- published: 20 Oct 2014
- views: 1
-
remove the playlistOceanic Crust
- remove the playlistOceanic Crust
- published: 19 Oct 2015
- views: 0
- published: 28 Dec 2011
- views: 21318
- author: scienceclassisgreat
- published: 26 Aug 2007
- views: 1627158
- author: Michael Freudiger
- published: 17 Oct 2012
- views: 841
- author: University of Derby
- published: 20 Oct 2014
- views: 1
- published: 17 Oct 2014
- views: 1
- published: 26 Sep 2015
- views: 3
- published: 25 Feb 2013
- views: 42
- author: themathgraph
- published: 01 Dec 2011
- views: 478
- author: mingming li

Oceanic crust has a crust made up of basalt and gabbro and the upper mantle consits of peridoite. Oceanic crust is the part of Earth's lithosphere that surfaces in the ocean basins. Oceanic crust is primarily composed of mafic rocks, or sima, which is rich in iron and magnesium. It is thinner than continental crust, or sial, generally less than 10 kilometers thick, however it is denser, having a mean density of about 2.9 grams per cubic centimeter.
Although a complete section of oceanic crust has not yet been drilled, geologists have several pieces of evidence that help them understand the ocean floor. Estimations of composition are based on analyses of ophiolites (sections of oceanic crust that are preserved on the continents), comparisons of the seismic structure of the oceanic crust with laboratory determinations of seismic velocities in known rock types, and samples recovered from the ocean floor by submersibles, dredging (especially from ridge crests and fracture zones) and drilling. Oceanic crust is significantly simpler than continental crust and generally can be divided in three layers.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Ioánnis Fokás (Greek: Ιωάννης Φωκάς), better known by the Spanish transcription of his name, Juan de Fuca (born 1536 on the Ionian island of Cefalonia; died there 1602), was a Greek-born maritime pilot in the service of the king of Spain, Philip II. He is best known for his claim to have explored the Strait of Anián, now known as the Strait of Juan de Fuca, between Vancouver Island, now part of British Columbia, Canada, and northwestern Washington State, United States.
Fokás's grandfather, Emmanouíl Fokás (Gk: Εμμανουήλ Φωκάς), fled Constantinople at its fall in 1453, accompanied by his brother Andrónikos (Gk: Ανδρόνικος). The two settled first in the Peloponnese, where Andrónikos remained, but in 1470 Emmanouíl moved to the island of Cefalonia. Iákovos (Gk: Ιάκωβος), Ioánnis's father established himself in the village of Valerianos (Gk: Βαλεριάνος) on the island and came to be known as "the Valeriáno Fokás" (Gk: ο Φωκάς ο Βαλεριάνος) to distinguish him from his brothers.
It was in this village of Valeriáno that Fokás was born in 1536. Little to nothing is known about his life before he entered the service of Spain, some time around 1555.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
Oceanic Crust
Oceanic CrustOceanic Crust
I created this video with the YouTube Video Editor (http://www.youtube.com/editor) -
Oceanic crust
Oceanic crustOceanic crust
Oceanic crust is the part of Earth's lithosphere that surfaces in the ocean basins. Oceanic crust is primarily composed of mafic rocks, or sima, which is rich in iron and magnesium. It is thinner than continental crust, or sial, generally less than 10 kilometers thick; however it is denser, having a mean density of about 2.9 grams per cubic centimeter as opposed to continental crust which has a density of about 2.7 grams per cubic centimeter. This video is targeted to blind users. Attribution: Article text available under CC-BY-SA Creative Commons image source in video -
Ocean Basins (Part 1): Features of the Ocean Floor (Continental Margin)
Ocean Basins (Part 1): Features of the Ocean Floor (Continental Margin)Ocean Basins (Part 1): Features of the Ocean Floor (Continental Margin)
Mr. Lima discusses the difference between continental and oceanic crust, types of tectonic plates, and discusses features of the ocean floor associated with ... -
The Early Earth and Plate Tectonics
The Early Earth and Plate TectonicsThe Early Earth and Plate Tectonics
The Earth is formed by accretion of spatial particulates and large masses and eventually forms an outer crust. Video follows with speculation of early plates... -
Oman Ophiolite - Lower oceanic crust and moho
Oman Ophiolite - Lower oceanic crust and mohoOman Ophiolite - Lower oceanic crust and moho
Geological field excursion to the Oman ophiolite. In these videos Hugh Rollinson, from the University of Derby, takes you on a geological journey from the oc... -
Continental and Oceanic Crust
Continental and Oceanic CrustContinental and Oceanic Crust
I created this video with the YouTube Video Editor (http://www.youtube.com/editor) -
CONTINENTAL AND OCEANIC CRUST
CONTINENTAL AND OCEANIC CRUSTCONTINENTAL AND OCEANIC CRUST
-
Continental and oceanic crust
Continental and oceanic crustContinental and oceanic crust
I created this video with the YouTube Video Editor (http://www.youtube.com/editor) -
Oceanic and Continental Crust
Oceanic and Continental CrustOceanic and Continental Crust
Tayte and David -
What Happens When Continental Crust And Oceanic Crust Collide
What Happens When Continental Crust And Oceanic Crust CollideWhat Happens When Continental Crust And Oceanic Crust Collide
Collide . , . . . . Oceanic crust tends to be denser and thinner than continental crust, so the denser oceanic crust gets bent what happens when two continental plates collide?. Here are some more compilation of topics and latest discussions relates to this video, which we found thorough the internet. Hope this information will helpful to get idea in brief about this. When an oceanic plate collides with a continental plate the crust forming the the continental crust is called subduction and the zone at which this occurs at the and the difference between them is continental crust is older right? and when oceanic and continental pla -
The Oceanic Crust
The Oceanic CrustThe Oceanic Crust
A brief video on the oceanic crust. -
The difficulty for subducted oceanic crust to accumulate at the core-mantle boundary
The difficulty for subducted oceanic crust to accumulate at the core-mantle boundaryThe difficulty for subducted oceanic crust to accumulate at the core-mantle boundary
The results of our numerical melding shows that, under present-day Earth-like conditions, it is difficult for the subducted oceanic crust to accumulate into ... -
Interaction between subducted oceanic crust and primordial reservoir at the lower mantle
Interaction between subducted oceanic crust and primordial reservoir at the lower mantleInteraction between subducted oceanic crust and primordial reservoir at the lower mantle
We find that oceanic crust subducted to the lowermost mantle is viscously dragged toward upwelling regions, where primordial reservoirs are hypothesized to e... -
Oceanic Crust movements.m4v
Oceanic Crust movements.m4vOceanic Crust movements.m4v
school work.
- Abyssal plain
- Airy wave theory
- Amphidromic point
- Arctic Ocean
- Argo (oceanography)
- Atoll
- Azores
- Ballantine Scale
- Baroclinity
- Basalt
- Bathymetric chart
- Benthic lander
- Benthic zone
- Black smoker
- Boundary current
- Breaking wave
- Category Tides
- Category Water waves
- Clapotis
- Cnoidal wave
- Coastal geography
- Cold seep
- Color of water
- Continental crust
- Continental margin
- Continental rise
- Continental shelf
- Contourite
- Convergent boundary
- Coriolis effect
- Cross sea
- Cumulate rock
- Deep ocean water
- Deep sea
- Diabase
- Dike (geology)
- Divergent boundary
- Downwelling
- DSV Alvin
- Earth tide
- Edge wave
- Ekman layer
- Ekman spiral
- Ekman transport
- Equatorial waves
- Fetch (geography)
- Fracture zone
- Future sea level
- Gabbro
- Gakkel Ridge
- Galapagos Islands
- Geomagnetic reversal
- Geostrophic current
- Grams
- Gravity wave
- Gulf Stream
- Guyot
- Head of tide
- Hotspot (geology)
- Humboldt Current
- Hydroacoustics
- Hydrography
- Hydrothermal vent
- Iceland
- Incompatible element
- Infragravity waves
- Internal tide
- Internal wave
- Kelvin wave
- Landform
- Langmuir circulation
- Lithosphere
- Littoral zone
- Longshore drift
- Loop Current
- Lunitidal interval
- Maelstrom
- Mafic
- Magma
- Mantle plume
- Marginal sea
- Marine geology
- Marine pollution
- Mesopelagic
- Mid-ocean ridge
- Mid-Ocean Ridge
- Mild-slope equation
- Modular Ocean Model
- Ocean
- Ocean current
- Ocean dynamics
- Ocean energy
- Ocean exploration
- Ocean gyre
- Ocean observations
- Ocean reanalysis
- Oceanic basin
- Oceanic crust
- Oceanic plateau
- Oceanic trench
- Oceanic zone
- Oceanography
- Ophiolite
- Outer trench swell
- Passive margin
- Pelagic sediments
- Pelagic zone
- Perigean spring tide
- Photic zone
- Pillow lava
- Plate tectonics
- Potassium
- Radiation stress
- Ridge push
- Rip current
- Rogue wave
- Rossby wave
- Rossby-gravity waves
- Rule of twelfths
- Science On a Sphere
- Sea level
- Sea state
- Sea-level curve
- Seabed
- Seafloor spreading
- Seamount
- Seawater
- Sediment
- Sediment transport
- Seiche
- Sial
- Sima (geology)
- Slab pull
- Slab suction
- Slab window
- Slack water
- Sneaker wave
- Sofar bomb
- SOFAR channel
- Solidus (chemistry)
- Soliton
- Spring tide
- Stokes drift
- Subduction
- Submarine canyon
- Submersible
- Subsurface currents
- Surf wave
- Surf zone
- Sverdrup balance
- Swell (ocean)
- Thermocline
- Tidal bore
- Tidal force
- Tidal power
- Tidal race
- Tidal range
- Tidal resonance
- Tide
- Tide gauge
- Tideline
- Transform fault
- Tsunami
- Turbidity current
- Ultramafic
- Underwater acoustics
- Underwater glider
- Upwelling
- Ursell number
- Volcanic arc
- Water column
- Wave base
- Wave height
- Wave power
- Wave radar
- Wave setup
- Wave shoaling
- Wave turbulence
- Whirlpool
- Wilson cycle
- Wind wave
- Wind wave model
- World Ocean Atlas
-

Oceanic Crust
I created this video with the YouTube Video Editor (http://www.youtube.com/editor) -

Oceanic crust
Oceanic crust is the part of Earth's lithosphere that surfaces in the ocean basins. Oceanic crust is primarily composed of mafic rocks, or sima, which is rich in iron and magnesium. It is thinner than continental crust, or sial, generally less than 10 kilometers thick; however it is denser, having a mean density of about 2.9 grams per cubic centimeter as opposed to continental crust which has a de -

Ocean Basins (Part 1): Features of the Ocean Floor (Continental Margin)
Mr. Lima discusses the difference between continental and oceanic crust, types of tectonic plates, and discusses features of the ocean floor associated with ... -

The Early Earth and Plate Tectonics
The Earth is formed by accretion of spatial particulates and large masses and eventually forms an outer crust. Video follows with speculation of early plates... -

Oman Ophiolite - Lower oceanic crust and moho
Geological field excursion to the Oman ophiolite. In these videos Hugh Rollinson, from the University of Derby, takes you on a geological journey from the oc... -

Continental and Oceanic Crust
I created this video with the YouTube Video Editor (http://www.youtube.com/editor) -

CONTINENTAL AND OCEANIC CRUST
-

Continental and oceanic crust
I created this video with the YouTube Video Editor (http://www.youtube.com/editor) -

Oceanic and Continental Crust
Tayte and David -

What Happens When Continental Crust And Oceanic Crust Collide
Collide . , . . . . Oceanic crust tends to be denser and thinner than continental crust, so the denser oceanic crust gets bent what happens when two continental plates collide?. Here are some more compilation of topics and latest discussions relates to this video, which we found thorough the internet. Hope this information will helpful to get idea in brief about this. When an oceanic p -

The Oceanic Crust
A brief video on the oceanic crust. -
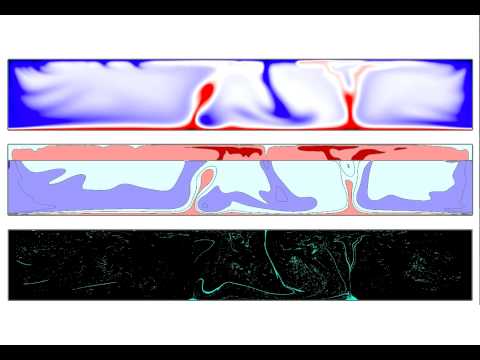
The difficulty for subducted oceanic crust to accumulate at the core-mantle boundary
The results of our numerical melding shows that, under present-day Earth-like conditions, it is difficult for the subducted oceanic crust to accumulate into ... -

Interaction between subducted oceanic crust and primordial reservoir at the lower mantle
We find that oceanic crust subducted to the lowermost mantle is viscously dragged toward upwelling regions, where primordial reservoirs are hypothesized to e... -

Oceanic Crust movements.m4v
school work. -

Continental oceanic crust
-

Learn About Lithospheric Plates || Earth's crust || Earth Science
Lithospheric plates Lithospheric plates are regions of Earth's crust and upper mantle that are fractured into plates that move across a deeper plasticine mantle. Earth's crust is fractured into 13 major and approximately 20 total lithospheric plates. Each lithospheric plate is composed of a layer of oceanic crust or continental crust superficial to an outer layer of the mantle. Containing both cru -

Cores of Juan de Fuca ocean crust, croûte océanique, basalt, sediments, pillow lavas, bioturbation
www.ronbleud.fr for further information Movie showing cores of Juan de Fuca oceanic crust. You'll see sediments, basalt, breccia, pillow lavas... For further... -

Earth's Structure
Table of Contents: 00:00 - Continental vs. Oceanic Crust 00:03 - Objectives 00:24 - Basics 06:56 - Objectives. -

Continental or Oceanic crust
Description -

Science oceanic crust.m4v
Aatiqah, Daisy, Nick and Mike hope you enjoyed it and its just a short movie of us pretending to be an oceanic crust and converging and diverging. -

Young Oceanic Crust
Provided to YouTube by Phonofile Young Oceanic Crust · Yumiko Tanaka & Ivar Grydeland ℗ 2005 Sofa Music Released on: 2005-05-20 Auto-generated by YouTube. -

Massive Underground Ocean Exists Beneath Earth's Crust, Study Says
Scientists believe they've found evidence of a potential ocean beneath our home planet's crust. A study from researchers at Northwestern University and the U... -

Earth Movements - Activity 2: The Earth's Crust
Students explore the structure and composition of the Earth's crust. They compare oceanic crust with continental crust and discuss some of the geographic features of each. Then they build a model of the Earth's crust that consists of ocean floor and an adjacent continent.
Oceanic Crust
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:00
- Updated: 20 Oct 2014
- views: 1
- published: 20 Oct 2014
- views: 1
Oceanic crust
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:27
- Updated: 19 Oct 2015
- views: 0
- published: 19 Oct 2015
- views: 0
Ocean Basins (Part 1): Features of the Ocean Floor (Continental Margin)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:39
- Updated: 02 Sep 2014
- views: 21318
- author: scienceclassisgreat
- published: 28 Dec 2011
- views: 21318
- author: scienceclassisgreat
The Early Earth and Plate Tectonics
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:17
- Updated: 06 Sep 2014
- views: 1627158
- author: Michael Freudiger
- published: 26 Aug 2007
- views: 1627158
- author: Michael Freudiger
Oman Ophiolite - Lower oceanic crust and moho
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:29
- Updated: 29 Dec 2013
- views: 841
- author: University of Derby
- published: 17 Oct 2012
- views: 841
- author: University of Derby
Continental and Oceanic Crust
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:52
- Updated: 20 Oct 2014
- views: 1
- published: 20 Oct 2014
- views: 1
CONTINENTAL AND OCEANIC CRUST
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:29
- Updated: 08 Dec 2014
- views: 0
- published: 08 Dec 2014
- views: 0
Continental and oceanic crust
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:48
- Updated: 17 Oct 2014
- views: 1
- published: 17 Oct 2014
- views: 1
Oceanic and Continental Crust
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:56
- Updated: 06 Feb 2014
- views: 5
- published: 06 Feb 2014
- views: 5
What Happens When Continental Crust And Oceanic Crust Collide
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:59
- Updated: 26 Sep 2015
- views: 3
- published: 26 Sep 2015
- views: 3
The Oceanic Crust
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:01
- Updated: 25 Feb 2013
- views: 42
- author: themathgraph
- published: 25 Feb 2013
- views: 42
- author: themathgraph
The difficulty for subducted oceanic crust to accumulate at the core-mantle boundary
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:26
- Updated: 03 Feb 2012
- views: 478
- author: mingming li
- published: 01 Dec 2011
- views: 478
- author: mingming li
Interaction between subducted oceanic crust and primordial reservoir at the lower mantle
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:46
- Updated: 30 Nov 2012
- views: 65
- author: mingming li
- published: 30 Nov 2012
- views: 65
- author: mingming li
Oceanic Crust movements.m4v
- published: 24 Feb 2012
- views: 77
- author: TheTdyne
Continental oceanic crust
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:27
- Updated: 24 Nov 2014
- views: 1
- published: 24 Nov 2014
- views: 1
Learn About Lithospheric Plates || Earth's crust || Earth Science
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:26
- Updated: 27 Aug 2015
- views: 3
- published: 27 Aug 2015
- views: 3
Cores of Juan de Fuca ocean crust, croûte océanique, basalt, sediments, pillow lavas, bioturbation
- published: 17 Oct 2010
- views: 122
- author: jiemje
Earth's Structure
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:33
- Updated: 13 Apr 2013
- views: 84
- author: Sean Fisher-Rohde
- published: 13 Apr 2013
- views: 84
- author: Sean Fisher-Rohde
Continental or Oceanic crust
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:35
- Updated: 30 Apr 2015
- views: 7
- published: 30 Apr 2015
- views: 7
Science oceanic crust.m4v
- published: 18 Feb 2011
- views: 190
- author: iskl4aw
Young Oceanic Crust
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 12:01
- Updated: 23 Jun 2015
- views: 0
- published: 23 Jun 2015
- views: 0
Massive Underground Ocean Exists Beneath Earth's Crust, Study Says
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:25
- Updated: 05 Sep 2014
- views: 14343
- author: GeoBeats News
- published: 13 Jun 2014
- views: 14343
- author: GeoBeats News
Earth Movements - Activity 2: The Earth's Crust
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:36
- Updated: 01 Jun 2015
- views: 0
- published: 01 Jun 2015
- views: 0
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

Oceanic Crust
- published: 20 Oct 2014
- views: 1

Oceanic crust
- published: 19 Oct 2015
- views: 0

Ocean Basins (Part 1): Features of the Ocean Floor (Continental Margin)
- published: 28 Dec 2011
- views: 21318
-
author:
scienceclassisgreat
Add Playlist for this Author

The Early Earth and Plate Tectonics
- published: 26 Aug 2007
- views: 1627158
-
author:
Michael Freudiger
Add Playlist for this Author

Oman Ophiolite - Lower oceanic crust and moho
- published: 17 Oct 2012
- views: 841
-
author:
University of Derby
Add Playlist for this Author

Continental and Oceanic Crust
- published: 20 Oct 2014
- views: 1

CONTINENTAL AND OCEANIC CRUST
- published: 08 Dec 2014
- views: 0

Continental and oceanic crust
- published: 17 Oct 2014
- views: 1

Oceanic and Continental Crust
- published: 06 Feb 2014
- views: 5

What Happens When Continental Crust And Oceanic Crust Collide
- published: 26 Sep 2015
- views: 3

The Oceanic Crust
- published: 25 Feb 2013
- views: 42
-
author:
themathgraph
Add Playlist for this Author

The difficulty for subducted oceanic crust to accumulate at the core-mantle boundary
- published: 01 Dec 2011
- views: 478
-
author:
mingming li
Add Playlist for this Author

Interaction between subducted oceanic crust and primordial reservoir at the lower mantle
- published: 30 Nov 2012
- views: 65
-
author:
mingming li
Add Playlist for this Author

Oceanic Crust movements.m4v
- published: 24 Feb 2012
- views: 77
-
author:
TheTdyne
Add Playlist for this Author
Islamic State video threatens France a day after Paris bloodshed
Edit Yahoo Daily News 14 Nov 2015Paris terror attacks: Eight attackers dead after killing 150 people
Edit The Irish Times 14 Nov 2015Over 150 killed in Paris attacks, Francois Hollande declares emergency
Edit The Times of India 14 Nov 2015Hollande Blames ISIS for ‘Act of War’ on Paris
Edit New York Times 14 Nov 2015French Police End Raid on Paris Concert Hall, at Least Two Attackers Dead: AP
Edit Bloomberg 14 Nov 2015Traces Found Of Ancient Nearby Supernova
Edit IFL Science 09 Oct 2015Scientists Reveal Birth Date Of Earth's Inner Core
Edit IFL Science 08 Oct 2015BMG Annual Report 2015 (BMG Resources Limited)
Edit Public Technologies 07 Oct 2015Silence of the scientists: how the global warming RICO letter backfired
Edit The Examiner 24 Sep 2015Scientists discover how tectonic plates collide (The University of Nottingham)
Edit Public Technologies 08 Sep 2015Past, present and future of studying life on the rocks (Bigelow Laboratory for Ocean Sciences) ...
Edit Public Technologies 08 Sep 2015Siam Copper Project Thailand Second Assay Confirms Very High Grade Copper (Matsa Resources Limited)
Edit Public Technologies 02 Sep 2015Sea Ice: Ancient Oceans Birthed Diamonds
Edit Yahoo Daily News 28 Aug 2015ONC embarks on 'most exciting' expedition (University of Victoria)
Edit Public Technologies 24 Aug 2015Curiosity finds first evidence for possible ‘continental crust’ on Mars
Edit The Examiner 31 Jul 2015Curiosity rover finds evidence of Mars’ primitive continental crust (Los Alamos National Laboratory)
Edit Public Technologies 31 Jul 2015Siam Copper Project Thailand Update (Matsa Resources Limited)
Edit Public Technologies 27 Jul 2015Search for life now extends to outer reaches of solar system
Edit The Guardian 19 Jul 2015- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »






