-
Crust (geology)
In geology, the crust is the outermost solid shell of a rocky planet or natural satellite, which is chemically distinct from the underlying mantle. The crusts of Earth, the Moon, Mercury, Venus, Mars, Io, and other planetary bodies have been generated largely by igneous processes, and these crusts are richer in incompatible elements than their respective mantles.
This video is targeted to blind
-
Geology: Continental Crust
continental crust
-
FULL EPISODE Lesson 10 Deformation of the Crust - Understanding the Earth
Deformation of the crust - Geological Interpretation - How rocks behave under stress, to better understand earthquakes. (60minutes) Host; Dr. David Pearson. ...
-
What Is A Geologic Fold?
Hi, I'm Emerald Robinson, and in this "What is" video, we're going to talk about geology as we try to answer the question, "What is a fold?" A fold is a rock...
-
The Early Earth and Plate Tectonics
The Earth is formed by accretion of spatial particulates and large masses and eventually forms an outer crust. Video follows with speculation of early plates...
-
Crustal Deformation - Part 1
Lecture on crustal deformation - 1.
-
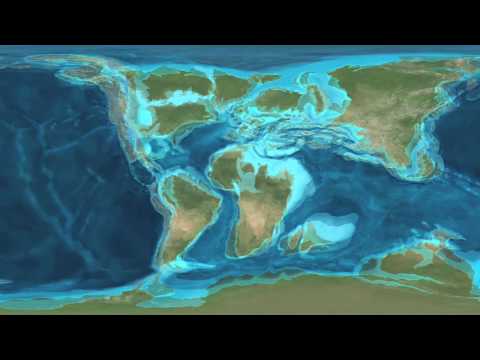
Earth 100 Million Years From Now
Earth's landmasses were not always what they are today. Continents formed as Earth's crustal plates shifted and collided over long periods of time. This video shows how today's continents are thought to have evolved over the last 600 million years, and where they'll end up in the next 100 million years. Paleogeographic Views of Earth's History provided by Ron Blakey, Professor of Geology, Northern
-
Living Rock: An Introduction to Earth's Geology
Living Rock - An Introduction to Earth's Geology movie was released Aug 13, 2002 by the DVD International studio. Ever wonder why earthquakes happen, or how a volcano works? Living Rock - An Introduction to Earth's Geology movie Find the answers to these and many other questions in LIVING ROCK, a fun and educational program about the Earth's geology, jointly produced by the US Geological Survey an
-
Oman Ophiolite - Lower oceanic crust and moho
Geological field excursion to the Oman ophiolite. In these videos Hugh Rollinson, from the University of Derby, takes you on a geological journey from the oc...
-
Geology in Quran
PLEASE READ IT ALL!!! In Geology, the phenomenon of folding is a recently discovered fact. Folding is responsible for the formation of mountain ranges. The e...
-
Reverse Fault | Geology
Reverse Fault | Geology
A type of fault formed when the hanging wall fault block moves up along a fault surface relative to the footwall. Such movement can occur in areas where the Earth's crust is compressed. A thrust fault, sometimes called an overthrust if the displacement is particularly great, is a reverse fault in which the fault plane has a shallow dip, typically much less than 45.
This
-
Geology Kitchen #9 - Plate Tectonics
This episode discusses the scientific theory of plate tectonics, in which the Earth's crust is subdivided into a series of large and small tectonic plates. C...
-
Earth Science: Geology - Our Restless Planet - K4518DVD
Excerpt from Geology: Our Restless Planet from the Show Me Science series from TMW Media to purchase this title on DVD, go to http://www.tmwmedia.com/Wonders...
-
The Amazing Under Sea World The Deepest Geology On Earth Geology Documentary
The Earth's crust is made up of a jigsaw puzzle of plates, moving like ice floes in a frozen sea. Where two plates collide, the edge of one usually slides down into the Earth's interior, forming a deep ocean trench. Where two plates move apart, magma has to fill the gap between them which melts as it rises from the Earth's mantle below and feeds chains of undersea volcanoes creating too many extra
-
Geological Isostatic Adjustment and The Great Lakes Region
This video details highlights of the effects Geological Isostatic Adjustment has had on the formation of the Great Lakes Region and provides possible insight...
-
Structural Geology Research with Dr. Randy Merrett
Dr. Randy Merrett is an Associate Professor in the Department of Geological Sciences at the University of Texas. Dr. Marrett's research concentrates on defor...
-
Geology Kitchen #11 - Igneous Rocks
Igneous rocks are rocks derived from the cooling of magma, molten material originating from the upper Mantle/lower crust. Igneous rocks are classified by the...
-
Geology
This video is made by Science & Faith. MOUNTAINS ARE LIKE PEGS (STAKES) In Geology, the phenomenon of 'folding' is a recently discovered fact. Folding is res...
-
On Structural Geology, Faults, and Rocks
Richard Sibson discusses changing emphasis in structural geology from a focus on continuous structures (e.g., folding) to the modern recognition of discontinuities accommodating major crustal displacements. Hydrothermal veins also demonstrate that fault systems are dominant conduits for fluid redistribution in the crust, with episodes of overpressure and fluid flow tied to the earthquake stress cy
-
Geologist Says Major Earthquake Imminent for California - Jim Berkland
Interviewer is Bil Carroll KFI 640 am Los Angeles Within days of the Sendai event, retired geologist Jim Berkland began sounding warnings that another earthq...
-
Overview of the Hadean Eon
Overview of the Hadean Eon. Geology 101 at the University of Kansas Made by Group 27: Timothy Frese, Riley Uecker, and Matthew Cunningham Planetary Accretion...
-
Mantle (geology)
The mantle is a part of a terrestrial planet or other rocky body large enough to have differentiation by density. The interior of Earth, similar to the other...
-
Geology of Mars - Video Learning - WizScience.com
The "geology of Mars" is the scientific study of the surface, crust, and interior of the planet Mars. It emphasizes the composition, structure, history, and physical processes that shape the planet. It is fully analogous to the field of terrestrial geology. In planetary science, the term "geology" is used in its broadest sense to mean the study of the solid parts of planets and moons. The term inc
Crust (geology)
In geology, the crust is the outermost solid shell of a rocky planet or natural satellite, which is chemically distinct from the underlying mantle. The crusts o...
In geology, the crust is the outermost solid shell of a rocky planet or natural satellite, which is chemically distinct from the underlying mantle. The crusts of Earth, the Moon, Mercury, Venus, Mars, Io, and other planetary bodies have been generated largely by igneous processes, and these crusts are richer in incompatible elements than their respective mantles.
This video is targeted to blind users.
Attribution:
Article text available under CC-BY-SA
Creative Commons image source in video
wn.com/Crust (Geology)
In geology, the crust is the outermost solid shell of a rocky planet or natural satellite, which is chemically distinct from the underlying mantle. The crusts of Earth, the Moon, Mercury, Venus, Mars, Io, and other planetary bodies have been generated largely by igneous processes, and these crusts are richer in incompatible elements than their respective mantles.
This video is targeted to blind users.
Attribution:
Article text available under CC-BY-SA
Creative Commons image source in video
- published: 25 Aug 2014
- views: 0
FULL EPISODE Lesson 10 Deformation of the Crust - Understanding the Earth
Deformation of the crust - Geological Interpretation - How rocks behave under stress, to better understand earthquakes. (60minutes) Host; Dr. David Pearson. ......
Deformation of the crust - Geological Interpretation - How rocks behave under stress, to better understand earthquakes. (60minutes) Host; Dr. David Pearson. ...
wn.com/Full Episode Lesson 10 Deformation Of The Crust Understanding The Earth
Deformation of the crust - Geological Interpretation - How rocks behave under stress, to better understand earthquakes. (60minutes) Host; Dr. David Pearson. ...
- published: 30 May 2014
- views: 251
-
author: mineguy101
What Is A Geologic Fold?
Hi, I'm Emerald Robinson, and in this "What is" video, we're going to talk about geology as we try to answer the question, "What is a fold?" A fold is a rock......
Hi, I'm Emerald Robinson, and in this "What is" video, we're going to talk about geology as we try to answer the question, "What is a fold?" A fold is a rock...
wn.com/What Is A Geologic Fold
Hi, I'm Emerald Robinson, and in this "What is" video, we're going to talk about geology as we try to answer the question, "What is a fold?" A fold is a rock...
- published: 04 Apr 2013
- views: 406
-
author: redorbit
The Early Earth and Plate Tectonics
The Earth is formed by accretion of spatial particulates and large masses and eventually forms an outer crust. Video follows with speculation of early plates......
The Earth is formed by accretion of spatial particulates and large masses and eventually forms an outer crust. Video follows with speculation of early plates...
wn.com/The Early Earth And Plate Tectonics
The Earth is formed by accretion of spatial particulates and large masses and eventually forms an outer crust. Video follows with speculation of early plates...
Crustal Deformation - Part 1
Lecture on crustal deformation - 1....
Lecture on crustal deformation - 1.
wn.com/Crustal Deformation Part 1
Lecture on crustal deformation - 1.
- published: 06 Apr 2010
- views: 1181
-
author: DrJCHickey
Earth 100 Million Years From Now
Earth's landmasses were not always what they are today. Continents formed as Earth's crustal plates shifted and collided over long periods of time. This video s...
Earth's landmasses were not always what they are today. Continents formed as Earth's crustal plates shifted and collided over long periods of time. This video shows how today's continents are thought to have evolved over the last 600 million years, and where they'll end up in the next 100 million years. Paleogeographic Views of Earth's History provided by Ron Blakey, Professor of Geology, Northern Arizona University.
wn.com/Earth 100 Million Years From Now
Earth's landmasses were not always what they are today. Continents formed as Earth's crustal plates shifted and collided over long periods of time. This video shows how today's continents are thought to have evolved over the last 600 million years, and where they'll end up in the next 100 million years. Paleogeographic Views of Earth's History provided by Ron Blakey, Professor of Geology, Northern Arizona University.
- published: 12 Feb 2010
- views: 8482214
Living Rock: An Introduction to Earth's Geology
Living Rock - An Introduction to Earth's Geology movie was released Aug 13, 2002 by the DVD International studio. Ever wonder why earthquakes happen, or how a v...
Living Rock - An Introduction to Earth's Geology movie was released Aug 13, 2002 by the DVD International studio. Ever wonder why earthquakes happen, or how a volcano works? Living Rock - An Introduction to Earth's Geology movie Find the answers to these and many other questions in LIVING ROCK, a fun and educational program about the Earth's geology, jointly produced by the US Geological Survey and Alpha DVD.
Living Rock - An Introduction to Earth's Geology video Introduces concepts such as Geologic Time, Continental Crust, Plate Tectonics, Volcanic Activity, Earthquakes, Subduction Zones, Erosion, and Glaciers.
Facebook Page: https://www.facebook.com/geology.page
Twitter : http://twitter.com/geologypage
Youtube : http://www.youtube.com/user/GeologyPage
Google+ : https://plus.google.com/101351700113202974849
LinkedIn : http://www.linkedin.com/company/geology-page
Pinterest : http://www.pinterest.com/GeologyPage
Instagram : http://instagram.com/geologypage
Geology Page: http://www.geologypage.com/
wn.com/Living Rock An Introduction To Earth's Geology
Living Rock - An Introduction to Earth's Geology movie was released Aug 13, 2002 by the DVD International studio. Ever wonder why earthquakes happen, or how a volcano works? Living Rock - An Introduction to Earth's Geology movie Find the answers to these and many other questions in LIVING ROCK, a fun and educational program about the Earth's geology, jointly produced by the US Geological Survey and Alpha DVD.
Living Rock - An Introduction to Earth's Geology video Introduces concepts such as Geologic Time, Continental Crust, Plate Tectonics, Volcanic Activity, Earthquakes, Subduction Zones, Erosion, and Glaciers.
Facebook Page: https://www.facebook.com/geology.page
Twitter : http://twitter.com/geologypage
Youtube : http://www.youtube.com/user/GeologyPage
Google+ : https://plus.google.com/101351700113202974849
LinkedIn : http://www.linkedin.com/company/geology-page
Pinterest : http://www.pinterest.com/GeologyPage
Instagram : http://instagram.com/geologypage
Geology Page: http://www.geologypage.com/
- published: 18 Jul 2015
- views: 10
Oman Ophiolite - Lower oceanic crust and moho
Geological field excursion to the Oman ophiolite. In these videos Hugh Rollinson, from the University of Derby, takes you on a geological journey from the oc......
Geological field excursion to the Oman ophiolite. In these videos Hugh Rollinson, from the University of Derby, takes you on a geological journey from the oc...
wn.com/Oman Ophiolite Lower Oceanic Crust And Moho
Geological field excursion to the Oman ophiolite. In these videos Hugh Rollinson, from the University of Derby, takes you on a geological journey from the oc...
Geology in Quran
PLEASE READ IT ALL!!! In Geology, the phenomenon of folding is a recently discovered fact. Folding is responsible for the formation of mountain ranges. The e......
PLEASE READ IT ALL!!! In Geology, the phenomenon of folding is a recently discovered fact. Folding is responsible for the formation of mountain ranges. The e...
wn.com/Geology In Quran
PLEASE READ IT ALL!!! In Geology, the phenomenon of folding is a recently discovered fact. Folding is responsible for the formation of mountain ranges. The e...
Reverse Fault | Geology
Reverse Fault | Geology
A type of fault formed when the hanging wall fault block moves up along a fault surface relative to the footwall. Such movement can oc...
Reverse Fault | Geology
A type of fault formed when the hanging wall fault block moves up along a fault surface relative to the footwall. Such movement can occur in areas where the Earth's crust is compressed. A thrust fault, sometimes called an overthrust if the displacement is particularly great, is a reverse fault in which the fault plane has a shallow dip, typically much less than 45.
This Video From : Incorporated Research Institutions for Seismology
Geology page on :
Facebook
https://www.facebook.com/geology.page
Twitter
http://twitter.com/geologypage
Website :
http://www.geologypage.com
wn.com/Reverse Fault | Geology
Reverse Fault | Geology
A type of fault formed when the hanging wall fault block moves up along a fault surface relative to the footwall. Such movement can occur in areas where the Earth's crust is compressed. A thrust fault, sometimes called an overthrust if the displacement is particularly great, is a reverse fault in which the fault plane has a shallow dip, typically much less than 45.
This Video From : Incorporated Research Institutions for Seismology
Geology page on :
Facebook
https://www.facebook.com/geology.page
Twitter
http://twitter.com/geologypage
Website :
http://www.geologypage.com
- published: 15 Aug 2012
- views: 10018
Geology Kitchen #9 - Plate Tectonics
This episode discusses the scientific theory of plate tectonics, in which the Earth's crust is subdivided into a series of large and small tectonic plates. C......
This episode discusses the scientific theory of plate tectonics, in which the Earth's crust is subdivided into a series of large and small tectonic plates. C...
wn.com/Geology Kitchen 9 Plate Tectonics
This episode discusses the scientific theory of plate tectonics, in which the Earth's crust is subdivided into a series of large and small tectonic plates. C...
- published: 03 Dec 2012
- views: 12218
-
author: tkent22
Earth Science: Geology - Our Restless Planet - K4518DVD
Excerpt from Geology: Our Restless Planet from the Show Me Science series from TMW Media to purchase this title on DVD, go to http://www.tmwmedia.com/Wonders......
Excerpt from Geology: Our Restless Planet from the Show Me Science series from TMW Media to purchase this title on DVD, go to http://www.tmwmedia.com/Wonders...
wn.com/Earth Science Geology Our Restless Planet K4518Dvd
Excerpt from Geology: Our Restless Planet from the Show Me Science series from TMW Media to purchase this title on DVD, go to http://www.tmwmedia.com/Wonders...
- published: 16 Jul 2009
- views: 5924
-
author: TMWMedia
The Amazing Under Sea World The Deepest Geology On Earth Geology Documentary
The Earth's crust is made up of a jigsaw puzzle of plates, moving like ice floes in a frozen sea. Where two plates collide, the edge of one usually slides down ...
The Earth's crust is made up of a jigsaw puzzle of plates, moving like ice floes in a frozen sea. Where two plates collide, the edge of one usually slides down into the Earth's interior, forming a deep ocean trench. Where two plates move apart, magma has to fill the gap between them which melts as it rises from the Earth's mantle below and feeds chains of undersea volcanoes creating too many extraordinary geological phenomenons...
wn.com/The Amazing Under Sea World The Deepest Geology On Earth Geology Documentary
The Earth's crust is made up of a jigsaw puzzle of plates, moving like ice floes in a frozen sea. Where two plates collide, the edge of one usually slides down into the Earth's interior, forming a deep ocean trench. Where two plates move apart, magma has to fill the gap between them which melts as it rises from the Earth's mantle below and feeds chains of undersea volcanoes creating too many extraordinary geological phenomenons...
- published: 22 Apr 2015
- views: 9
Geological Isostatic Adjustment and The Great Lakes Region
This video details highlights of the effects Geological Isostatic Adjustment has had on the formation of the Great Lakes Region and provides possible insight......
This video details highlights of the effects Geological Isostatic Adjustment has had on the formation of the Great Lakes Region and provides possible insight...
wn.com/Geological Isostatic Adjustment And The Great Lakes Region
This video details highlights of the effects Geological Isostatic Adjustment has had on the formation of the Great Lakes Region and provides possible insight...
- published: 05 Apr 2012
- views: 2134
-
author: David Yole
Structural Geology Research with Dr. Randy Merrett
Dr. Randy Merrett is an Associate Professor in the Department of Geological Sciences at the University of Texas. Dr. Marrett's research concentrates on defor......
Dr. Randy Merrett is an Associate Professor in the Department of Geological Sciences at the University of Texas. Dr. Marrett's research concentrates on defor...
wn.com/Structural Geology Research With Dr. Randy Merrett
Dr. Randy Merrett is an Associate Professor in the Department of Geological Sciences at the University of Texas. Dr. Marrett's research concentrates on defor...
- published: 06 Mar 2007
- views: 39427
-
author: UTesi
Geology Kitchen #11 - Igneous Rocks
Igneous rocks are rocks derived from the cooling of magma, molten material originating from the upper Mantle/lower crust. Igneous rocks are classified by the......
Igneous rocks are rocks derived from the cooling of magma, molten material originating from the upper Mantle/lower crust. Igneous rocks are classified by the...
wn.com/Geology Kitchen 11 Igneous Rocks
Igneous rocks are rocks derived from the cooling of magma, molten material originating from the upper Mantle/lower crust. Igneous rocks are classified by the...
- published: 04 Feb 2013
- views: 11319
-
author: tkent22
Geology
This video is made by Science & Faith. MOUNTAINS ARE LIKE PEGS (STAKES) In Geology, the phenomenon of 'folding' is a recently discovered fact. Folding is res......
This video is made by Science & Faith. MOUNTAINS ARE LIKE PEGS (STAKES) In Geology, the phenomenon of 'folding' is a recently discovered fact. Folding is res...
wn.com/Geology
This video is made by Science & Faith. MOUNTAINS ARE LIKE PEGS (STAKES) In Geology, the phenomenon of 'folding' is a recently discovered fact. Folding is res...
On Structural Geology, Faults, and Rocks
Richard Sibson discusses changing emphasis in structural geology from a focus on continuous structures (e.g., folding) to the modern recognition of discontinuit...
Richard Sibson discusses changing emphasis in structural geology from a focus on continuous structures (e.g., folding) to the modern recognition of discontinuities accommodating major crustal displacements. Hydrothermal veins also demonstrate that fault systems are dominant conduits for fluid redistribution in the crust, with episodes of overpressure and fluid flow tied to the earthquake stress cycle. Rocks in and around fault zones are "memory banks" that record these processes.
Recorded: October 29, 2013
wn.com/On Structural Geology, Faults, And Rocks
Richard Sibson discusses changing emphasis in structural geology from a focus on continuous structures (e.g., folding) to the modern recognition of discontinuities accommodating major crustal displacements. Hydrothermal veins also demonstrate that fault systems are dominant conduits for fluid redistribution in the crust, with episodes of overpressure and fluid flow tied to the earthquake stress cycle. Rocks in and around fault zones are "memory banks" that record these processes.
Recorded: October 29, 2013
- published: 04 Sep 2015
- views: 40
Geologist Says Major Earthquake Imminent for California - Jim Berkland
Interviewer is Bil Carroll KFI 640 am Los Angeles Within days of the Sendai event, retired geologist Jim Berkland began sounding warnings that another earthq......
Interviewer is Bil Carroll KFI 640 am Los Angeles Within days of the Sendai event, retired geologist Jim Berkland began sounding warnings that another earthq...
wn.com/Geologist Says Major Earthquake Imminent For California Jim Berkland
Interviewer is Bil Carroll KFI 640 am Los Angeles Within days of the Sendai event, retired geologist Jim Berkland began sounding warnings that another earthq...
Overview of the Hadean Eon
Overview of the Hadean Eon. Geology 101 at the University of Kansas Made by Group 27: Timothy Frese, Riley Uecker, and Matthew Cunningham Planetary Accretion......
Overview of the Hadean Eon. Geology 101 at the University of Kansas Made by Group 27: Timothy Frese, Riley Uecker, and Matthew Cunningham Planetary Accretion...
wn.com/Overview Of The Hadean Eon
Overview of the Hadean Eon. Geology 101 at the University of Kansas Made by Group 27: Timothy Frese, Riley Uecker, and Matthew Cunningham Planetary Accretion...
Mantle (geology)
The mantle is a part of a terrestrial planet or other rocky body large enough to have differentiation by density. The interior of Earth, similar to the other......
The mantle is a part of a terrestrial planet or other rocky body large enough to have differentiation by density. The interior of Earth, similar to the other...
wn.com/Mantle (Geology)
The mantle is a part of a terrestrial planet or other rocky body large enough to have differentiation by density. The interior of Earth, similar to the other...
- published: 28 Aug 2014
- views: 1
-
author: Audiopedia
Geology of Mars - Video Learning - WizScience.com
The "geology of Mars" is the scientific study of the surface, crust, and interior of the planet Mars. It emphasizes the composition, structure, history, and phy...
The "geology of Mars" is the scientific study of the surface, crust, and interior of the planet Mars. It emphasizes the composition, structure, history, and physical processes that shape the planet. It is fully analogous to the field of terrestrial geology. In planetary science, the term "geology" is used in its broadest sense to mean the study of the solid parts of planets and moons. The term incorporates aspects of geophysics, geochemistry, mineralogy, geodesy, and cartography. A neologism, "areology", from the Greek word "Arēs" , sometimes appears as a synonym for Mars's geology in the popular media and works of science fiction , but the term is rarely, if ever, used by professional geologists and planetary scientists.
The following imagemap of the planet Mars has embedded links to geographical features in addition to the noted Rover and Lander locations. Click on the features and you will be taken to the corresponding article pages. North is at the top; Elevations: red , yellow , blue .
Mars is a differentiated, terrestrial planet.
Most of our current knowledge about the geology of Mars comes from studying landforms and relief features seen in images taken by orbiting spacecraft. Mars has a number of distinct, large-scale surface features that indicate the types of geological processes that have operated on the planet over time. This section introduces several of the larger physiographic regions of Mars. Together, these regions illustrate how geologic processes involving volcanism, tectonism, water, ice, and impacts have shaped the planet on a global scale.
Wiz Science™ is "the" learning channel for children and all ages.
SUBSCRIBE TODAY
Disclaimer: This video is for your information only. The author or publisher does not guarantee the accuracy of the content presented in this video. USE AT YOUR OWN RISK.
Background Music:
"The Place Inside" by Silent Partner (royalty-free) from YouTube Audio Library.
This video uses material/images from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geology+of+Mars, which is released under Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/ . This video is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/ . To reuse/adapt the content in your own work, you must comply with the license terms.
wn.com/Geology Of Mars Video Learning Wizscience.Com
The "geology of Mars" is the scientific study of the surface, crust, and interior of the planet Mars. It emphasizes the composition, structure, history, and physical processes that shape the planet. It is fully analogous to the field of terrestrial geology. In planetary science, the term "geology" is used in its broadest sense to mean the study of the solid parts of planets and moons. The term incorporates aspects of geophysics, geochemistry, mineralogy, geodesy, and cartography. A neologism, "areology", from the Greek word "Arēs" , sometimes appears as a synonym for Mars's geology in the popular media and works of science fiction , but the term is rarely, if ever, used by professional geologists and planetary scientists.
The following imagemap of the planet Mars has embedded links to geographical features in addition to the noted Rover and Lander locations. Click on the features and you will be taken to the corresponding article pages. North is at the top; Elevations: red , yellow , blue .
Mars is a differentiated, terrestrial planet.
Most of our current knowledge about the geology of Mars comes from studying landforms and relief features seen in images taken by orbiting spacecraft. Mars has a number of distinct, large-scale surface features that indicate the types of geological processes that have operated on the planet over time. This section introduces several of the larger physiographic regions of Mars. Together, these regions illustrate how geologic processes involving volcanism, tectonism, water, ice, and impacts have shaped the planet on a global scale.
Wiz Science™ is "the" learning channel for children and all ages.
SUBSCRIBE TODAY
Disclaimer: This video is for your information only. The author or publisher does not guarantee the accuracy of the content presented in this video. USE AT YOUR OWN RISK.
Background Music:
"The Place Inside" by Silent Partner (royalty-free) from YouTube Audio Library.
This video uses material/images from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geology+of+Mars, which is released under Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/ . This video is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/ . To reuse/adapt the content in your own work, you must comply with the license terms.
- published: 01 Sep 2015
- views: 0
-
Plate Tectonics (The Fiery Birth of planet Earth) - Construction and Deconstruction of Continents
The crash of the Indian plate into Asia is the biggest known collision in geological history, and it continues today. The result is the Himalaya and Karakoram - one of the largest mountain ranges on Earth. The Karakoram has half of the world's highest mountains and a reputation as being one of the most remote and savage ranges of all. In this beautifully illustrated book, Mike Searle, a geologist
-
Making the Himalaya: oozing, squashing or sliding?
Lecture by Matt Kohn (Boise State University) given at the Geological Society on 20 February 2013.
As well as raising Earth's highest mountain range, the Himalaya, the collision between India and Asia has caused lively debate between geologists about how continental crust behaves during plate collisions. Matt Kohn will look at the various models for how the middle of the crust deforms. Does it 'o
-
Rocks to know (most important rocks in the Earth crust)
The rocks to know is a video I made for my Physical geology students to help them to learn the rocks.
I started with the igneous rocks (Felsic, intermediate, mafic, ultramafic), followed by the sedimentary rocks (Clastic, Chemical/biochemical) and the metamorphic rocks.
-
G1/P2: Earth’s Interior, S & P waves, Rock-Cycle, Geological Time-eras
Language: Hindi, Topics Covered:
1. Origin of the earth, Nebular theory of Laplace
2. Speculation about earth’s interior: Heaviest elements are placed at the core and lighter elements are at the surface.
3. Interior of the earth: Density study, Temperature study, Direct and indirect evidences
4. SIAL and SIMA concepts- Edward Suess
5. Seismic wave studies: Propagation of S-Waves and P-Waves
6. La
-
The generation and destruction of continental crust
The recipient of the 2012 Wollaston Medal, Chris Hawkesworth, delivers a talk on 'The generation and destruction of continental crust'
-
Geology and Deep Time (strong evidence for a global flood) by Dr. Emil Silvestru
Dr. Emil Silvestru has published over 40 peer reviewed papers, a book, & worked as a professor & scientist in secular institutions. He explains the evidence for a global flood, including some very interesting new research..very strong evidence that only a global flood can answer. It gets better & better as it goes on..the best evidence is in the last 1/2 or so.
In history, Lyell & Cuvier were opp
-
Geology - The Study Of The Earth
This video answers the following questions: How does the earth illustrate purpose and design? Why is the earth's atmosphere so important to us? What is the f...
-
Dig - A Journey Into the Earth (1972)
Original Air Date: April 08, 1972
A boy and his dog take a wondrous trip under the earth's crust and through the geological eras of time, introducing children to geology in the form of a musical fantasy.
-
The History of the Rocky Mountains
The rocks in the Rocky Mountains were formed before the mountains were raised by tectonic forces. The oldest rock is Precambrian metamorphic rock that forms the core of the North American continent. There is also Precambrian sedimentary argillite, dating back to 1.7 billion years ago. During the Paleozoic, western North America lay underneath a shallow sea, which deposited many kilometers of limes
-
FM13 SinoProbe An Unprecedented View Inside Earth's Largest Continent PressConference
SinoProbe: An Unprecedented View Inside Earth's Largest Continent Monday, 9 December 11:30 a.m. SinoProbe is a Chinese earth science research program aimed a...
-
The Great Mystery of earth history-documentary
The Great Mystery of earth history-documentary
Imagine cameras have been around since the creation of Earth to record every major event.
Take a photographic journey thorough time from the violent birth of our planet four and a half billion years ago, through ice-ages, massive volcanic eruptions and the dinosaurs' reign to the first humans. For the first time, see the incredible story of our plane
-
Faults, Folds and Earthquakes Powerpoint for Educators - Download at www. science powerpoint .com
This is Powerpoint is one small part of a Geology Topics Unit that can be downloaded at http://sciencepowerpoint.com/index.html. The Geology Topics Unit whic...
-
Solar System History: How Was the Earth Formed? - Full Documentary HD
--- ABDH Media - Space ---
It's astonishing what you can achieve with just a bit of gas and dust. Kate Ravilious guides us through the birth of our solar system
It all started with a tremendous bang. Somewhere in our galaxy a star exploded, throwing out masses of gas and dust. This supernova, as these explosions are called, happened about 5bn years ago. The wreckage from the explosion then crash
-
Moon 101. 03. Physiography and Geology of the Moon
Dr. Paul Spudis discusses the physiography and geology of the moon including: terrains, landforms, topography (photogeology), impact crater formation, excava...
-
2015 6 1 USAEBN
3,600 Signature - San Andreas movie, predicting quakes, Thera explosion in Mediterranean relationship to Jewish Exodus, extinction of Mammoth on Wrangle Island, Greenland ice heavy, crustal shift implied, Velikovsky books, sea level drop or rise, Ice Ages, Madagascar extinction caves, reading geology.
-
Jeff Karson- Discovering the Deep Oceans-Guest Night lecture
Dr. Jeff Karson, Syracuse University Professor of Earth Science, spoke in a featured presentation at the Houston Geological Society 2015 Guest Night June 6. Karson discusses the geology of seafloor spreading centers and intrusion of basalt into the mid ocean rifts. Dr. Karson is an author on a new 2015 book “Discovering the Deep: An Photographic Atlas of the Seafloor and Ocean Crust” just publishe
-
FULL EPSIODE 06 Oceanic Geology - Understanding the Earth HD
Fundamentals of oceanic geology https://sites.google.com/site/mineguy101/home/lessons/lesson-6---oceanic-geology This geology course through Laurentian Unive...
-
Volcanoes in Virginia!
The recent earthquake may have you wondering what other surprises Virginia's geology may hold. Could there be a volcanic eruption in Virginia? Probably not t...
-
Professor Jade Star Lackey: Zoned Crystals and the Pace of Earth Processes
In this lecture from October 2, 2013 -- Zoned Crystals and the Pace of Earth Processes -- Associate Professor of Geology Jade Star Lackey discusses case stud...
-
"How and when did plate tectonics start on Earth, what came before, and why does it matter?"
Robert Stern, a research scientist in the geosciences department at The University of Texas at Dallas and current Merle A. Tuve Senior Fellow at DTM, gave his Tuve Lecture titled "How and when did plate tectonics start on Earth, what came before, and why does it matter?" at 11 a.m. on Wednesday, 13 May 2015, in the Greenewalt Lecture Hall.
Stern received his Ph.D. in Earth sciences from the Unive
Plate Tectonics (The Fiery Birth of planet Earth) - Construction and Deconstruction of Continents
The crash of the Indian plate into Asia is the biggest known collision in geological history, and it continues today. The result is the Himalaya and Karakoram -...
The crash of the Indian plate into Asia is the biggest known collision in geological history, and it continues today. The result is the Himalaya and Karakoram - one of the largest mountain ranges on Earth. The Karakoram has half of the world's highest mountains and a reputation as being one of the most remote and savage ranges of all. In this beautifully illustrated book, Mike Searle, a geologist at the University of Oxford and one of the most experienced field geologists of our time, presents a rich account of the geological forces that were involved in creating these mountain ranges. Using his personal accounts of extreme mountaineering and research in the region, he pieces together the geological processes that formed such impressive peaks.
Continental collision is a phenomenon of the plate tectonics of Earth that occurs at convergent boundaries. Continental collision is a variation on the fundamental process of subduction, whereby the subduction zone is destroyed, mountains produced, and two continents sutured together. Continental collision is known only from this planet and is an interesting example of how our different crusts, oceanic and continental, behave during subduction.
Continental collision is not an instantaneous event, but may take several tens of millions of years before the faulting and folding caused by collision stop. Collision between India and Asia has been going on for about 50 million years already and shows no signs of abating. Collision between East and West Gondwana to form the East African Orogen took about 100 million years from beginning (610 Ma) to end (510 Ma). Collision between Gondwana and Laurasia to form Pangea occurred in a relatively brief interval, about 50 million years long.
The process begins as two continents (different bits of continental crust), separated across a tract of ocean (and oceanic crust), approach each other, while the oceanic crust is slowly consumed at a subduction zone. The subduction zone runs along the edge of one of the continents and dips under it, raising volcanic mountain chains at some distance behind it, such as the Andes of South America today. Subduction involves the whole lithosphere, the density of which is largely controlled by the nature of the crust it carries. Oceanic crust is thin (~6 km thick) and dense (about 3.3 g/cm³), consisting of basalt, gabbro, and peridotite. Consequently, most oceanic crust is subducted easily at an oceanic trench. In contrast, continental crust is thick (~45 km thick) and buoyant, composed mostly of granitic rocks (average density about 2.5 g/cm³). Continental crust is subducted with difficulty, but is subducted to depths of 90-150 km or more, as evidenced by ultra-high pressure (UHP) metamorphic suites. Normal subduction continues as long as the ocean exists, but the subduction system is disrupted as the continent carried by the downgoing plate enters the trench. Because it contains thick continental crust, this lithosphere is less dense than the underlying asthenospheric mantle and normal subduction is disrupted. The volcanic arc on the upper plate is slowly extinguished. Resisting subduction, the crust buckles up and under, raising mountains where a trench used to be. The position of the trench becomes a zone that marks the suture between the two continental terranes. Suture zones are often marked by fragments of the pre-existing oceanic crust and mantle rocks, known as ophiolites.
wn.com/Plate Tectonics (The Fiery Birth Of Planet Earth) Construction And Deconstruction Of Continents
The crash of the Indian plate into Asia is the biggest known collision in geological history, and it continues today. The result is the Himalaya and Karakoram - one of the largest mountain ranges on Earth. The Karakoram has half of the world's highest mountains and a reputation as being one of the most remote and savage ranges of all. In this beautifully illustrated book, Mike Searle, a geologist at the University of Oxford and one of the most experienced field geologists of our time, presents a rich account of the geological forces that were involved in creating these mountain ranges. Using his personal accounts of extreme mountaineering and research in the region, he pieces together the geological processes that formed such impressive peaks.
Continental collision is a phenomenon of the plate tectonics of Earth that occurs at convergent boundaries. Continental collision is a variation on the fundamental process of subduction, whereby the subduction zone is destroyed, mountains produced, and two continents sutured together. Continental collision is known only from this planet and is an interesting example of how our different crusts, oceanic and continental, behave during subduction.
Continental collision is not an instantaneous event, but may take several tens of millions of years before the faulting and folding caused by collision stop. Collision between India and Asia has been going on for about 50 million years already and shows no signs of abating. Collision between East and West Gondwana to form the East African Orogen took about 100 million years from beginning (610 Ma) to end (510 Ma). Collision between Gondwana and Laurasia to form Pangea occurred in a relatively brief interval, about 50 million years long.
The process begins as two continents (different bits of continental crust), separated across a tract of ocean (and oceanic crust), approach each other, while the oceanic crust is slowly consumed at a subduction zone. The subduction zone runs along the edge of one of the continents and dips under it, raising volcanic mountain chains at some distance behind it, such as the Andes of South America today. Subduction involves the whole lithosphere, the density of which is largely controlled by the nature of the crust it carries. Oceanic crust is thin (~6 km thick) and dense (about 3.3 g/cm³), consisting of basalt, gabbro, and peridotite. Consequently, most oceanic crust is subducted easily at an oceanic trench. In contrast, continental crust is thick (~45 km thick) and buoyant, composed mostly of granitic rocks (average density about 2.5 g/cm³). Continental crust is subducted with difficulty, but is subducted to depths of 90-150 km or more, as evidenced by ultra-high pressure (UHP) metamorphic suites. Normal subduction continues as long as the ocean exists, but the subduction system is disrupted as the continent carried by the downgoing plate enters the trench. Because it contains thick continental crust, this lithosphere is less dense than the underlying asthenospheric mantle and normal subduction is disrupted. The volcanic arc on the upper plate is slowly extinguished. Resisting subduction, the crust buckles up and under, raising mountains where a trench used to be. The position of the trench becomes a zone that marks the suture between the two continental terranes. Suture zones are often marked by fragments of the pre-existing oceanic crust and mantle rocks, known as ophiolites.
- published: 09 Jun 2015
- views: 0
Making the Himalaya: oozing, squashing or sliding?
Lecture by Matt Kohn (Boise State University) given at the Geological Society on 20 February 2013.
As well as raising Earth's highest mountain range, the Himal...
Lecture by Matt Kohn (Boise State University) given at the Geological Society on 20 February 2013.
As well as raising Earth's highest mountain range, the Himalaya, the collision between India and Asia has caused lively debate between geologists about how continental crust behaves during plate collisions. Matt Kohn will look at the various models for how the middle of the crust deforms. Does it 'ooze' like toothpaste, develop wedges like a snow plough, or become flattened like the collapse of a weakened pile? Each model carries with it its own implications for reconstructing how the Himalaya and the Tibetan plateau were formed.
wn.com/Making The Himalaya Oozing, Squashing Or Sliding
Lecture by Matt Kohn (Boise State University) given at the Geological Society on 20 February 2013.
As well as raising Earth's highest mountain range, the Himalaya, the collision between India and Asia has caused lively debate between geologists about how continental crust behaves during plate collisions. Matt Kohn will look at the various models for how the middle of the crust deforms. Does it 'ooze' like toothpaste, develop wedges like a snow plough, or become flattened like the collapse of a weakened pile? Each model carries with it its own implications for reconstructing how the Himalaya and the Tibetan plateau were formed.
- published: 15 Mar 2013
- views: 1786
Rocks to know (most important rocks in the Earth crust)
The rocks to know is a video I made for my Physical geology students to help them to learn the rocks.
I started with the igneous rocks (Felsic, intermediate, m...
The rocks to know is a video I made for my Physical geology students to help them to learn the rocks.
I started with the igneous rocks (Felsic, intermediate, mafic, ultramafic), followed by the sedimentary rocks (Clastic, Chemical/biochemical) and the metamorphic rocks.
wn.com/Rocks To Know (Most Important Rocks In The Earth Crust)
The rocks to know is a video I made for my Physical geology students to help them to learn the rocks.
I started with the igneous rocks (Felsic, intermediate, mafic, ultramafic), followed by the sedimentary rocks (Clastic, Chemical/biochemical) and the metamorphic rocks.
- published: 12 Oct 2015
- views: 25
G1/P2: Earth’s Interior, S & P waves, Rock-Cycle, Geological Time-eras
Language: Hindi, Topics Covered:
1. Origin of the earth, Nebular theory of Laplace
2. Speculation about earth’s interior: Heaviest elements are placed at the co...
Language: Hindi, Topics Covered:
1. Origin of the earth, Nebular theory of Laplace
2. Speculation about earth’s interior: Heaviest elements are placed at the core and lighter elements are at the surface.
3. Interior of the earth: Density study, Temperature study, Direct and indirect evidences
4. SIAL and SIMA concepts- Edward Suess
5. Seismic wave studies: Propagation of S-Waves and P-Waves
6. Layers of earth’s interior: Lithosphere, asthenosphere, mantle, outer core, inner core.
7. Composition of interior of the earth and the crust.
8. Rocks of the continental crust
9. Rock-cycle (Igneous rock, sedimentary, metamorphous)
10. Properties of Igneous rocks
11. Properties of sedimentary rocks
12. Properties of metamorphous rocks
13. Prev. years question on rocks
14. Geological history of the earth: Super continent –Rodinia, Breaking up of Rodinia
15. Formation and breaking of Pangaea
16. What are Panthalasa
17. Laurasia, Gondwana and Tethys sea
18. Breaking up of Gondwana
19. Movement of Indian plate
Faculty Name: Ms. Rajtanil Solanki
Powerpoint available at http://Mrunal.org/download
Venue: Sardar Patel Institute of Public Administration (SPIPA), Ahmedabad
Exam-Utility: UPSC CSAT, CDS, CAPF
wn.com/G1 P2 Earth’S Interior, S P Waves, Rock Cycle, Geological Time Eras
Language: Hindi, Topics Covered:
1. Origin of the earth, Nebular theory of Laplace
2. Speculation about earth’s interior: Heaviest elements are placed at the core and lighter elements are at the surface.
3. Interior of the earth: Density study, Temperature study, Direct and indirect evidences
4. SIAL and SIMA concepts- Edward Suess
5. Seismic wave studies: Propagation of S-Waves and P-Waves
6. Layers of earth’s interior: Lithosphere, asthenosphere, mantle, outer core, inner core.
7. Composition of interior of the earth and the crust.
8. Rocks of the continental crust
9. Rock-cycle (Igneous rock, sedimentary, metamorphous)
10. Properties of Igneous rocks
11. Properties of sedimentary rocks
12. Properties of metamorphous rocks
13. Prev. years question on rocks
14. Geological history of the earth: Super continent –Rodinia, Breaking up of Rodinia
15. Formation and breaking of Pangaea
16. What are Panthalasa
17. Laurasia, Gondwana and Tethys sea
18. Breaking up of Gondwana
19. Movement of Indian plate
Faculty Name: Ms. Rajtanil Solanki
Powerpoint available at http://Mrunal.org/download
Venue: Sardar Patel Institute of Public Administration (SPIPA), Ahmedabad
Exam-Utility: UPSC CSAT, CDS, CAPF
- published: 06 Feb 2015
- views: 96
The generation and destruction of continental crust
The recipient of the 2012 Wollaston Medal, Chris Hawkesworth, delivers a talk on 'The generation and destruction of continental crust'...
The recipient of the 2012 Wollaston Medal, Chris Hawkesworth, delivers a talk on 'The generation and destruction of continental crust'
wn.com/The Generation And Destruction Of Continental Crust
The recipient of the 2012 Wollaston Medal, Chris Hawkesworth, delivers a talk on 'The generation and destruction of continental crust'
Geology and Deep Time (strong evidence for a global flood) by Dr. Emil Silvestru
Dr. Emil Silvestru has published over 40 peer reviewed papers, a book, & worked as a professor & scientist in secular institutions. He explains the evidence for...
Dr. Emil Silvestru has published over 40 peer reviewed papers, a book, & worked as a professor & scientist in secular institutions. He explains the evidence for a global flood, including some very interesting new research..very strong evidence that only a global flood can answer. It gets better & better as it goes on..the best evidence is in the last 1/2 or so.
In history, Lyell & Cuvier were opponents & Lyell's concepts of uniformitarianism triumphed over catastrophism for some decades & those who advocated catastrophism were ridiculed. When Harlan Bretz proposed a flood in the Missoula area, it was ridiculed due to people accepting Lyell's uniformitarianism & evolution. But now we know Bretsz was right. This area was for certain made by a flood.
Loius Agassiz predicted massive ice sheets in the USA...Darwin didn't believe him...Agassiz came to America & found evidence of massive ice sheets causing many features on the continent. He stayed as Harvard Professor.
In the grand Canyon, we have the coconino sandstone lying on top of the hermit shale. But, there are 10 million years missing between them (A paraconformity). So for 10 million years, the Hermite shale was exposed to erosion, but has hardly a scratch of evidence of this & yet the prevailing evolutionary wisdom is that the whole Grand Canyon was cut out of rock in 1 million years? How does that work logically?
People often ask how the flood could lay down layers of rock. Well, flumes of water have demonstrated that many layers, smoothly bound, can be laid down in moving water. Many layers laid down with no erosion between them is a very strong evidence of fast deposition. If a global flood happened, we should have more of them & we do.
Monterey Canyon is wider, deeper & longer & is bigger than the Grand Canyon. What could make this on the bottom of the ocean? No rivers are flowing there. For creationists, it's pretty simple...the global flood. Evolutionists have no answer. & more & more of these canyons are being found.
Creationists like evolutionists invent hypotheses that are not always right & need to correct them (ex: the canopy hypothesis). Baumgardner's creationist plate tectonics theory has a lot of excellent explanations for the flood, but there were some things it could explain well. This has been improved by Michael Oard, but he also admits weak points that need to be figured out. Oard published papers on vertical lift of plates that could move them up or down 1000s of feet in just a short time***. But, he didn't have a mechanism to explain how. He predicted a mechanism would be found for that . In 2011, a mechanism for vertical lift of continents was published.
Evolutionists claim that you can't produce fine sediments & sequences of silts in moving water. "This has led to bias Schieber explains, that whenever mudstones are encountered in the sedimentary rock record, they are generally interpreted as quiet water deposits." As waters clear, Science Daily A "tarred" issue (~81:00). But, the Bouma sequence shows that it can be done even from 1962.
Her are some examples of layers with gaps & no erosion:
The Bottom layer is the Waterways Formation, Middle Devonian, 390 million years. Above it is the Ft. McMurray Formation, Cretaceous, 130 million years. 260 million year different..and yet the top of the lowest layer is perfectly flat...and exposed for 260 million years & no erosion??? How???
The Himalaya erosion rate is ~2.7 mm/year. That means 135 km had to be eroded...so the mountain would have had to start in the mantle***...which is not possible.
Folding in geology can be seen is everywhere. This is a prediction of creation science & a global flood & we see it everywhere as well as in situ fossil trees (polystrate fossils) such as in Shamokin, Penn. The Whaleback Anticline. Evolution can't explain these well. Creation science can.
You need cement to bind grains to turn sand into sandstone & trees into stone fossils. A global flood is by far best explanation. As plates went down fast, they would drag down water, sediments & other things very deep down into the earth (1000 km??) . If you do that, it would turn it into volatiles (?), highly active chemical solutions. These are lighter & will move up. As they come to the crust, they'll change sand & other sediments into stone & also turn dead things into fossils. This is the ONLY valid scenario on a global scale.
There are many Large Igneous Provinces all over the globe. Only a global catastrophe could cause this.
What would be expected from a global flood? See the predictions and confirmations that a global flood makes in the script here:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-9teU_2xpLg
Many more videos are at http://www.biblediscoverytv.com/
See the creation super conference link.
wn.com/Geology And Deep Time (Strong Evidence For A Global Flood) By Dr. Emil Silvestru
Dr. Emil Silvestru has published over 40 peer reviewed papers, a book, & worked as a professor & scientist in secular institutions. He explains the evidence for a global flood, including some very interesting new research..very strong evidence that only a global flood can answer. It gets better & better as it goes on..the best evidence is in the last 1/2 or so.
In history, Lyell & Cuvier were opponents & Lyell's concepts of uniformitarianism triumphed over catastrophism for some decades & those who advocated catastrophism were ridiculed. When Harlan Bretz proposed a flood in the Missoula area, it was ridiculed due to people accepting Lyell's uniformitarianism & evolution. But now we know Bretsz was right. This area was for certain made by a flood.
Loius Agassiz predicted massive ice sheets in the USA...Darwin didn't believe him...Agassiz came to America & found evidence of massive ice sheets causing many features on the continent. He stayed as Harvard Professor.
In the grand Canyon, we have the coconino sandstone lying on top of the hermit shale. But, there are 10 million years missing between them (A paraconformity). So for 10 million years, the Hermite shale was exposed to erosion, but has hardly a scratch of evidence of this & yet the prevailing evolutionary wisdom is that the whole Grand Canyon was cut out of rock in 1 million years? How does that work logically?
People often ask how the flood could lay down layers of rock. Well, flumes of water have demonstrated that many layers, smoothly bound, can be laid down in moving water. Many layers laid down with no erosion between them is a very strong evidence of fast deposition. If a global flood happened, we should have more of them & we do.
Monterey Canyon is wider, deeper & longer & is bigger than the Grand Canyon. What could make this on the bottom of the ocean? No rivers are flowing there. For creationists, it's pretty simple...the global flood. Evolutionists have no answer. & more & more of these canyons are being found.
Creationists like evolutionists invent hypotheses that are not always right & need to correct them (ex: the canopy hypothesis). Baumgardner's creationist plate tectonics theory has a lot of excellent explanations for the flood, but there were some things it could explain well. This has been improved by Michael Oard, but he also admits weak points that need to be figured out. Oard published papers on vertical lift of plates that could move them up or down 1000s of feet in just a short time***. But, he didn't have a mechanism to explain how. He predicted a mechanism would be found for that . In 2011, a mechanism for vertical lift of continents was published.
Evolutionists claim that you can't produce fine sediments & sequences of silts in moving water. "This has led to bias Schieber explains, that whenever mudstones are encountered in the sedimentary rock record, they are generally interpreted as quiet water deposits." As waters clear, Science Daily A "tarred" issue (~81:00). But, the Bouma sequence shows that it can be done even from 1962.
Her are some examples of layers with gaps & no erosion:
The Bottom layer is the Waterways Formation, Middle Devonian, 390 million years. Above it is the Ft. McMurray Formation, Cretaceous, 130 million years. 260 million year different..and yet the top of the lowest layer is perfectly flat...and exposed for 260 million years & no erosion??? How???
The Himalaya erosion rate is ~2.7 mm/year. That means 135 km had to be eroded...so the mountain would have had to start in the mantle***...which is not possible.
Folding in geology can be seen is everywhere. This is a prediction of creation science & a global flood & we see it everywhere as well as in situ fossil trees (polystrate fossils) such as in Shamokin, Penn. The Whaleback Anticline. Evolution can't explain these well. Creation science can.
You need cement to bind grains to turn sand into sandstone & trees into stone fossils. A global flood is by far best explanation. As plates went down fast, they would drag down water, sediments & other things very deep down into the earth (1000 km??) . If you do that, it would turn it into volatiles (?), highly active chemical solutions. These are lighter & will move up. As they come to the crust, they'll change sand & other sediments into stone & also turn dead things into fossils. This is the ONLY valid scenario on a global scale.
There are many Large Igneous Provinces all over the globe. Only a global catastrophe could cause this.
What would be expected from a global flood? See the predictions and confirmations that a global flood makes in the script here:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-9teU_2xpLg
Many more videos are at http://www.biblediscoverytv.com/
See the creation super conference link.
- published: 26 Aug 2011
- views: 18128
Geology - The Study Of The Earth
This video answers the following questions: How does the earth illustrate purpose and design? Why is the earth's atmosphere so important to us? What is the f......
This video answers the following questions: How does the earth illustrate purpose and design? Why is the earth's atmosphere so important to us? What is the f...
wn.com/Geology The Study Of The Earth
This video answers the following questions: How does the earth illustrate purpose and design? Why is the earth's atmosphere so important to us? What is the f...
Dig - A Journey Into the Earth (1972)
Original Air Date: April 08, 1972
A boy and his dog take a wondrous trip under the earth's crust and through the geological eras of time, introducing children ...
Original Air Date: April 08, 1972
A boy and his dog take a wondrous trip under the earth's crust and through the geological eras of time, introducing children to geology in the form of a musical fantasy.
wn.com/Dig A Journey Into The Earth (1972)
Original Air Date: April 08, 1972
A boy and his dog take a wondrous trip under the earth's crust and through the geological eras of time, introducing children to geology in the form of a musical fantasy.
- published: 20 Mar 2015
- views: 11
The History of the Rocky Mountains
The rocks in the Rocky Mountains were formed before the mountains were raised by tectonic forces. The oldest rock is Precambrian metamorphic rock that forms the...
The rocks in the Rocky Mountains were formed before the mountains were raised by tectonic forces. The oldest rock is Precambrian metamorphic rock that forms the core of the North American continent. There is also Precambrian sedimentary argillite, dating back to 1.7 billion years ago. During the Paleozoic, western North America lay underneath a shallow sea, which deposited many kilometers of limestone and dolomite.
In the southern Rocky Mountains, near present-day Colorado, these ancestral rocks were disturbed by mountain building approximately 300 Ma, during the Pennsylvanian. This mountain building produced the Ancestral Rocky Mountains. They consisted largely of Precambrian metamorphic rock forced upward through layers of the limestone laid down in the shallow sea. The mountains eroded throughout the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic, leaving extensive deposits of sedimentary rock.
Terranes started to collide with the western edge of North America in the Mississippian (approximately 350 million years ago), causing the Antler orogeny. For 270 million years, the effects of plate collisions were focused very near the edge of the North American plate boundary, far to the west of the Rocky Mountain region. It was not until 80 Ma that these effects began to reach the Rockies.
The current Rocky Mountains were raised in the Laramide orogeny from between 80 to 55 Ma. For the Canadian Rockies, the mountain building is analogous to a rug being pushed on a hardwood floor: the rug bunches up and forms wrinkles (mountains). In Canada, the terranes and subduction are the foot pushing the rug, the ancestral rocks are the rug, and the Canadian Shield in the middle of the continent is the hardwood floor.
Further south, the growth of the Rocky Mountains in the United States was probably caused by an unusual subduction, where the Farallon plate dove at a shallow angle below the North American plate. This low angle moved the focus of melting and mountain building much farther inland than the normal 200 to 300 miles (300 to 500 km). It is postulated that the shallow angle of the subducting plate greatly increased the friction and other interactions with the thick continental mass above it. Tremendous thrusts piled sheets of crust on top of each other, building the extraordinarily broad, high Rocky Mountain range.
wn.com/The History Of The Rocky Mountains
The rocks in the Rocky Mountains were formed before the mountains were raised by tectonic forces. The oldest rock is Precambrian metamorphic rock that forms the core of the North American continent. There is also Precambrian sedimentary argillite, dating back to 1.7 billion years ago. During the Paleozoic, western North America lay underneath a shallow sea, which deposited many kilometers of limestone and dolomite.
In the southern Rocky Mountains, near present-day Colorado, these ancestral rocks were disturbed by mountain building approximately 300 Ma, during the Pennsylvanian. This mountain building produced the Ancestral Rocky Mountains. They consisted largely of Precambrian metamorphic rock forced upward through layers of the limestone laid down in the shallow sea. The mountains eroded throughout the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic, leaving extensive deposits of sedimentary rock.
Terranes started to collide with the western edge of North America in the Mississippian (approximately 350 million years ago), causing the Antler orogeny. For 270 million years, the effects of plate collisions were focused very near the edge of the North American plate boundary, far to the west of the Rocky Mountain region. It was not until 80 Ma that these effects began to reach the Rockies.
The current Rocky Mountains were raised in the Laramide orogeny from between 80 to 55 Ma. For the Canadian Rockies, the mountain building is analogous to a rug being pushed on a hardwood floor: the rug bunches up and forms wrinkles (mountains). In Canada, the terranes and subduction are the foot pushing the rug, the ancestral rocks are the rug, and the Canadian Shield in the middle of the continent is the hardwood floor.
Further south, the growth of the Rocky Mountains in the United States was probably caused by an unusual subduction, where the Farallon plate dove at a shallow angle below the North American plate. This low angle moved the focus of melting and mountain building much farther inland than the normal 200 to 300 miles (300 to 500 km). It is postulated that the shallow angle of the subducting plate greatly increased the friction and other interactions with the thick continental mass above it. Tremendous thrusts piled sheets of crust on top of each other, building the extraordinarily broad, high Rocky Mountain range.
- published: 15 Feb 2015
- views: 0
FM13 SinoProbe An Unprecedented View Inside Earth's Largest Continent PressConference
SinoProbe: An Unprecedented View Inside Earth's Largest Continent Monday, 9 December 11:30 a.m. SinoProbe is a Chinese earth science research program aimed a......
SinoProbe: An Unprecedented View Inside Earth's Largest Continent Monday, 9 December 11:30 a.m. SinoProbe is a Chinese earth science research program aimed a...
wn.com/Fm13 Sinoprobe An Unprecedented View Inside Earth's Largest Continent Pressconference
SinoProbe: An Unprecedented View Inside Earth's Largest Continent Monday, 9 December 11:30 a.m. SinoProbe is a Chinese earth science research program aimed a...
The Great Mystery of earth history-documentary
The Great Mystery of earth history-documentary
Imagine cameras have been around since the creation of Earth to record every major event.
Take a photographic jo...
The Great Mystery of earth history-documentary
Imagine cameras have been around since the creation of Earth to record every major event.
Take a photographic journey thorough time from the violent birth of our planet four and a half billion years ago, through ice-ages, massive volcanic eruptions and the dinosaurs' reign to the first humans. For the first time, see the incredible story of our planet unfold in one single, seamless camera move.
History of The Earth Full Documentary
The history of the Earth concerns the development of the planet Earth from its formation to the present day.[1][2] Nearly all branches of natural science have contributed to the understanding of the main events of the Earth's past. The age of Earth is approximately one-third of the age of the universe. An immense amount of biological and geological change has occurred in that time span.
Earth formed around 4.54 billion (4.54×109) years ago by accretion from the solar nebula. Volcanic outgassing probably created the primordial atmosphere, but it contained almost no oxygen and would have been toxic to humans and most modern life. Much of the Earth was molten because of frequent collisions with other bodies which led to extreme volcanism. One very large collision is thought to have been responsible for tilting the Earth at an angle and forming the Moon. Over time, the planet cooled and formed a solid crust, allowing liquid water to exist on the surface.
The first life forms appeared between 3.8 and 3.5 billion years ago. The earliest evidences for life on Earth are graphite found to be biogenic in 3.7-billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks discovered in Western Greenland[3] and microbial mat fossils found in 3.48-billion-year-old sandstone discovered in Western Australia.[4][5] Photosynthetic life appeared around 2 billion years ago, enriching the atmosphere with oxygen. Life remained mostly small and microscopic until about 580 million years ago, when complex multicellular life arose. During the Cambrian period it experienced a rapid diversification into most major phyla. Although more than 99 percent of all species that ever lived on the planet are estimated to be extinct,[6][7] there are currently 10–14 million species of life on the Earth.[8]
Geological change has been constantly occurring on Earth since the time of its formation and biological change since the first appearance of life. Species continuously evolve, taking on new forms, splitting into daughter species, or going extinct in response to an ever-changing planet. The process of plate tectonics has played a major role in the shaping of Earth's oceans and continents, as well as the life they harbor. The biosphere, in turn, has had a significant effect on the atmosphere and other abiotic conditions on the planet, such as the formation of the ozone layer, the proliferation of oxygen, and the creation of soil.
This is copied description
source: https://youtu.be/cabUQ09NT8Q
wn.com/The Great Mystery Of Earth History Documentary
The Great Mystery of earth history-documentary
Imagine cameras have been around since the creation of Earth to record every major event.
Take a photographic journey thorough time from the violent birth of our planet four and a half billion years ago, through ice-ages, massive volcanic eruptions and the dinosaurs' reign to the first humans. For the first time, see the incredible story of our planet unfold in one single, seamless camera move.
History of The Earth Full Documentary
The history of the Earth concerns the development of the planet Earth from its formation to the present day.[1][2] Nearly all branches of natural science have contributed to the understanding of the main events of the Earth's past. The age of Earth is approximately one-third of the age of the universe. An immense amount of biological and geological change has occurred in that time span.
Earth formed around 4.54 billion (4.54×109) years ago by accretion from the solar nebula. Volcanic outgassing probably created the primordial atmosphere, but it contained almost no oxygen and would have been toxic to humans and most modern life. Much of the Earth was molten because of frequent collisions with other bodies which led to extreme volcanism. One very large collision is thought to have been responsible for tilting the Earth at an angle and forming the Moon. Over time, the planet cooled and formed a solid crust, allowing liquid water to exist on the surface.
The first life forms appeared between 3.8 and 3.5 billion years ago. The earliest evidences for life on Earth are graphite found to be biogenic in 3.7-billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks discovered in Western Greenland[3] and microbial mat fossils found in 3.48-billion-year-old sandstone discovered in Western Australia.[4][5] Photosynthetic life appeared around 2 billion years ago, enriching the atmosphere with oxygen. Life remained mostly small and microscopic until about 580 million years ago, when complex multicellular life arose. During the Cambrian period it experienced a rapid diversification into most major phyla. Although more than 99 percent of all species that ever lived on the planet are estimated to be extinct,[6][7] there are currently 10–14 million species of life on the Earth.[8]
Geological change has been constantly occurring on Earth since the time of its formation and biological change since the first appearance of life. Species continuously evolve, taking on new forms, splitting into daughter species, or going extinct in response to an ever-changing planet. The process of plate tectonics has played a major role in the shaping of Earth's oceans and continents, as well as the life they harbor. The biosphere, in turn, has had a significant effect on the atmosphere and other abiotic conditions on the planet, such as the formation of the ozone layer, the proliferation of oxygen, and the creation of soil.
This is copied description
source: https://youtu.be/cabUQ09NT8Q
- published: 21 Mar 2015
- views: 2
Faults, Folds and Earthquakes Powerpoint for Educators - Download at www. science powerpoint .com
This is Powerpoint is one small part of a Geology Topics Unit that can be downloaded at http://sciencepowerpoint.com/index.html. The Geology Topics Unit whic......
This is Powerpoint is one small part of a Geology Topics Unit that can be downloaded at http://sciencepowerpoint.com/index.html. The Geology Topics Unit whic...
wn.com/Faults, Folds And Earthquakes Powerpoint For Educators Download At Www. Science Powerpoint .Com
This is Powerpoint is one small part of a Geology Topics Unit that can be downloaded at http://sciencepowerpoint.com/index.html. The Geology Topics Unit whic...
Solar System History: How Was the Earth Formed? - Full Documentary HD
--- ABDH Media - Space ---
It's astonishing what you can achieve with just a bit of gas and dust. Kate Ravilious guides us through the birth of our solar syste...
--- ABDH Media - Space ---
It's astonishing what you can achieve with just a bit of gas and dust. Kate Ravilious guides us through the birth of our solar system
It all started with a tremendous bang. Somewhere in our galaxy a star exploded, throwing out masses of gas and dust. This supernova, as these explosions are called, happened about 5bn years ago. The wreckage from the explosion then crashed into a nearby cloud of gas, bringing together the ingredients for our solar system to form.
Because the explosion was so energetic it made the dust mixture very hot and things began to cook. Little bits of dust began to cluster, making bigger and bigger lumps, and the mixture began to pull together under its own gravity.
Eventually the central lump became so hot and dense that it started to generate its own energy, igniting nuclear fires. This was the birth of our sun. The remaining dusty mixture swirled around the star, fanning out into a disc.
Gradually the sun grew in size and the dusty disc cooled. Over millions of years the dust clustered into grains, then lumps, boulders and eventually planetesimals - chunks of rock big enough to have their own gravitational field. Some of these planetesimals became the embryonic forms of the planets in our solar system today.
Slowly these rocky planets began to organise themselves, settling at a comfortable distance from the sun and finding their own orbit. Earth found its path as third planet from the sun. In the early days rocky pile-ups were still common, leaving craters on the surface of all of the planets.
One of these collisions, about 4.5bn years ago, is thought to have very nearly destroyed the Earth, and was probably responsible for our moon. A large planetesimal, about the size of Mars, gave Earth a glancing blow, chucking a chunk of Earth's crust out into space. Some of the planetesimal merged with Earth, while the ejected lump started its own orbit around Earth and became the moon.
Read More: http://www.theguardian.com/science/2008/apr/28/starsgalaxiesandplanets.geology
*Subscribe for more Educative & Space Documentaries (Like & Share)
* Visit our website: http://www.advexon.com
* ABDH Media Documentaries: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCHx69kZbXbX6WgMq_njRvFA
*NOVA | PBS Documentaries (HD): https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCYMWnCecPvpQJj8sBPUi4bA
#ABDH
#space
#spacedocumentary
#AlienPlanets
#NEWFullScienceDocumentaries
#SpaceDocumentary2015
#alien
#spacedocumentarynationalgeographic
#spacedocumentaryhd
#spacedocumentarybbc
#spacedocumentary2015hd
#spacedocumentaryplaylist #spacedocumentarynationalgeographic2015 #spacedocumentaryblackholes
#spacedocumentaryforkids
#spacedocumentaryalienplanets
#spacedocumentaryasteroidthedoomsdayrock
#spacedocumentary2015aliens
#aspaceodysseydocumentary
#spacedocumentaryblackholesfdc
#spacedocumentarybriancox
#spacedocumentarybest
#spacedocumentarybbc2015
#spacedocumentaryblacksky
#spacedocumentarybigbang
#bestspacedocumentary2015
#spacedocumentarycosmos
#spacedocumentaryconspiracy
#spacedocumentarychannel
#spacedocumentarychildren
#discoverychanneldocumentaryspace
#spacecolonizationdocumentary
#spaceshuttlechallengerdocumentary
#spacetimecontinuumdocumentary
#historychanneldocumentaryspace
#spacedocumentarydiscoverychannel
#spacedocumentarydarkmatter
#spacedocumentarydiscovery
#deepspacedocumentary
#deepspacedocumentary2015
#spacedisastersdocumentary
#spacedivedocumentary
#spaceshuttledisasterdocumentary
#davidattenboroughspacedocumentary
#spaceelevatordocumentary
#spaceexplorationdocumentary2015
#earthfromspacedocumentary
#spaceexplorationdocumentary2015
#spaceengineeringdocumentary
#edgeofspacedocumentary
#emptyspacedocumentary
#spacedocumentaryforchildren
#spacedocumentaryfilms
#spacedocumentaryfull
#spacedocumentaryfulllength
#spacedocumentaryfuture
#spacedocumentaryfunny
#2015spacedocumentaryfull
#spacedocumentarygalaxies
#spacedocumentarygravity
#spaceuniversegalaxydocumentary
#spacedocumentarynationalgeographic2015
#spacetraveldocumentarynationalgeographic
#spacedocumentarynationalgeographichd
#spacedocumentaryhd2015
#spacedocumentaryhd1080p
#spacedocumentaryinhd
wn.com/Solar System History How Was The Earth Formed Full Documentary Hd
--- ABDH Media - Space ---
It's astonishing what you can achieve with just a bit of gas and dust. Kate Ravilious guides us through the birth of our solar system
It all started with a tremendous bang. Somewhere in our galaxy a star exploded, throwing out masses of gas and dust. This supernova, as these explosions are called, happened about 5bn years ago. The wreckage from the explosion then crashed into a nearby cloud of gas, bringing together the ingredients for our solar system to form.
Because the explosion was so energetic it made the dust mixture very hot and things began to cook. Little bits of dust began to cluster, making bigger and bigger lumps, and the mixture began to pull together under its own gravity.
Eventually the central lump became so hot and dense that it started to generate its own energy, igniting nuclear fires. This was the birth of our sun. The remaining dusty mixture swirled around the star, fanning out into a disc.
Gradually the sun grew in size and the dusty disc cooled. Over millions of years the dust clustered into grains, then lumps, boulders and eventually planetesimals - chunks of rock big enough to have their own gravitational field. Some of these planetesimals became the embryonic forms of the planets in our solar system today.
Slowly these rocky planets began to organise themselves, settling at a comfortable distance from the sun and finding their own orbit. Earth found its path as third planet from the sun. In the early days rocky pile-ups were still common, leaving craters on the surface of all of the planets.
One of these collisions, about 4.5bn years ago, is thought to have very nearly destroyed the Earth, and was probably responsible for our moon. A large planetesimal, about the size of Mars, gave Earth a glancing blow, chucking a chunk of Earth's crust out into space. Some of the planetesimal merged with Earth, while the ejected lump started its own orbit around Earth and became the moon.
Read More: http://www.theguardian.com/science/2008/apr/28/starsgalaxiesandplanets.geology
*Subscribe for more Educative & Space Documentaries (Like & Share)
* Visit our website: http://www.advexon.com
* ABDH Media Documentaries: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCHx69kZbXbX6WgMq_njRvFA
*NOVA | PBS Documentaries (HD): https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCYMWnCecPvpQJj8sBPUi4bA
#ABDH
#space
#spacedocumentary
#AlienPlanets
#NEWFullScienceDocumentaries
#SpaceDocumentary2015
#alien
#spacedocumentarynationalgeographic
#spacedocumentaryhd
#spacedocumentarybbc
#spacedocumentary2015hd
#spacedocumentaryplaylist #spacedocumentarynationalgeographic2015 #spacedocumentaryblackholes
#spacedocumentaryforkids
#spacedocumentaryalienplanets
#spacedocumentaryasteroidthedoomsdayrock
#spacedocumentary2015aliens
#aspaceodysseydocumentary
#spacedocumentaryblackholesfdc
#spacedocumentarybriancox
#spacedocumentarybest
#spacedocumentarybbc2015
#spacedocumentaryblacksky
#spacedocumentarybigbang
#bestspacedocumentary2015
#spacedocumentarycosmos
#spacedocumentaryconspiracy
#spacedocumentarychannel
#spacedocumentarychildren
#discoverychanneldocumentaryspace
#spacecolonizationdocumentary
#spaceshuttlechallengerdocumentary
#spacetimecontinuumdocumentary
#historychanneldocumentaryspace
#spacedocumentarydiscoverychannel
#spacedocumentarydarkmatter
#spacedocumentarydiscovery
#deepspacedocumentary
#deepspacedocumentary2015
#spacedisastersdocumentary
#spacedivedocumentary
#spaceshuttledisasterdocumentary
#davidattenboroughspacedocumentary
#spaceelevatordocumentary
#spaceexplorationdocumentary2015
#earthfromspacedocumentary
#spaceexplorationdocumentary2015
#spaceengineeringdocumentary
#edgeofspacedocumentary
#emptyspacedocumentary
#spacedocumentaryforchildren
#spacedocumentaryfilms
#spacedocumentaryfull
#spacedocumentaryfulllength
#spacedocumentaryfuture
#spacedocumentaryfunny
#2015spacedocumentaryfull
#spacedocumentarygalaxies
#spacedocumentarygravity
#spaceuniversegalaxydocumentary
#spacedocumentarynationalgeographic2015
#spacetraveldocumentarynationalgeographic
#spacedocumentarynationalgeographichd
#spacedocumentaryhd2015
#spacedocumentaryhd1080p
#spacedocumentaryinhd
- published: 11 May 2015
- views: 0
Moon 101. 03. Physiography and Geology of the Moon
Dr. Paul Spudis discusses the physiography and geology of the moon including: terrains, landforms, topography (photogeology), impact crater formation, excava......
Dr. Paul Spudis discusses the physiography and geology of the moon including: terrains, landforms, topography (photogeology), impact crater formation, excava...
wn.com/Moon 101. 03. Physiography And Geology Of The Moon
Dr. Paul Spudis discusses the physiography and geology of the moon including: terrains, landforms, topography (photogeology), impact crater formation, excava...
2015 6 1 USAEBN
3,600 Signature - San Andreas movie, predicting quakes, Thera explosion in Mediterranean relationship to Jewish Exodus, extinction of Mammoth on Wrangle Island,...
3,600 Signature - San Andreas movie, predicting quakes, Thera explosion in Mediterranean relationship to Jewish Exodus, extinction of Mammoth on Wrangle Island, Greenland ice heavy, crustal shift implied, Velikovsky books, sea level drop or rise, Ice Ages, Madagascar extinction caves, reading geology.
wn.com/2015 6 1 Usaebn
3,600 Signature - San Andreas movie, predicting quakes, Thera explosion in Mediterranean relationship to Jewish Exodus, extinction of Mammoth on Wrangle Island, Greenland ice heavy, crustal shift implied, Velikovsky books, sea level drop or rise, Ice Ages, Madagascar extinction caves, reading geology.
- published: 02 Jun 2015
- views: 1022
Jeff Karson- Discovering the Deep Oceans-Guest Night lecture
Dr. Jeff Karson, Syracuse University Professor of Earth Science, spoke in a featured presentation at the Houston Geological Society 2015 Guest Night June 6. Kar...
Dr. Jeff Karson, Syracuse University Professor of Earth Science, spoke in a featured presentation at the Houston Geological Society 2015 Guest Night June 6. Karson discusses the geology of seafloor spreading centers and intrusion of basalt into the mid ocean rifts. Dr. Karson is an author on a new 2015 book “Discovering the Deep: An Photographic Atlas of the Seafloor and Ocean Crust” just published by Cambridge University Press, in May 2015. Jeff Karson has been Chief Scientist and Co-Chief Scientist on multiple deep sea ALVIN DSV-2 missions from 1990-2005. The “ALVIN” is a three person operated deep-ocean research submersible operated by Woods Hole Institute that is accompanied by smaller remote operated vehicles (ROV) which conduct photography and sampling at ocean depths below 10,000 ft. Dr. Karson has been involved with deep ocean research since he was a professor at Duke University 1996-2006, continuing to Syracuse University in New York State, where he was recently Chair of the Earth Sciences Department.
wn.com/Jeff Karson Discovering The Deep Oceans Guest Night Lecture
Dr. Jeff Karson, Syracuse University Professor of Earth Science, spoke in a featured presentation at the Houston Geological Society 2015 Guest Night June 6. Karson discusses the geology of seafloor spreading centers and intrusion of basalt into the mid ocean rifts. Dr. Karson is an author on a new 2015 book “Discovering the Deep: An Photographic Atlas of the Seafloor and Ocean Crust” just published by Cambridge University Press, in May 2015. Jeff Karson has been Chief Scientist and Co-Chief Scientist on multiple deep sea ALVIN DSV-2 missions from 1990-2005. The “ALVIN” is a three person operated deep-ocean research submersible operated by Woods Hole Institute that is accompanied by smaller remote operated vehicles (ROV) which conduct photography and sampling at ocean depths below 10,000 ft. Dr. Karson has been involved with deep ocean research since he was a professor at Duke University 1996-2006, continuing to Syracuse University in New York State, where he was recently Chair of the Earth Sciences Department.
- published: 10 Jun 2015
- views: 3
FULL EPSIODE 06 Oceanic Geology - Understanding the Earth HD
Fundamentals of oceanic geology https://sites.google.com/site/mineguy101/home/lessons/lesson-6---oceanic-geology This geology course through Laurentian Unive......
Fundamentals of oceanic geology https://sites.google.com/site/mineguy101/home/lessons/lesson-6---oceanic-geology This geology course through Laurentian Unive...
wn.com/Full Epsiode 06 Oceanic Geology Understanding The Earth Hd
Fundamentals of oceanic geology https://sites.google.com/site/mineguy101/home/lessons/lesson-6---oceanic-geology This geology course through Laurentian Unive...
- published: 08 May 2014
- views: 256
-
author: mineguy101
Volcanoes in Virginia!
The recent earthquake may have you wondering what other surprises Virginia's geology may hold. Could there be a volcanic eruption in Virginia? Probably not t......
The recent earthquake may have you wondering what other surprises Virginia's geology may hold. Could there be a volcanic eruption in Virginia? Probably not t...
wn.com/Volcanoes In Virginia
The recent earthquake may have you wondering what other surprises Virginia's geology may hold. Could there be a volcanic eruption in Virginia? Probably not t...
Professor Jade Star Lackey: Zoned Crystals and the Pace of Earth Processes
In this lecture from October 2, 2013 -- Zoned Crystals and the Pace of Earth Processes -- Associate Professor of Geology Jade Star Lackey discusses case stud......
In this lecture from October 2, 2013 -- Zoned Crystals and the Pace of Earth Processes -- Associate Professor of Geology Jade Star Lackey discusses case stud...
wn.com/Professor Jade Star Lackey Zoned Crystals And The Pace Of Earth Processes
In this lecture from October 2, 2013 -- Zoned Crystals and the Pace of Earth Processes -- Associate Professor of Geology Jade Star Lackey discusses case stud...
"How and when did plate tectonics start on Earth, what came before, and why does it matter?"
Robert Stern, a research scientist in the geosciences department at The University of Texas at Dallas and current Merle A. Tuve Senior Fellow at DTM, gave his T...
Robert Stern, a research scientist in the geosciences department at The University of Texas at Dallas and current Merle A. Tuve Senior Fellow at DTM, gave his Tuve Lecture titled "How and when did plate tectonics start on Earth, what came before, and why does it matter?" at 11 a.m. on Wednesday, 13 May 2015, in the Greenewalt Lecture Hall.
Stern received his Ph.D. in Earth sciences from the University of California at San Diego in 1979. After finishing his Ph.D, Stern became a postdoctoral fellow at DTM from 1979-1982. His research interests include:
- Evolution of the continental crust as approached by tectonic, chemical, and isotopic studies of modern processes and ancient products.
- Geographic foci of such studies include Izu-Bonin-Mariana island arc system in the Western Pacific and Neoproterozoic crust of northeast Africa. These processes and products are studied using a wide range of analytical techniques, including major and trace element analyses, radiogenic isotopic compositions of Sr, Nd, and Pb, and U-Pb zircon geochronology, and Remote Sensing
- Applications of Remote Sensing for understanding the tectonics and resources of arid regions. Special focus is given to using synthetic aperture radar and Landsat-TM imagery to mapping basement structures and river systems and exploring for water, gold, and oil deposits in arid regions
- Geology of the Dallas-Fort Worth Metroplex
- Geography, resources, and environment of Latin America and the Middle East
wn.com/How And When Did Plate Tectonics Start On Earth, What Came Before, And Why Does It Matter
Robert Stern, a research scientist in the geosciences department at The University of Texas at Dallas and current Merle A. Tuve Senior Fellow at DTM, gave his Tuve Lecture titled "How and when did plate tectonics start on Earth, what came before, and why does it matter?" at 11 a.m. on Wednesday, 13 May 2015, in the Greenewalt Lecture Hall.
Stern received his Ph.D. in Earth sciences from the University of California at San Diego in 1979. After finishing his Ph.D, Stern became a postdoctoral fellow at DTM from 1979-1982. His research interests include:
- Evolution of the continental crust as approached by tectonic, chemical, and isotopic studies of modern processes and ancient products.
- Geographic foci of such studies include Izu-Bonin-Mariana island arc system in the Western Pacific and Neoproterozoic crust of northeast Africa. These processes and products are studied using a wide range of analytical techniques, including major and trace element analyses, radiogenic isotopic compositions of Sr, Nd, and Pb, and U-Pb zircon geochronology, and Remote Sensing
- Applications of Remote Sensing for understanding the tectonics and resources of arid regions. Special focus is given to using synthetic aperture radar and Landsat-TM imagery to mapping basement structures and river systems and exploring for water, gold, and oil deposits in arid regions
- Geology of the Dallas-Fort Worth Metroplex
- Geography, resources, and environment of Latin America and the Middle East
- published: 22 May 2015
- views: 2