Naloxonazine
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
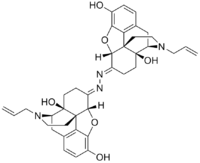 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
NIH 10894; NSC 612113, Bis-[5-α-4,5-Epoxy-3,14-dihydroxy-17-(2-propenyl)-morphinan-6-ylidene] hydrazine dihydrochloride
|
|
| Identifiers | |
| 82824-01-9 |
|
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL1618376 |
| ChemSpider | 7850858 |
| 1677 | |
| Jmol 3D model | Interactive image |
| PubChem | 9576413 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C38H42N4O6 | |
| Molar mass | 650.78 g·mol−1 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Naloxonazine is a potent, irreversible μ-opioid receptor antagonist.[1] Naloxonazine forms spontaneously in acidic solutions of naloxazone, and may be responsible for much or all of the irreversible μ opioid receptor binding displayed by the latter.[2]
See also[edit]
- Oxymorphone-3-methoxynaltrexonazine (OM-3-MNZ) a similarly structured opioid also having two complete and mirrored morphinan carbon skeletons but which is a full agonist instead.[citation needed][3]
References[edit]
- ^ Naloxonazine dihydrochloride
- ^ Hahn, E. F.; Pasternak, G. W. (September 1982). "Naloxonazine, a potent, long-lasting inhibitor of opiate binding sites". Life Sciences. 31 (12-13): 1385–1388. doi:10.1016/0024-3205(82)90387-3. PMID 6292633. Retrieved 2011-10-18.
- ^ Image of OM-3-MNZ
| This analgesic-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |