------------------------------------- Steamwork shop Attila Mods I'm using: http://steamcommunity.com/sharedfiles/filedetails/?id=434870578 ----------------------------------------------------------------------- Check out my First Impressions of Total War: Attila here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Z-3nX5UlQfg New Upload Schedule: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zJkmsxEoAHQ Check Out My New PS4 Gaming Channel - Deadly Duo Gaming: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC54GEeD-46UtFzK6ZHaqY9Q Missing My Uploads - Subscribe to Email Updates everytime I upload a new Video: http://www.youtube.com/subscription_manager?feature=feed How To Use the New Google+ Comment System on YouTube: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LdKNk-tSbhw&feature;=c4-overview&list;=UUIeaxRCoSLFLHvrCInghqcw ----------------------------------------------------------------------- Please Comment, Thumb UP and Subscribe! ----------------------------------------------------------------------- Connect with me! Email: contact@lionheartx10.co.uk Twitch: http://www.twitch.tv/lionheartx10 Twitter: https://twitter.com/#!/lionheartx10 Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/Lionheartx10 Steam: http://steamcommunity.com/groups/LionheartsLegion 2nd Channel: http://www.youtube.com/user/LionheartsDen Donate: http://tinyurl.com/a7mlfuz -
 36:07
36:07Medieval II - Holy Roman Empire Campaign #1
Medieval II - Holy Roman Empire Campaign #1Medieval II - Holy Roman Empire Campaign #1
Medieval II: Total War. Vanilla Grand Campaign. Playing as Holy Roman Empire on VH/VH Goal: Conquer all 112 regions and defeat all factions including Mongols, Timurids, and Aztecs. Check out my secondary gaming channel: https://www.youtube.com/user/Legendoftw Visit me on Facebook! http://www.facebook.com/legendoftotalwar For cheap games check out G2A Games https://www.g2a.com/r/paypal-discounted-games Also come visit the forum where you can check out other awesome let's players at: http://www.twcenter.net/forums/forumdisplay.php?1988-The-HUB-Total-War-Media Please note this is an unofficial video and is not endorsed by SEGA or the Creative Assembly in any way. For more information on Total War, please visit http://www.totalwar.com -
 4:06
4:06Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman EmpireHoly Roman Empire
Wir kommen wieder... -
 1:28
1:28*Holy Roman Empire (962-1806)
*Holy Roman Empire (962-1806)*Holy Roman Empire (962-1806)
(*) official name: - Holy Roman Empire of German Nation - Imperium Romanum Sacrum Nationis Germanicæ - Heiliges Römisches Reich Deutscher Nation "Gott erhalte Franz den Kaiser" Imperial anthem - Sources: made using Flag 3D screensaver audio from: LordDaine https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pvT3XAPGenI&list;=PLF4ZIGkgLN1qWmr1Kl-0Q0F6e16MDvVtt&index;=4 -
 274:55
274:55The Holy Roman Empire Rules Today Pt 1,2,3 Full Length
The Holy Roman Empire Rules Today Pt 1,2,3 Full LengthThe Holy Roman Empire Rules Today Pt 1,2,3 Full Length
IN THE BEGINNING http://www.varchive.org/itb/index.htm The Worship of Saturn http://www.varchive.org/itb/satwor.htm A History of the New World Order https://sites.google.com/site/nocancerfoundation/a-history-of-the-new-world-order Playlist https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLBAM35HZ_cLsUvuUvUx4y1R_VGrJBE6CN&feature;=mh_lolz Documents in Law,That go Way Back to Medieval and ancient times http://avalon.law.yale.edu/default.asp Queen Elizabeth controls and has amended U.S. Social Security http://www.apfn.org/apfn/queen.htm You're not a STATUTORY "citizen" under the Internal Revenue Code http://famguardian.org/Subjects/Taxes/Citizenship/NotACitizenUnderIRC.htm We are a Corporation http://www.viewzone.com/collateralx.html The United States the inalienable right to acquire and possess property without paying property tax, etc. http://usa-the-republic.com/revenue/true_history/Chap6.html The original thirteen colonies of America were each separately established by charters from the English Crown. Outside of the common bond of each being a dependency and colony of the mother country, England, the colonies were not otherwise united. Each had its own governor, legislative assembly and courts, and each was governed separately and independently by the English Parliament. http://www.constitution.org/juris/fedjur1.htm The United States Isn't a Country -- It's a Corporation! http://www.serendipity.li/jsmill/us_corporation.htm True History TABLE OF CONTENTS http://usa-the-republic.com/revenue/true_history/Contents.html American Citizen, or U.S. citizen? http://usa-the-republic.com/revenue/true_history/AffTruth.html DECLARATION OF INDEPENDENCE http://usa-the-republic.com/revenue/true_history/Declaration.html Google search:: The D.C Code America is a Corporation https://www.google.com/#q=The+D.C+Code+America+is+a+Corporation THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA INCORPORATED A private foreign owned off-shore corporation copyrighted, trademarked and registered in the state of Delaware for tax purposes circa 1783, and again in 1925 prior to the manipulated and illegally fomented covert bankruptcy of our once Constitutional Republic, in 1933-1938. There is no actual Constitutional governing body as of 1933. Only a foreign owned private corporation controlled by the IMF, and the Federal Reserve which are both corporations owned by international banksters. BLM, TSA, DHS, IRS, NSA, FEMA, CIA, FBI, BATFE, DOD, DOJ, Park Service, all state, and city police are sub-corporations to USA Inc., and do not represent WE The People only the criminal international banksters that own them. Learn more: http://stopthecrime.net/ THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA INCORPORATED A private foreign owned off-shore corporation copyrighted, trademarked and registered in the state of Delaware for tax purposes circa 1783, and again in 1925 prior to the manipulated and illegally fomented covert bankruptcy of our once Constitutional Republic, in 1933-1938. There is no actual Constitutional governing body as of 1933. Only a foreign owned private corporation controlled by the IMF, and the Federal Reserve which are both corporations owned by international banksters. BLM, TSA, DHS, IRS, NSA, FEMA, CIA, FBI, BATFE, DOD, DOJ, Park Service, all state, and city police are sub-corporations to USA Inc., and do not represent WE The People only the criminal international banksters that own them. Learn more: http://stopthecrime.net/ Documents in Description The British Israel World Federation https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RjmFO4po-bA Stuck in the Middle with You! U.S is a CORPORATION https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KMFWER86j68 Code of Canon Law http://www.vatican.va/archive/ENG1104/__P1D.HTM The pope's power is supreme, as nobody on earth can overrule it. http://www.newadvent.org/cathen/09056a.htm I. What is UCC? https://law.duke.edu/lib/researchguides/ucc/ List of Roman deities http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_Roman_deities "The Pope has the power to change time and he did in 1572 http://planksandnails.hubpages.com/hub/The-Switch-and-Bait-of-Easter Request to all the members of the United Nations (UN) and beyond concerning international support saving Europe, America and finally the rest of the world from total destruction by stopping Agenda 21 and still implementing the on January 25, 1944 by de Belgian King Leopold III completed, but for public withheld "political testament" which is still to be carried out as the Belgian Constitution provides https://sites.google.com/site/nocancerfoundation/eu www.nocancerfoundation.org ▀█▀ █▀ █_█ ▀█▀ █▬█ -
 3:13
3:13Marukaite Chikyuu: Holy Roman Empire (eng sub)
Marukaite Chikyuu: Holy Roman Empire (eng sub)
- Aalen
- Abbasid Caliphate
- Abbot
- Achaemenid Empire
- Adal Sultanate
- Adelaide of Italy
- Adhemar de Monteil
- Afsharid dynasty
- Age of Enlightenment
- Ajuuraan State
- Akkadian Empire
- Alaouite dynasty
- Alfonso X of Castile
- Almohad Caliphate
- Almoravid dynasty
- Alsace
- Alsace-Lorraine
- Anabaptism
- Ancient history
- Angevin Empire
- Annexation
- Anti-popes
- Antipope
- Archduke of Austria
- Arnulf of Carinthia
- Artois
- Asia Minor
- Augsburg
- Aulic Council
- Austria
- Austria-Hungary
- Austrian Circle
- Austrian Empire
- Ayyubid dynasty
- Azania
- Bad Buchau
- Bad Wimpfen
- Bad Windsheim
- Banner
- Baroque period
- Basel
- Battle of Lechfeld
- Battle of Riade
- Battle of Vienna
- Bavaria
- Bavarian Circle
- Belgium
- Benin Empire
- Berengar I
- Berengar I of Italy
- Biberach an der Riss
- Bishop
- Bopfingen
- Bornu Empire
- Bourgeoisie
- Brakel, Germany
- Bremen (state)
- British Empire
- Bulgarian Empire
- Burgenland
- Burgundian Circle
- Buyid dynasty
- Byzantine Emperor
- Byzantine Empire
- Caliphate
- Caliphate of Córdoba
- Calvinism
- Cambrai
- Carolingian dynasty
- Carolingian Empire
- Category Germany
- Catholic Church
- Central Europe
- Chagatai Khanate
- Charlemagne
- Charles the Bald
- Charles the Fat
- Chola Dynasty
- Christendom
- Cluniac Reforms
- Colmar
- Cologne
- Cologne War
- Colonial empire
- Concordat of Worms
- Conrad IV of Germany
- Conrad of Franconia
- Corpus Juris Civilis
- Council of Constance
- Council of Electors
- Council of Princes
- Count
- County
- Crown of Aragon
- Crusader states
- Czech Republic
- Delhi Sultanate
- Dervish State
- Diessenhofen
- Dinkelsbühl
- Diocese
- Donauwörth
- Dortmund
- Duchy
- Duchy of Bavaria
- Duchy of Franconia
- Duchy of Saxony
- Duchy of Swabia
- Duisburg
- Duke
- Duke of Bavaria
- Duke of Saxony
- Dutch Empire
- Dutch Republic
- Décapole
- Düren
- Early modern Europe
- Early modern period
- East Francia
- East Germany
- Eastern Francia
- Ecclesiastical
- Elective monarchy
- Emilia-Romagna
- Emperor of Austria
- Empire
- Empire of Brazil
- Empire of Japan
- Esslingen am Neckar
- Ethiopian Empire
- Fatimid Caliphate
- Feudal law
- Feudalism
- First French Empire
- First Mexican Empire
- Flensburg Government
- Fourth Reich
- France
- Franche-Comté
- Francia
- Franconia
- Franconian Circle
- Frankfurt
- Franks
- Free City of Danzig
- Free City of Lübeck
- Free Imperial City
- Free imperial city
- Freiburg
- French Flanders
- French Revolution
- Friedberg, Hesse
- Friedrichshafen
- Frisians
- Fritzlar
- Gelnhausen
- Gengenbach
- German Austria
- German Confederation
- German dualism
- German Empire
- German language
- German Mediatisation
- German Reformation
- German Reich
- German Renaissance
- German reunification
- Germanic peoples
- Germanization
- Germans
- Germany
- Ghana Empire
- Ghaznavids
- Giengen
- Gobroon Dynasty
- Golden Bull of 1356
- Golden Horde
- Goslar
- Gothic art
- Great Seljuq Empire
- Gupta Empire
- Gurjara-Pratihara
- Guy III of Spoleto
- Habsburg
- Habsburg Monarchy
- Haguenau
- Hamburg
- Han Dynasty
- Hanseatic League
- Heilbronn
- Henry the Fowler
- Henry the Lion
- Herford
- High Middle Ages
- Historical powers
- History of Berlin
- History of Bern
- History of China
- History of France
- History of Germany
- History of Haiti
- History of India
- History of Iran
- History of Morocco
- History of Zürich
- Hohenstaufen
- Holy Lance
- Holy Roman Emperor
- Holy Roman Empire
- House of Lorraine
- House of Luxembourg
- House of Welf
- Hunnic Empire
- Hussites
- Idrisid dynasty
- Ifat Sultanate
- Ilkhanate
- Imperial Circle
- Imperial Free City
- Imperial immediacy
- Imperial Knights
- Imperial Reform
- Imperial State
- Inca Empire
- Interregnum
- Isny im Allgäu
- Italian Empire
- Italian language
- Italy
- Joanna of Castile
- John III Sobieski
- Kaiserpfalz
- Kanem Empire
- Kaufbeuren
- Kaysersberg
- Kessenich
- Khmer Empire
- Khwarazmian dynasty
- Kievan Rus'
- King
- King of Bohemia
- King of Hungary
- King of the Romans
- Kingdom of Aksum
- Kingdom of Arles
- Kingdom of England
- Kingdom of Germany
- Kingdom of Kush
- Kingdom of Prussia
- Klaipėda Region
- Kleinstaaterei
- Knights
- Konrad of Masovia
- Konstanz
- Korean Empire
- Kushan Empire
- Land of Punt
- Landau
- Landfrieden
- Late Middle Ages
- Latin
- Latin language
- Lemgo
- Leutkirch im Allgäu
- Liechtenstein
- Lindau
- List of empires
- Lombardy
- Lordship of Jever
- Lorraine (province)
- Lorraine (region)
- Lothair I
- Lotharingia
- Louis II of Italy
- Louis the Blind
- Louis the Child
- Louis the Pious
- Louis XIV of France
- Lower Saxon Circle
- Lucerne
- Lutheranism
- Luxembourg
- Lübeck
- Magdeburg
- Magyars
- Mainz
- Majapahit
- Majeerteen Sultanate
- Mali Empire
- Maratha Empire
- Marinid dynasty
- Martin Luther
- Martin Waldseemüller
- Maurya Empire
- Medes
- Mediatization
- Medieval Armenia
- Medieval art
- Medieval commune
- Medieval Georgia
- Medieval literature
- Medieval Livonia
- Medieval music
- Medieval philosophy
- Medieval poetry
- Medieval technology
- Medieval university
- Medieval warfare
- Memmingen
- Metz
- Mexican Empire
- Middle Ages
- Middle Francia
- Migration Period
- Milan
- Ming Dynasty
- Modern history
- Monaco
- Monarchy
- Mongol Empire
- Mughal Empire
- Mulhouse
- Munich
- Munster, Haut-Rhin
- Mühlhausen
- Names of Germany
- Napoleon Bonaparte
- Napoleon I of France
- Napoleonic Wars
- Nationalism
- Nazi Germany
- Neo-Assyrian Empire
- Netherlands
- Neumark
- New Kingdom
- Nicolas de Fer
- Nordhausen
- North Sea Empire
- Northern Netherlands
- Nuremberg
- Nördlingen
- Obernai
- Offenburg
- Old Prussians
- Ostsiedlung
- Otto I
- Ottoman Empire
- Ottonian dynasty
- OUP
- Oyo Empire
- Pahlavi dynasty
- Pala Empire
- Papacy
- Parthian Empire
- Patchwork
- Paul IV
- Peace of Augsburg
- Peace of Westphalia
- Persianate society
- Pfullendorf
- Phenomenon
- Philip II of Spain
- Philip of Swabia
- Piedmont
- Pier Gerlofs Donia
- Poland
- Pomerania
- Pope
- Pope Alexander III
- Pope Gregory VII
- Pope Innocent III
- Pope Leo III
- Portal Germany
- Portuguese Empire
- Power (sociology)
- Prekmurje
- Prince
- Prince of the church
- Prince-bishop
- Prince-elector
- Principality
- Protestant
- Protestant Union
- Prussia
- Prussia (region)
- Ptolemaic Kingdom
- Qajar dynasty
- Qin Dynasty
- Qing Dynasty
- Rashidun Caliphate
- Ravensburg
- Regensburg
- Regino of Prüm
- Reich
- Reichsfreiheit
- Reichskammergericht
- Reichssturmfahne
- Reutlingen
- Rheinfelden
- Rhine
- Richard I of England
- Ripuarian Franks
- Roman Catholic
- Roman Empire
- Romance languages
- Rosheim
- Rottweil
- Rudolf II
- Rudolf of Swabia
- Rule of law
- Russian Empire
- Saadi dynasty
- Saar (protectorate)
- Safavid dynasty
- Salian
- Salian Franks
- Sallarid
- Samanids
- San Marino
- Sarrebourg
- Sassanid Empire
- Satellite state
- Savoy
- Saxons
- Schaffhausen
- Schmalkalden
- Schweinfurt
- Schwäbisch Gmünd
- Schwäbisch Hall
- Second French Empire
- Secularization
- Seleucid Empire
- Serbian Empire
- Sikh Empire
- Silesia
- Sixth Crusade
- Slavic languages
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Soest, Germany
- Solomonic dynasty
- Solothurn
- Somali people
- Song Dynasty
- Songhai Empire
- South Tyrol
- Southern Schleswig
- Sovereignty
- Spanish Crown
- Spanish Empire
- Speyer
- Srivijaya
- St. Gallen
- Stem duchy
- Strasbourg
- Styria (duchy)
- Städtebund
- Sudetenland
- Sui Dynasty
- Sultanate of Hobyo
- Swabia
- Swabian Circle
- Swedish Empire
- Swiss Confederation
- Switzerland
- Sélestat
- Tahirid Dynasty
- Tang Dynasty
- Template Empires
- Teotihuacan
- Teutonic Knights
- Theophanu
- Third Crusade
- Thirty Years War
- Thirty Years' War
- Timurid dynasty
- Toul
- Translatio imperii
- Treaty of Pressburg
- Trentino
- Trier
- Tu'i Tonga Empire
- Turckheim
- Tuscany
- Umayyad Caliphate
- Upper Rhenish Circle
- Upper Saxon Circle
- Vehmic court
- Verden an der Aller
- Verdun
- Voltaire
- Walk to Canossa
- Wangen im Allgäu
- Warburg
- Warsangali Sultanate
- Weil der Stadt
- Weimar Republic
- Weißenburg in Bayern
- West Germany
- West Slavs
- Western Francia
- Western Roman Empire
- Wetzlar
- Wijerd Jelckama
- Wissembourg
- Wittelsbach
- Worms, Germany
- Worms-Pfeddersheim
- Yuan Dynasty
- Zagwe dynasty
- Zand dynasty
- Zell am Harmersbach
- Ziyarid dynasty
- Zollverein
- Zwingliism
- Überlingen
- Achaemenid Empire
- Akkadian Empire
- Alsace
- Artois
- Austria
- Austrian Empire
- Bavaria
- Belgium
- British Empire
- Burgenland
- Caliphate of Córdoba
- Cambrai
- Colmar
- Council of Constance
- Czech Republic
- Dutch Empire
- Dutch Republic
- East Germany
- Empire of Brazil
- Empire of Japan
- First French Empire
- France
- Franconia
- Free City of Danzig
- Free City of Lübeck
- German Confederation
- German Empire
- Germany
- Ghana Empire
- Haguenau
- Hamburg
- Han Dynasty
- Hanseatic League
- Idrisid dynasty
- Italian Empire
- Italy
- Kaysersberg
- Kessenich
- Khmer Empire
- Kingdom of England
- Korean Empire
- Liechtenstein
- Luxembourg
- Medes
- Metz
- Milan
- Ming Dynasty
- Monaco
- Mughal Empire
- Mulhouse
- Nazi Germany
- Netherlands
- Obernai
- Parthian Empire
- Poland
- Pomerania
- Portuguese Empire
- Prekmurje
- Qing Dynasty
- Reichskammergericht
- Rosheim
- Russian Empire
- Safavid dynasty
- San Marino
- Sarrebourg
- Savoy
- Second French Empire
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- South Tyrol
- Southern Schleswig
- Spanish Empire
- Strasbourg
- Switzerland
- Sélestat
- Teotihuacan
- Toul
- Trentino
- Turckheim
- Verdun
- Wangen im Allgäu
- Warsangali Sultanate
- Weimar Republic
- West Germany
- Wissembourg
- Yuan Dynasty
- Adelaide of Italy
- Alfonso X of Castile
- Almohad Caliphate
- Alsace
- Arnulf of Carinthia
- Austria
- Berengar I of Italy
- Buyid dynasty
- Charlemagne
- Charles the Bald
- Charles the Fat
- Conrad IV of Germany
- Franks
- Frisians
- Germanic peoples
- Germans
- Guy III of Spoleto
- Henry the Fowler
- Henry the Lion
- House of Luxembourg
- Hunnic Empire
- Inca Empire
- Joanna of Castile
- John III Sobieski
- Kingdom of Kush
- Lothair I
- Louis II of Italy
- Louis the Blind
- Louis the Child
- Louis the Pious
- Louis XIV of France
- Martin Luther
- Martin Waldseemüller
- Medes
- Old Prussians
- Ottonian dynasty
- Philip II of Spain
- Philip of Swabia
- Pier Gerlofs Donia
- Pope Alexander III
- Pope Gregory VII
- Pope Innocent III
- Pope Leo III
- Rashidun Caliphate
- Regino of Prüm
- Richard I of England
- Ripuarian Franks
- Salian Franks
- Saxons
- Somali people
- Songhai Empire
- Teotihuacan
- Theophanu
- Voltaire
- Wijerd Jelckama
Holy Roman Empire
ALBUMS
- Egress released:
Egress
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Egress
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Before You Settle
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Halogens
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Scaling the U of I Art Building
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Gnosssiennes Pour Iowam
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Red Shoelaces
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Duffle Bag
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Uneven Lanes
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Through the Streets of Everywhere
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Ghost Sheets
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Bed Bugs
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Dead Dream Girl Ship
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Night Could Cover Up
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Worried Fingers
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen A Kettle to Let the Heat In
Holy Roman Empire
ALBUMS
- The Longue Durée released: 2007
The Longue Durée
Released 2007- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Undeserving You
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Ace
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen An Alliance of Thieves
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Hail Mary
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Our Whole Lives, Waiting
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Shatter Historic
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Olympus
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Mute Hearts
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Action Figures
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Take It Outside
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Fire Drill
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Vicarious Haunting
-

Charles V and the Holy Roman Empire: Crash Course World History #219
Get the new Crash Course World History Character poster here: http://store.dftba.com/products/crashcourse-characters-poster In which John Green teaches you about the Holy Roman Empire by teaching you about Charles V. Charles Hapsburg was the holy Roman Emperor, but he was also the King of Spain. And the King of Germany. And the King of Italy and the Lord of the Netherlands and Count Palatine of Burgundy. In short, Charles was runnin' thangs in much of the world during his reign. Charles ruled a lot of countries, and he was also known for encouraging intellectual discourse and he even spoke out against slavery, in a limited. So why did he consider himself a failure, and why did he break up the Empire when he abdicated in 1556? Mainly because the Holy Roman Empire didn't work very well. It ... -

The Holy Roman Empire: Every State, Every Year
The Kingdom of East Francia was created in 843 as a partition of the Frankish Empire and result of the Treaty of Verdun. Through Crusades, conquests, and inheritance, it expanded significantly thought the next 200 years, becoming the Holy Roman Empire in 962 after the conquest of Rome. After this point, the Empire began to divide to the point where it was more of the union than a state, allowing foreign powers to control large swaths of imperial territory. It shrank to the benefit of France during the Renaissance, whilst other states, such as the Netherlands and Switzerland, broke off in 1648 due to the Peace of Westphalia. As Prussia and Austria became increasingly dominant through the 1700s, it finally came to an end when they were defeat at the hands of Napoleon in 1806. After Napoleon... -

The Holy Roman Empire
See the history of the Holy Roman Empire from its birth 962 to the fall of the empire in 1806. -

The Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation. Originally established in A.D. 800. Continuous existence from A.D. 926-1806. -

The Dark Ages... Christ Conquers Rome
United Preterist Church... https://www.facebook.com/groups/alliancepreterists/ From the fall of Rome to the rise of the Holy Roman Empire...The Kingdom Of God moves forward in history. From The History Channel documentary. -

Peter H. Wilson: "The Holy Roman Empire: 1000 Years of Europe's History" (Free Thinking, 10/3/16)
*** Rana Mitter reads a new history of the Holy Roman Empire written by Chichele Professor of History Peter H. Wilson. *** -

Charlemagne's Holy Roman Empire and the Divine Right to Rule Video Lesson Transcript Study com
Material taken from Study.com A helpful video on Charlemagne and his accomplishments/conquests, especially the massacre of verden. -

CHASING A KING! Total War: Attila - Age of Charlemagne - Holy Roman Empire Campaign #45
#45 of My Total War: Attila - Age of Charlemagne - Kingdom of The Franks Campaign! Leave a Like For Charlemagne?! Timestamps: Feel Free To Suggest More! 15:05 - Night Sally Out! Battle ----------------------------------------------------------------------- Green Man Gaming Link: http://www.greenmangaming.com/?tap_a=1964-996bbb&tap;_s=2555-b18801 Green Man Gaming Discount Code 20% Off: LIONHE-ARTG20-GAMING ----------------------------------------------------------------------- Check Out EPIC Gaming Laptops from XMG: http://mysn.co.uk/shop?acc=c4ca4238a0b923820dcc509a6f75849b Get £30 OFF XMG Orders with this code: XMG-LIONHEART (Note these cannot be used in conjunction with any monthly special offers nor any other affiliate schemes) -------------------------------------------------------... -

CHARGE POWER! Total War: Attila - Age of Charlemagne - Holy Roman Empire Campaign #44
#44 of My Total War: Attila - Age of Charlemagne - Kingdom of The Franks Campaign! Leave a Like For Charlemagne?! Timestamps: Feel Free To Suggest More! Coming Soon! ----------------------------------------------------------------------- Green Man Gaming Link: http://www.greenmangaming.com/?tap_a=1964-996bbb&tap;_s=2555-b18801 Green Man Gaming Discount Code 20% Off: LIONHE-ARTG20-GAMING ----------------------------------------------------------------------- Check Out EPIC Gaming Laptops from XMG: http://mysn.co.uk/shop?acc=c4ca4238a0b923820dcc509a6f75849b Get £30 OFF XMG Orders with this code: XMG-LIONHEART (Note these cannot be used in conjunction with any monthly special offers nor any other affiliate schemes) ----------------------------------------------------------------------- Ge... -

Medieval II - Holy Roman Empire Campaign #1
Medieval II: Total War. Vanilla Grand Campaign. Playing as Holy Roman Empire on VH/VH Goal: Conquer all 112 regions and defeat all factions including Mongols, Timurids, and Aztecs. Check out my secondary gaming channel: https://www.youtube.com/user/Legendoftw Visit me on Facebook! http://www.facebook.com/legendoftotalwar For cheap games check out G2A Games https://www.g2a.com/r/paypal-discounted-games Also come visit the forum where you can check out other awesome let's players at: http://www.twcenter.net/forums/forumdisplay.php?1988-The-HUB-Total-War-Media Please note this is an unofficial video and is not endorsed by SEGA or the Creative Assembly in any way. For more information on Total War, please visit http://www.totalwar.com -

Holy Roman Empire
Wir kommen wieder... -

*Holy Roman Empire (962-1806)
(*) official name: - Holy Roman Empire of German Nation - Imperium Romanum Sacrum Nationis Germanicæ - Heiliges Römisches Reich Deutscher Nation "Gott erhalte Franz den Kaiser" Imperial anthem - Sources: made using Flag 3D screensaver audio from: LordDaine https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pvT3XAPGenI&list;=PLF4ZIGkgLN1qWmr1Kl-0Q0F6e16MDvVtt&index;=4 -

The Holy Roman Empire Rules Today Pt 1,2,3 Full Length
IN THE BEGINNING http://www.varchive.org/itb/index.htm The Worship of Saturn http://www.varchive.org/itb/satwor.htm A History of the New World Order https://sites.google.com/site/nocancerfoundation/a-history-of-the-new-world-order Playlist https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLBAM35HZ_cLsUvuUvUx4y1R_VGrJBE6CN&feature;=mh_lolz Documents in Law,That go Way Back to Medieval and ancient times http://avalon.law.yale.edu/default.asp Queen Elizabeth controls and has amended U.S. Social Security http://www.apfn.org/apfn/queen.htm You're not a STATUTORY "citizen" under the Internal Revenue Code http://famguardian.org/Subjects/Taxes/Citizenship/NotACitizenUnderIRC.htm We are a Corporation http://www.viewzone.com/collateralx.html The United States the inalienable right to acquire and possess p... -

-

Europa Universalis IV Renovatio Imperii - Unite The Holy Roman Empire!
I have united the Holy Roman Empire in Europa Universalis IV with Austria. I think, this is awesome! Historically, The Holy Roman Empire was a multi-ethnic and complex union of territories in Central Europe existing from 962 to 1806. The territories making up the Empire lay predominantly in Central Europe. At its peak in 1050, under Emperor Henry III, it included the Kingdom of Germany, the Kingdom of Bohemia, the Kingdom of Italy, and the Kingdom of Burgundy. The Holy Roman Empire never achieved the extent of political unification formed in France, evolving instead into a decentralized, limited elective monarchy composed of hundreds of smaller sub-units, principalities, duchies, counties, Free Imperial Cities, and other domains. The power of the emperor was limited, and while the various ... -

"Gott erhalte Franz den Kaiser" The Imperial Anthem of the Holy Roman Empire
I own no audio or visual content heard/seen in this video. "Gott erhalte Franz den Kaiser" (God Save Emperor Francis) is an anthem to Francis II, Emperor of the Holy Roman Empire and later of Austria. The lyrics were by Lorenz Leopold Haschka (1749–1827), and the melody by Joseph Haydn. It is sometimes called the "Kaiserhymne" (Emperor's Hymn). Haydn's tune has since been widely employed in other contexts: in works of classical music, in Christian hymns, in alma maters, and as the tune of the Deutschlandlied, the national anthem of Germany. -

UNEXPECTED ATTACK! Total War: Attila - Age of Charlemagne - Holy Roman Empire Campaign #43
#43 of My Total War: Attila - Age of Charlemagne - Kingdom of The Franks Campaign! Leave a Like For Charlemagne?! Timestamps: Feel Free To Suggest More! 11:01 - A Fine Day To Die! Battle ----------------------------------------------------------------------- Green Man Gaming Link: http://www.greenmangaming.com/?tap_a=1964-996bbb&tap;_s=2555-b18801 Green Man Gaming Discount Code 20% Off: LIONHE-ARTG20-GAMING ----------------------------------------------------------------------- Check Out EPIC Gaming Laptops from XMG: http://mysn.co.uk/shop?acc=c4ca4238a0b923820dcc509a6f75849b Get £30 OFF XMG Orders with this code: XMG-LIONHEART (Note these cannot be used in conjunction with any monthly special offers nor any other affiliate schemes) -----------------------------------------------------... -

Medieval II Total War - Official Holy Roman Empire Feature PC Game Trailer
The Holy Roman Empire (HRE; German: Heiliges Römisches Reich (HRR), Latin: Imperium Romanum Sacrum (IRS), Italian: Sacro Romano Impero (SRI)) was an empire that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe. It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes. In its last centuries, its character became quite close to a union of territories. The empire's territory was centered on the Kingdom of Germany, and included neighboring territories, which at its peak included the Kingdom of Italy and the Kingdom of Burgundy. For much of its history, the Empire consisted of hundreds of smaller sub-units, principalities, duchies, counties, Free Imperial Cities and othe... -

Europa Universalis IV 4 What is The Holy Roman Empire
I answer no the not so simple question of what is the Holy Roman Empire in Europa Universalis 4 and how exactly does it work -

Fall of The Roman Empire...in the 15th Century: Crash Course World History #12
Crash Course World History is now available on DVD! Visit http://store.dftba.com/products/crashcourse-world-history-the-complete-series-dvd-set to buy a set for your home or classroom. You can directly support Crash Course at http://www.patreon.com/crashcourse Subscribe for as little as $0 to keep up with everything we're doing. Free is nice, but if you can afford to pay a little every month, it really helps us to continue producing this content. In which John Green teaches you about the fall of the Roman Empire, which happened considerably later than you may have been told. While the Western Roman Empire fell to barbarians in 476 CE, the Byzantines in Constantinople continued the Eastern Empire nicely, calling themselves Romans for a further 1000 years. Find out what Justinian and the r... -

EUIV The Holy Roman Record Race 1
Let's play Europa Universalis IV with the Art of War expansion! We will be playing as Austria and attempting to conquer the world in a record breaking time. This will involve a few... questionable game mechanics. ;) If you enjoyed this video please consider hitting the Like button, it helps the channel grow by affecting search results on YouTube. Make sure to subscribe to the channel so you stay up to date on new releases!: http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=Arumba07 This series is best viewed from the playlist: http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLH-huzMEgGWBt15tyffeTcNcUZwDlJgas -

Medieval II - Holy Roman Empire Campaign #36 FINAL
Medieval II: Total War. Vanilla Grand Campaign. Playing as Holy Roman Empire on VH/VH Goal: Conquer all 112 regions and defeat all factions including Mongols, Timurids, and Aztecs. Check out my secondary gaming channel: https://www.youtube.com/user/Legendoftw Visit me on Facebook! http://www.facebook.com/legendoftotalwar For cheap games check out G2A Games https://www.g2a.com/r/paypal-discounted-games Also come visit the forum where you can check out other awesome let's players at: http://www.twcenter.net/forums/forumdisplay.php?1988-The-HUB-Total-War-Media Please note this is an unofficial video and is not endorsed by SEGA or the Creative Assembly in any way. For more information on Total War, please visit http://www.totalwar.com -

Holy Roman Empire Newspaper Headline
A British journalist recently advised the European Union to follow in the tradition of Charlemagne. What is Charlemagne’s legacy? Few people know, even though the most prestigious prize in Europe is named after him. The rise of a European beast power is one of the most critical prophecies in the Bible. Learn how Europe will go the way of Charlemagne one last time—next, on The Key of David, with Gerald Flurry. ++++++++++++++ Connect with Gerald Flurry and the Key of David at: https://www.facebook.com/GeraldRFlurry https://plus.google.com/+GeraldFlurry https://twitter.com/keyofdavidtv Read or watch everything Gerald Flurry here: https://www.thetrumpet.com/columnist/4/gerald-flurry Learn more about Gerald Flurry here: https://www.pcog.org/about/gerald-flurry www.geraldflurry.com www.geral...
Charles V and the Holy Roman Empire: Crash Course World History #219
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 13:16
- Updated: 06 Dec 2014
- views: 832925
- published: 06 Dec 2014
- views: 832925
The Holy Roman Empire: Every State, Every Year
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:39
- Updated: 21 Oct 2015
- views: 37550
- published: 21 Oct 2015
- views: 37550
The Holy Roman Empire
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:59
- Updated: 26 Apr 2015
- views: 79702
- published: 26 Apr 2015
- views: 79702
The Holy Roman Empire
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 56:56
- Updated: 02 Nov 2014
- views: 4105
- published: 02 Nov 2014
- views: 4105
The Dark Ages... Christ Conquers Rome
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 90:40
- Updated: 05 Jun 2014
- views: 41061
- published: 05 Jun 2014
- views: 41061
Peter H. Wilson: "The Holy Roman Empire: 1000 Years of Europe's History" (Free Thinking, 10/3/16)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 12:44
- Updated: 11 Mar 2016
- views: 20
- published: 11 Mar 2016
- views: 20
Charlemagne's Holy Roman Empire and the Divine Right to Rule Video Lesson Transcript Study com
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:12
- Updated: 15 Dec 2015
- views: 114
- published: 15 Dec 2015
- views: 114
CHASING A KING! Total War: Attila - Age of Charlemagne - Holy Roman Empire Campaign #45
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 29:30
- Updated: 24 Mar 2016
- views: 388
- published: 24 Mar 2016
- views: 388
CHARGE POWER! Total War: Attila - Age of Charlemagne - Holy Roman Empire Campaign #44
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 27:36
- Updated: 22 Mar 2016
- views: 552
- published: 22 Mar 2016
- views: 552
Medieval II - Holy Roman Empire Campaign #1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 36:07
- Updated: 01 May 2015
- views: 25242
- published: 01 May 2015
- views: 25242
Holy Roman Empire
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:06
- Updated: 22 Dec 2011
- views: 34004
*Holy Roman Empire (962-1806)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:28
- Updated: 30 Apr 2014
- views: 8231
- published: 30 Apr 2014
- views: 8231
The Holy Roman Empire Rules Today Pt 1,2,3 Full Length
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 274:55
- Updated: 23 May 2014
- views: 8574
- published: 23 May 2014
- views: 8574
Marukaite Chikyuu: Holy Roman Empire (eng sub)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:13
- Updated: 09 Aug 2012
- views: 255038
Europa Universalis IV Renovatio Imperii - Unite The Holy Roman Empire!
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:45
- Updated: 20 Sep 2013
- views: 35182
- published: 20 Sep 2013
- views: 35182
"Gott erhalte Franz den Kaiser" The Imperial Anthem of the Holy Roman Empire
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:35
- Updated: 16 May 2015
- views: 13282
- published: 16 May 2015
- views: 13282
UNEXPECTED ATTACK! Total War: Attila - Age of Charlemagne - Holy Roman Empire Campaign #43
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 27:35
- Updated: 20 Mar 2016
- views: 63
- published: 20 Mar 2016
- views: 63
Medieval II Total War - Official Holy Roman Empire Feature PC Game Trailer
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:46
- Updated: 24 Mar 2012
- views: 1364
- published: 24 Mar 2012
- views: 1364
Europa Universalis IV 4 What is The Holy Roman Empire
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:49
- Updated: 13 Aug 2013
- views: 25928
- published: 13 Aug 2013
- views: 25928
Fall of The Roman Empire...in the 15th Century: Crash Course World History #12
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 12:44
- Updated: 13 Apr 2012
- views: 3062767
- published: 13 Apr 2012
- views: 3062767
EUIV The Holy Roman Record Race 1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 16:18
- Updated: 05 Dec 2014
- views: 110455
- published: 05 Dec 2014
- views: 110455
Medieval II - Holy Roman Empire Campaign #36 FINAL
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 43:45
- Updated: 17 Oct 2015
- views: 5655
- published: 17 Oct 2015
- views: 5655
Holy Roman Empire Newspaper Headline
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 27:39
- Updated: 04 Feb 2016
- views: 401
- published: 04 Feb 2016
- views: 401
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

Charles V and the Holy Roman Empire: Crash Course World History #219
- Report rights infringement
- published: 06 Dec 2014
- views: 832925

The Holy Roman Empire: Every State, Every Year
- Report rights infringement
- published: 21 Oct 2015
- views: 37550

The Holy Roman Empire
- Report rights infringement
- published: 26 Apr 2015
- views: 79702

The Holy Roman Empire
- Report rights infringement
- published: 02 Nov 2014
- views: 4105

The Dark Ages... Christ Conquers Rome
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Jun 2014
- views: 41061

Peter H. Wilson: "The Holy Roman Empire: 1000 Years of Europe's History" (Free Thinking, 10/3/16)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 11 Mar 2016
- views: 20

Charlemagne's Holy Roman Empire and the Divine Right to Rule Video Lesson Transcript Study com
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Dec 2015
- views: 114

CHASING A KING! Total War: Attila - Age of Charlemagne - Holy Roman Empire Campaign #45
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 Mar 2016
- views: 388

CHARGE POWER! Total War: Attila - Age of Charlemagne - Holy Roman Empire Campaign #44
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 Mar 2016
- views: 552

Medieval II - Holy Roman Empire Campaign #1
- Report rights infringement
- published: 01 May 2015
- views: 25242

Holy Roman Empire
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 Dec 2011
- views: 34004

*Holy Roman Empire (962-1806)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 30 Apr 2014
- views: 8231

The Holy Roman Empire Rules Today Pt 1,2,3 Full Length
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 May 2014
- views: 8574

Marukaite Chikyuu: Holy Roman Empire (eng sub)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 09 Aug 2012
- views: 255038
-
Lyrics list:text lyricsplay full screenplay karaoke
Miley Cyrus joining ‘The Voice’ for Season 11 as a judge
Edit Zap2it 26 Mar 2016UN slams 'gruesome' killing of Palestinian
Edit Dawn 26 Mar 2016Islamic State suicide bomber kills dozens at soccer game in Iraq
Edit Sydney Morning Herald 26 Mar 2016Amy Adams' wedding setting inspired by Forrest Gump movie
Edit Belfast Telegraph 26 Mar 2016Pope Francis slams Europe’s ‘anaesthetised conscience’ over migrants
Edit Indian Express 26 Mar 2016In the Capital of Europe
Edit The New York Review of Books 22 Mar 2016Rick Steves' Europe: Luzern offers Swiss mix of urban delights
Edit The Oklahoman 20 Mar 2016the changing face of Euroscepticism
Edit New Statesman 09 Mar 2016Gerardus Mercator
Edit Topix 05 Mar 2016'Heart of Europe' is history at its most engaging
Edit The Christian Science Monitor 01 Mar 2016Starkland releases a CD of ICE surveying two emerging composers
Edit The Examiner 29 Feb 2016What to Do with Dilapidated Nuremberg Nazi Rally Grounds?
Edit World History Online 29 Feb 2016The civil wars of Louis the Pious
Edit The Examiner 27 Feb 2016Liverpool v Augsburg: Europa League second leg – live!
Edit The Guardian 25 Feb 2016Brexit still a big gamble for sceptics of unionism
Edit Belfast Telegraph 24 Feb 2016Matilda of Tuscany
Edit About.com 22 Feb 2016Witch Hunts in Europe: Timeline
Edit About.com 22 Feb 2016- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »







