- published: 03 Dec 2014
- views: 545
-
remove the playlistCopula (linguistics)
- remove the playlistCopula (linguistics)
- published: 24 Sep 2012
- views: 2132
- published: 27 Jul 2014
- views: 213565
- published: 06 Dec 2015
- views: 1371
- published: 10 Jul 2016
- views: 132618
- published: 27 Sep 2010
- views: 65398
- published: 14 Nov 2011
- views: 106344
- published: 24 Aug 2012
- views: 122323
- published: 12 Apr 2015
- views: 405
Copula (linguistics)
In linguistics, a copula (plural: copulas or copulae) is a word used to link the subject of a sentence with a predicate (a subject complement), such as the word is in the sentence "The sky is blue." The word copula derives from the Latin noun for a "link" or "tie" that connects two different things.
A copula is often a verb or a verb-like word, though this is not universally the case. A verb that is a copula is sometimes called a copulative or copular verb. In English primary education grammar courses, a copula is often called a linking verb. In other languages, copulas show more resemblances to pronouns, as in Classical Chinese and Guarani, or may take the form of suffixes attached to a noun, as in Beja, Ket, and Inuit languages.
Most languages have one main copula, although some (such as Spanish, Portuguese and Thai) have more than one, and some have none. In the case of English, this is the verb to be. While the term copula is generally used to refer to such principal forms, it may also be used to refer to some other verbs with similar functions, like become, get, feel and seem in English (these may also be called "semi-copulas" or "pseudo-copulas").
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
Structural linguistics
Structural linguistics is an approach to linguistics originating from the work of Swiss linguist Ferdinand de Saussure and is part of the overall approach of structuralism. De Saussure's Course in General Linguistics, published posthumously in 1916, stressed examining language as a static system of interconnected units. He is thus known as a father of modern linguistics for bringing about the shift from diachronic (historical) to synchronic (non-historical) analysis, as well as for introducing several basic dimensions of semiotic analysis that are still important today, such as syntagmatic and paradigmatic analysis (or 'associations' as Saussure was still calling them).
Structural linguistics involves collecting a corpus of utterances and then attempting to classify all of the elements of the corpus at their different linguistic levels: the phonemes, morphemes, lexical categories, noun phrases, verb phrases, and sentence types. Two of Saussure's key methods were syntagmatic and paradigmatic analysis, which define units syntactically and lexically, respectively, according to their contrast with the other units in the system.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 3:15
3:15Copula 'Be' & Subject-Verb Agreement
Copula 'Be' & Subject-Verb AgreementCopula 'Be' & Subject-Verb Agreement
-
 32:40
32:40The Copula & Subject-Verb Agreement
The Copula & Subject-Verb AgreementThe Copula & Subject-Verb Agreement
A mini-lecture on teaching ELLs the BE verb (the copula and & auxiliary verb) and Subjcect-Verb Agreement -
 13:53
13:53Basic English Grammar: What is an auxiliary verb?
Basic English Grammar: What is an auxiliary verb?Basic English Grammar: What is an auxiliary verb?
Important basic English grammar lesson. When you're teaching yourself English, there are aspects of basic grammar that you don't know about or understand. This makes it sometimes difficult to understand your English lessons. That's why today I'm telling you all about "auxiliary verbs" -- also known as "helper verbs". They are extra verbs in the sentence that don't usually contribute to the main meaning of the sentence. They usually just show you what verb tense the sentence is. I explain everything you need to know about them, and how to find them in a sentence. Let's get started! Test yourself with the quiz at http://www.engvid.com/basic-english-grammar-auxiliary-verb/ TRANSCRIPT Hi. I'm Jade. What we're talking about today is auxiliary verbs. You don't have to be scared of that word, "auxiliary", because it's a grammar word. Basically, what they are is they're helper verbs. They are not the most important verb in the sentence, but they're important so we know what tense it is. So the reason I made this lesson today is I found that people who taught English to themselves get to a point where some confusion comes in because if you're watching videos about learning English and things like that, sometimes, you're going to hear grammar words that you're not sure about. And then, some confusion can happen. So if the teacher says, "Find the verb in the sentence", sometimes, what happens is you just find the verb you know, but you don't realize that it's not the important verb there. So the whole idea of this lesson is to just teach you a bit of grammar so that you don't get confused in the future when you're watching videos and things like that. So yeah. They're helper verbs. They're not the most important verb in the sentence. There can be more than one of them in a sentence and even still not being the main verb. It's important because it will help you to recognize the tense, the different tenses of English. Maybe you don't use all the tenses actively, but it's still good to be able to recognize them. And also, the most important thing about auxiliary verbs is that it's not helpful for you to directly translate these words because you'll just get a really confusing, confusing meaning. And sometimes, that's a mistake people make. So what we're going to do is go through the different auxiliary verbs in English and look at the different ways that we use them. So the first one you might not think of as being a helping verb, but it's a good example of what I mean when you see the verb, and then you try to translate it, and it doesn't really give you a good meaning; it doesn't really explain what it means well. The best example of that is "be" in the present and past simple. "She is my boss." What does "be" mean? What does it -- what does "be" mean? I don't know. I was personally confused about that even though I didn't need to learn English. And what it's doing is being a linking verb. In grammar terms, all it's doing is joining subject to object. It doesn't carry its own meaning, you could say. So in that sense, the verb isn't that important here. It's the subject and the object that are important. Anyway. The next examples, they start to get a little more complicated, but not too bad. Another example of "be", but this time in the continuous sentence -- in the continuous tenses. "He is sleeping." Let's have a think. What tense is that one? That one is the present continuous. And this one, "They have been talking." This one is the present perfect continuous. And what I mean by "auxiliary verb" in these is that they're not the most important verb in those examples. The most important verb is "sleeping" here. And the most important verb is "talking" here. In this example, the present perfect continuous actually has two auxiliaries because you can have more than one auxiliary verb in a sentence. Next example. "Have" in the perfect tenses. We've got two examples here. We've got, "I've got a car" and, "They had gone home." What tenses are we talking about here? "I've got a car." That one is the present perfect. And what about this one? What's this one? This one is the past perfect. Where's the most important verb? The most important verb is "get" here. We're using it for possession. It means "to own something, to possess something" here. In the second example, the most important verb is "go". This is a past participle. It becomes "gone". Let's move on to "do" -- our first example of "do". When we're making a negative sentence in the present simple or the past simple, in the negative form, we use "do". Let's look at the examples. "I do not like Peter." I'm sorry, Peter. "Do" shows us that we're making a negative sentence. What's the most important verb? The most important verb is "like". What about next example? "We didn't go." Again -- naughty me -- no full stop. The most important verb is "go". There's our negative, this time in a contracted form. -
 15:53
15:53Structural linguistics
Structural linguisticsStructural linguistics
Structural linguistics is an approach to linguistics originating from the work of Swiss linguist Ferdinand de Saussure and is part of the overall approach of structuralism. De Saussure's Course in General Linguistics, published posthumously in 1916, stressed examining language as a static system of interconnected units. He is thus known as a father of modern linguistics for bringing about the shift from diachronic to synchronic analysis, as well as for introducing several basic dimensions of semiotic analysis that are still important today, such as syntagmatic and paradigmatic analysis. Structural linguistics involves collecting a corpus of utterances and then attempting to classify all of the elements of the corpus at their different linguistic levels: the phonemes, morphemes, lexical categories, noun phrases, verb phrases, and sentence types. Two of Saussure's key methods were syntagmatic and paradigmatic analysis, which define units syntactically and lexically, respectively, according to their contrast with the other units in the system. This video is targeted to blind users. Attribution: Article text available under CC-BY-SA Creative Commons image source in video -
 14:40
14:40The Kurdish Language
The Kurdish LanguageThe Kurdish Language
► Learn a language online with native teachers. Special italki "buy 1 get 1 free" offer for Langfocus viewers: http://go.italki.com/1Ojye8x **THIS CHANNEL IS ABOUT LANGUAGES OF THE WORLD, NOT POLITICS. I RESERVE THE RIGHT TO DELETE ANY COMMENTS ABOUT POLITICS, ESPECIALLY VIOLENT OR RACIST COMMENTS. PLEASE TALK ABOUT THE *LANGUAGE*. Thank you! ** Today's video is about the Kurdish language, spoken by the Kurdish people in the Kurdish region. Special thanks to Haqqi Bahram and Aram Rafeq for their voice recordings and their explanations of Kurmanji/Sorani sentences; and İbrahim Halil Yücedil for answering my numerous questions about Kurdish. Support Langfocus on Patreon: http://patreon.com/langfocus Special thanks to: Nicholas Shelokov, Sebastian Langshaw, Brandon Gonzalez, Brian Michalowski, Adrian Zhang, Vadim Sobolev, Yixin Alfred Wong, Kaan Ergen, Sky Vied, Romain Paulus, Panot, Erik Edelmann, Bennet, James Zavaleta, Ulrike Baumann, Ian Martyn, Justin Faist, Jeff Miller, Stephen Lawson, Howard Stratton, George Greene, Panthea Madjidi, Nicholas Gentry, Sergios Tsakatikas, Bruno Filippi, Sergio Tsakatikas, Qarion, and Pedro Flores for their generous Patreon support. http://facebook.com/langfocus http://instagram.com/langfocus http://twitter.com/langfocus http://langfocus.com Sources of intro Kurdistan clips: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=n7kk93CXhHA https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qdX8WJvZboc https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Kr8LiVwabqQ Music: Main music: "Strength in" by The Passion Hi-Fi. This track is unequivocally free for commercial use. Do not try to copyright claim this video. Source: https://www.soundclick.com/bands/page_songInfo.cfm?bandID=156970&songID;=11939997 Intro: "Take You" by Vibe Tracks. Outro: "TFB3" by Vibe Tracks. -
 20:56
20:56Linguistics Tense Aspect Modality System
Linguistics Tense Aspect Modality System -
 7:16
7:16Phrase Structure Rules
Phrase Structure RulesPhrase Structure Rules
Step by Step Explanation. I am no expert! Just did it to practice and help other classmates. -
 10:55
10:55Human Language Sentences - Basic Parse Trees, X-Bar Theory & Ambiguity -- Linguistics 101
Human Language Sentences - Basic Parse Trees, X-Bar Theory & Ambiguity -- Linguistics 101Human Language Sentences - Basic Parse Trees, X-Bar Theory & Ambiguity -- Linguistics 101
A short introduction to modern grammars of natural language. Use the fundamentals of generative grammar to learn about syntax (the grammar & rules of sentences). Follow along as I work through the structure of a simple sentence, building a parse tree for that sentence with X-Bar Theory. Learn to walk through the tree, compare types of structures and identify ambiguities. Basic but helpful for nonspecialists interested in computational grammars, the syntax of native & foreign languages, and natural language processing. Online text version of this lesson: http://www.nativlang.com/linguistics/grammar-xbar-lessons.php To learn more about word classes and word formation (nouns, verbs, morphemes, affixes), please visit: http://www.nativlang.com/linguistics/grammar-morphology-lessons.php If you're rusty on the grammar of sentences (clauses, phrases, rules), please visit: http://www.nativlang.com/linguistics/grammar-syntax-lessons.php I mention two previous lessons during the video ("Introduction to the Grammar of Sentences" and "The Verb & Its Arguments"): http://www.nativlang.com/linguistics/grammar-syntax-lessons.php http://www.nativlang.com/linguistics/grammar-morphosyntax-lessons.php -
![[HD] INDO-EUROPEAN ORIGIN; updated 24 Aug 2012; published 24 Aug 2012](http://web.archive.org./web/20170525004614im_/https://i.ytimg.com/vi/DpbjquTQT98/0.jpg) 4:44
4:44[HD] INDO-EUROPEAN ORIGIN
[HD] INDO-EUROPEAN ORIGIN[HD] INDO-EUROPEAN ORIGIN
The Proto-Indo-Europeans were the speakers of the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE), an unattested but now reconstructed prehistoric language. Knowledge of them comes chiefly from the linguistic reconstruction, along with material evidence from archaeology and archaeogenetics. Linguistic reconstruction is fraught with significant uncertainties and room for speculation, and PIE speakers cannot be assumed to have been a single, identifiable people or tribe. Rather, they were a group of loosely related populations ancestral to the later, still partially prehistoric, Bronze Age Indo-Europeans. The Proto-Indo-Europeans in this sense likely lived during the Copper Age, or roughly the 5th to 4th millennia BC. Mainstream scholarship places them in the general region of the Pontic-Caspian steppe in Eastern Europe and Central Asia. Some scholars would extend the time depth of PIE or Pre-PIE to the Neolithic or even the last glacial maximum, and suggest alternative location hypotheses. By the mid-2nd millennium BC offshoots of the Proto-Indo-Europeans had reached Anatolia, the Aegean, Northern India, and likely Western Europe. MUSIC: Prince of Persia Movie MAIN THEME -
 0:53
0:53Copula Meaning
Copula MeaningCopula Meaning
Video shows what copula means. A word, usually a verb, used to link the subject of a sentence with a predicate (usually a subject complement or an adverbial), that unites or associates the subject with the predicate.. A function that represents the association between two or more variables, independent of the individual marginal distributions of the variables.. A device that connects two or more keyboards of an organ.. copula synonyms: linking verb, copular, copular verb. copula pronunciation. How to pronounce, definition by Wiktionary dictionary. copula meaning. Powered by MaryTTS
-

Copula 'Be' & Subject-Verb Agreement
published: 03 Dec 2014 -

The Copula & Subject-Verb Agreement
A mini-lecture on teaching ELLs the BE verb (the copula and & auxiliary verb) and Subjcect-Verb Agreement
published: 24 Sep 2012 -

Basic English Grammar: What is an auxiliary verb?
Important basic English grammar lesson. When you're teaching yourself English, there are aspects of basic grammar that you don't know about or understand. This makes it sometimes difficult to understand your English lessons. That's why today I'm telling you all about "auxiliary verbs" -- also known as "helper verbs". They are extra verbs in the sentence that don't usually contribute to the main meaning of the sentence. They usually just show you what verb tense the sentence is. I explain everything you need to know about them, and how to find them in a sentence. Let's get started! Test yourself with the quiz at http://www.engvid.com/basic-english-grammar-auxiliary-verb/ TRANSCRIPT Hi. I'm Jade. What we're talking about today is auxiliary verbs. You don't have to be scared of that word, "...
published: 27 Jul 2014 -

Structural linguistics
Structural linguistics is an approach to linguistics originating from the work of Swiss linguist Ferdinand de Saussure and is part of the overall approach of structuralism. De Saussure's Course in General Linguistics, published posthumously in 1916, stressed examining language as a static system of interconnected units. He is thus known as a father of modern linguistics for bringing about the shift from diachronic to synchronic analysis, as well as for introducing several basic dimensions of semiotic analysis that are still important today, such as syntagmatic and paradigmatic analysis. Structural linguistics involves collecting a corpus of utterances and then attempting to classify all of the elements of the corpus at their different linguistic levels: the phonemes, morphemes, lexical cat...
published: 06 Dec 2015 -

The Kurdish Language
► Learn a language online with native teachers. Special italki "buy 1 get 1 free" offer for Langfocus viewers: http://go.italki.com/1Ojye8x **THIS CHANNEL IS ABOUT LANGUAGES OF THE WORLD, NOT POLITICS. I RESERVE THE RIGHT TO DELETE ANY COMMENTS ABOUT POLITICS, ESPECIALLY VIOLENT OR RACIST COMMENTS. PLEASE TALK ABOUT THE *LANGUAGE*. Thank you! ** Today's video is about the Kurdish language, spoken by the Kurdish people in the Kurdish region. Special thanks to Haqqi Bahram and Aram Rafeq for their voice recordings and their explanations of Kurmanji/Sorani sentences; and İbrahim Halil Yücedil for answering my numerous questions about Kurdish. Support Langfocus on Patreon: http://patreon.com/langfocus Special thanks to: Nicholas Shelokov, Sebastian Langshaw, Brandon Gonzalez, Brian Michal...
published: 10 Jul 2016 -

-

Phrase Structure Rules
Step by Step Explanation. I am no expert! Just did it to practice and help other classmates.
published: 27 Sep 2010 -

Human Language Sentences - Basic Parse Trees, X-Bar Theory & Ambiguity -- Linguistics 101
A short introduction to modern grammars of natural language. Use the fundamentals of generative grammar to learn about syntax (the grammar & rules of sentences). Follow along as I work through the structure of a simple sentence, building a parse tree for that sentence with X-Bar Theory. Learn to walk through the tree, compare types of structures and identify ambiguities. Basic but helpful for nonspecialists interested in computational grammars, the syntax of native & foreign languages, and natural language processing. Online text version of this lesson: http://www.nativlang.com/linguistics/grammar-xbar-lessons.php To learn more about word classes and word formation (nouns, verbs, morphemes, affixes), please visit: http://www.nativlang.com/linguistics/grammar-morphology-lessons.php ...
published: 14 Nov 2011 -
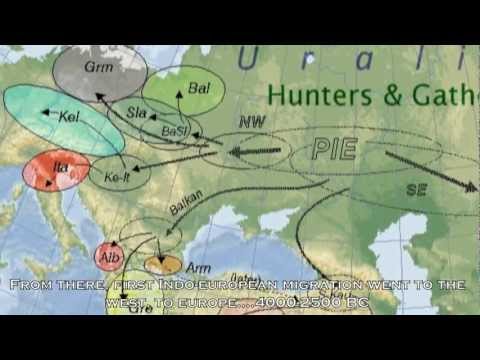
[HD] INDO-EUROPEAN ORIGIN
The Proto-Indo-Europeans were the speakers of the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE), an unattested but now reconstructed prehistoric language. Knowledge of them comes chiefly from the linguistic reconstruction, along with material evidence from archaeology and archaeogenetics. Linguistic reconstruction is fraught with significant uncertainties and room for speculation, and PIE speakers cannot be assumed to have been a single, identifiable people or tribe. Rather, they were a group of loosely related populations ancestral to the later, still partially prehistoric, Bronze Age Indo-Europeans. The Proto-Indo-Europeans in this sense likely lived during the Copper Age, or roughly the 5th to 4th millennia BC. Mainstream scholarship places them in the general region of the Pontic-Caspian steppe...
published: 24 Aug 2012 -

Copula Meaning
Video shows what copula means. A word, usually a verb, used to link the subject of a sentence with a predicate (usually a subject complement or an adverbial), that unites or associates the subject with the predicate.. A function that represents the association between two or more variables, independent of the individual marginal distributions of the variables.. A device that connects two or more keyboards of an organ.. copula synonyms: linking verb, copular, copular verb. copula pronunciation. How to pronounce, definition by Wiktionary dictionary. copula meaning. Powered by MaryTTS
published: 12 Apr 2015
Copula 'Be' & Subject-Verb Agreement
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:15
- Updated: 03 Dec 2014
- views: 545
- published: 03 Dec 2014
- views: 545
The Copula & Subject-Verb Agreement
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 32:40
- Updated: 24 Sep 2012
- views: 2132
- published: 24 Sep 2012
- views: 2132
Basic English Grammar: What is an auxiliary verb?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 13:53
- Updated: 27 Jul 2014
- views: 213565
- published: 27 Jul 2014
- views: 213565
Structural linguistics
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 15:53
- Updated: 06 Dec 2015
- views: 1371
- published: 06 Dec 2015
- views: 1371
The Kurdish Language
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 14:40
- Updated: 10 Jul 2016
- views: 132618
- published: 10 Jul 2016
- views: 132618
Linguistics Tense Aspect Modality System
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 20:56
- Updated: 15 Nov 2012
- views: 2796
Phrase Structure Rules
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:16
- Updated: 27 Sep 2010
- views: 65398
- published: 27 Sep 2010
- views: 65398
Human Language Sentences - Basic Parse Trees, X-Bar Theory & Ambiguity -- Linguistics 101
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:55
- Updated: 14 Nov 2011
- views: 106344
- published: 14 Nov 2011
- views: 106344
[HD] INDO-EUROPEAN ORIGIN
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:44
- Updated: 24 Aug 2012
- views: 122323
- published: 24 Aug 2012
- views: 122323
Copula Meaning
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:53
- Updated: 12 Apr 2015
- views: 405
- published: 12 Apr 2015
- views: 405

- Playlist
- Chat

- Playlist
- Chat

Copula 'Be' & Subject-Verb Agreement
- Report rights infringement
- published: 03 Dec 2014
- views: 545

The Copula & Subject-Verb Agreement
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 Sep 2012
- views: 2132

Basic English Grammar: What is an auxiliary verb?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 27 Jul 2014
- views: 213565

Structural linguistics
- Report rights infringement
- published: 06 Dec 2015
- views: 1371

The Kurdish Language
- Report rights infringement
- published: 10 Jul 2016
- views: 132618


Phrase Structure Rules
- Report rights infringement
- published: 27 Sep 2010
- views: 65398

Human Language Sentences - Basic Parse Trees, X-Bar Theory & Ambiguity -- Linguistics 101
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Nov 2011
- views: 106344

[HD] INDO-EUROPEAN ORIGIN
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 Aug 2012
- views: 122323

Copula Meaning
- Report rights infringement
- published: 12 Apr 2015
- views: 405
NYT: Trump Told Duterte Two U.S. Nuclear Subs Patrolling Korean Waters
Edit WorldNews.com 24 May 2017Younger Brother Of Manchester Bomber Likely Planned Libyan Attack, Authorities Say
Edit WorldNews.com 24 May 2017S. Korea fires warning shots at North balloons
Edit The Japan News 24 May 2017Melania and Ivanka Trump Wore Veils to Meet the Pope
Edit Time Magazine 24 May 2017Massive Landslide In California Decimates Iconic Coastal Highway 1
Edit WorldNews.com 24 May 2017Mumbai Cricket Association bans 16 players for being over-aged
Edit Cricket Country 04 May 2017Poem of the week: Signals from the Simple Life by Lorna Goodison
Edit The Guardian 01 May 2017YIT's (YITYY) CEO Kari Kauniskangas on Q1 2017 Results - Earnings Call Transcript
Edit Seeking Alpha 29 Apr 2017How banks can aggregate individual risk exposures
Edit Graphic 24 Jan 2017Sound smart in Japanese / The weather was very beautiful.
Edit The Japan News 26 Oct 2016Why I'm Fascinated By Parasitic Worms
Edit National Public Radio 13 Aug 2016Harrogate: Yorkshire’s gem
Edit Belfast Telegraph 05 Aug 2016The Fascinating Lexicography of a Dirty Adjective
Edit Slate 26 May 2016Sound Smart in Japanese / “What country are you from?”
Edit The Japan News 10 May 2016Graveyard Clay/Cré na Cille review: New lease of life for Irish classic
Edit The Irish Times 09 Apr 2016$1.45 million San Marco Place penthouse for sale
Edit Business Journal 01 Apr 2016Hillary Clinton’s Speech to Goldman Sachs
Edit CounterPunch 26 Feb 2016Being a Beast by Charles Foster review – a true walk on the wild side
Edit The Guardian 14 Feb 2016- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »








