- published: 06 Dec 2014
- views: 318305
-
remove the playlistMultiplexer
- remove the playlistMultiplexer
- Multiplexer
- 4+1 architectural view model
- Mathematical fallacy
- Digital electronics
- Quadraphonic sound
- published: 03 Apr 2017
- views: 13846
- published: 20 Apr 2013
- views: 93534
- published: 08 Dec 2014
- views: 208049
- published: 11 Mar 2017
- views: 9875
- published: 04 Apr 2017
- views: 11690
- published: 08 Dec 2014
- views: 190875
- published: 07 Jan 2015
- views: 186029
- published: 05 Apr 2017
- views: 15629
- published: 20 Mar 2017
- views: 415

Multiplexer
In electronics, a multiplexer (or mux) is a device that selects one of several analog or digital input signals and forwards the selected input into a single line. A multiplexer of 2n inputs has n select lines, which are used to select which input line to send to the output. Multiplexers are mainly used to increase the amount of data that can be sent over the network within a certain amount of time and bandwidth. A multiplexer is also called a data selector.
An electronic multiplexer makes it possible for several signals to share one device or resource, for example one A/D converter or one communication line, instead of having one device per input signal.
Conversely, a demultiplexer (or demux) is a device taking a single input signal and selecting one of many data-output-lines, which is connected to the single input. A multiplexer is often used with a complementary demultiplexer on the receiving end.
An electronic multiplexer can be considered as a multiple-input, single-output switch, and a demultiplexer as a single-input, multiple-output switch. The schematic symbol for a multiplexer is an isosceles trapezoid with the longer parallel side containing the input pins and the short parallel side containing the output pin. The schematic on the right shows a 2-to-1 multiplexer on the left and an equivalent switch on the right. The  wire connects the desired input to the output.
wire connects the desired input to the output.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

4+1 architectural view model
4+1 is a view model designed by Philippe Kruchten for "describing the architecture of software-intensive systems, based on the use of multiple, concurrent views". The views are used to describe the system from the viewpoint of different stakeholders, such as end-users, developers and project managers. The four views of the model are logical, development, process and physical view. In addition selected use cases or scenarios are used to illustrate the architecture serving as the 'plus one' view. Hence the model contains 4+1 views:
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Mathematical fallacy
In mathematics, certain kinds of mistaken proof are often exhibited, and sometimes collected, as illustrations of a concept of mathematical fallacy. There is a distinction between a simple mistake and a mathematical fallacy in a proof: a mistake in a proof leads to an invalid proof just in the same way, but in the best-known examples of mathematical fallacies, there is some concealment in the presentation of the proof. For example, the reason validity fails may be a division by zero that is hidden by algebraic notation. There is a striking quality of the mathematical fallacy: as typically presented, it leads not only to an absurd result, but does so in a crafty or clever way. Therefore, these fallacies, for pedagogic reasons, usually take the form of spurious proofs of obvious contradictions. Although the proofs are flawed, the errors, usually by design, are comparatively subtle, or designed to show that certain steps are conditional, and should not be applied in the cases that are the exceptions to the rules.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Digital electronics
Digital electronics or digital (electronic) circuits are electronics that handle digital signals - discrete bands of analog levels - rather than by continuous ranges (as used in analogue electronics). All levels within a band of values represent the same numeric value. Because of this discretization, relatively small changes to the analog signal levels due to manufacturing tolerance, signal attenuation or parasitic noise do not leave the discrete envelope, and as a result are ignored by signal state sensing circuitry.
In most cases, the number of these states is two, and they are represented by two voltage bands: one near a reference value (typically termed as "ground" or zero volts), and the other a value near the supply voltage. These correspond to the "false" ("0") and "true" ("1") values of the Boolean domain respectively, named after its inventor, George Boole, yielding binary code.
Digital techniques are useful because it is easier to get an electronic device to switch into one of a number of known states than to accurately reproduce a continuous range of values.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Quadraphonic sound
Quadraphonic (or Quadrophonic and sometimes Quadrasonic) sound – similar to what is now called 4.0 surround sound – uses four channels in which speakers are positioned at the four corners of the listening space, reproducing signals that are (wholly or in part) independent of one another. Quadraphonic audio was the earliest consumer product in surround sound and thousands of quadraphonic recordings were made during the 1970s.
It was a commercial failure due to many technical problems and format incompatibilities. Quadraphonic audio formats were more expensive to produce than standard two-channel stereo. Playback required additional speakers and specially designed decoders and amplifiers.
Operation
Quadraphonic audio reproduction on vinyl records was problematic, because some systems were based on discrete sound channels (allowing for full separation of the four original recorded channels, albeit with restricted high-frequency response and reduced record life), while others were matrix encoded into two tracks that would also play back in standard, two-channel, stereo on normal audio equipment (so-called 'compatible' quadraphonic). Also, there were inexpensive "derived" solutions that only provided back ambiance channels, not a defined placement of individual instruments.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 12:27
12:27Introduction to Multiplexers | MUX Basic
Introduction to Multiplexers | MUX BasicIntroduction to Multiplexers | MUX Basic
Digital Electronics: Introduction to Multiplexers's. Contribute: http://www.nesoacademy.org/donate Website ► http://www.nesoacademy.org/ Facebook ► https://goo.gl/Nt0PmB Twitter ► https://twitter.com/nesoacademy Pinterest ► http://www.pinterest.com/nesoacademy/ -
 7:27
7:27MULTIPLEXER
MULTIPLEXERMULTIPLEXER
Multiplexers || Data selectors || MUX Multiplexers in hindi mux analog multiplexer multiplexers digital multiplexer demultiplexer multiplexer ic multiplexer circuit multiplexer chip analogue multiplexer signal multiplexer analog multiplexer ic multiplexer analog multiplexer demultiplexer mux switch ic multiplexer 4 channel multiplexer 4 to 1 multiplexer mux multiplexer 8 to 1 multiplexer serial multiplexer 4 1 multiplexer 8 1 multiplexer multiplex switch multiplexer switch usb multiplexer digital mux demultiplexer ic mux and demux optical multiplexer 16 to 1 multiplexer fiber multiplexer 4 1 mux analog signal multiplexer analog demultiplexer 2 1 multiplexer electronic multiplexers analog switch analog mux ic 2 to 1 multiplexer mux ic multiplexer and demultiplexer 16 channel multiplexer video multiplexer 2 1 mux multiplexer mux high voltage multiplexer multiplexer logic analog switch multiplexer analog multiplexer circuit multiplexer design digital multiplexer ic switch multiplexer voltage reference 8 1 mux ethernet multiplexer data multiplexer analog multiplexer demultiplexer i2c analog multiplexer 8 input multiplexer 16 input multiplexer 16 channel digital multiplexer 8 to 1 mux 2 input multiplexer 16 channel analog multiplexer 16 bit multiplexer multiplexer 4 to 1 multiplexer 8 to 1 4 input multiplexer i2c multiplexer high speed multiplexer multiplexer 16 to 1 multiplexer 2 to 1 logic multiplexer add drop multiplexer differential multiplexer 2 bit multiplexer quad multiplexer staco energy nmea multiplexer 16 multiplexer mux chip analog multiplexing multiplexer applications digital logic multiplexer multiplexer digital 16 to 1 mux multiplexer digital logic multiplexer in digital electronics multiplexer in dld cctv multiplexer mux 4 to 1 cmos multiplexer power multiplexer ic power multiplexer analog switches and multiplexers 16 to 4 multiplexer multiplexer and demultiplexer in digital electronics 4 to 16 multiplexer adc multiplexer 4 way multiplexer Raul s tutorial -
 8:00
8:00Digital Logic - Multiplexers
Digital Logic - MultiplexersDigital Logic - Multiplexers
This is one of a series of videos where I cover concepts relating to digital electronics. In this video I talk about multiplexers, what they do, how they work internally, and a couple of ways that you can use them. -
 5:52
5:524X1 Multiplexer
4X1 Multiplexer4X1 Multiplexer
Digital Electronics: 4X1 Multiplexer Contribute: http://www.nesoacademy.org/donate Website ► http://www.nesoacademy.org/ Facebook ► https://goo.gl/Nt0PmB Twitter ► https://twitter.com/nesoacademy Pinterest ► http://www.pinterest.com/nesoacademy/ -
 18:42
18:42GATE Lecture on Introduction to Multiplexer (part-1) (Digital Electronics) (Hindi Language )
GATE Lecture on Introduction to Multiplexer (part-1) (Digital Electronics) (Hindi Language )GATE Lecture on Introduction to Multiplexer (part-1) (Digital Electronics) (Hindi Language )
Subject Name : Digital Electronics Topic Name : Multiplexer Faculty : Sujay Jasuja Sir If you have any questions/queries you can either email us or post it in our closed facebook group made for GATE/ESE/PSU aspirants. Email id- info@gateacademy.co.in For more queries - https://www.facebook.com/groups/gateconcepts Facebook Page - https://www.facebook.com/gateacademy.official/ -
 5:27
5:274:1 MULTIPLEXER
4:1 MULTIPLEXER4:1 MULTIPLEXER
4:1 multiplexer Multiplexers in hindi mux analog multiplexer multiplexers digital multiplexer demultiplexer multiplexer ic multiplexer circuit multiplexer chip analogue multiplexer signal multiplexer analog multiplexer ic multiplexer analog multiplexer demultiplexer mux switch ic multiplexer 4 channel multiplexer 4 to 1 multiplexer mux multiplexer 8 to 1 multiplexer serial multiplexer 4 1 multiplexer 8 1 multiplexer multiplex switch multiplexer switch usb multiplexer digital mux demultiplexer ic mux and demux optical multiplexer 16 to 1 multiplexer fiber multiplexer 4 1 mux analog signal multiplexer analog demultiplexer 2 1 multiplexer electronic multiplexers analog switch analog mux ic 2 to 1 multiplexer mux ic multiplexer and demultiplexer 16 channel multiplexer video multiplexer 2 1 mux multiplexer mux high voltage multiplexer multiplexer logic analog switch multiplexer analog multiplexer circuit multiplexer design digital multiplexer ic switch multiplexer voltage reference 8 1 mux ethernet multiplexer data multiplexer analog multiplexer demultiplexer i2c analog multiplexer 8 input multiplexer 16 input multiplexer 16 channel digital multiplexer 8 to 1 mux 2 input multiplexer 16 channel analog multiplexer 16 bit multiplexer multiplexer 4 to 1 multiplexer 8 to 1 4 input multiplexer i2c multiplexer high speed multiplexer multiplexer 16 to 1 multiplexer 2 to 1 logic multiplexer add drop multiplexer differential multiplexer 2 bit multiplexer quad multiplexer staco energy nmea multiplexer 16 multiplexer mux chip analog multiplexing multiplexer applications digital logic multiplexer multiplexer digital 16 to 1 mux multiplexer digital logic multiplexer in digital electronics multiplexer in dld cctv multiplexer mux 4 to 1 cmos multiplexer power multiplexer ic power multiplexer analog switches and multiplexers 16 to 4 multiplexer multiplexer and demultiplexer in digital electronics 4 to 16 multiplexer adc multiplexer 4 way multiplexer Raul s tutorial -
 5:51
5:518X1 Multiplexer
8X1 Multiplexer8X1 Multiplexer
Digital Electronics: 8X1 Multiplexer Contribute: http://www.nesoacademy.org/donate Website ► http://www.nesoacademy.org/ Facebook ► https://goo.gl/Nt0PmB Twitter ► https://twitter.com/nesoacademy Pinterest ► http://www.pinterest.com/nesoacademy/ -
 8:34
8:34Implementation of Boolean Function using Multiplexers
Implementation of Boolean Function using MultiplexersImplementation of Boolean Function using Multiplexers
Digital Electronics: Implementation of Boolean Function using Multiplexers Contribute: http://www.nesoacademy.org/donate Website ► http://www.nesoacademy.org/ Facebook ► https://goo.gl/Nt0PmB Twitter ► https://twitter.com/nesoacademy Pinterest ► http://www.pinterest.com/nesoacademy/ -
 7:29
7:298:1 multiplexer
8:1 multiplexer8:1 multiplexer
8:1 MUX || data selector Multiplexers in hindi Raul s tutorialmux analog multiplexer multiplexers digital multiplexer demultiplexer multiplexer ic multiplexer circuit multiplexer chip analogue multiplexer signal multiplexer analog multiplexer ic multiplexer analog multiplexer demultiplexer mux switch ic multiplexer 4 channel multiplexer 4 to 1 multiplexer mux multiplexer 8 to 1 multiplexer serial multiplexer 4 1 multiplexer 8 1 multiplexer multiplex switch multiplexer switch usb multiplexer digital mux demultiplexer ic mux and demux optical multiplexer 16 to 1 multiplexer fiber multiplexer 4 1 mux analog signal multiplexer analog demultiplexer 2 1 multiplexer electronic multiplexers analog switch analog mux ic 2 to 1 multiplexer mux ic multiplexer and demultiplexer 16 channel multiplexer video multiplexer 2 1 mux multiplexer mux high voltage multiplexer multiplexer logic analog switch multiplexer analog multiplexer circuit multiplexer design digital multiplexer ic switch multiplexer voltage reference 8 1 mux ethernet multiplexer data multiplexer analog multiplexer demultiplexer i2c analog multiplexer 8 input multiplexer 16 input multiplexer 16 channel digital multiplexer 8 to 1 mux 2 input multiplexer 16 channel analog multiplexer 16 bit multiplexer multiplexer 4 to 1 multiplexer 8 to 1 4 input multiplexer i2c multiplexer high speed multiplexer multiplexer 16 to 1 multiplexer 2 to 1 logic multiplexer add drop multiplexer differential multiplexer 2 bit multiplexer quad multiplexer staco energy nmea multiplexer 16 multiplexer mux chip analog multiplexing multiplexer applications digital logic multiplexer multiplexer digital 16 to 1 mux multiplexer digital logic multiplexer in digital electronics multiplexer in dld cctv multiplexer mux 4 to 1 cmos multiplexer power multiplexer ic power multiplexer analog switches and multiplexers 16 to 4 multiplexer multiplexer and demultiplexer in digital electronics 4 to 16 multiplexer adc multiplexer 4 way multiplexer -
 21:34
21:34Multiplexers Examples
Multiplexers ExamplesMultiplexers Examples
Multiplexers Examples -
 5:58
5:58Understanding a 2:1 Multiplexer
Understanding a 2:1 MultiplexerUnderstanding a 2:1 Multiplexer
Here is a short video for understanding 2:1 Multiplexers -
 16:48
16:48Analog Multiplexers
Analog MultiplexersAnalog Multiplexers
Learn about using analog multiplexers for adding more analog inputs to your microcontroller project. -
 20:10
20:10Arduino MIDI Controller: Part 3 - Multiplexers
Arduino MIDI Controller: Part 3 - MultiplexersArduino MIDI Controller: Part 3 - Multiplexers
Part 3 of the Arduino Midi Controller project. This time we add more inputs with the help of Multiplexers. Visit Notes and Volts for full Parts List and Software Download http://www.notesandvolts.com/2016/07/arduino-midi-controller-multiplexers.html Like my videos? Please consider supporting Notes and Volts on Patreon https://www.patreon.com/notesandvolts -
 6:45
6:45Multiplexer in Hindi
Multiplexer in HindiMultiplexer in Hindi
4x1 multiplexer, block diagram -
 4:32
4:328:1 multiplexer using 4:1 and 2:1 Multiplexers
8:1 multiplexer using 4:1 and 2:1 Multiplexers8:1 multiplexer using 4:1 and 2:1 Multiplexers
8:1 multiplexer using 4:1 and 2:1 Multiplexers implementation of Boolean function using multiplexer 8:1 MUX || data selector Multiplexers in hindi Raul s tutorialmux analog multiplexer multiplexers digital multiplexer demultiplexer multiplexer ic multiplexer circuit multiplexer chip analogue multiplexer signal multiplexer analog multiplexer ic multiplexer analog multiplexer demultiplexer mux switch ic multiplexer 4 channel multiplexer 4 to 1 multiplexer mux multiplexer 8 to 1 multiplexer serial multiplexer 4 1 multiplexer 8 1 multiplexer multiplex switch multiplexer switch usb multiplexer digital mux demultiplexer ic mux and demux optical multiplexer 16 to 1 multiplexer fiber multiplexer 4 1 mux analog signal multiplexer analog demultiplexer 2 1 multiplexer electronic multiplexers analog switch analog mux ic 2 to 1 multiplexer mux ic multiplexer and demultiplexer 16 channel multiplexer video multiplexer 2 1 mux multiplexer mux high voltage multiplexer multiplexer logic analog switch multiplexer analog multiplexer circuit multiplexer design digital multiplexer ic switch multiplexer voltage reference 8 1 mux ethernet multiplexer data multiplexer analog multiplexer demultiplexer i2c analog multiplexer 8 input multiplexer 16 input multiplexer 16 channel digital multiplexer 8 to 1 mux 2 input multiplexer 16 channel analog multiplexer 16 bit multiplexer multiplexer 4 to 1 multiplexer 8 to 1 4 input multiplexer i2c multiplexer high speed multiplexer multiplexer 16 to 1 multiplexer 2 to 1 logic multiplexer add drop multiplexer differential multiplexer 2 bit multiplexer quad multiplexer staco energy nmea multiplexer 16 multiplexer mux chip analog multiplexing multiplexer applications digital logic multiplexer multiplexer digital 16 to 1 mux multiplexer digital logic multiplexer in digital electronics multiplexer in dld cctv multiplexer mux 4 to 1 cmos multiplexer power multiplexer ic power multiplexer analog switches and multiplexers 16 to 4 multiplexer multiplexer and demultiplexer in digital electronics 4 to 16 multiplexer adc multiplexer 4 way multiplexer Raul s tutorial Raul s tutorial -
 39:07
39:07SAYISAL ELEKTRONİK DERSLERİ: Veri Seçiciler (MULTİPLEXER)
SAYISAL ELEKTRONİK DERSLERİ: Veri Seçiciler (MULTİPLEXER)SAYISAL ELEKTRONİK DERSLERİ: Veri Seçiciler (MULTİPLEXER)
N tane giriş içerisinden seçme uçları yardımıyla seçilen girişi çıkışa aktaran devrelere veri seçiciler (multiplexer) adı verilir. Bu dersimizde Multiplexer konusu anlatılacaktır. Sorularınızı yorum kısmına yazabilirsiniz. Sayısal Elektronik (Lojik-Dijital Elektronik-Mantık Devreleri) eğitim setinin tamamını izlemek için tıklayınız►►https://goo.gl/VWIocN Eğitim videosu hoşunuza gittiyse "beğenmeyi" unutmayın! En yeni videolardan haberdar olmak için buradan abone olabilirsiniz►►https://goo.gl/3uP9eU Eğitim Setlerimiz: -DEVRE ANALİZİ 1 Eğitim Setimiz ►►https://goo.gl/gLkn7D -DEVRE ANALİZİ 2 Eğitim Setimiz ►►https://goo.gl/jdh2M1 -SAYISAL ELEKTRONİK (LOJİK-MANTIK DEVRELERİ) Eğitim Setimiz►►https://goo.gl/VWIocN -PİC PROGRAMLAMA Eğitim Setimiz ►►https://goo.gl/S0nvAh -PROTEUS Eğitim Setimiz ►►https://goo.gl/VchPln -BASKI DEVRE Eğitim Setimiz ►►https://goo.gl/SqlPUu -OHM Kanunu Eğitim Setimiz ►►https://goo.gl/H5achb Sayısal elektronik dersi, lojik devreler, mantık devreleri, dijital elektronik gibi isimler de alabilirler. İçerikleri aynıdır. Elektronik te kullanılan sinyaller Anolog ve Dijital olarak ikiye ayrılır. Anolog sinyaller sonsuz büyüklükte olan sinyallerdir. Yani analog sinyaller çok çeşitli değerler alabilir. Dijital büyüklükler ise sadece Lojik 0 ve Lojik 1 değerlerinden oluşurlar. Sayısal elektronikte biz genel olarak dijital sinyaller ile ilgileneceğiz. Sosyal Medya Ağlarımız: ►https://www.youtube.com/c/elektronikderslerimizle ►https://www.facebook.com/elektronikderslerimizle ►https://twitter.com/eloderslerim ►https://www.instagram.com/elektronikderslerim ►https://plus.google.com/+elektronikderslerimizle Merhaba elektronikDerslerim takipçileri. Bu kanalda, hayatımızın büyük bölümüne etki eden teknolojinin en temel bilimi olan ELEKTRİK-ELEKTRONİK-YAZILIM-MEKATRONİK vb. alanlar ile ilgili "herkes" için önemli eğitimler yer almaktadır. Siz de kanalımıza destek olmak istiyorsanız videoları "beğenip", kanalımıza "ABONE" olmayı unutmayın! -
 3:10
3:10Introduction and working of Multiplexers
Introduction and working of MultiplexersIntroduction and working of Multiplexers
Multiplexers: Many to one..basics and working!! -
 8:20
8:20implementation of Boolean function using multiplexer (first method)
implementation of Boolean function using multiplexer (first method)implementation of Boolean function using multiplexer (first method)
implementation of Boolean function using multiplexer (first method) 8:1 MUX || data selector Multiplexers in hindi Raul s tutorialmux analog multiplexer multiplexers digital multiplexer demultiplexer multiplexer ic multiplexer circuit multiplexer chip analogue multiplexer signal multiplexer analog multiplexer ic multiplexer analog multiplexer demultiplexer mux switch ic multiplexer 4 channel multiplexer 4 to 1 multiplexer mux multiplexer 8 to 1 multiplexer serial multiplexer 4 1 multiplexer 8 1 multiplexer multiplex switch multiplexer switch usb multiplexer digital mux demultiplexer ic mux and demux optical multiplexer 16 to 1 multiplexer fiber multiplexer 4 1 mux analog signal multiplexer analog demultiplexer 2 1 multiplexer electronic multiplexers analog switch analog mux ic 2 to 1 multiplexer mux ic multiplexer and demultiplexer 16 channel multiplexer video multiplexer 2 1 mux multiplexer mux high voltage multiplexer multiplexer logic analog switch multiplexer analog multiplexer circuit multiplexer design digital multiplexer ic switch multiplexer voltage reference 8 1 mux ethernet multiplexer data multiplexer analog multiplexer demultiplexer i2c analog multiplexer 8 input multiplexer 16 input multiplexer 16 channel digital multiplexer 8 to 1 mux 2 input multiplexer 16 channel analog multiplexer 16 bit multiplexer multiplexer 4 to 1 multiplexer 8 to 1 4 input multiplexer i2c multiplexer high speed multiplexer multiplexer 16 to 1 multiplexer 2 to 1 logic multiplexer add drop multiplexer differential multiplexer 2 bit multiplexer quad multiplexer staco energy nmea multiplexer 16 multiplexer mux chip analog multiplexing multiplexer applications digital logic multiplexer multiplexer digital 16 to 1 mux multiplexer digital logic multiplexer in digital electronics multiplexer in dld cctv multiplexer mux 4 to 1 cmos multiplexer power multiplexer ic power multiplexer analog switches and multiplexers 16 to 4 multiplexer multiplexer and demultiplexer in digital electronics 4 to 16 multiplexer adc multiplexer 4 way multiplexer Raul s tutorial -
 14:54
14:54Multiplexer (MUX)- Data selector-Digital Electronics(English)
Multiplexer (MUX)- Data selector-Digital Electronics(English)Multiplexer (MUX)- Data selector-Digital Electronics(English)
Lecture by Dr.M.Balasubramanian Multiplexer- Data selector-Digital Electronics(English). Multiplexer - MUX means many to one. Here the basic concept of MUX is explained with truth table and circuit is also designed. -
 11:42
11:42Full adder using 4x1 Multiplexer(MUX) (2)- Digital Electronics (English)
Full adder using 4x1 Multiplexer(MUX) (2)- Digital Electronics (English)Full adder using 4x1 Multiplexer(MUX) (2)- Digital Electronics (English)
Lecture by Dr.M.Balasubramanian Full adder using 4x1 Multiplexer -MUX (2)- Digital Electronics (English) Full adder truth table is explained and K-map is used to prepare implementation table . Than circuit is designed using 4x1 MUX -
 6:36
6:36Multiplex
MultiplexMultiplex
-
 0:11
0:11Multiplex
MultiplexMultiplex
-
 0:46
0:46Multiplex
MultiplexMultiplex
-
 43:37
43:37Multiplex
MultiplexMultiplex
-
 35:56
35:56Multiplexer
MultiplexerMultiplexer
-

Introduction to Multiplexers | MUX Basic
Digital Electronics: Introduction to Multiplexers's. Contribute: http://www.nesoacademy.org/donate Website ► http://www.nesoacademy.org/ Facebook ► https://goo.gl/Nt0PmB Twitter ► https://twitter.com/nesoacademy Pinterest ► http://www.pinterest.com/nesoacademy/
published: 06 Dec 2014 -

MULTIPLEXER
Multiplexers || Data selectors || MUX Multiplexers in hindi mux analog multiplexer multiplexers digital multiplexer demultiplexer multiplexer ic multiplexer circuit multiplexer chip analogue multiplexer signal multiplexer analog multiplexer ic multiplexer analog multiplexer demultiplexer mux switch ic multiplexer 4 channel multiplexer 4 to 1 multiplexer mux multiplexer 8 to 1 multiplexer serial multiplexer 4 1 multiplexer 8 1 multiplexer multiplex switch multiplexer switch usb multiplexer digital mux demultiplexer ic mux and demux optical multiplexer 16 to 1 multiplexer fiber multiplexer 4 1 mux analog signal multiplexer analog demultiplexer 2 1 multiplexer electronic multiplexers analog switch analog mux ic 2 to 1 multiplexer mux ic multiplexer and ...
published: 03 Apr 2017 -

Digital Logic - Multiplexers
This is one of a series of videos where I cover concepts relating to digital electronics. In this video I talk about multiplexers, what they do, how they work internally, and a couple of ways that you can use them.
published: 20 Apr 2013 -

4X1 Multiplexer
Digital Electronics: 4X1 Multiplexer Contribute: http://www.nesoacademy.org/donate Website ► http://www.nesoacademy.org/ Facebook ► https://goo.gl/Nt0PmB Twitter ► https://twitter.com/nesoacademy Pinterest ► http://www.pinterest.com/nesoacademy/
published: 08 Dec 2014 -

GATE Lecture on Introduction to Multiplexer (part-1) (Digital Electronics) (Hindi Language )
Subject Name : Digital Electronics Topic Name : Multiplexer Faculty : Sujay Jasuja Sir If you have any questions/queries you can either email us or post it in our closed facebook group made for GATE/ESE/PSU aspirants. Email id- info@gateacademy.co.in For more queries - https://www.facebook.com/groups/gateconcepts Facebook Page - https://www.facebook.com/gateacademy.official/
published: 11 Mar 2017 -

4:1 MULTIPLEXER
4:1 multiplexer Multiplexers in hindi mux analog multiplexer multiplexers digital multiplexer demultiplexer multiplexer ic multiplexer circuit multiplexer chip analogue multiplexer signal multiplexer analog multiplexer ic multiplexer analog multiplexer demultiplexer mux switch ic multiplexer 4 channel multiplexer 4 to 1 multiplexer mux multiplexer 8 to 1 multiplexer serial multiplexer 4 1 multiplexer 8 1 multiplexer multiplex switch multiplexer switch usb multiplexer digital mux demultiplexer ic mux and demux optical multiplexer 16 to 1 multiplexer fiber multiplexer 4 1 mux analog signal multiplexer analog demultiplexer 2 1 multiplexer electronic multiplexers analog switch analog mux ic 2 to 1 multiplexer mux ic multiplexer and demultiplexer 16 ch...
published: 04 Apr 2017 -

8X1 Multiplexer
Digital Electronics: 8X1 Multiplexer Contribute: http://www.nesoacademy.org/donate Website ► http://www.nesoacademy.org/ Facebook ► https://goo.gl/Nt0PmB Twitter ► https://twitter.com/nesoacademy Pinterest ► http://www.pinterest.com/nesoacademy/
published: 08 Dec 2014 -

Implementation of Boolean Function using Multiplexers
Digital Electronics: Implementation of Boolean Function using Multiplexers Contribute: http://www.nesoacademy.org/donate Website ► http://www.nesoacademy.org/ Facebook ► https://goo.gl/Nt0PmB Twitter ► https://twitter.com/nesoacademy Pinterest ► http://www.pinterest.com/nesoacademy/
published: 07 Jan 2015 -

8:1 multiplexer
8:1 MUX || data selector Multiplexers in hindi Raul s tutorialmux analog multiplexer multiplexers digital multiplexer demultiplexer multiplexer ic multiplexer circuit multiplexer chip analogue multiplexer signal multiplexer analog multiplexer ic multiplexer analog multiplexer demultiplexer mux switch ic multiplexer 4 channel multiplexer 4 to 1 multiplexer mux multiplexer 8 to 1 multiplexer serial multiplexer 4 1 multiplexer 8 1 multiplexer multiplex switch multiplexer switch usb multiplexer digital mux demultiplexer ic mux and demux optical multiplexer 16 to 1 multiplexer fiber multiplexer 4 1 mux analog signal multiplexer analog demultiplexer 2 1 multiplexer electronic multiplexers analog switch analog mux ic 2 to 1 multiplexer mux ic multiplexer a...
published: 05 Apr 2017 -

Multiplexers Examples
Multiplexers Examples
published: 28 Oct 2014 -

Understanding a 2:1 Multiplexer
Here is a short video for understanding 2:1 Multiplexers
published: 14 Oct 2014 -

Analog Multiplexers
Learn about using analog multiplexers for adding more analog inputs to your microcontroller project.
published: 20 Mar 2017 -

Arduino MIDI Controller: Part 3 - Multiplexers
Part 3 of the Arduino Midi Controller project. This time we add more inputs with the help of Multiplexers. Visit Notes and Volts for full Parts List and Software Download http://www.notesandvolts.com/2016/07/arduino-midi-controller-multiplexers.html Like my videos? Please consider supporting Notes and Volts on Patreon https://www.patreon.com/notesandvolts
published: 11 Jul 2016 -

Multiplexer in Hindi
4x1 multiplexer, block diagram
published: 29 Mar 2017 -

8:1 multiplexer using 4:1 and 2:1 Multiplexers
8:1 multiplexer using 4:1 and 2:1 Multiplexers implementation of Boolean function using multiplexer 8:1 MUX || data selector Multiplexers in hindi Raul s tutorialmux analog multiplexer multiplexers digital multiplexer demultiplexer multiplexer ic multiplexer circuit multiplexer chip analogue multiplexer signal multiplexer analog multiplexer ic multiplexer analog multiplexer demultiplexer mux switch ic multiplexer 4 channel multiplexer 4 to 1 multiplexer mux multiplexer 8 to 1 multiplexer serial multiplexer 4 1 multiplexer 8 1 multiplexer multiplex switch multiplexer switch usb multiplexer digital mux demultiplexer ic mux and demux optical multiplexer 16 to 1 multiplexer fiber multiplexer 4 1 mux analog signal multiplexer analog demultiplexer 2 1 multipl...
published: 13 Apr 2017 -

SAYISAL ELEKTRONİK DERSLERİ: Veri Seçiciler (MULTİPLEXER)
N tane giriş içerisinden seçme uçları yardımıyla seçilen girişi çıkışa aktaran devrelere veri seçiciler (multiplexer) adı verilir. Bu dersimizde Multiplexer konusu anlatılacaktır. Sorularınızı yorum kısmına yazabilirsiniz. Sayısal Elektronik (Lojik-Dijital Elektronik-Mantık Devreleri) eğitim setinin tamamını izlemek için tıklayınız►►https://goo.gl/VWIocN Eğitim videosu hoşunuza gittiyse "beğenmeyi" unutmayın! En yeni videolardan haberdar olmak için buradan abone olabilirsiniz►►https://goo.gl/3uP9eU Eğitim Setlerimiz: -DEVRE ANALİZİ 1 Eğitim Setimiz ►►https://goo.gl/gLkn7D -DEVRE ANALİZİ 2 Eğitim Setimiz ►►https://goo.gl/jdh2M1 -SAYISAL ELEKTRONİK (LOJİK-MANTIK DEVRELERİ) Eğitim Setimiz►►https://goo.gl/VWIocN -PİC PROGRAMLAMA Eğitim Setimiz ►►https://goo.gl...
published: 23 Dec 2015 -

Introduction and working of Multiplexers
Multiplexers: Many to one..basics and working!!
published: 11 Nov 2013 -

implementation of Boolean function using multiplexer (first method)
implementation of Boolean function using multiplexer (first method) 8:1 MUX || data selector Multiplexers in hindi Raul s tutorialmux analog multiplexer multiplexers digital multiplexer demultiplexer multiplexer ic multiplexer circuit multiplexer chip analogue multiplexer signal multiplexer analog multiplexer ic multiplexer analog multiplexer demultiplexer mux switch ic multiplexer 4 channel multiplexer 4 to 1 multiplexer mux multiplexer 8 to 1 multiplexer serial multiplexer 4 1 multiplexer 8 1 multiplexer multiplex switch multiplexer switch usb multiplexer digital mux demultiplexer ic mux and demux optical multiplexer 16 to 1 multiplexer fiber multiplexer 4 1 mux analog signal multiplexer analog demultiplexer 2 1 multiplexer electronic multiplexers ana...
published: 12 Apr 2017 -

Multiplexer (MUX)- Data selector-Digital Electronics(English)
Lecture by Dr.M.Balasubramanian Multiplexer- Data selector-Digital Electronics(English). Multiplexer - MUX means many to one. Here the basic concept of MUX is explained with truth table and circuit is also designed.
published: 15 Apr 2017 -

Full adder using 4x1 Multiplexer(MUX) (2)- Digital Electronics (English)
Lecture by Dr.M.Balasubramanian Full adder using 4x1 Multiplexer -MUX (2)- Digital Electronics (English) Full adder truth table is explained and K-map is used to prepare implementation table . Than circuit is designed using 4x1 MUX
published: 17 Apr 2017 -

Multiplex
published: 23 Nov 2016 -

Multiplex
published: 23 Oct 2016 -

Multiplex
published: 14 Oct 2016 -

Multiplex
published: 04 May 2016 -

Multiplexer
published: 12 Dec 2015
Introduction to Multiplexers | MUX Basic
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 12:27
- Updated: 06 Dec 2014
- views: 318305
- published: 06 Dec 2014
- views: 318305
MULTIPLEXER
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:27
- Updated: 03 Apr 2017
- views: 13846
- published: 03 Apr 2017
- views: 13846
Digital Logic - Multiplexers
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:00
- Updated: 20 Apr 2013
- views: 93534
- published: 20 Apr 2013
- views: 93534
4X1 Multiplexer
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:52
- Updated: 08 Dec 2014
- views: 208049
- published: 08 Dec 2014
- views: 208049
GATE Lecture on Introduction to Multiplexer (part-1) (Digital Electronics) (Hindi Language )
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 18:42
- Updated: 11 Mar 2017
- views: 9875
- published: 11 Mar 2017
- views: 9875
4:1 MULTIPLEXER
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:27
- Updated: 04 Apr 2017
- views: 11690
- published: 04 Apr 2017
- views: 11690
8X1 Multiplexer
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:51
- Updated: 08 Dec 2014
- views: 190875
- published: 08 Dec 2014
- views: 190875
Implementation of Boolean Function using Multiplexers
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:34
- Updated: 07 Jan 2015
- views: 186029
- published: 07 Jan 2015
- views: 186029
8:1 multiplexer
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:29
- Updated: 05 Apr 2017
- views: 15629
- published: 05 Apr 2017
- views: 15629
Multiplexers Examples
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 21:34
- Updated: 28 Oct 2014
- views: 72874
- published: 28 Oct 2014
- views: 72874
Understanding a 2:1 Multiplexer
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:58
- Updated: 14 Oct 2014
- views: 21755
Analog Multiplexers
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 16:48
- Updated: 20 Mar 2017
- views: 415
- published: 20 Mar 2017
- views: 415
Arduino MIDI Controller: Part 3 - Multiplexers
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 20:10
- Updated: 11 Jul 2016
- views: 26264
- published: 11 Jul 2016
- views: 26264
Multiplexer in Hindi
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:45
- Updated: 29 Mar 2017
- views: 7636
- published: 29 Mar 2017
- views: 7636
8:1 multiplexer using 4:1 and 2:1 Multiplexers
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:32
- Updated: 13 Apr 2017
- views: 6134
- published: 13 Apr 2017
- views: 6134
SAYISAL ELEKTRONİK DERSLERİ: Veri Seçiciler (MULTİPLEXER)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 39:07
- Updated: 23 Dec 2015
- views: 21956
- published: 23 Dec 2015
- views: 21956
Introduction and working of Multiplexers
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:10
- Updated: 11 Nov 2013
- views: 24438
implementation of Boolean function using multiplexer (first method)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:20
- Updated: 12 Apr 2017
- views: 7908
- published: 12 Apr 2017
- views: 7908
Multiplexer (MUX)- Data selector-Digital Electronics(English)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 14:54
- Updated: 15 Apr 2017
- views: 1980
- published: 15 Apr 2017
- views: 1980
Full adder using 4x1 Multiplexer(MUX) (2)- Digital Electronics (English)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 11:42
- Updated: 17 Apr 2017
- views: 4423
- published: 17 Apr 2017
- views: 4423
Multiplex
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:36
- Updated: 23 Nov 2016
- views: 8
- published: 23 Nov 2016
- views: 8
Multiplex
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:11
- Updated: 23 Oct 2016
- views: 7
- published: 23 Oct 2016
- views: 7
Multiplex
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:46
- Updated: 14 Oct 2016
- views: 0
- published: 14 Oct 2016
- views: 0
Multiplex
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 43:37
- Updated: 04 May 2016
- views: 40
- published: 04 May 2016
- views: 40
Multiplexer
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 35:56
- Updated: 12 Dec 2015
- views: 106
- published: 12 Dec 2015
- views: 106

- Playlist
- Chat

- Playlist
- Chat

Introduction to Multiplexers | MUX Basic
- Report rights infringement
- published: 06 Dec 2014
- views: 318305

MULTIPLEXER
- Report rights infringement
- published: 03 Apr 2017
- views: 13846

Digital Logic - Multiplexers
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Apr 2013
- views: 93534

4X1 Multiplexer
- Report rights infringement
- published: 08 Dec 2014
- views: 208049

GATE Lecture on Introduction to Multiplexer (part-1) (Digital Electronics) (Hindi Language )
- Report rights infringement
- published: 11 Mar 2017
- views: 9875

4:1 MULTIPLEXER
- Report rights infringement
- published: 04 Apr 2017
- views: 11690

8X1 Multiplexer
- Report rights infringement
- published: 08 Dec 2014
- views: 190875

Implementation of Boolean Function using Multiplexers
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Jan 2015
- views: 186029

8:1 multiplexer
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Apr 2017
- views: 15629

Multiplexers Examples
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Oct 2014
- views: 72874

Understanding a 2:1 Multiplexer
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Oct 2014
- views: 21755

Analog Multiplexers
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Mar 2017
- views: 415

Arduino MIDI Controller: Part 3 - Multiplexers
- Report rights infringement
- published: 11 Jul 2016
- views: 26264

Multiplexer in Hindi
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Mar 2017
- views: 7636
Ex-CIA director quits Harvard over Chelsea Manning posting
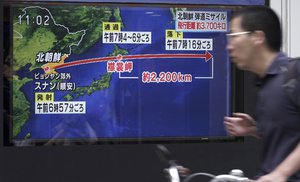
Edit Graphic 15 Sep 2017'Missile launch, take cover': Japan's terrifying wake-up call
Edit Deccan Herald 15 Sep 2017Police Investigating 'Terrorist Incident' At London Station Leaving 22 People Injured
Edit WorldNews.com 15 Sep 2017National Hurricane Center Says Tropical Storm Jose's Path Shifts West Toward U.S.
Edit WorldNews.com 14 Sep 2017Heavy Rain Lashes Penang, Causing Floods, Landslides And Uprooting Trees
Edit Malaysian National News Agency 15 Sep 2017ONAM BOX OFFICE: Mammootty & Mohanlal Movies Overpowered At The Kochi Multiplexes?
Edit One India 15 Sep 2017Republic of Uzbekistan Lays Groundwork for Move to Digital Television with SES Video
Edit Market Watch 15 Sep 2017LTC4418 dual input power prioritiser.
Edit Eweekly 15 Sep 2017Priyanka Chopra’s Sikkim comment not isolated, she called the state ‘trouble spot’ before too
Edit Hindustan Times 15 Sep 201710 Insane TV Theories You Won't Believe
Edit What Culture 15 Sep 2017Defensive steps against EMP attacks must be taken at command centers
Edit The Japan News 15 Sep 2017No Number of Exclamation Points Will Prepare You for Mother!
Edit Slate 15 Sep 2017How a Sylvester Stallone film unlocked door to China market for smaller foreign films
Edit South China Morning Post 14 Sep 2017Yes, Louis C.K. dares to go there: No stranger to upending convention, he puts sexual ...
Edit Sacramento Bee 14 Sep 2017Sexual taboo at heart of Louis C.K.’s ‘Daddy’
Edit The Recorder 14 Sep 2017Women hold forte
Edit The Hindu 14 Sep 2017Immunoassays Markets
Edit Market Watch 14 Sep 2017Superstars vs ensemble cast: How a group of good actors is winning against the biggies
Edit Hindustan Times 14 Sep 2017- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »