- published: 03 May 2016
- views: 150107
-
remove the playlistFile System
-
remove the playlistLatest Videos
-
remove the playlistLongest Videos
- remove the playlistFile System
- remove the playlistLatest Videos
- remove the playlistLongest Videos
- published: 10 Apr 2013
- views: 61076
- published: 27 Dec 2014
- views: 49219
- published: 25 May 2014
- views: 45685
- published: 09 Apr 2014
- views: 4009
- published: 15 Jul 2014
- views: 32178
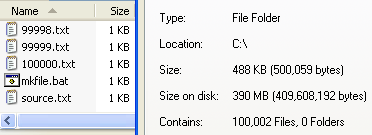
File system
In computing, a file system (or filesystem) is used to control how data is stored and retrieved. Without a file system, information placed in a storage area would be one large body of data with no way to tell where one piece of information stops and the next begins. By separating the data into individual pieces, and giving each piece a name, the information is easily separated and identified. Taking its name from the way paper-based information systems are named, each group of data is called a "file". The structure and logic rules used to manage the groups of information and their names is called a "file system".
There are many different kinds of file systems. Each one has different structure and logic, properties of speed, flexibility, security, size and more. Some file systems have been designed to be used for specific applications. For example, the ISO 9660 file system is designed specifically for optical discs.
File systems can be used on many different kinds of storage devices. Each storage device uses a different kind of media. The most common storage device in use today is a hard drive whose media is a disc that has been coated with a magnetic film. The film has ones and zeros 'written' on it sending electrical pulses to a magnetic "read-write" head. Other media that are used are magnetic tape, optical disc, and flash memory. In some cases, such as with tmpfs, the computer's main memory (RAM) is used to create a temporary file system for short-term use.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
File
File or filing may refer to:
Services
Information
Computing
- file URI scheme
- file (command), a Unix program for determining the type of data contained in a computer file
Other uses
See also
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 5:46
5:46File Systems as Fast As Possible
File Systems as Fast As PossibleFile Systems as Fast As Possible
NTFS, FAT32, exFAT...what are the differences between file systems, and what does a file system actually do, anyway? lynda.com message: Sign up for your 10-day FREE trial at http://lynda.com/techquickie Follow: http://twitter.com/luke_lafr Join the community: http://linustechtips.com License for images used in this video: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/legalcode -
 37:29
37:29Understanding File Systems
Understanding File SystemsUnderstanding File Systems
-
 46:51
46:5127 File System Architecture - 1
27 File System Architecture - 127 File System Architecture - 1
For More Video lectures from IIT Professors .......visit www.satishkashyap.com Video lectures and Lecture Notes on "Operating Systems" by Prof. P.K. Biswas sir, IITKGP 1 introduction to operating system 2 process management 1 3 process management 2 4 concurrent management 1 5 concurrent management 2 6 concurrent management 3 7 critical section problem 1 8 critical section problem 2 9 critical section problem 3 10 deadlock 1 11 deadlock 2 12 deadlock 3 13 deadlock 4 14 deadlock 5 15 memory mangement 1 16 memory mangement 2 17 memory mangement 3 18 memory mangement 4 19 cache memory 1 20 cache memory 2 21 secondary storage 22 buffer cache 1 23 buffer cache 2 24 file represenation 1 25 file represenation 2 26 file represenation 3 27 file system architecture 1 28 file system architecture 2 29 file system architecture 3 30 introduction to distributed file system 31 conclusion Introduction and history of Operating systems, structure and operations; processes and files Processor management: inter process communication, mutual exclusion, semaphores, wait and signal procedures, process scheduling and algorithms, critical sections, threads, multi threading Memory management: contiguous memory allocation, virtual memory, paging, page table structure, demand paging, page replacement policies, thrashing, segmentation, case study Deadlock: Shared resources, resource allocation and scheduling, resource graph models, deadlock detection, deadlock avoidance, deadlock prevention algorithms Device management: devices and their characteristics, device drivers, device handling, disk scheduling algorithms and policies File management: file concept, types and structures, directory structure, cases studies, access methods and matrices, file security, user authentication UNIX and Linux operating systems as case studies Time OS and case studies of Mobile OS -
 5:55
5:55The Linux File System
The Linux File SystemThe Linux File System
This video explains how the Linux file system is structured in a friendly way using cool animations. The full course could be found here for free ! https://www.udemy.com/linux-command-line-volume1/ -
 17:18
17:18Windows File Systems
Windows File SystemsWindows File Systems
This video looks at the four file systems supported by Windows. These are ReFS, NTFS, FAT and exFAT. The video looks at what each file system is capable of and its limitations. Download the PDF handout http://ITFreeTraining.com/handouts/server/file-systems.pdf Resilient File System (ReFS) The Resilient File System is a new file system built from scratch by Microsoft. Since it is a new file system it requires Windows 8 or Windows Server 2012 in order to operate. The main design difference between it and previous operating systems is that it is designed to fix problems while the operating system is online. For this reason the check disk feature that is found in previous operating systems that can be run to fix problems no longer exists. Given a new approach has been taken in the operating system, it is better at ensuring data integrity and corruption than previous operating systems. ReFS Limitations ReFS was designed to replace NTFS, but at the present time there are some limitations which may mean that you will need to stay with NTFS. Disk quotas: Disk quotes are not supported. Microsoft states in a blog post that this is a feature that can be supported outside the file system so it is possible for this feature to be supported in software. Possibly Microsoft will add this feature later on or some 3rd party software is available that will add this feature. NTFS compression and EFS: File compression and encryption (Encrypting File System) are not supported. Hard links: Hard links are not supported which is required by data duplication. Data duplication allows a file in the drive to be stored in one location but referenced in many different locations. It is used in the Windows Side by Side store (used to store software and drivers in the Windows directory) and may be the reason why ReFS cannot be used for the operating system at this time. Booting the OS: The biggest limitation is that ReFS does not support being used to boot the operating system. For the present, the drive containing the operating system will need to use a different operating system. Named streams/Object ID's: Named stream allows a name to be given to a file stream by the software. This is generally a feature that is used on alternative operating systems not Windows systems. Object ID's allow a file to be given a number. This is generally used for indexing software. Extended attributes/8.3 Filenames: Extended attributes are also not supported. Extended attributes is a feature that allows software to add additional attributes to a file in addition to the standard read only, hidden, archive and system. This feature is mostly used on alternative operating systems. It is rare for Windows software to use these features. 8.3 filenames are not supported. This dates back to the MS-Dos days. Windows 95 introduced long file names. Software support: Because ReFS also does not support named streams and object ID's. Some software does make use of these features so it is important to check all software before using it. For example SQL does not fully support ReFS. Convert from NTFS: Currently there is no software available which will convert a drive for NTFS to ReFS or ReFS to NTFS. If you want to change file systems you will need to back up your data, reformat the drive and then restore the data to the drive. Description to long for YouTube. Please see the following link for the rest of the description. http://itfreetraining.com/server#file-systems See http://YouTube.com/ITFreeTraining or http://itfreetraining.com for our always free training videos. This is only one video from the many free courses available on YouTube. References "Installing and Configuring Windows Server 2012 Exam Ref 70-410" pg 45 "ReFS" http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ReFS "Resilient File System Overview" http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh831724.aspx "Building the next generation file system for Windows: ReFS" http://blogs.msdn.com/b/b8/archive/2012/01/16/building-the-next-generation-file-system-for-windows-refs.aspx http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comparison_of_file_systems "Maximum Volume Sizes" http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc938432.aspx "Windows Server 2012: Does ReFS replace NTFS? When should I use it?" http://blogs.technet.com/b/askpfeplat/archive/2013/01/02/windows-server-2012-does-refs-replace-ntfs-when-should-i-use-it.aspx "NTFS" http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NTFS "File Allocation Table" http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File_Allocation_Table "exFAT" http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ExFAT "NTFS vs FAT vs exFAT" http://www.ntfs.com/ntfs_vs_fat.htm "File System Functionality Comparison" http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/desktop/ee681827(v=vs.85).aspx -
 56:44
56:44Vinay Mathur- File systems and storage of files in Unix
Vinay Mathur- File systems and storage of files in UnixVinay Mathur- File systems and storage of files in Unix
-
 25:09
25:09Learning the Linux File System
Learning the Linux File System -
 17:19
17:19Storage Abstractions (File Systems)
Storage Abstractions (File Systems)Storage Abstractions (File Systems)
cs4414: Operating Systems (http://rust-class.org) Class 16: Storage Embedded notes are available at: http://rust-class.org/class-16-storage.html Segment 4: Storage Abstractions Storage Abstractions File Systems Unix System 5 File System inodes How to make a file -
 5:45
5:45The Linux File System - Explained
The Linux File System - Explained -
 8:55
8:55Database vs Filesystem | Database Management System
Database vs Filesystem | Database Management SystemDatabase vs Filesystem | Database Management System
This lecture explains the difference between Database and Filesystem, and discusses about the features of Database. To ask your doubts on this topic and much more, click on this Direct Link: http://www.techtud.com/video-lecture/lecture-7 IMPORTANT LINKS: 1) Official Website: http://www.techtud.com/ 2) Virtual GATE(for 'All India Test Series for GATE-2016'): http://virtualgate.in/login/index.php Both of the above mentioned platforms are COMPLETELY FREE, so feel free to Explore, Learn, Practice & Share! Our Social Media Links: Facebook Page: https://www.facebook.com/techtuduniversity Facebook Group: https://www.facebook.com/groups/virtualgate/ Google+ Page: https://plus.google.com/+techtud/posts Last but not the least, SUBSCRIBE our YouTube channel to stay updated about our regularly uploaded new videos.
-

File Systems as Fast As Possible
NTFS, FAT32, exFAT...what are the differences between file systems, and what does a file system actually do, anyway? lynda.com message: Sign up for your 10-day FREE trial at http://lynda.com/techquickie Follow: http://twitter.com/luke_lafr Join the community: http://linustechtips.com License for images used in this video: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/legalcode
published: 03 May 2016 -

Understanding File Systems
published: 04 Feb 2014 -

27 File System Architecture - 1
For More Video lectures from IIT Professors .......visit www.satishkashyap.com Video lectures and Lecture Notes on "Operating Systems" by Prof. P.K. Biswas sir, IITKGP 1 introduction to operating system 2 process management 1 3 process management 2 4 concurrent management 1 5 concurrent management 2 6 concurrent management 3 7 critical section problem 1 8 critical section problem 2 9 critical section problem 3 10 deadlock 1 11 deadlock 2 12 deadlock 3 13 deadlock 4 14 deadlock 5 15 memory mangement 1 16 memory mangement 2 17 memory mangement 3 18 memory mangement 4 19 cache memory 1 20 cache memory 2 21 secondary storage 22 buffer cache 1 23 buffer cache 2 24 file represenation 1 25 file represenation 2 26 file represenation 3 27 file system architecture 1...
published: 10 Apr 2013 -

The Linux File System
This video explains how the Linux file system is structured in a friendly way using cool animations. The full course could be found here for free ! https://www.udemy.com/linux-command-line-volume1/
published: 27 Dec 2014 -

Windows File Systems
This video looks at the four file systems supported by Windows. These are ReFS, NTFS, FAT and exFAT. The video looks at what each file system is capable of and its limitations. Download the PDF handout http://ITFreeTraining.com/handouts/server/file-systems.pdf Resilient File System (ReFS) The Resilient File System is a new file system built from scratch by Microsoft. Since it is a new file system it requires Windows 8 or Windows Server 2012 in order to operate. The main design difference between it and previous operating systems is that it is designed to fix problems while the operating system is online. For this reason the check disk feature that is found in previous operating systems that can be run to fix problems no longer exists. Given a new approach has been taken in the operating ...
published: 25 May 2014 -

Vinay Mathur- File systems and storage of files in Unix
published: 26 Nov 2013 -

-

Storage Abstractions (File Systems)
cs4414: Operating Systems (http://rust-class.org) Class 16: Storage Embedded notes are available at: http://rust-class.org/class-16-storage.html Segment 4: Storage Abstractions Storage Abstractions File Systems Unix System 5 File System inodes How to make a file
published: 09 Apr 2014 -

-

Database vs Filesystem | Database Management System
This lecture explains the difference between Database and Filesystem, and discusses about the features of Database. To ask your doubts on this topic and much more, click on this Direct Link: http://www.techtud.com/video-lecture/lecture-7 IMPORTANT LINKS: 1) Official Website: http://www.techtud.com/ 2) Virtual GATE(for 'All India Test Series for GATE-2016'): http://virtualgate.in/login/index.php Both of the above mentioned platforms are COMPLETELY FREE, so feel free to Explore, Learn, Practice & Share! Our Social Media Links: Facebook Page: https://www.facebook.com/techtuduniversity Facebook Group: https://www.facebook.com/groups/virtualgate/ Google+ Page: https://plus.google.com/+techtud/posts Last but not the least, SUBSCRIBE our YouTube channel to stay updated about our regularly uplo...
published: 15 Jul 2014
File Systems as Fast As Possible
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:46
- Updated: 03 May 2016
- views: 150107
- published: 03 May 2016
- views: 150107
Understanding File Systems
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 37:29
- Updated: 04 Feb 2014
- views: 39950
- published: 04 Feb 2014
- views: 39950
27 File System Architecture - 1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 46:51
- Updated: 10 Apr 2013
- views: 61076
- published: 10 Apr 2013
- views: 61076
The Linux File System
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:55
- Updated: 27 Dec 2014
- views: 49219
- published: 27 Dec 2014
- views: 49219
Windows File Systems
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 17:18
- Updated: 25 May 2014
- views: 45685
- published: 25 May 2014
- views: 45685
Vinay Mathur- File systems and storage of files in Unix
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 56:44
- Updated: 26 Nov 2013
- views: 47187
- published: 26 Nov 2013
- views: 47187
Learning the Linux File System
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 25:09
- Updated: 07 Jul 2015
- views: 115456
Storage Abstractions (File Systems)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 17:19
- Updated: 09 Apr 2014
- views: 4009
- published: 09 Apr 2014
- views: 4009
The Linux File System - Explained
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:45
- Updated: 17 Nov 2012
- views: 422611
Database vs Filesystem | Database Management System
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:55
- Updated: 15 Jul 2014
- views: 32178
- published: 15 Jul 2014
- views: 32178
-

File System
published: 02 Oct 2016 -

FAT File System Explained
published: 30 Oct 2014 -

Understanding File Systems
published: 04 Feb 2014 -

-

Xtc2clip Repair File system
published: 08 Jul 2015 -

25 Upload File System
published: 02 Sep 2016 -

File System Management File System Interface
published: 26 Jan 2014 -

Pulseman - File Systems
published: 14 Jan 2017 -

File System Forensic Analysis
published: 15 Dec 2016 -

Linux File System Types
published: 25 Nov 2016
File System
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 27:09
- Updated: 02 Oct 2016
- views: 0
- published: 02 Oct 2016
- views: 0
FAT File System Explained
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:39
- Updated: 30 Oct 2014
- views: 24112
- published: 30 Oct 2014
- views: 24112
Understanding File Systems
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 37:29
- Updated: 04 Feb 2014
- views: 39950
- published: 04 Feb 2014
- views: 39950
Linux File System
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:06
- Updated: 05 Oct 2016
- views: 0
Xtc2clip Repair File system
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:28
- Updated: 08 Jul 2015
- views: 1926
- published: 08 Jul 2015
- views: 1926
25 Upload File System
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 37:56
- Updated: 02 Sep 2016
- views: 175
- published: 02 Sep 2016
- views: 175
File System Management File System Interface
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 59:54
- Updated: 26 Jan 2014
- views: 2681
- published: 26 Jan 2014
- views: 2681
Pulseman - File Systems
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:08
- Updated: 14 Jan 2017
- views: 0
- published: 14 Jan 2017
- views: 0
File System Forensic Analysis
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:20
- Updated: 15 Dec 2016
- views: 4
- published: 15 Dec 2016
- views: 4
Linux File System Types
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 13:55
- Updated: 25 Nov 2016
- views: 46
- published: 25 Nov 2016
- views: 46
-

Accessing file system
S7
published: 02 Oct 2016 -

025 File Systems
published: 02 Sep 2016 -

025 File Systems
published: 30 Apr 2016 -

025 File Systems
published: 05 Oct 2014 -

Distributed File System 2012
published: 22 Aug 2016 -

Network File System
published: 23 Dec 2015 -

Android file System
published: 25 Sep 2014
Accessing file system
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 52:03
- Updated: 02 Oct 2016
- views: 0
- published: 02 Oct 2016
- views: 0
025 File Systems
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 34:13
- Updated: 02 Sep 2016
- views: 0
- published: 02 Sep 2016
- views: 0
025 File Systems
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 34:13
- Updated: 30 Apr 2016
- views: 2
- published: 30 Apr 2016
- views: 2
025 File Systems
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 34:13
- Updated: 05 Oct 2014
- views: 5
- published: 05 Oct 2014
- views: 5
Distributed File System 2012
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:15:52
- Updated: 22 Aug 2016
- views: 3
- published: 22 Aug 2016
- views: 3
Network File System
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 34:37
- Updated: 23 Dec 2015
- views: 23
- published: 23 Dec 2015
- views: 23
Android file System
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 47:40
- Updated: 25 Sep 2014
- views: 142
- published: 25 Sep 2014
- views: 142
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

File Systems as Fast As Possible
- Report rights infringement
- published: 03 May 2016
- views: 150107

Understanding File Systems
- Report rights infringement
- published: 04 Feb 2014
- views: 39950

27 File System Architecture - 1
- Report rights infringement
- published: 10 Apr 2013
- views: 61076

The Linux File System
- Report rights infringement
- published: 27 Dec 2014
- views: 49219

Windows File Systems
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 May 2014
- views: 45685

Vinay Mathur- File systems and storage of files in Unix
- Report rights infringement
- published: 26 Nov 2013
- views: 47187

Learning the Linux File System
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Jul 2015
- views: 115456

Storage Abstractions (File Systems)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 09 Apr 2014
- views: 4009

The Linux File System - Explained
- Report rights infringement
- published: 17 Nov 2012
- views: 422611

Database vs Filesystem | Database Management System
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Jul 2014
- views: 32178
- Playlist
- Chat

File System
- Report rights infringement
- published: 02 Oct 2016
- views: 0

FAT File System Explained
- Report rights infringement
- published: 30 Oct 2014
- views: 24112

Understanding File Systems
- Report rights infringement
- published: 04 Feb 2014
- views: 39950


Xtc2clip Repair File system
- Report rights infringement
- published: 08 Jul 2015
- views: 1926

25 Upload File System
- Report rights infringement
- published: 02 Sep 2016
- views: 175

File System Management File System Interface
- Report rights infringement
- published: 26 Jan 2014
- views: 2681

Pulseman - File Systems
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Jan 2017
- views: 0

File System Forensic Analysis
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Dec 2016
- views: 4

Linux File System Types
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 Nov 2016
- views: 46
- Playlist
- Chat

Accessing file system
- Report rights infringement
- published: 02 Oct 2016
- views: 0

025 File Systems
- Report rights infringement
- published: 02 Sep 2016
- views: 0

025 File Systems
- Report rights infringement
- published: 30 Apr 2016
- views: 2

025 File Systems
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Oct 2014
- views: 5

Distributed File System 2012
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 Aug 2016
- views: 3

Network File System
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Dec 2015
- views: 23

Android file System
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 Sep 2014
- views: 142
BREAKING: Half-Brother Of North Korean Leader Kim Jong-un Assassinated In Malaysia
Edit WorldNews.com 14 Feb 2017NYT: Russia Secretly Deploys New Cruise Missile, Raises Trump Arms Control Issue
Edit WorldNews.com 14 Feb 2017How US could stop a North Korean missile
Edit CNN 14 Feb 2017‘Extraordinary’ levels of toxic pollution found in Mariana Trench, deepest place on the planet
Edit South China Morning Post 14 Feb 2017Simmons law firm files more suits against New York counties
Edit Business Journal 14 Feb 2017Critics of Bountiful's plan to move City Hall file lawsuit
Edit The Salt Lake Tribune 14 Feb 2017Tejas Networks files IPO papers with Sebi
Edit Financial Express 14 Feb 2017LGUs, PNP top 2 agencies with most number of cases filed before Ombudsman
Edit Sun Star (NewsDB Live) 14 Feb 2017Sporting goods retailer with 9 N.C. stores reportedly near bankruptcy filing
Edit Business Journal 14 Feb 2017Sporting goods retailer with Charlotte store reportedly near bankruptcy filing
Edit Business Journal 14 Feb 2017Sporting goods retailer with Jax store reportedly near bankruptcy filing
Edit Business Journal 14 Feb 2017Outdoor sporting goods retailer with 4 Houston stores reportedly near bankruptcy filing
Edit Business Journal 14 Feb 2017BRIEF-Aina Le'a files for non-timely 10-Q
Edit Reuters 14 Feb 2017Warren Buffett's firm expected to file update on its stocks
Edit Fresno Bee 14 Feb 2017BRIEF-Philip Morris International - files for potential debt shelf size not disclosed
Edit Reuters 14 Feb 2017Electronic filing for annual tax forms revamped
Edit The Jakarta Post 14 Feb 2017Bill to require e-filing of finances advances
Edit Arkansas Online 14 Feb 2017- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »








