Methamphetamine
Methamphetamine[note 1] (contracted from N-methylamphetamine) is a strong central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is mainly used as a recreational drug and less commonly as a treatment for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and obesity. Methamphetamine was discovered in 1893 and exists as two enantiomers: levo-methamphetamine and dextro-methamphetamine.[note 2] Methamphetamine properly refers to a specific chemical, the racemic free base, which is an equal mixture of levomethamphetamine and dextromethamphetamine in their pure amine forms. It is rarely prescribed due to concerns involving human neurotoxicity and potential for recreational use as an aphrodisiac and euphoriant, among other concerns, as well as the availability of safer substitute drugs with comparable treatment efficacy. Dextromethamphetamine is a much stronger CNS stimulant than levomethamphetamine.
Both methamphetamine and dextromethamphetamine are illicitly trafficked and sold owing to their potential for recreational use. The highest prevalence of illegal methamphetamine use occurs in parts of Asia, Oceania, and in the United States, where racemic methamphetamine, levomethamphetamine, and dextromethamphetamine are classified as schedule II controlled substances. Levomethamphetamine is available as an over-the-counter (OTC) drug for use as an inhaled nasal decongestant in the United States.[note 3] Internationally, the production, distribution, sale, and possession of methamphetamine is restricted or banned in many countries, due to its placement in schedule II of the United Nations Convention on Psychotropic Substances treaty. While dextromethamphetamine is a more potent drug, racemic methamphetamine is sometimes illicitly produced due to the relative ease of synthesis and limited availability of chemical precursors.
In low doses, methamphetamine can elevate mood, increase alertness, concentration and energy in fatigued individuals, reduce appetite and promote (initial) weight loss. At higher doses, it can induce psychosis, breakdown of skeletal muscle, seizures and bleeding in the brain. Chronic high-dose use can precipitate unpredictable and rapid mood swings, prominent delusions and violent behavior. Recreationally, methamphetamine's ability to increase energy has been reported to lift mood and increase sexual desire to such an extent that users are able to engage in sexual activity continuously for several days.[17] Methamphetamine is known to have a high addiction liability (i.e. compulsive methamphetamine use) and dependence liability (i.e. withdrawal symptoms occur when methamphetamine use ceases). Heavy recreational use of methamphetamine may lead to a post-acute-withdrawal syndrome, which can persist for months beyond the typical withdrawal period. Unlike amphetamine, methamphetamine is neurotoxic to human midbrain dopaminergic neurons.[18] It has also been shown to damage serotonin neurons in the CNS.[19][20] This damage includes adverse changes in brain structure and function, such as reductions in grey matter volume in several brain regions and adverse changes in markers of metabolic integrity.[20]
Methamphetamine belongs to the substituted phenethylamine and substituted amphetamine chemical classes. It is related to the other dimethylphenethylamines as a positional isomer of these compounds, which share the common chemical formula: C10H15N1.
Uses
Medical
In the United States, methamphetamine hydrochloride, under the trade name Desoxyn, has been approved by the FDA for treating ADHD and obesity in both adults and children;[21][22] however, the FDA also indicates that the limited therapeutic usefulness of methamphetamine should be weighed against the inherent risks associated with its use.[21] Methamphetamine is sometimes prescribed off label for narcolepsy and idiopathic hypersomnia.[23][24] In the United States, methamphetamine's levorotary form is available in some over-the-counter (OTC) nasal decongestant products.[note 3]
As methamphetamine is associated with a high potential for misuse, the drug is regulated under the Controlled Substances Act and is listed under schedule II in the United States.[21] Methamphetamine hydrochloride dispensed in the United States is required to include a boxed warning regarding its potential for recreational misuse and addiction liability.[21]
Recreational
Methamphetamine is often used recreationally for its effects as a potent euphoriant and stimulant as well as aphrodisiac qualities.[17] According to a National Geographic TV documentary on methamphetamine, "an entire subculture known as party and play is based around methamphetamine use".[17] Members of this San Francisco sub-culture, which consists almost entirely of gay male methamphetamine users, will typically meet up through internet dating sites and have sex.[17] Due to its strong stimulant and aphrodisiac effects and inhibitory effect on ejaculation, with repeated use, these sexual encounters will sometimes occur continuously for several days on end.[17] The crash following the use of methamphetamine in this manner is very often severe, with marked hypersomnia (excessive daytime sleepiness).[17] Methamphetamine use has also been noted among men having sex with men in New York City.[25]
Contraindications
Methamphetamine is contraindicated in individuals with a history of substance use disorder, heart disease, or severe agitation or anxiety, or in individuals currently experiencing arteriosclerosis, glaucoma, hyperthyroidism, or severe hypertension.[21] The USFDA states that individuals who have experienced hypersensitivity reactions to other stimulants in the past or are currently taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors should not take methamphetamine.[21] The USFDA also advises individuals with bipolar disorder, depression, elevated blood pressure, liver or kidney problems, mania, psychosis, Raynaud's phenomenon, seizures, thyroid problems, tics, or Tourette syndrome to monitor their symptoms while taking methamphetamine.[21] Due to the potential for stunted growth, the USFDA advises monitoring the height and weight of growing children and adolescents during treatment.[21]
Side effects
Physical
The physical effects of methamphetamine can include loss of appetite, hyperactivity, dilated pupils, flushed skin, excessive sweating, increased movement, dry mouth and teeth grinding (leading to "meth mouth"), headache, irregular heartbeat (usually as accelerated heartbeat or slowed heartbeat), rapid breathing, high blood pressure, low blood pressure, high body temperature, diarrhea, constipation, blurred vision, dizziness, twitching, numbness, tremors, dry skin, acne, and pale appearance.[21][26] Methamphetamine that is present in a mother's bloodstream can pass through the placenta to a fetus and can also be secreted into breast milk.[27] Infants born to methamphetamine-abusing mothers were found to have a significantly smaller gestational age-adjusted head circumference and birth weight measurements.[27] Methamphetamine exposure was also associated with neonatal withdrawal symptoms of agitation, vomiting and fast breathing.[27] This withdrawal syndrome is relatively mild and only requires medical intervention in approximately 4% of cases.[28]
Meth mouth
Methamphetamine users and addicts may lose their teeth abnormally quickly, regardless of the route of administration, from a condition informally known as meth mouth.[29] The condition is generally most severe in users who inject the drug, rather than swallow, smoke, or inhale it.[29] According to the American Dental Association, meth mouth "is probably caused by a combination of drug-induced psychological and physiological changes resulting in xerostomia (dry mouth), extended periods of poor oral hygiene, frequent consumption of high-calorie, carbonated beverages and bruxism (teeth grinding and clenching)".[29][30] As dry mouth is also a common side effect of other stimulants, which are not known to contribute severe tooth decay, many researchers suggest that methamphetamine associated tooth decay is more due to users' other choices. They suggest the side effect has been exaggerated and stylized to create a stereotype of current users to deter new ones.[31]
Sexually transmitted infection
Methamphetamine use was found to be related to higher frequencies of unprotected sexual intercourse in both HIV-positive and unknown casual partners, an association more pronounced in HIV-positive participants.[32] These findings suggest that methamphetamine use and engagement in unprotected anal intercourse are co-occurring risk behaviors, behaviors that potentially heighten the risk of HIV transmission among gay and bisexual men.[32] Methamphetamine use allows users of both sexes to engage in prolonged sexual activity, which may cause genital sores and abrasions as well as priapism in men.[21][33] Methamphetamine may also cause sores and abrasions in the mouth via bruxism, increasing the risk of sexually transmitted infection.[21][33]
Besides the sexual transmission of HIV, it may also be transmitted between users who share a common needle.[34] The level of needle sharing among methamphetamine users is similar to that among other drug injection users.[34]
Psychological
The psychological effects of methamphetamine can include euphoria, dysphoria, changes in libido, alertness, apprehension and concentration, decreased sense of fatigue, insomnia or wakefulness, self-confidence, sociability, irritability, restlessness, grandiosity and repetitive and obsessive behaviors.[21][26][35] Methamphetamine use also has a high association with anxiety, depression, amphetamine psychosis, suicide, and violent behaviors.[36]
Neurotoxicity and neuroimmune response
| This section is incomplete. This is because coverage of this review and effects on glia are missing. (November 2015) |

Unlike amphetamine, methamphetamine is directly neurotoxic to dopamine neurons in both lab animals and humans.[18][19][20] Moreover, methamphetamine neurotoxicity is associated with an increased risk of Parkinson's disease, an effect which partially arises through excessive cytosolic and synaptic production of reactive oxygen species and autoxidation of dopamine.[40][41][42][43][44] In addition to dopaminergic neurotoxicity, a review of evidence in humans also indicated that high-dose methamphetamine use can be neurotoxic to serotonin neurons.[20] It has been demonstrated that a high core temperature is correlated with an increase in the neurotoxic effects of methamphetamine.[45] As a result of methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity to dopamine neurons, chronic use may also lead to post-acute withdrawal which persists months beyond the typical withdrawal period.[41]
Magnetic resonance imaging studies on human methamphetamine users have also found evidence of neurodegeneration, or adverse neuroplastic changes in brain structure and function.[20] In particular, methamphetamine appears to cause hyperintensity and hypertrophy of white matter, marked shrinkage of hippocampi, and reduced gray matter in the cingulate cortex, limbic cortex, and paralimbic cortex in recreational methamphetamine users.[20] Moreover, evidence suggests that adverse changes in the level of biomarkers of metabolic integrity and synthesis occur in recreational users, such as a reduction in N-acetylaspartate and creatine levels and elevated levels of choline and myoinositol.[20]
Methamphetamine has been shown to activate TAAR1 in human astrocytes and generate cAMP as a result.[46] Activation of astrocyte-localized TAAR1 appears to function as a mechanism by which methamphetamine attenuates membrane-bound EAAT2 (SLC1A2) levels and function in these cells.[46]
Methamphetamine binds to and activates both sigma receptor subtypes, σ1 and σ2, in the brain.[39][47] Sigma receptor activation by methamphetamine promotes methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity by facilitating hyperthermia, increasing dopamine synthesis and release, influencing microglial activation, and modulating apoptotic signaling cascades and the formation of reactive oxygen species.[39][47]
Overdose
A methamphetamine overdose may result in a wide range of symptoms.[7][21] A moderate overdose of methamphetamine may induce symptoms such as: abnormal heart rhythm, confusion, difficult and/or painful urination, high or low blood pressure, high body temperature, over-active and/or over-responsive reflexes, muscle aches, severe agitation, rapid breathing, tremor, urinary hesitancy, and an inability to pass urine.[7][26] An extremely large overdose may produce symptoms such as adrenergic storm, methamphetamine psychosis, substantially reduced or no urine output, cardiogenic shock, bleeding in the brain, circulatory collapse, hyperpyrexia (i.e., dangerously high body temperature), pulmonary hypertension, kidney failure, rapid muscle breakdown, serotonin syndrome, and a form of stereotypy ("tweaking").[Refnote 1] A methamphetamine overdose will likely also result in mild brain damage due to dopaminergic and serotonergic neurotoxicity.[18][20] Death from methamphetamine poisoning is typically preceded by convulsions and coma.[21]
Psychosis
Abuse of methamphetamine can result in a stimulant psychosis which may present with a variety of symptoms (e.g. paranoia, hallucinations, delirium, delusions).[7][51] A Cochrane Collaboration review on treatment for amphetamine, dextroamphetamine, and methamphetamine abuse-induced psychosis states that about 5–15% of users fail to recover completely.[51][52] The same review asserts that, based upon at least one trial, antipsychotic medications effectively resolve the symptoms of acute amphetamine psychosis.[51] Amphetamine psychosis may also develop occasionally as a treatment-emergent side effect.[53]
Emergency treatment
Acute methamphetamine intoxication is largely managed by treating the symptoms and treatments may initially include administration of activated charcoal and sedation.[7] There is not enough evidence on hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis in cases of methamphetamine intoxication to determine their usefulness.[21] Forced acid diuresis (e.g., with vitamin C) will increase methamphetamine excretion but is not recommended as it may increase the risk of aggravating acidosis, or cause seizures or rhabdomyolysis.[7] Hypertension presents a risk for intracranial hemorrhage (i.e., bleeding in the brain) and, if severe, is typically treated with intravenous phentolamine or nitroprusside.[7] Blood pressure often drops gradually following sufficient sedation with a benzodiazepine and providing a calming environment.[7]
Antipsychotics such as haloperidol are useful in treating agitation and psychosis from methamphetamine overdose.[54][55] Beta blockers with lipophilic properties and CNS penetration such as metoprolol and labetalol may be useful for treating CNS and cardiovascular toxicity.[56] The mixed alpha- and beta-blocker labetalol is especially useful for treatment of concomitant tachycardia and hypertension induced by methamphetamine.[54] The phenomenon of "unopposed alpha stimulation" has not been reported with the use of beta-blockers for treatment of methamphetamine toxicity.[54]
Addiction
| Addiction and dependence glossary[57][58][59][60] |
|---|
| • addiction – a brain disorder characterized by compulsive engagement in rewarding stimuli despite adverse consequences |
| • addictive behavior – a behavior that is both rewarding and reinforcing |
| • addictive drug – a drug that is both rewarding and reinforcing |
| • dependence – an adaptive state associated with a withdrawal syndrome upon cessation of repeated exposure to a stimulus (e.g., drug intake) |
| • drug sensitization or reverse tolerance – the escalating effect of a drug resulting from repeated administration at a given dose |
| • drug withdrawal – symptoms that occur upon cessation of repeated drug use |
| • physical dependence – dependence that involves persistent physical–somatic withdrawal symptoms (e.g., fatigue and delirium tremens) |
| • psychological dependence – dependence that involves emotional–motivational withdrawal symptoms (e.g., dysphoria and anhedonia) |
| • reinforcing stimuli – stimuli that increase the probability of repeating behaviors paired with them |
| • rewarding stimuli – stimuli that the brain interprets as intrinsically positive or as something to be approached |
| • sensitization – an amplified response to a stimulus resulting from repeated exposure to it |
| • substance use disorder - a condition in which the use of substances leads to clinically and functionally significant impairment or distress |
| • tolerance – the diminishing effect of a drug resulting from repeated administration at a given dose |
| (edit | history) |
Current models of addiction from chronic drug use involve alterations in gene expression in certain parts of the brain, particularly the nucleus accumbens.[68][69] The most important transcription factors[note 4] that produce these alterations are ΔFosB, cAMP response element binding protein (CREB), and nuclear factor kappa B (NFκB).[69] ΔFosB plays a crucial role in the development of drug addictions, since its overexpression in D1-type medium spiny neurons in the nucleus accumbens is necessary and sufficient[note 5] for most of the behavioral and neural adaptations that arise from addiction.[69][71][58] Once ΔFosB is sufficiently overexpressed, it induces an addictive state that becomes increasingly more severe with further increases in ΔFosB expression.[71][58] It has been implicated in addictions to alcohol, cannabinoids, cocaine, methylphenidate, nicotine, opioids, phencyclidine, propofol, and substituted amphetamines, among others.[71][69][72][73][74]
ΔJunD, a transcription factor, and G9a, a histone methyltransferase enzyme, both directly oppose the induction of ΔFosB in the nucleus accumbens (i.e., they oppose increases in its expression).[69][58][75] Sufficiently overexpressing ΔJunD in the nucleus accumbens with viral vectors can completely block many of the neural and behavioral alterations seen in chronic drug abuse (i.e., the alterations mediated by ΔFosB).[69] ΔFosB also plays an important role in regulating behavioral responses to natural rewards, such as palatable food, sex, and exercise.[69][72][76] Since both natural rewards and addictive drugs induce expression of ΔFosB (i.e., they cause the brain to produce more of it), chronic acquisition of these rewards can result in a similar pathological state of addiction.[72][69] ΔFosB is the most significant factor involved in both amphetamine addiction and amphetamine-induced sex addictions, which are compulsive sexual behaviors that result from excessive sexual activity and amphetamine use.[note 6][72][77] These sex addictions (i.e., drug-induced compulsive sexual behaviors) are associated with a dopamine dysregulation syndrome which occurs in some patients taking dopaminergic drugs, such as amphetamine or methamphetamine.[72][76][77]
Treatment and management
Cognitive behavioral therapy is currently the most effective clinical treatment for psychostimulant addictions in general.[78] As of May 2014[update], there is no effective pharmacotherapy for methamphetamine addiction.[79][80][81] Methamphetamine addiction is largely mediated through increased activation of dopamine receptors and co-localized NMDA receptors[note 7] in the nucleus accumbens.[63][64] Magnesium ions inhibit NMDA receptors by blocking the receptor calcium channel.[82][83]
Dependence and withdrawal
Tolerance is expected to develop with regular methamphetamine use and, when used recreationally, this tolerance develops rapidly.[84][85] In dependent users, withdrawal symptoms are positively correlated with the level of drug tolerance.[86] Depression from methamphetamine withdrawal lasts longer and is more severe than that of cocaine withdrawal.[28]
According to the current Cochrane review on drug dependence and withdrawal in recreational users of methamphetamine, "when chronic heavy users abruptly discontinue [methamphetamine] use, many report a time-limited withdrawal syndrome that occurs within 24 hours of their last dose".[86] Withdrawal symptoms in chronic, high-dose users are frequent, occurring in up to 87.6% of cases, and persist for three to four weeks with a marked "crash" phase occurring during the first week.[86] Methamphetamine withdrawal symptoms can include anxiety, drug craving, dysphoric mood, fatigue, increased appetite, increased movement or decreased movement, lack of motivation, sleeplessness or sleepiness, and vivid or lucid dreams.[86]
| Form of neuroplasticity or behavioral plasticity |
Type of reinforcer | Sources | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opiates | Psychostimulants | High fat or sugar food | Sexual intercourse | Physical exercise (aerobic) |
Environmental enrichment |
||
| ΔFosB expression in nucleus accumbens D1-type MSNs |
↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | [72] |
| Behavioral plasticity | |||||||
| Escalation of intake | Yes | Yes | Yes | [72] | |||
| Psychostimulant cross-sensitization |
Yes | Not applicable | Yes | Yes | Attenuated | Attenuated | [72] |
| Psychostimulant self-administration |
↑ | ↑ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | [72] | |
| Psychostimulant conditioned place preference |
↑ | ↑ | ↓ | ↑ | ↓ | ↑ | [72] |
| Reinstatement of drug-seeking behavior | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | ↓ | [72] | ||
| Neurochemical plasticity | |||||||
| CREB phosphorylation in the nucleus accumbens |
↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | [72] | |
| Sensitized dopamine response in the nucleus accumbens |
No | Yes | No | Yes | [72] | ||
| Altered striatal dopamine signaling | ↓DRD2, ↑DRD3 | ↑DRD1, ↓DRD2, ↑DRD3 | ↑DRD1, ↓DRD2, ↑DRD3 | ↑DRD2 | ↑DRD2 | [72] | |
| Altered striatal opioid signaling | No change or ↑μ-opioid receptors |
↑μ-opioid receptors ↑κ-opioid receptors |
↑μ-opioid receptors | ↑μ-opioid receptors | No change | No change | [72] |
| Changes in striatal opioid peptides | ↑dynorphin No change: enkephalin |
↑dynorphin | ↓enkephalin | ↑dynorphin | ↑dynorphin | [72] | |
| Mesocorticolimbic synaptic plasticity | |||||||
| Number of dendrites in the nucleus accumbens | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ | [72] | |||
| Dendritic spine density in the nucleus accumbens |
↓ | ↑ | ↑ | [72] | |||
Interactions
Methamphetamine is metabolized by the liver enzyme CYP2D6, so CYP2D6 inhibitors will prolong the elimination half-life of methamphetamine.[87] Methamphetamine also interacts with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), since both MAOIs and methamphetamine increase plasma catecholamines; therefore, concurrent use of both is dangerous.[21] Methamphetamine may decrease the effects of sedatives and depressants and increase the effects of antidepressants and other stimulants as well.[21] Methamphetamine may counteract the effects of antihypertensives and antipsychotics due to its effects on the cardiovascular system and cognition respectively.[21] The pH of gastrointestinal content and urine affects the absorption and excretion of methamphetamine.[21] Specifically, acidic substances will reduce the absorption of methamphetamine and increase urinary excretion, while alkaline substances do the opposite.[21] Due to the effect pH has on absorption, proton pump inhibitors, which reduce gastric acid, are known to interact with methamphetamine.[21]
Pharmacology

Pharmacodynamics
Methamphetamine has been identified as a potent full agonist of trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1), a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that regulates brain catecholamine systems.[88][89] Activation of TAAR1 increases cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) production and either completely inhibits or reverses the transport direction of the dopamine transporter (DAT), norepinephrine transporter (NET), and serotonin transporter (SERT).[88][90] When methamphetamine binds to TAAR1, it triggers transporter phosphorylation via protein kinase A (PKA) and protein kinase C (PKC) signaling, ultimately resulting in the internalization or reverse function of monoamine transporters.[88][91] Methamphetamine is also known to increase intracellular calcium, an effect which is associated with DAT phosphorylation through a Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (CAMK)-dependent signaling pathway, in turn producing dopamine efflux.[92][93][94] TAAR1 also has been shown to reduce the firing rate of neurons through direct activation of G protein-coupled inwardly-rectifying potassium channels.[95][96][97] TAAR1 activation by methamphetamine in astrocytes appears to negatively modulate the membrane expression and function of EAAT2, a type of glutamate transporter.[46]
In addition to the plasma membrane monoamine transporters, methamphetamine inhibits uptake and induces efflux of neurotransmitters and other substrates at the vesicular monoamine transporters, VMAT1 and VMAT2.[98] In neurons, methamphetamine induces monoamine neurotransmitter efflux through VMAT2, resulting in the outflow of monoamines from synaptic vesicles into the cytosol (intracellular fluid) of the presynaptic neuron.[99] Other transporters that methamphetamine is known to inhibit are SLC22A3 and SLC22A5.[98] SLC22A3 is an extraneuronal monoamine transporter that is present in astrocytes, and SLC22A5 is a high-affinity carnitine transporter.[89][100]
Methamphetamine is also an agonist of the alpha-2 adrenergic receptors and sigma receptors with a greater affinity for σ1 than σ2, and inhibits monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B).[39][89][47] Sigma receptor activation by methamphetamine appears facilitate its central nervous system stimulant effects and promote neurotoxicity within the brain.[39][47] Methamphetamine is known to inhibit the CYP2D6 liver enzyme as well.[87] Dextromethamphetamine is a stronger psychostimulant (approximately ten times on striatal dopamine), but levomethamphetamine has stronger peripheral effects, a longer half-life, and longer perceived effects among addicts.[101][102][103] At high doses, both enantiomers of methamphetamine can induce similar stereotypy and methamphetamine psychosis,[102] but shorter psychodynamic effect for levomethamphetamine.[103]
Pharmacokinetics
Following oral administration, methamphetamine is well-absorbed into the bloodstream, with peak plasma methamphetamine concentrations achieved in approximately 3.13–6.3 hours post ingestion.[104] Methamphetamine is also well absorbed following inhalation and following intranasal administration.[7] Due to the high lipophilicity of methamphetamine, it can readily move through the blood–brain barrier faster than other stimulants, where it is more resistant to degradation by monoamine oxidase.[7][104] The amphetamine metabolite peaks at 10–24 hours.[7] It is excreted by the kidneys, with the rate of excretion into the urine heavily influenced by urinary pH.[21][104] When taken orally, 30–54% of the dose is excreted in urine as methamphetamine and 10–23% as amphetamine.[104] Following IV doses, about 45% is excreted as methamphetamine and 7% as amphetamine.[104] The half-life of methamphetamine is variable with a range of 5–30 hours.[7][104]
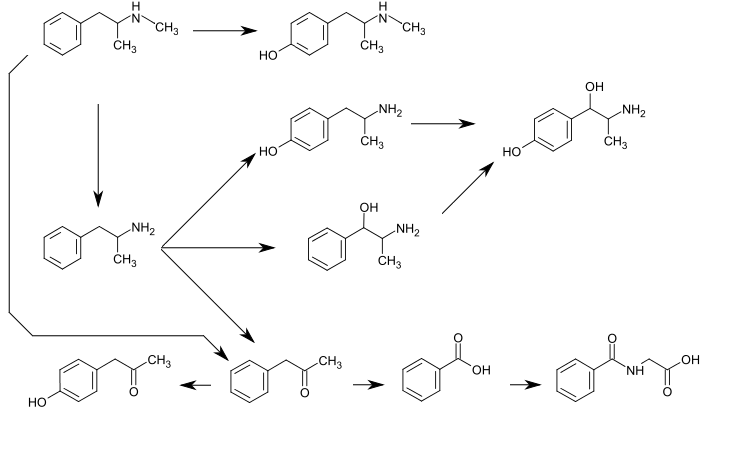
CYP2D6, dopamine β-hydroxylase, flavin-containing monooxygenase 3, butyrate-CoA ligase, and glycine N-acyltransferase are the enzymes known to metabolize methamphetamine or its metabolites in humans.[5][105][106][107][108] The primary metabolites are amphetamine and 4-hydroxymethamphetamine; other minor metabolites include: 4-hydroxyamphetamine, 4-hydroxynorephedrine, 4-hydroxyphenylacetone, benzoic acid, hippuric acid, norephedrine, and phenylacetone, the metabolites of amphetamine.[4][104][109][110] Among these metabolites, the active sympathomimetics are amphetamine, 4‑hydroxyamphetamine,[111] 4‑hydroxynorephedrine,[112] 4-hydroxymethamphetamine,[104] and norephedrine.[113]
The main metabolic pathways involve aromatic para-hydroxylation, aliphatic alpha- and beta-hydroxylation, N-oxidation, N-dealkylation, and deamination.[4][104][109] The known metabolic pathways include:[4][104][110]
Detection in biological fluids
Methamphetamine and amphetamine are often measured in urine or blood as part of a drug test for sports, employment, poisoning diagnostics, and forensics.[116][117][118][119] Chiral techniques may be employed to help distinguish the source the drug to determine whether it was obtained illicitly or legally via prescription or prodrug.[120] Chiral separation is needed to assess the possible contribution of levomethamphetamine, which is an active ingredients in some OTC nasal decongestants,[note 3] toward a positive test result.[120][121][122] Dietary zinc supplements can mask the presence of methamphetamine and other drugs in urine.[123]
Chemistry
Methamphetamine is a chiral compound with two enantiomers, dextromethamphetamine and levomethamphetamine. At room temperature, the free base of methamphetamine is a clear and colorless liquid with an odor characteristic of geranium leaves.[9] It is soluble in diethyl ether and ethanol as well as miscible with chloroform.[9] In contrast, the methamphetamine hydrochloride salt is odorless with a bitter taste.[9] It has a melting point between 170 to 175 °C (338 to 347 °F) and, at room temperature, occurs as white crystals or a white crystalline powder.[9] The hydrochloride salt is also freely soluble in ethanol and water.[9]
Degradation
Bleach exposure time and concentration are correlated with destruction of methamphetamine.[124] Methamphetamine in soils has shown to be a persistent pollutant.[125] Methamphetamine is largely degraded within 30 days in a study of bioreactors under exposure to light in wastewater.[126]
Synthesis
Racemic methamphetamine may be prepared starting from phenylacetone by either the Leuckart[127] or reductive amination methods.[128] In the Leuckart reaction, one equivalent of phenylacetone is reacted with two equivalents of N-methylformamide to produce the formyl amide of methamphetamine plus carbon dioxide and methylamine as side products.[128] In this reaction, an iminium cation is formed as an intermediate which is reduced by the second equivalent of N-methylformamide.[128] The intermediate formyl amide is then hydrolyzed under acidic aqueous conditions to yield methamphetamine as the final product.[128] Alternatively, phenylacetone can be reacted with methylamine under reducing conditions to yield methamphetamine.[128]
History, society, and culture

Amphetamine, discovered before methamphetamine, was first synthesized in 1887 in Germany by Romanian chemist Lazăr Edeleanu who named it phenylisopropylamine.[129][130] Shortly after, methamphetamine was synthesized from ephedrine in 1893 by Japanese chemist Nagai Nagayoshi.[131] Three decades later, in 1919, methamphetamine hydrochloride was synthesized by pharmacologist Akira Ogata via reduction of ephedrine using red phosphorus and iodine.[132]
During World War II, methamphetamine was sold in tablet form under the brand name Pervitin, produced by the Berlin-based Temmler pharmaceutical company. It was used extensively by all branches of the combined Wehrmacht armed forces of the Third Reich, and was popular with Luftwaffe pilots in particular, for its performance-enhancing stimulant effects and to induce extended wakefulness.[133][134] Pervitin became colloquially known among the German troops as "Stuka-Tablets" (Stuka-Tabletten) and "Herman-Göring-Pills" (Hermann-Göring-Pillen). Side effects were so serious that the army sharply cut back its usage in 1940[citation needed]. Historian Lukasz Kamienski says "A soldier going to battle on Pervitin usually found himself unable to perform effectively for the next day or two. Suffering from a drug hangover and looking more like a zombie than a great warrior, he had to recover from the side effects." Some soldiers turned very violent, committing war crimes against civilians; others attacked their own officers.[135]
Obetrol, patented by Obetrol Pharmaceuticals in the 1950s and indicated for treatment of obesity, was one of the first brands of pharmaceutical methamphetamine products.[136] Due to the psychological and stimulant effects of methamphetamine, Obetrol became a popular diet pill in America in the 1950s and 1960s.[136] Eventually, as the addictive properties of the drug became known, governments began to strictly regulate the production and distribution of methamphetamine.[130] For example, during the early 1970s in the United States, methamphetamine became a schedule II controlled substance under the Controlled Substances Act.[137] Currently, methamphetamine is sold under the trade name Desoxyn, trademarked by the Danish pharmaceutical company Lundbeck.[138] As of January 2013, the Desoxyn trademark had been sold to Italian pharmaceutical company Recordati.[139]
Legal status
The production, distribution, sale, and possession of methamphetamine is restricted or illegal in many jurisdictions.[140][141] Methamphetamine has been placed in schedule II of the United Nations Convention on Psychotropic Substances treaty.[141]
Australia
Methamphetamine is a Schedule 8 prohibited substance in Australia under the Poisons Standard (July 2016).[142] A schedule 8 substance is a controlled drug – substances which should be available for use but require restriction of manufacture, supply, distribution, possession and use to reduce abuse, misuse and physical or psychological dependence.[142]
In Western Australia under the Misuse of Drugs Act 1981 4.0 g of methamphetamine is the amount of prohibited drugs determining a court of trial, 2.0 g is the amount required for the presumption of intention to sell or supply and 28.0 g is the amount required for purposes of drug trafficking.[143]
Research
It has been suggested, based on animal research, that Calcitriol, the active metabolite of vitamin D, can provide significant protection against the DA- and 5-HT-depleting effects of neurotoxic doses of methamphetamine.[144]
See also
- Breaking Bad, a TV series centered around illicit methamphetamine synthesis
- Faces of Meth, a drug prevention project
- Methamphetamine in the United States
- Montana Meth Project
- Rolling meth lab
- Ya ba
Notes
- ^ Synonyms and alternate spellings include: metamfetamine (International Nonproprietary Name (INN)), N-methylamphetamine, desoxyephedrine, Syndrox, Methedrine, and Desoxyn.[10][11][12] Common slang terms for methamphetamine include: speed, meth, crystal, crystal meth, glass, shards, ice, and tic[13] and, in New Zealand, "P".[14]
- ^ Enantiomers are molecules that are mirror images of one another; they are structurally identical, but of the opposite orientation.
- ^ a b c The active ingredient in some OTC inhalers in the United States is listed as levmetamfetamine, the INN and USAN of levomethamphetamine.[15][16]
- ^ Transcription factors are proteins that increase or decrease the expression of specific genes.[70]
- ^ In simpler terms, this necessary and sufficient relationship means that ΔFosB overexpression in the nucleus accumbens and addiction-related behavioral and neural adaptations always occur together and never occur alone.
- ^ The associated research only involved amphetamine, not methamphetamine; however, this statement is included here due to the similarity between the pharmacodynamics and aphrodisiac effects of amphetamine and methamphetamine.
- ^ NMDA receptors are voltage-dependent ligand-gated ion channels that requires simultaneous binding of glutamate and a co-agonist (D-serine or glycine) to open the ion channel.[82]
- Image legend
- ^
(Text color) Transcription factors
Reference notes
References
- ^ United States Congress Senate Committee on the Judiciary Subcommittee to Investigate Juvenile Delinquincy (1 January 1972). Amphetamine legislation 1971: Hearings, Ninety-second Congress, first session, pursuant to S. Res. 32, section 12, investigation of juvenile delinquency in the United States (PDF). U.S. Govt. Print. Off. p. 161. Retrieved 1 January 2016.
We made a decision in January of 1969 to cease the manufacture of injectable methamphetamines.
- ^ a b Rau T, Ziemniak J, Poulsen D (2015). "The neuroprotective potential of low-dose methamphetamine in preclinical models of stroke and traumatic brain injury". Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry. 64: 231–6. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2015.02.013. PMID 25724762.
In humans, the oral bioavailability of methamphetamine is approximately 70% but increases to 100% following intravenous (IV) delivery (Ares-Santos et al., 2013).
- ^ "Toxicity". Methamphetamine. PubChem Compound. National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved 31 December 2013.
- ^ a b c d "Adderall XR Prescribing Information" (PDF). United States Food and Drug Administration. December 2013. pp. 12–13. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
- ^ a b Krueger SK, Williams DE (June 2005). "Mammalian flavin-containing monooxygenases: structure/function, genetic polymorphisms and role in drug metabolism". Pharmacol. Ther. 106 (3): 357–387. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2005.01.001. PMC 1828602
 . PMID 15922018.
. PMID 15922018. - ^ a b Riviello, Ralph J. (2010). Manual of forensic emergency medicine : a guide for clinicians. Sudbury, Mass.: Jones and Bartlett Publishers. p. 41. ISBN 9780763744625.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Schep LJ, Slaughter RJ, Beasley DM (August 2010). "The clinical toxicology of metamfetamine". Clinical Toxicology (Philadelphia, Pa.). 48 (7): 675–694. doi:10.3109/15563650.2010.516752. ISSN 1556-3650. PMID 20849327.
- ^ "Properties: Predicted – EP|Suite". Methmphetamine. Chemspider. Retrieved 3 January 2013.
- ^ a b c d e f "Chemical and Physical Properties". Methamphetamine. PubChem Compound. National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved 31 December 2013.
- ^ "Methamphetamine". Drug profiles. European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA). 16 August 2010. Retrieved 1 September 2011.
- ^ "Identification". Methamphetamine. DrugBank. University of Alberta. 8 February 2013. Retrieved 31 December 2013.
- ^ "Methedrine (methamphetamine hydrochloride): Uses, Symptoms, Signs and Addiction Treatment". Addictionlibrary.org. Retrieved 16 January 2016.
- ^ "Meth Slang Names". MethhelpOnline. Retrieved 1 January 2014.
- ^ "Methamphetamine and the law".
- ^ "Part 341 – cold, cough, allergy, bronchodilator, and antiasthmatic drug products for over-the-counter human use". Code of Federal Regulations Title 21: Subchapter D – Drugs for human use. United States Food and Drug Administration. April 2015. Retrieved 7 March 2016.
Topical nasal decongestants --(i) For products containing levmetamfetamine identified in 341.20(b)(1) when used in an inhalant dosage form. The product delivers in each 800 milliliters of air 0.04 to 0.150 milligrams of levmetamfetamine.
- ^ "Identification". Levomethamphetamine. Pubchem Compound. National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved 2 January 2014.
- ^ a b c d e f San Francisco Meth Zombies (TV documentary). National Geographic Channel. August 2013. ASIN B00EHAOBAO.
- ^ a b c Malenka RC, Nestler EJ, Hyman SE (2009). "15". In Sydor A, Brown RY. Molecular Neuropharmacology: A Foundation for Clinical Neuroscience (2nd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. p. 370. ISBN 978-0-07-148127-4.
Unlike cocaine and amphetamine, methamphetamine is directly toxic to midbrain dopamine neurons.
- ^ a b Yu S, Zhu L, Shen Q, Bai X, Di X (2015). "Recent advances in methamphetamine neurotoxicity mechanisms and its molecular pathophysiology". Behav Neurol. 2015: 103969. doi:10.1155/2015/103969. PMC 4377385
 . PMID 25861156.
. PMID 25861156. - ^ a b c d e f g h Krasnova IN, Cadet JL (May 2009). "Methamphetamine toxicity and messengers of death". Brain Res. Rev. 60 (2): 379–407. doi:10.1016/j.brainresrev.2009.03.002. PMC 2731235
 . PMID 19328213.
. PMID 19328213. Neuroimaging studies have revealed that METH can indeed cause neurodegenerative changes in the brains of human addicts (Aron and Paulus, 2007; Chang et al., 2007). These abnormalities include persistent decreases in the levels of dopamine transporters (DAT) in the orbitofrontal cortex, dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, and the caudate-putamen (McCann et al., 1998, 2008; Sekine et al., 2003; Volkow et al., 2001a, 2001c). The density of serotonin transporters (5-HTT) is also decreased in the midbrain, caudate, putamen, hypothalamus, thalamus, the orbitofrontal, temporal, and cingulate cortices of METH-dependent individuals (Sekine et al., 2006) ...
Neuropsychological studies have detected deficits in attention, working memory, and decision-making in chronic METH addicts ...
There is compelling evidence that the negative neuropsychiatric consequences of METH abuse are due, at least in part, to drug-induced neuropathological changes in the brains of these METH-exposed individuals ...
Structural magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) studies in METH addicts have revealed substantial morphological changes in their brains. These include loss of gray matter in the cingulate, limbic and paralimbic cortices, significant shrinkage of hippocampi, and hypertrophy of white matter (Thompson et al., 2004). In addition, the brains of METH abusers show evidence of hyperintensities in white matter (Bae et al., 2006; Ernst et al., 2000), decreases in the neuronal marker, N-acetylaspartate (Ernst et al., 2000; Sung et al., 2007), reductions in a marker of metabolic integrity, creatine (Sekine et al., 2002) and increases in a marker of glial activation, myoinositol (Chang et al., 2002; Ernst et al., 2000; Sung et al., 2007; Yen et al., 1994). Elevated choline levels, which are indicative of increased cellular membrane synthesis and turnover are also evident in the frontal gray matter of METH abusers (Ernst et al., 2000; Salo et al., 2007; Taylor et al., 2007). - ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w "Desoxyn Prescribing Information" (PDF). United States Food and Drug Administration. December 2013. Retrieved 6 January 2014.
- ^ Hart, Carl; Marvin, Caroline; Silver, Rae; Smith, Edward (16 November 2011). "Is Cognitive Functioning Impaired in Methamphetamine Users? A Critical Review". Neuropsychopharmacology. 37: 586–608. doi:10.1038/npp.2011.276. PMC 3260986
 . PMID 22089317. Retrieved 6 March 2015.
. PMID 22089317. Retrieved 6 March 2015. - ^ Mitler MM, Hajdukovic R, Erman MK (1993). "Treatment of narcolepsy with methamphetamine". Sleep. 16 (4): 306–317. PMC 2267865
 . PMID 8341891.
. PMID 8341891. - ^ Morgenthaler TI, Kapur VK, Brown T, Swick TJ, Alessi C, Aurora RN, Boehlecke B, Chesson AL Jr, Friedman L, Maganti R, Owens J, Pancer J, Zak R, Standards of Practice Committee of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine (2007). "Practice parameters for the treatment of narcolepsy and other hypersomnias of central origin". Sleep. 30: 1705–11. PMC 2276123
 . PMID 18246980.
. PMID 18246980. - ^ Nelson, Lewis S.; Lewin, Neal A.; Howland, Mary Ann; Hoffman, Robert S.; Goldfrank, Lewis R.; Flomenbaum, Neal E. (2011). Goldfrank's toxicologic emergencies (9th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. p. 1080. ISBN 978-0071605939.
- ^ a b c d Westfall DP, Westfall TC (2010). "Miscellaneous Sympathomimetic Agonists". In Brunton LL, Chabner BA, Knollmann BC. Goodman & Gilman's Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics (12th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-162442-8.
- ^ a b c Chomchai C, Na Manorom N, Watanarungsan P, Yossuck P, Chomchai S (2004). "Methamphetamine abuse during pregnancy and its health impact on neonates born at Siriraj Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand". The Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health. 35 (1): 228–31. PMID 15272773.
- ^ a b Winslow BT, Voorhees KI, Pehl KA (2007). "Methamphetamine abuse". American Family Physician. 76 (8): 1169–1174. PMID 17990840.
- ^ a b c Hussain F, Frare RW, Py Berrios KL (2012). "Drug abuse identification and pain management in dental patients: a case study and literature review". Gen. Dent. 60 (4): 334–345. PMID 22782046.
- ^ "Methamphetamine Use (Meth Mouth)". American Dental Association. Archived from the original on June 2008. Retrieved December 2006. Check date values in:
|access-date=(help) - ^ Hart CL, Marvin CB, Silver R, Smith EE (February 2012). "Is cognitive functioning impaired in methamphetamine users? A critical review". Neuropsychopharmacology. 37 (3): 586–608. doi:10.1038/npp.2011.276. PMC 3260986
 . PMID 22089317.
. PMID 22089317. - ^ a b Halkitis PN, Pandey Mukherjee P, Palamar JJ (2008). "Longitudinal Modeling of Methamphetamine Use and Sexual Risk Behaviors in Gay and Bisexual Men". AIDS and Behavior. 13 (4): 783–791. doi:10.1007/s10461-008-9432-y. PMID 18661225.
- ^ a b Patrick Moore (June 2005). "We Are Not OK". VillageVoice. Retrieved January 2011. Check date values in:
|access-date=(help) - ^ a b "Methamphetamine Use and Health | UNSW: The University of New South Wales – Faculty of Medicine" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on August 2008. Retrieved January 2011. Check date values in:
|access-date=(help) - ^ a b O'Connor PG (February 2012). "Amphetamines". Merck Manual for Health Care Professionals. Merck. Retrieved 8 May 2012.
- ^ Darke S, Kaye S, McKetin R, Duflou J (May 2008). "Major physical and psychological harms of methamphetamine use". Drug Alcohol Rev. 27 (3): 253–262. doi:10.1080/09595230801923702. PMID 18368606.
- ^ a b Beardsley PM, Hauser KF (2014). "Glial modulators as potential treatments of psychostimulant abuse". Adv. Pharmacol. 69: 1–69. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-420118-7.00001-9. PMC 4103010
 . PMID 24484974.
. PMID 24484974. Glia (including astrocytes, microglia, and oligodendrocytes), which constitute the majority of cells in the brain, have many of the same receptors as neurons, secrete neurotransmitters and neurotrophic and neuroinflammatory factors, control clearance of neurotransmitters from synaptic clefts, and are intimately involved in synaptic plasticity. Despite their prevalence and spectrum of functions, appreciation of their potential general importance has been elusive since their identification in the mid-1800s, and only relatively recently have they been gaining their due respect. This development of appreciation has been nurtured by the growing awareness that drugs of abuse, including the psychostimulants, affect glial activity, and glial activity, in turn, has been found to modulate the effects of the psychostimulants
- ^ Loftis JM, Janowsky A (2014). "Neuroimmune basis of methamphetamine toxicity". Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 118: 165–197. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-801284-0.00007-5. PMC 4418472
 . PMID 25175865.
. PMID 25175865. Collectively, these pathological processes contribute to neurotoxicity (e.g., increased BBB permeability, inflammation, neuronal degeneration, cell death) and neuropsychiatric impairments (e.g., cognitive deficits, mood disorders)
"Figure 7.1: Neuroimmune mechanisms of methamphetamine-induced CNS toxicity" - ^ a b c d e Kaushal N, Matsumoto RR (March 2011). "Role of sigma receptors in methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity". Curr Neuropharmacol. 9 (1): 54–57. doi:10.2174/157015911795016930. PMC 3137201
 . PMID 21886562.
. PMID 21886562. σ Receptors seem to play an important role in many of the effects of METH. They are present in the organs that mediate the actions of METH (e.g. brain, heart, lungs) [5]. In the brain, METH acts primarily on the dopaminergic system to cause acute locomotor stimulant, subchronic sensitized, and neurotoxic effects. σ Receptors are present on dopaminergic neurons and their activation stimulates dopamine synthesis and release [11-13]. σ-2 Receptors modulate DAT and the release of dopamine via protein kinase C (PKC) and Ca2+-calmodulin systems [14].
σ-1 Receptor antisense and antagonists have been shown to block the acute locomotor stimulant effects of METH [4]. Repeated administration or self administration of METH has been shown to upregulate σ-1 receptor protein and mRNA in various brain regions including the substantia nigra, frontal cortex, cerebellum, midbrain, and hippocampus [15, 16]. Additionally, σ receptor antagonists ... prevent the development of behavioral sensitization to METH [17, 18]. ...
σ Receptor agonists have been shown to facilitate dopamine release, through both σ-1 and σ-2 receptors [11-14]. - ^ Carvalho M, Carmo H, Costa VM, Capela JP, Pontes H, Remião F, Carvalho F, Bastos Mde L (August 2012). "Toxicity of amphetamines: an update". Arch. Toxicol. 86 (8): 1167–1231. doi:10.1007/s00204-012-0815-5. PMID 22392347.
- ^ a b Cruickshank CC, Dyer KR (July 2009). "A review of the clinical pharmacology of methamphetamine". Addiction. 104 (7): 1085–1099. doi:10.1111/j.1360-0443.2009.02564.x. PMID 19426289.
- ^ Thrash B, Thiruchelvan K, Ahuja M, Suppiramaniam V, Dhanasekaran M (2009). "Methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity: the road to Parkinson's disease" (PDF). Pharmacol Rep. 61 (6): 966–977. doi:10.1016/s1734-1140(09)70158-6. PMID 20081231.
- ^ Sulzer D, Zecca L (February 2000). "Intraneuronal dopamine-quinone synthesis: a review". Neurotox. Res. 1 (3): 181–195. doi:10.1007/BF03033289. PMID 12835101.
- ^ Miyazaki I, Asanuma M (June 2008). "Dopaminergic neuron-specific oxidative stress caused by dopamine itself". Acta Med. Okayama. 62 (3): 141–150. PMID 18596830.
- ^ Yuan J, Hatzidimitriou G, Suthar P, Mueller M, McCann U, Ricaurte G (March 2006). "Relationship between temperature, dopaminergic neurotoxicity, and plasma drug concentrations in methamphetamine-treated squirrel monkeys". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 316 (3): 1210–1218. doi:10.1124/jpet.105.096503. PMID 16293712.
- ^ a b c • Cisneros IE, Ghorpade A (October 2014). "Methamphetamine and HIV-1-induced neurotoxicity: role of trace amine associated receptor 1 cAMP signaling in astrocytes". Neuropharmacology. 85: 499–507. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.06.011. PMID 24950453.
TAAR1 overexpression significantly decreased EAAT-2 levels and glutamate clearance ... METH treatment activated TAAR1 leading to intracellular cAMP in human astrocytes and modulated glutamate clearance abilities. Furthermore, molecular alterations in astrocyte TAAR1 levels correspond to changes in astrocyte EAAT-2 levels and function.
• Jing L, Li JX (August 2015). "Trace amine-associated receptor 1: A promising target for the treatment of psychostimulant addiction". Eur. J. Pharmacol. 761: 345–352. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.06.019. PMID 26092759.TAAR1 is largely located in the intracellular compartments both in neurons (Miller, 2011), in glial cells (Cisneros and Ghorpade, 2014) and in peripheral tissues (Grandy, 2007)
- ^ a b c d Rodvelt KR, Miller DK (September 2010). "Could sigma receptor ligands be a treatment for methamphetamine addiction?". Curr Drug Abuse Rev. 3 (3): 156–162. doi:10.2174/1874473711003030156. PMID 21054260.
- ^ Albertson TE (2011). "Amphetamines". In Olson KR, Anderson IB, Benowitz NL, Blanc PD, Kearney TE, Kim-Katz SY, Wu AH. Poisoning & Drug Overdose (6th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. pp. 77–79. ISBN 978-0-07-166833-0.
- ^ Oskie SM, Rhee JW (11 February 2011). "Amphetamine Poisoning". Emergency Central. Unbound Medicine. Retrieved 11 June 2013.
- ^ Isbister GK, Buckley NA, Whyte IM (September 2007). "Serotonin toxicity: a practical approach to diagnosis and treatment" (PDF). Med. J. Aust. 187 (6): 361–365. PMID 17874986.
- ^ a b c Shoptaw SJ, Kao U, Ling W (2009). Shoptaw SJ, Ali R, eds. "Treatment for amphetamine psychosis". Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. (1): CD003026. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003026.pub3. PMID 19160215.
A minority of individuals who use amphetamines develop full-blown psychosis requiring care at emergency departments or psychiatric hospitals. In such cases, symptoms of amphetamine psychosis commonly include paranoid and persecutory delusions as well as auditory and visual hallucinations in the presence of extreme agitation. More common (about 18%) is for frequent amphetamine users to report psychotic symptoms that are sub-clinical and that do not require high-intensity intervention ...
About 5–15% of the users who develop an amphetamine psychosis fail to recover completely (Hofmann 1983) ...
Findings from one trial indicate use of antipsychotic medications effectively resolves symptoms of acute amphetamine psychosis. - ^ Hofmann FG (1983). A Handbook on Drug and Alcohol Abuse: The Biomedical Aspects (2nd ed.). New York: Oxford University Press. p. 329. ISBN 978-0-19-503057-0.
- ^ Berman SM, Kuczenski R, McCracken JT, London ED (February 2009). "Potential adverse effects of amphetamine treatment on brain and behavior: a review". Mol. Psychiatry. 14 (2): 123–142. doi:10.1038/mp.2008.90. PMC 2670101
 . PMID 18698321.
. PMID 18698321. - ^ a b c Richards JR, Albertson TE, Derlet RW, Lange RA, Olson KR, Horowitz BZ (May 2015). "Treatment of toxicity from amphetamines, related derivatives, and analogues: a systematic clinical review". Drug Alcohol Depend. 150: 1–13. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2015.01.040. PMID 25724076.
- ^ Richards JR, Derlet RW, Duncan DR (September 1997). "Methamphetamine toxicity: treatment with a benzodiazepine versus a butyrophenone". Eur. J. Emerg. Med. 4 (3): 130–135. doi:10.1097/00063110-199709000-00003. PMID 9426992.
- ^ Richards JR, Derlet RW, Albertson TE. "Treatment & Management". Methamphetamine Toxicity. Medscape. WebMD. Retrieved 20 April 2016.
- ^ Malenka RC, Nestler EJ, Hyman SE (2009). "Chapter 15: Reinforcement and Addictive Disorders". In Sydor A, Brown RY. Molecular Neuropharmacology: A Foundation for Clinical Neuroscience (2nd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. pp. 364–375. ISBN 9780071481274.
- ^ a b c d Nestler EJ (December 2013). "Cellular basis of memory for addiction". Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 15 (4): 431–443. PMC 3898681
 . PMID 24459410.
. PMID 24459410. DESPITE THE IMPORTANCE OF NUMEROUS PSYCHOSOCIAL FACTORS, AT ITS CORE, DRUG ADDICTION INVOLVES A BIOLOGICAL PROCESS: the ability of repeated exposure to a drug of abuse to induce changes in a vulnerable brain that drive the compulsive seeking and taking of drugs, and loss of control over drug use, that define a state of addiction. ... A large body of literature has demonstrated that such ΔFosB induction in D1-type [nucleus accumbens] neurons increases an animal's sensitivity to drug as well as natural rewards and promotes drug self-administration, presumably through a process of positive reinforcement ... Another ΔFosB target is cFos: as ΔFosB accumulates with repeated drug exposure it represses c-Fos and contributes to the molecular switch whereby ΔFosB is selectively induced in the chronic drug-treated state.41. ... Moreover, there is increasing evidence that, despite a range of genetic risks for addiction across the population, exposure to sufficiently high doses of a drug for long periods of time can transform someone who has relatively lower genetic loading into an addict.
- ^ "Glossary of Terms". Mount Sinai School of Medicine. Department of Neuroscience. Retrieved 9 February 2015.
- ^ Volkow ND, Koob GF, McLellan AT (January 2016). "Neurobiologic Advances from the Brain Disease Model of Addiction". N. Engl. J. Med. 374 (4): 363–371. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1511480. PMID 26816013.
- ^ a b c Renthal W, Nestler EJ (September 2009). "Chromatin regulation in drug addiction and depression". Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 11 (3): 257–268. PMC 2834246
 . PMID 19877494.
. PMID 19877494. [Psychostimulants] increase cAMP levels in striatum, which activates protein kinase A (PKA) and leads to phosphorylation of its targets. This includes the cAMP response element binding protein (CREB), the phosphorylation of which induces its association with the histone acetyltransferase, CREB binding protein (CBP) to acetylate histones and facilitate gene activation. This is known to occur on many genes including fosB and c-fos in response to psychostimulant exposure. ΔFosB is also upregulated by chronic psychostimulant treatments, and is known to activate certain genes (eg, cdk5) and repress others (eg, c-fos) where it recruits HDAC1 as a corepressor. ... Chronic exposure to psychostimulants increases glutamatergic [signaling] from the prefrontal cortex to the NAc. Glutamatergic signaling elevates Ca2+ levels in NAc postsynaptic elements where it activates CaMK (calcium/calmodulin protein kinases) signaling, which, in addition to phosphorylating CREB, also phosphorylates HDAC5.
Figure 2: Psychostimulant-induced signaling events - ^ Broussard JI (January 2012). "Co-transmission of dopamine and glutamate". J. Gen. Physiol. 139 (1): 93–96. doi:10.1085/jgp.201110659. PMC 3250102
 . PMID 22200950.
. PMID 22200950. - ^ a b Kanehisa Laboratories (10 October 2014). "Amphetamine – Homo sapiens (human)". KEGG Pathway. Retrieved 31 October 2014.
Most addictive drugs increase extracellular concentrations of dopamine (DA) in nucleus accumbens (NAc) and medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), projection areas of mesocorticolimbic DA neurons and key components of the "brain reward circuit". Amphetamine achieves this elevation in extracellular levels of DA by promoting efflux from synaptic terminals. ... Chronic exposure to amphetamine induces a unique transcription factor delta FosB, which plays an essential role in long-term adaptive changes in the brain.
- ^ a b Cadet JL, Brannock C, Jayanthi S, Krasnova IN (2015). "Transcriptional and epigenetic substrates of methamphetamine addiction and withdrawal: evidence from a long-access self-administration model in the rat". Mol. Neurobiol. 51 (2): 696–717. doi:10.1007/s12035-014-8776-8. PMC 4359351
 . PMID 24939695.
. PMID 24939695. Figure 1
- ^ a b c Robison AJ, Nestler EJ (November 2011). "Transcriptional and epigenetic mechanisms of addiction". Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 12 (11): 623–637. doi:10.1038/nrn3111. PMC 3272277
 . PMID 21989194.
. PMID 21989194. ΔFosB serves as one of the master control proteins governing this structural plasticity. ... ΔFosB also represses G9a expression, leading to reduced repressive histone methylation at the cdk5 gene. The net result is gene activation and increased CDK5 expression. ... In contrast, ΔFosB binds to the c-fos gene and recruits several co-repressors, including HDAC1 (histone deacetylase 1) and SIRT 1 (sirtuin 1). ... The net result is c-fos gene repression.
Figure 4: Epigenetic basis of drug regulation of gene expression - ^ a b c Nestler EJ (December 2012). "Transcriptional mechanisms of drug addiction". Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 10 (3): 136–143. doi:10.9758/cpn.2012.10.3.136. PMC 3569166
 . PMID 23430970.
. PMID 23430970. The 35-37 kD ΔFosB isoforms accumulate with chronic drug exposure due to their extraordinarily long half-lives. ... As a result of its stability, the ΔFosB protein persists in neurons for at least several weeks after cessation of drug exposure. ... ΔFosB overexpression in nucleus accumbens induces NFκB ... In contrast, the ability of ΔFosB to repress the c-Fos gene occurs in concert with the recruitment of a histone deacetylase and presumably several other repressive proteins such as a repressive histone methyltransferase
- ^ Nestler EJ (October 2008). "Review. Transcriptional mechanisms of addiction: role of DeltaFosB". Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond., B, Biol. Sci. 363 (1507): 3245–3255. doi:10.1098/rstb.2008.0067. PMC 2607320
 . PMID 18640924.
. PMID 18640924. Recent evidence has shown that ΔFosB also represses the c-fos gene that helps create the molecular switch—from the induction of several short-lived Fos family proteins after acute drug exposure to the predominant accumulation of ΔFosB after chronic drug exposure
- ^ Hyman SE, Malenka RC, Nestler EJ (July 2006). "Neural mechanisms of addiction: the role of reward-related learning and memory". Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 29: 565–598. doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro.29.051605.113009. PMID 16776597.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Robison AJ, Nestler EJ (November 2011). "Transcriptional and epigenetic mechanisms of addiction". Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 12 (11): 623–637. doi:10.1038/nrn3111. PMC 3272277
 . PMID 21989194.
. PMID 21989194. ΔFosB has been linked directly to several addiction-related behaviors ... Importantly, genetic or viral overexpression of ΔJunD, a dominant negative mutant of JunD which antagonizes ΔFosB- and other AP-1-mediated transcriptional activity, in the NAc or OFC blocks these key effects of drug exposure14,22–24. This indicates that ΔFosB is both necessary and sufficient for many of the changes wrought in the brain by chronic drug exposure. ΔFosB is also induced in D1-type NAc MSNs by chronic consumption of several natural rewards, including sucrose, high fat food, sex, wheel running, where it promotes that consumption14,26–30. This implicates ΔFosB in the regulation of natural rewards under normal conditions and perhaps during pathological addictive-like states.
- ^ Malenka RC, Nestler EJ, Hyman SE (2009). "Chapter 4: Signal Transduction in the Brain". In Sydor A, Brown RY. Molecular Neuropharmacology: A Foundation for Clinical Neuroscience (2nd ed.). New York, USA: McGraw-Hill Medical. p. 94. ISBN 9780071481274.
- ^ a b c Ruffle JK (November 2014). "Molecular neurobiology of addiction: what's all the (Δ)FosB about?". Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abuse. 40 (6): 428–437. doi:10.3109/00952990.2014.933840. PMID 25083822.
ΔFosB is an essential transcription factor implicated in the molecular and behavioral pathways of addiction following repeated drug exposure.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r Olsen CM (December 2011). "Natural rewards, neuroplasticity, and non-drug addictions". Neuropharmacology. 61 (7): 1109–1122. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.03.010. PMC 3139704
 . PMID 21459101.
. PMID 21459101. Similar to environmental enrichment, studies have found that exercise reduces self-administration and relapse to drugs of abuse (Cosgrove et al., 2002; Zlebnik et al., 2010). There is also some evidence that these preclinical findings translate to human populations, as exercise reduces withdrawal symptoms and relapse in abstinent smokers (Daniel et al., 2006; Prochaska et al., 2008), and one drug recovery program has seen success in participants that train for and compete in a marathon as part of the program (Butler, 2005). ... In humans, the role of dopamine signaling in incentive-sensitization processes has recently been highlighted by the observation of a dopamine dysregulation syndrome in some patients taking dopaminergic drugs. This syndrome is characterized by a medication-induced increase in (or compulsive) engagement in non-drug rewards such as gambling, shopping, or sex (Evans et al., 2006; Aiken, 2007; Lader, 2008).
- ^ Kanehisa Laboratories (29 October 2014). "Alcoholism – Homo sapiens (human)". KEGG Pathway. Retrieved 31 October 2014.
- ^ Kim Y, Teylan MA, Baron M, Sands A, Nairn AC, Greengard P (February 2009). "Methylphenidate-induced dendritic spine formation and DeltaFosB expression in nucleus accumbens". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106 (8): 2915–2920. doi:10.1073/pnas.0813179106. PMC 2650365
 . PMID 19202072.
. PMID 19202072. - ^ Nestler EJ (January 2014). "Epigenetic mechanisms of drug addiction". Neuropharmacology. 76 Pt B: 259–268. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.04.004. PMC 3766384
 . PMID 23643695.
. PMID 23643695. - ^ a b Blum K, Werner T, Carnes S, Carnes P, Bowirrat A, Giordano J, Oscar-Berman M, Gold M (March 2012). "Sex, drugs, and rock 'n' roll: hypothesizing common mesolimbic activation as a function of reward gene polymorphisms". J. Psychoactive Drugs. 44 (1): 38–55. doi:10.1080/02791072.2012.662112. PMC 4040958
 . PMID 22641964.
. PMID 22641964. It has been found that deltaFosB gene in the NAc is critical for reinforcing effects of sexual reward. Pitchers and colleagues (2010) reported that sexual experience was shown to cause DeltaFosB accumulation in several limbic brain regions including the NAc, medial pre-frontal cortex, VTA, caudate, and putamen, but not the medial preoptic nucleus. ... these findings support a critical role for DeltaFosB expression in the NAc in the reinforcing effects of sexual behavior and sexual experience-induced facilitation of sexual performance. ... both drug addiction and sexual addiction represent pathological forms of neuroplasticity along with the emergence of aberrant behaviors involving a cascade of neurochemical changes mainly in the brain's rewarding circuitry.
- ^ a b Pitchers KK, Vialou V, Nestler EJ, Laviolette SR, Lehman MN, Coolen LM (February 2013). "Natural and drug rewards act on common neural plasticity mechanisms with ΔFosB as a key mediator". J. Neurosci. 33 (8): 3434–3442. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4881-12.2013. PMC 3865508
 . PMID 23426671.
. PMID 23426671. Drugs of abuse induce neuroplasticity in the natural reward pathway, specifically the nucleus accumbens (NAc), thereby causing development and expression of addictive behavior. ... Together, these findings demonstrate that drugs of abuse and natural reward behaviors act on common molecular and cellular mechanisms of plasticity that control vulnerability to drug addiction, and that this increased vulnerability is mediated by ΔFosB and its downstream transcriptional targets. ... Sexual behavior is highly rewarding (Tenk et al., 2009), and sexual experience causes sensitized drug-related behaviors, including cross-sensitization to amphetamine (Amph)-induced locomotor activity (Bradley and Meisel, 2001; Pitchers et al., 2010a) and enhanced Amph reward (Pitchers et al., 2010a). Moreover, sexual experience induces neural plasticity in the NAc similar to that induced by psychostimulant exposure, including increased dendritic spine density (Meisel and Mullins, 2006; Pitchers et al., 2010a), altered glutamate receptor trafficking, and decreased synaptic strength in prefrontal cortex-responding NAc shell neurons (Pitchers et al., 2012). Finally, periods of abstinence from sexual experience were found to be critical for enhanced Amph reward, NAc spinogenesis (Pitchers et al., 2010a), and glutamate receptor trafficking (Pitchers et al., 2012). These findings suggest that natural and drug reward experiences share common mechanisms of neural plasticity
- ^ Malenka RC, Nestler EJ, Hyman SE (2009). "Chapter 15: Reinforcement and Addictive Disorders". In Sydor A, Brown RY. Molecular Neuropharmacology: A Foundation for Clinical Neuroscience (2nd ed.). New York, USA: McGraw-Hill Medical. p. 386. ISBN 9780071481274.
Currently, cognitive–behavioral therapies are the most successful treatment available for preventing the relapse of psychostimulant use.
- ^ Stoops WW, Rush CR (May 2014). "Combination pharmacotherapies for stimulant use disorder: a review of clinical findings and recommendations for future research". Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 7 (3): 363–374. doi:10.1586/17512433.2014.909283. PMID 24716825.
Despite concerted efforts to identify a pharmacotherapy for managing stimulant use disorders, no widely effective medications have been approved.
- ^ Perez-Mana C, Castells X, Torrens M, Capella D, Farre M (September 2013). "Efficacy of psychostimulant drugs for amphetamine abuse or dependence". Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 9: CD009695. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009695.pub2. PMID 23996457.
To date, no pharmacological treatment has been approved for [addiction], and psychotherapy remains the mainstay of treatment. ... Results of this review do not support the use of psychostimulant medications at the tested doses as a replacement therapy
- ^ Forray A, Sofuoglu M (February 2014). "Future pharmacological treatments for substance use disorders". Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 77 (2): 382–400. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.2012.04474.x. PMC 4014020
 . PMID 23039267.
. PMID 23039267. - ^ a b Malenka RC, Nestler EJ, Hyman SE (2009). "Chapter 5: Excitatory and Inhibitory Amino Acids". In Sydor A, Brown RY. Molecular Neuropharmacology: A Foundation for Clinical Neuroscience (2nd ed.). New York, USA: McGraw-Hill Medical. pp. 124–125. ISBN 9780071481274.
At membrane potentials more negative than approximately −50 mV, the Mg2+ in the extracellular fluid of the brain virtually abolishes ion flux through NMDA receptor channels, even in the presence of glutamate. ... The NMDA receptor is unique among all neurotransmitter receptors in that its activation requires the simultaneous binding of two different agonists. In addition to the binding of glutamate at the conventional agonist-binding site, the binding of glycine appears to be required for receptor activation. Because neither of these agonists alone can open this ion channel, glutamate and glycine are referred to as coagonists of the NMDA receptor. The physiologic significance of the glycine binding site is unclear because the normal extracellular concentration of glycine is believed to be saturating. However, recent evidence suggests that D-serine may be the endogenous agonist for this site.
- ^ Nechifor M (March 2008). "Magnesium in drug dependences". Magnes. Res. 21 (1): 5–15. PMID 18557129.
- ^ O'Connor, Patrick. "Amphetamines: Drug Use and Abuse". Merck Manual Home Health Handbook. Merck. Retrieved 26 September 2013.
- ^ Pérez-Mañá C, Castells X, Torrens M, Capellà D, Farre M (2013). Pérez-Mañá, Clara, ed. "Efficacy of psychostimulant drugs for amphetamine abuse or dependence". Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 9: CD009695. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009695.pub2. PMID 23996457.
- ^ a b c d Shoptaw SJ, Kao U, Heinzerling K, Ling W (2009). Shoptaw SJ, ed. "Treatment for amphetamine withdrawal". Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. (2): CD003021. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003021.pub2. PMID 19370579.
The prevalence of this withdrawal syndrome is extremely common (Cantwell 1998; Gossop 1982) with 87.6% of 647 individuals with amphetamine dependence reporting six or more signs of amphetamine withdrawal listed in the DSM when the drug is not available (Schuckit 1999) ... Withdrawal symptoms typically present within 24 hours of the last use of amphetamine, with a withdrawal syndrome involving two general phases that can last 3 weeks or more. The first phase of this syndrome is the initial "crash" that resolves within about a week (Gossop 1982;McGregor 2005)
- ^ a b "Enzymes". Methamphetamine. DrugBank. University of Alberta. 8 February 2013. Retrieved 31 December 2013.
- ^ a b c Miller GM (January 2011). "The emerging role of trace amine-associated receptor 1 in the functional regulation of monoamine transporters and dopaminergic activity". J. Neurochem. 116 (2): 164–176. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.07109.x. PMC 3005101
 . PMID 21073468.
. PMID 21073468. - ^ a b c "Targets". Methamphetamine. DrugBank. University of Alberta. 8 February 2013. Retrieved 31 December 2013.
- ^ Borowsky B, Adham N, Jones KA, Raddatz R, Artymyshyn R, Ogozalek KL, Durkin MM, Lakhlani PP, Bonini JA, Pathirana S, Boyle N, Pu X, Kouranova E, Lichtblau H, Ochoa FY, Branchek TA, Gerald C (July 2001). "Trace amines: identification of a family of mammalian G protein-coupled receptors". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98 (16): 8966–8971. doi:10.1073/pnas.151105198. PMC 55357
 . PMID 11459929.
. PMID 11459929. - ^ Xie Z, Miller GM (July 2009). "A receptor mechanism for methamphetamine action in dopamine transporter regulation in brain". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 330 (1): 316–325. doi:10.1124/jpet.109.153775. PMC 2700171
 . PMID 19364908.
. PMID 19364908. - ^ Maguire JJ, Davenport AP (2 December 2014). "TA1 receptor". IUPHAR database. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. Retrieved 8 December 2014.
- ^ Underhill SM, Wheeler DS, Li M, Watts SD, Ingram SL, Amara SG (July 2014). "Amphetamine modulates excitatory neurotransmission through endocytosis of the glutamate transporter EAAT3 in dopamine neurons". Neuron. 83 (2): 404–416. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2014.05.043. PMC 4159050
 . PMID 25033183.
. PMID 25033183. AMPH also increases intracellular calcium (Gnegy et al., 2004) that is associated with calmodulin/CamKII activation (Wei et al., 2007) and modulation and trafficking of the DAT (Fog et al., 2006; Sakrikar et al., 2012).
- ^ Vaughan RA, Foster JD (September 2013). "Mechanisms of dopamine transporter regulation in normal and disease states". Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 34 (9): 489–496. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2013.07.005. PMC 3831354
 . PMID 23968642.
. PMID 23968642. AMPH and METH also stimulate DA efflux, which is thought to be a crucial element in their addictive properties [80], although the mechanisms do not appear to be identical for each drug [81]. These processes are PKCβ– and CaMK–dependent [72, 82], and PKCβ knock-out mice display decreased AMPH-induced efflux that correlates with reduced AMPH-induced locomotion [72].
- ^ Ledonne A, Berretta N, Davoli A, Rizzo GR, Bernardi G, Mercuri NB (July 2011). "Electrophysiological effects of trace amines on mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons". Front. Syst. Neurosci. 5: 56. doi:10.3389/fnsys.2011.00056. PMC 3131148
 . PMID 21772817.
. PMID 21772817. inhibition of firing due to increased release of dopamine; (b) reduction of D2 and GABAB receptor-mediated inhibitory responses (excitatory effects due to disinhibition); and (c) a direct TA1 receptor-mediated activation of GIRK channels which produce cell membrane hyperpolarization.
- ^ mct (28 January 2012). "TAAR1". GenAtlas. University of Paris. Retrieved 29 May 2014.
• tonically activates inwardly rectifying K(+) channels, which reduces the basal firing frequency of dopamine (DA) neurons of the ventral tegmental area (VTA) - ^ Revel FG, Moreau JL, Gainetdinov RR, Bradaia A, Sotnikova TD, Mory R, Durkin S, Zbinden KG, Norcross R, Meyer CA, Metzler V, Chaboz S, Ozmen L, Trube G, Pouzet B, Bettler B, Caron MG, Wettstein JG, Hoener MC (May 2011). "TAAR1 activation modulates monoaminergic neurotransmission, preventing hyperdopaminergic and hypoglutamatergic activity". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108 (20): 8485–8490. doi:10.1073/pnas.1103029108. PMC 3101002
 . PMID 21525407.
. PMID 21525407. - ^ a b "Transporters". Methamphetamine. DrugBank. University of Alberta. 8 February 2013. Retrieved 31 December 2013.
- ^ Eiden LE, Weihe E (January 2011). "VMAT2: a dynamic regulator of brain monoaminergic neuronal function interacting with drugs of abuse". Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1216: 86–98. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05906.x. PMC 4183197
 . PMID 21272013.
. PMID 21272013. - ^ Inazu M, Takeda H, Matsumiya T (August 2003). "[The role of glial monoamine transporters in the central nervous system]". Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi (in Japanese). 23 (4): 171–178. PMID 13677912.
- ^ Melega WP, Cho AK, Schmitz D, Kuczenski R, Segal DS (February 1999). "l-methamphetamine pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics for assessment of in vivo deprenyl-derived l-methamphetamine". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 288 (2): 752–758. PMID 9918585.
- ^ a b Kuczenski R, Segal DS, Cho AK, Melega W (February 1995). "Hippocampus norepinephrine, caudate dopamine and serotonin, and behavioral responses to the stereoisomers of amphetamine and methamphetamine". J. Neurosci. 15 (2): 1308–1317. PMID 7869099.
- ^ a b Mendelson J, Uemura N, Harris D, Nath RP, Fernandez E, Jacob P, Everhart ET, Jones RT (October 2006). "Human pharmacology of the methamphetamine stereoisomers". Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 80 (4): 403–420. doi:10.1016/j.clpt.2006.06.013. PMID 17015058.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k "Pharmacology". Methamphetamine. DrugBank. University of Alberta. 8 February 2013. Retrieved 31 December 2013.
- ^ Lemke TL, Williams DA, Roche VF, Zito W (2013). Foye's Principles of Medicinal Chemistry (7th ed.). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 648. ISBN 1609133455.
Alternatively, direct oxidation of amphetamine by DA β-hydroxylase can afford norephedrine.
- ^ "Substrate/Product". butyrate-CoA ligase. BRENDA. Technische Universität Braunschweig. Retrieved 7 May 2014.
- ^ "Substrate/Product". glycine N-acyltransferase. BRENDA. Technische Universität Braunschweig. Retrieved 7 May 2014.
- ^ "Enzymes". Amphetamine. DrugBank. University of Alberta. 8 February 2013. Retrieved 30 September 2013.
- ^ a b "Amphetamine". Pubchem Compound. National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved 12 October 2013.
- ^ a b Santagati NA, Ferrara G, Marrazzo A, Ronsisvalle G (September 2002). "Simultaneous determination of amphetamine and one of its metabolites by HPLC with electrochemical detection". J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 30 (2): 247–255. doi:10.1016/S0731-7085(02)00330-8. PMID 12191709.
- ^ "Compound Summary". p-Hydroxyamphetamine. PubChem Compound. National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved 15 October 2013.
- ^ "Compound Summary". p-Hydroxynorephedrine. PubChem Compound. National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved 15 October 2013.
- ^ "Compound Summary". Phenylpropanolamine. PubChem Compound. National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved 15 October 2013.
- ^ Haiser HJ, Turnbaugh PJ (March 2013). "Developing a metagenomic view of xenobiotic metabolism". Pharmacol. Res. 69 (1): 21–31. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2012.07.009. PMC 3526672
 . PMID 22902524.
. PMID 22902524.
Table 2: Xenobiotics metabolized by the human gut microbiota - ^ Caldwell J, Hawksworth GM (May 1973). "The demethylation of methamphetamine by intestinal microflora". J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 25 (5): 422–424. doi:10.1111/j.2042-7158.1973.tb10043.x. PMID 4146404.
- ^ Liddle DG, Connor DJ (June 2013). "Nutritional supplements and ergogenic AIDS". Prim. Care. 40 (2): 487–505. doi:10.1016/j.pop.2013.02.009. PMID 23668655.
- ^ Kraemer T, Maurer HH (August 1998). "Determination of amphetamine, methamphetamine and amphetamine-derived designer drugs or medicaments in blood and urine". J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 713 (1): 163–187. doi:10.1016/S0378-4347(97)00515-X. PMID 9700558.
- ^ Kraemer T, Paul LD (August 2007). "Bioanalytical procedures for determination of drugs of abuse in blood". Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 388 (7): 1415–1435. doi:10.1007/s00216-007-1271-6. PMID 17468860.
- ^ Goldberger BA, Cone EJ (July 1994). "Confirmatory tests for drugs in the workplace by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry". J. Chromatogr. A. 674 (1–2): 73–86. doi:10.1016/0021-9673(94)85218-9. PMID 8075776.
- ^ a b Paul BD, Jemionek J, Lesser D, Jacobs A, Searles DA (September 2004). "Enantiomeric separation and quantitation of (+/-)-amphetamine, (+/-)-methamphetamine, (+/-)-MDA, (+/-)-MDMA, and (+/-)-MDEA in urine specimens by GC-EI-MS after derivatization with (R)-(−)- or (S)-(+)-alpha-methoxy-alpha-(trifluoromethy)phenylacetyl chloride (MTPA)". J Anal Toxicol. 28 (6): 449–455. doi:10.1093/jat/28.6.449. PMID 15516295.
- ^ de la Torre R, Farré M, Navarro M, Pacifici R, Zuccaro P, Pichini S (2004). "Clinical pharmacokinetics of amfetamine and related substances: monitoring in conventional and non-conventional matrices". Clin Pharmacokinet. 43 (3): 157–185. doi:10.2165/00003088-200443030-00002. PMID 14871155.
- ^ Baselt RC (2011). Disposition of toxic drugs and chemicals in man. Seal Beach, Ca.: Biomedical Publications. pp. 1027–1030. ISBN 0-9626523-8-5.
- ^ Venkatratnam A, Lents NH (July 2011). "Zinc reduces the detection of cocaine, methamphetamine, and THC by ELISA urine testing". J. Anal. Toxicol. 35 (6): 333–340. doi:10.1093/anatox/35.6.333. PMID 21740689.
- ^ Nakayama, MT. "Chemical Interaction of Bleach and Methamphetamine: A Study of Degradation and Transformation Effects". gradworks. UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, DAVIS. Retrieved 17 October 2014.
- ^ Pal R, Megharaj M, Kirkbride KP, Heinrich T, Naidu R (October 2011). "Biotic and abiotic degradation of illicit drugs, their precursor, and by-products in soil". Chemosphere. 85 (6): 1002–9. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.06.102. PMID 21777940.
- ^ Bagnall J, Malia L, Lubben A, Kasprzyk-Hordern B (October 2013). "Stereoselective biodegradation of amphetamine and methamphetamine in river microcosms". Water Res. 47 (15): 5708–18. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2013.06.057. PMID 23886544.
- ^ Crossley FS, Moore ML (November 1944). "Studies on the Leuckart reaction". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 9 (6): 529–536. doi:10.1021/jo01188a006.
- ^ a b c d e Kunalan V, Nic Daéid N, Kerr WJ, Buchanan HA, McPherson AR (September 2009). "Characterization of route specific impurities found in methamphetamine synthesized by the Leuckart and reductive amination methods". Anal. Chem. 81 (17): 7342–7348. doi:10.1021/ac9005588. PMC 3662403
 . PMID 19637924.
. PMID 19637924. - ^ Rassool GH (2009). Alcohol and Drug Misuse: A Handbook for Students and Health Professionals. London: Routledge. p. 113. ISBN 978-0-203-87117-1.
- ^ a b "Historical overview of methamphetamine". Vermont Department of Health. Government of Vermont. Retrieved 29 January 2012.
- ^ Grobler, Sias R.; Chikte, Usuf; Westraat, Jaco (2011). "The pH Levels of Different Methamphetamine Drug Samples on the Street Market in Cape Town". ISRN Dentistry. 2011: 1–4. doi:10.5402/2011/974768. PMC 3189445
 . PMID 21991491.
. PMID 21991491. - ^ "Historical overview of methamphetamine". Vermont Department of Health. Retrieved January 2012. Check date values in:
|access-date=(help) - ^ "The Nazi Death Machine: Hitler's Drugged Soldiers". Der Spiegel, 6 May 2005.
- ^ Defalque RJ, Wright AJ (April 2011). "Methamphetamine for Hitler's Germany: 1937 to 1945". Bull. Anesth. Hist. 29 (2): 21–24, 32. doi:10.1016/s1522-8649(11)50016-2. PMID 22849208.
- ^ Lukasz Kamienski (2016). Shooting Up: A Short History of Drugs and War. Oxford University Press. pp. 111–13.
- ^ a b Rasmussen, Nicolas (March 2008). On Speed: The Many Lives of Amphetamine (1 ed.). New York University Press. p. 148. ISBN 0-8147-7601-9.
- ^ "Controlled Substances Act". United States Food and Drug Administration. 11 June 2009. Retrieved 4 November 2013.
- ^ "Desoxyn". Lundbeck: Desoxyn. Retrieved December 2012. Check date values in:
|access-date=(help) - ^ "Recordati: Desoxyn". Recordati SP. Retrieved May 2013. Check date values in:
|access-date=(help) - ^ United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (2007). Preventing Amphetamine-type Stimulant Use Among Young People: A Policy and Programming Guide (PDF). New York: United Nations. ISBN 978-92-1-148223-2. Retrieved 11 November 2013.
- ^ a b "List of psychotropic substances under international control" (PDF). International Narcotics Control Board. United Nations. August 2003. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 December 2005. Retrieved 19 November 2005.
- ^ a b Poisons Standard July 2016 Comlaw.gov.au
- ^ Misuse of Drugs Act 1981 (2015) Slp.wa.gov.au
- ^ Cass WA, Smith MP, Peters LE (2006). "Calcitriol protects against the dopamine- and serotonin-depleting effects of neurotoxic doses of methamphetamine". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1074: 261–71. Bibcode:2006NYASA1074..261C. doi:10.1196/annals.1369.023. PMID 17105922.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Methamphetamine. |
- Methamphetamine
- Anorectics
- Aphrodisiacs
- Cardiac stimulants
- Euphoriants
- Excitatory amino acid reuptake inhibitors
- Japanese inventions
- Management of obesity
- Norepinephrine-dopamine releasing agents
- Phenethylamines
- Sigma agonists
- Stimulants
- Sympathomimetics
- TAAR1 agonists
- Treatment and management of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
- VMAT inhibitors