-
remove the playlistMtdna
- remove the playlistMtdna












Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in organelles called mitochondria, structures within eukaryotic cells that convert the chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Most other DNA present in eukaryotic organisms is found in the cell nucleus.
Mitochondrial DNA can be regarded as the smallest chromosome, and was the first significant part of the human genome to be sequenced. In most species, including humans, mtDNA is inherited solely from the mother.
The DNA sequence of mtDNA has been determined from a large number of organisms and individuals (including some organisms that are extinct), and the comparison of those DNA sequences represents a mainstay of phylogenetics, in that it allows biologists to elucidate the evolutionary relationships among species. It also permits an examination of the relatedness of populations, and so has become important in anthropology and field biology.
Nuclear and mitochondrial DNA are thought to be of separate evolutionary origin, with the mtDNA being derived from the circular genomes of the bacteria that were engulfed by the early ancestors of today's eukaryotic cells. This theory is called the endosymbiotic theory. Each mitochondrion is estimated to contain 2-10 mtDNA copies. In the cells of extant organisms, the vast majority of the proteins present in the mitochondria (numbering approximately 1500 different types in mammals) are coded for by nuclear DNA, but the genes for some of them, if not most, are thought to have originally been of bacterial origin, having since been transferred to the eukaryotic nucleus during evolution.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
Chromosome (24) mtDNA - Lynn Margulis and the mitochondrial DNA
Chromosome (24) mtDNA - Lynn Margulis and the mitochondrial DNA -
Our mtDNA ancestor
Our mtDNA ancestorOur mtDNA ancestor
mtDNA is our mitochondrial DNA. mtDNA is a circular piece of DNA. It is passed only through the egg (not sperm). So, it can be used to trace back through the... -
Family Tree DNA Results Explained: mtDNA Matching & Genealogy
Family Tree DNA Results Explained: mtDNA Matching & GenealogyFamily Tree DNA Results Explained: mtDNA Matching & Genealogy
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is passed down almost unchanged from a mother to her children. Family Tree DNA’s mtDNA tests enable you to trace your maternal line using the world’s largest mtDNA database. In this webinar, attendees will learn how to read and understand your mtDNA results and matches, and how to use those matches in conjunction with your genealogy research. mtDNA results pages covered: Matches, Ancestral Origins, Matches Maps, Results -
mtDNA Tutorial
mtDNA TutorialmtDNA Tutorial
Learn how mtDNA can be used to trace your maternal ancestry. -
Family Tree DNA Results Explained: mtDNA Haplogroups & Deep Ancestry
Family Tree DNA Results Explained: mtDNA Haplogroups & Deep AncestryFamily Tree DNA Results Explained: mtDNA Haplogroups & Deep Ancestry
In addition to genealogical matching, mtDNA testing uncovers the deep ancestry of your direct maternal line. This webinar focuses on mtDNA haplogroups and how they relate to your deep ancestry. mtDNA results pages covered: Results (Haplogroup section), Matches (mtDNA Haplogroup column), Haplogroup Origins, Migration Maps -
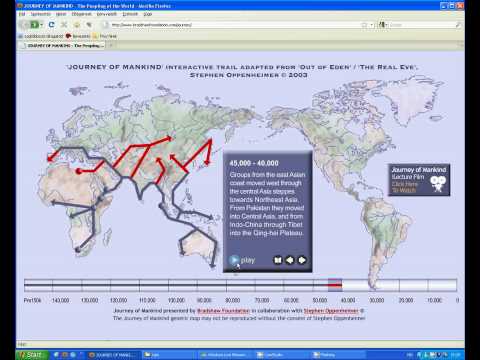
MAP OF MIGRATIONS OF MTDNA MARKERS- HUMAN MIGGRATIONS MAP
MAP OF MIGRATIONS OF MTDNA MARKERS- HUMAN MIGGRATIONS MAPMAP OF MIGRATIONS OF MTDNA MARKERS- HUMAN MIGGRATIONS MAP
http://www.bradshawfoundation.com/journey/ MTDNA. -
IBIS 2009 : 03 : Intro to mtDNA
IBIS 2009 : 03 : Intro to mtDNAIBIS 2009 : 03 : Intro to mtDNA
Part of the free online training workshop "Mitochondrial and STR DNA Analysis by Mass Spectrometry Using the Ibis Biosciences, Inc. Platform" at the NFSTC - ... -
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNAMitochondrial DNA
For more information, log on to- http://shomusbiology.weebly.com/ Download the study materials here- http://shomusbiology.weebly.com/bio-materials.html Mitoc... -
On the Origins of mtDNA Haplogroup V
On the Origins of mtDNA Haplogroup VOn the Origins of mtDNA Haplogroup V
Origins of mtDNA Haplogroup V. From Asturias/Cantabria, northern Spain to me in northern Portugal. Haplogroup V has been in Iberia since Upper Paleolithic ti... -
European mtDNA and Y-DNA Haplogroups
European mtDNA and Y-DNA HaplogroupsEuropean mtDNA and Y-DNA Haplogroups
Classification of the regional genetic European Haplotypes, and it's geographical predominance. I1: pre.Germanic (Nordic) - {Blue} I2: pre-Celto-Germanic - {Blue} I2a1: Sardinian, Iberian - {Blue} I2a2: Dinarc, Danubian - {Blue} N1c1: Uralo-Finic, Baltic, Siberian - {Ligh Yellow} R1a: Balto-Slavic, Germanic, Indo-Iranian - {Yellow} R1b: Italo-Celtic, Germanic, Hittie, Armenian, Tocharian - {Purple/Red} E1b1b: North African, Near Eastern, Balkanic - {Gray} J1: Caucasian, Mesopotamian, Semitic (Jewish, Arabic) - {Dark Green} J2: Greco-Anatolian, Mesopotamian, Caucasian - {Light Green} Note: Only the main Haplogrous have annotations. (Removabl -
Advanced Topics at Family Tree DNA: mtDNA
Advanced Topics at Family Tree DNA: mtDNAAdvanced Topics at Family Tree DNA: mtDNA
The Advanced Topics series goes beyond the Family Tree DNA Results Explained series, providing more in-depth detail about the genetics and usage of the tests offered by Family Tree DNA. Part 2 of this series focuses on mtDNA. Topics include Advanced Matching, mtDNA nomenclature, and mtDNA Haplogroups. -
NUNOLOGY CLASS #2 - THE POWER OF 9ETHER, MTDNA, NATURAL HAIR AND THE AFRICAN WOMAN!
NUNOLOGY CLASS #2 - THE POWER OF 9ETHER, MTDNA, NATURAL HAIR AND THE AFRICAN WOMAN!NUNOLOGY CLASS #2 - THE POWER OF 9ETHER, MTDNA, NATURAL HAIR AND THE AFRICAN WOMAN!
TUNE INTO NUNOLOGY CLASS # 2: In this Class you will learn: What is the Power of 9ETHER? and How we NUNOLOGIST see and view it! Why So Many Sisters in America and World Over are now going Natural? Why Women are 1st before Man? And so much more... Nunology Online Classes are present to you by: THE ETERNAL TEMPLE OF NUN Visit us @ http://www.nupu-nun.com/ For More Information about "THE SCIENCE OF NUNOLOGY" -
Irrefutable Proof of Evolution- Part 1 (mtDNA, ERVs, Fusion)
Irrefutable Proof of Evolution- Part 1 (mtDNA, ERVs, Fusion)Irrefutable Proof of Evolution- Part 1 (mtDNA, ERVs, Fusion)
EXPAND ME Irrefutable proof of evolution, along with their 'rebuttals'. ERV human chromosome 2 neanderthal mtDNA DNA summation. Yes, Im using the term proof.... -
mtdna U5a1
mtdna U5a1mtdna U5a1
mtdna haplogroup U5a1, the Clan of Ursula © Druidikal Music 2013.
- Adenylate kinase
- Agnate
- Alanine
- ALDH2
- Aldosterone synthase
- Alexandra of Denmark
- Anthropology
- Antisense RNA
- Arginine
- Asparagine
- Aspartic acid
- ATP synthase
- ATP synthase chain A
- Austria
- Bacteria
- Base pair
- Biochemistry
- Blastocyst
- BMC Biol.
- Bryan Sykes
- Cell nucleus
- Cell signaling
- Chloroplast DNA
- Chromosome
- Ciliate
- Circular DNA
- Citrate synthase
- Citric acid cycle
- Cloning vector
- Cnidaria
- Complementary DNA
- CORR Hypothesis
- Cosmid
- Creatine kinase
- Cucumis sativus
- Cysteine
- Cytochrome b
- Cytochrome c
- Cytochrome c oxidase
- Deoxynucleotides
- DNA
- DNA polymerase
- DNA repair
- Electron microscope
- Embryo
- Embryogenesis
- Endosymbiotic theory
- Eukaryotic
- Evolution
- Evolutionary
- Evolutionary tree
- Exercise intolerance
- Fosmid
- Frataxin
- Fumarase
- GDNA
- Genetic genealogy
- Glutamic acid
- Glutamine
- Glycine
- Glycol nucleic acid
- Gottfried Schatz
- Green alga
- Guide RNA
- Hans Tuppy
- Haplogroup
- Heteroplasmy
- Histidine
- Human
- Human genome
- In vitro
- In vivo
- Inner cell mass
- Isoleucine
- Jesse James
- Kynureninase
- Lambda phage
- Leucine
- Locked nucleic acid
- Lysine
- Magicicada
- Malate dehydrogenase
- Mammal
- Matrilineage
- Matrilineality
- Medical faculty
- Messenger RNA
- Metazoans
- Methionine
- MicroRNA
- Missing person
- Mitochondria
- Mitochondrial DNA
- Mitochondrial Eve
- Mitochondrial matrix
- Mitochondrion
- Molecule
- Monoamine oxidase
- Morpholino
- MT-ATP6
- MT-ATP8
- MT-CO1
- MT-CO2
- MT-CO3
- MT-CYB
- MT-ND1
- MT-ND2
- MT-ND3
- MT-ND4
- MT-ND4L
- MT-ND5
- MT-ND6
- MT-RNR1
- MT-RNR2
- MT-TA
- MT-TC
- MT-TD
- MT-TE
- MT-TF
- MT-TG
- MT-TH
- MT-TI
- MT-TK
- MT-TL1
- MT-TL2
- MT-TM
- MT-TN
- MT-TP
- MT-TQ
- MT-TR
- MT-TS1
- MT-TS2
- MT-TT
- MT-TW
- MT-TY
- Mussel
- Mutation rate
- NADH dehydrogenase
- Nature (journal)
- Non-coding RNA
- Nuclear DNA
- Nucleic acid
- Nucleobases
- Nucleosides
- Nucleotides
- Oocyte
- Organelles
- Pathogen
- Peptide nucleic acid
- Phagemid
- Phenylalanine
- Phylogenetics
- Phylogeny
- Piwi-interacting RNA
- Plasmid
- PMPCB
- POLG
- POLG2
- Precursor mRNA
- Proline
- Prostate biopsy
- PubMed Central
- PubMed Identifier
- Replication
- Respiratory chain
- Ribosomal RNA
- RNA
- RNA interference
- RRNA
- Science (journal)
- Serine
- Sexual reproduction
- Single origin theory
- Small hairpin RNA
- Small nuclear RNA
- Small nucleolar RNA
- Small temporal RNA
- Sperm
- Spermatozoon
- Steroidogenesis
- Subgenomic RNA
- Sutherland RNA
- Telomer
- Telomerase
- Template Alcohols
- Template AminoAcids
- Template Centrosome
- Template Eicosanoids
- Template Fatty acids
- Template Glycosides
- Template Lipids
- Template Metabolism
- Template Nucleus
- Tetrahymena
- Threonine
- Threose nucleic acid
- TIM TOM Complex
- Trans-acting siRNA
- Transfer RNA
- TRNA
- Trophectoderm
- Tryptophan
- Tyrosine
- Ubiquitin
- Uncoupling protein
- United States
- University of Vienna
- Urea cycle
- Valine
- Vienna
- Wellcome Trust
- Y chromosome
-
Chromosome (24) mtDNA - Lynn Margulis and the mitochondrial DNA
Chromosome (24) mtDNA - Lynn Margulis and the mitochondrial DNAChromosome (24) mtDNA - Lynn Margulis and the mitochondrial DNA
EXPLORE THE RI ADVENT CALENDAR: http://rigb.org.uk/advent When we're born we usually inherit our father's surname but we also inherit a rather unique type of... -
Our mtDNA ancestor
Our mtDNA ancestorOur mtDNA ancestor
mtDNA is our mitochondrial DNA. mtDNA is a circular piece of DNA. It is passed only through the egg (not sperm). So, it can be used to trace back through the... -
Family Tree DNA Results Explained: mtDNA Matching & Genealogy
Family Tree DNA Results Explained: mtDNA Matching & GenealogyFamily Tree DNA Results Explained: mtDNA Matching & Genealogy
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is passed down almost unchanged from a mother to her children. Family Tree DNA’s mtDNA tests enable you to trace your maternal line using the world’s largest mtDNA database. In this webinar, attendees will learn how to read and understand your mtDNA results and matches, and how to use those matches in conjunction with your genealogy research. mtDNA results pages covered: Matches, Ancestral Origins, Matches Maps, Results -
mtDNA Tutorial
mtDNA TutorialmtDNA Tutorial
Learn how mtDNA can be used to trace your maternal ancestry. -
Family Tree DNA Results Explained: mtDNA Haplogroups & Deep Ancestry
Family Tree DNA Results Explained: mtDNA Haplogroups & Deep AncestryFamily Tree DNA Results Explained: mtDNA Haplogroups & Deep Ancestry
In addition to genealogical matching, mtDNA testing uncovers the deep ancestry of your direct maternal line. This webinar focuses on mtDNA haplogroups and how they relate to your deep ancestry. mtDNA results pages covered: Results (Haplogroup section), Matches (mtDNA Haplogroup column), Haplogroup Origins, Migration Maps -
MAP OF MIGRATIONS OF MTDNA MARKERS- HUMAN MIGGRATIONS MAP
MAP OF MIGRATIONS OF MTDNA MARKERS- HUMAN MIGGRATIONS MAPMAP OF MIGRATIONS OF MTDNA MARKERS- HUMAN MIGGRATIONS MAP
http://www.bradshawfoundation.com/journey/ MTDNA. -
IBIS 2009 : 03 : Intro to mtDNA
IBIS 2009 : 03 : Intro to mtDNAIBIS 2009 : 03 : Intro to mtDNA
Part of the free online training workshop "Mitochondrial and STR DNA Analysis by Mass Spectrometry Using the Ibis Biosciences, Inc. Platform" at the NFSTC - ... -
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNAMitochondrial DNA
For more information, log on to- http://shomusbiology.weebly.com/ Download the study materials here- http://shomusbiology.weebly.com/bio-materials.html Mitoc... -
On the Origins of mtDNA Haplogroup V
On the Origins of mtDNA Haplogroup VOn the Origins of mtDNA Haplogroup V
Origins of mtDNA Haplogroup V. From Asturias/Cantabria, northern Spain to me in northern Portugal. Haplogroup V has been in Iberia since Upper Paleolithic ti... -
European mtDNA and Y-DNA Haplogroups
European mtDNA and Y-DNA HaplogroupsEuropean mtDNA and Y-DNA Haplogroups
Classification of the regional genetic European Haplotypes, and it's geographical predominance. I1: pre.Germanic (Nordic) - {Blue} I2: pre-Celto-Germanic - {Blue} I2a1: Sardinian, Iberian - {Blue} I2a2: Dinarc, Danubian - {Blue} N1c1: Uralo-Finic, Baltic, Siberian - {Ligh Yellow} R1a: Balto-Slavic, Germanic, Indo-Iranian - {Yellow} R1b: Italo-Celtic, Germanic, Hittie, Armenian, Tocharian - {Purple/Red} E1b1b: North African, Near Eastern, Balkanic - {Gray} J1: Caucasian, Mesopotamian, Semitic (Jewish, Arabic) - {Dark Green} J2: Greco-Anatolian, Mesopotamian, Caucasian - {Light Green} Note: Only the main Haplogrous have annotations. (Removabl -
Advanced Topics at Family Tree DNA: mtDNA
Advanced Topics at Family Tree DNA: mtDNAAdvanced Topics at Family Tree DNA: mtDNA
The Advanced Topics series goes beyond the Family Tree DNA Results Explained series, providing more in-depth detail about the genetics and usage of the tests offered by Family Tree DNA. Part 2 of this series focuses on mtDNA. Topics include Advanced Matching, mtDNA nomenclature, and mtDNA Haplogroups. -
NUNOLOGY CLASS #2 - THE POWER OF 9ETHER, MTDNA, NATURAL HAIR AND THE AFRICAN WOMAN!
NUNOLOGY CLASS #2 - THE POWER OF 9ETHER, MTDNA, NATURAL HAIR AND THE AFRICAN WOMAN!NUNOLOGY CLASS #2 - THE POWER OF 9ETHER, MTDNA, NATURAL HAIR AND THE AFRICAN WOMAN!
TUNE INTO NUNOLOGY CLASS # 2: In this Class you will learn: What is the Power of 9ETHER? and How we NUNOLOGIST see and view it! Why So Many Sisters in America and World Over are now going Natural? Why Women are 1st before Man? And so much more... Nunology Online Classes are present to you by: THE ETERNAL TEMPLE OF NUN Visit us @ http://www.nupu-nun.com/ For More Information about "THE SCIENCE OF NUNOLOGY" -
Irrefutable Proof of Evolution- Part 1 (mtDNA, ERVs, Fusion)
Irrefutable Proof of Evolution- Part 1 (mtDNA, ERVs, Fusion)Irrefutable Proof of Evolution- Part 1 (mtDNA, ERVs, Fusion)
EXPAND ME Irrefutable proof of evolution, along with their 'rebuttals'. ERV human chromosome 2 neanderthal mtDNA DNA summation. Yes, Im using the term proof.... -
mtdna U5a1
mtdna U5a1mtdna U5a1
mtdna haplogroup U5a1, the Clan of Ursula © Druidikal Music 2013. -
Mtdna Haplogroup A- Ayana's clan
Mtdna Haplogroup A- Ayana's clanMtdna Haplogroup A- Ayana's clan
It's a journey through time. -
Genetic Inheritance, Autosomal Dominant, X-linked Recessive, Mitochondrial Disease Polygenic mtDNA
Genetic Inheritance, Autosomal Dominant, X-linked Recessive, Mitochondrial Disease Polygenic mtDNAGenetic Inheritance, Autosomal Dominant, X-linked Recessive, Mitochondrial Disease Polygenic mtDNA
http://www.stomponstep1.com/genetic-inheritance-autosomal-dominant-x-linked-recessive-mitochondrial-disease/ Autosomal Dominant Inheritance is when one allele, on any chromosome other than X or Y, is expressed over another allele of the same gene. This allele determines the phenotype (observable characteristics) and is referred to as dominant. The allele that is does not affect the phenotype is referred to as recessive. The dominant allele is often given the capital letter for a character while the recessive allele is given the lower case. Therefore, a heterozygous individual who is a carrier for the recessive gene would be represented as Aa -
mtDNA Haplogroup V
mtDNA Haplogroup VmtDNA Haplogroup V
I did this little video. It is about how mtDNA Haplogroup V must have arrived to me. In human mitochondrial genetics, Haplogroup V is a human mitochondrial D... -
mtDNA Use in DNA Profiling - Seminar Video
mtDNA Use in DNA Profiling - Seminar VideomtDNA Use in DNA Profiling - Seminar Video
My research topic presentation for Senior Seminar at SUNY Brockport. -
mtDNA Match Tutorial
mtDNA Match TutorialmtDNA Match Tutorial
Learn how to find mtDNA matches on GeneTree. -
Genetics of Russians (maternal mtDNA) - Генетика етнічних росіян
Genetics of Russians (maternal mtDNA) - Генетика етнічних росіянGenetics of Russians (maternal mtDNA) - Генетика етнічних росіян
Maternal genetics of Russians, based on new research: http://download.springer.com/static/pdf/403/art%253A10.1007%252Fs11177-005-0197-3.pdf?auth66=1354745582... -
Trás-os-Montes, NE Portugal. Land of mtDNA Haplogroup V
Trás-os-Montes, NE Portugal. Land of mtDNA Haplogroup VTrás-os-Montes, NE Portugal. Land of mtDNA Haplogroup V
Province of Trás-os-Montes, Northeastern Portugal. Land of mtDNA Haplogroup V. This is my birthplace and I belong to mtDNA Haplogroup V (subclade V*). -
mtDNA distribution in WT and fusion/fission deficient yeast cells
mtDNA distribution in WT and fusion/fission deficient yeast cellsmtDNA distribution in WT and fusion/fission deficient yeast cells
from Osman C, Noriega TR, Okreglak V, Fung JC, & Walter P (2015) Integrity of the yeast mitochondrial genome, but not its distribution and inheritance, relies on mitochondrial fission and fusion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 112: E947-E956, 1501737112 -
Rescue of mtDNA mutations by allotopic expression of engineered mitochondrial genes - MatthewOConnor
Rescue of mtDNA mutations by allotopic expression of engineered mitochondrial genes - MatthewOConnorRescue of mtDNA mutations by allotopic expression of engineered mitochondrial genes - MatthewOConnor
Mutations in mitochondrial genes occur as we age, and the human body does not have a good system to repair them. At SENS Research Foundation we are in the ea...

Chromosome (24) mtDNA - Lynn Margulis and the mitochondrial DNA
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:37
- Updated: 03 Sep 2014
- views: 12517
- author: The Royal Institution
- published: 24 Dec 2013
- views: 12517
- author: The Royal Institution

Our mtDNA ancestor
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:13
- Updated: 18 Aug 2013
- views: 1407
- author: Melissa Wilson Sayres
- published: 08 Aug 2013
- views: 1407
- author: Melissa Wilson Sayres

Family Tree DNA Results Explained: mtDNA Matching & Genealogy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 115:51
- Updated: 21 Mar 2015
- views: 9
- published: 21 Mar 2015
- views: 9

mtDNA Tutorial
- published: 19 Jan 2012
- views: 977
- author: genetree

Family Tree DNA Results Explained: mtDNA Haplogroups & Deep Ancestry
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 77:30
- Updated: 21 Mar 2015
- views: 17
- published: 21 Mar 2015
- views: 17

MAP OF MIGRATIONS OF MTDNA MARKERS- HUMAN MIGGRATIONS MAP
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:24
- Updated: 06 Sep 2014
- views: 26898
- author: SabirOnogur
- published: 11 Sep 2009
- views: 26898
- author: SabirOnogur

IBIS 2009 : 03 : Intro to mtDNA
- published: 25 Oct 2012
- views: 336
- author: NFSTC

Mitochondrial DNA
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:58
- Updated: 04 Sep 2014
- views: 4427
- author: Suman Bhattacharjee
- published: 25 Dec 2012
- views: 4427
- author: Suman Bhattacharjee

On the Origins of mtDNA Haplogroup V
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:10
- Updated: 03 Sep 2014
- views: 885
- author: Joao Bessa Santos
- published: 04 Mar 2013
- views: 885
- author: Joao Bessa Santos

European mtDNA and Y-DNA Haplogroups
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:01
- Updated: 18 Mar 2012
- views: 46455
- published: 18 Mar 2012
- views: 46455

Advanced Topics at Family Tree DNA: mtDNA
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 84:51
- Updated: 21 Mar 2015
- views: 4
- published: 21 Mar 2015
- views: 4

NUNOLOGY CLASS #2 - THE POWER OF 9ETHER, MTDNA, NATURAL HAIR AND THE AFRICAN WOMAN!
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 58:24
- Updated: 23 Sep 2015
- views: 172
- published: 23 Sep 2015
- views: 172

Irrefutable Proof of Evolution- Part 1 (mtDNA, ERVs, Fusion)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:00
- Updated: 05 Sep 2014
- views: 181725
- author: DonExodus2
- published: 13 Dec 2007
- views: 181725
- author: DonExodus2

mtdna U5a1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:18
- Updated: 04 Aug 2014
- views: 637
- author: Ye Olde Appalachia Obscura
- published: 28 Mar 2013
- views: 637
- author: Ye Olde Appalachia Obscura

Mtdna Haplogroup A- Ayana's clan
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:21
- Updated: 15 Aug 2014
- views: 5949
- author: Eternidad195
- published: 05 Nov 2011
- views: 5949
- author: Eternidad195

Genetic Inheritance, Autosomal Dominant, X-linked Recessive, Mitochondrial Disease Polygenic mtDNA
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 14:19
- Updated: 15 Jun 2014
- views: 5029
- published: 15 Jun 2014
- views: 5029

mtDNA Haplogroup V
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:34
- Updated: 11 Jul 2014
- views: 2074
- author: Joao Bessa Santos
- published: 25 Apr 2012
- views: 2074
- author: Joao Bessa Santos

mtDNA Use in DNA Profiling - Seminar Video
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 12:45
- Updated: 12 Apr 2014
- views: 101
- author: xangelchisex
- published: 12 Apr 2014
- views: 101
- author: xangelchisex

mtDNA Match Tutorial
- published: 23 Jan 2012
- views: 309
- author: genetree

Genetics of Russians (maternal mtDNA) - Генетика етнічних росіян
- published: 04 Dec 2012
- views: 2095
- author: Zakharii

Trás-os-Montes, NE Portugal. Land of mtDNA Haplogroup V
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:08
- Updated: 24 Jun 2014
- views: 161
- author: Joao Bessa Santos
- published: 06 Nov 2013
- views: 161
- author: Joao Bessa Santos

mtDNA distribution in WT and fusion/fission deficient yeast cells
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:11
- Updated: 12 Mar 2015
- views: 2
- published: 12 Mar 2015
- views: 2

Rescue of mtDNA mutations by allotopic expression of engineered mitochondrial genes - MatthewOConnor
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 20:17
- Updated: 11 Jul 2014
- views: 319
- author: SENS Foundation
- published: 31 Jan 2014
- views: 319
- author: SENS Foundation
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

Chromosome (24) mtDNA - Lynn Margulis and the mitochondrial DNA
- published: 24 Dec 2013
- views: 12517
-
author:
The Royal Institution
Add Playlist for this Author

Our mtDNA ancestor
- published: 08 Aug 2013
- views: 1407
-
author:
Melissa Wilson Sayres
Add Playlist for this Author

Family Tree DNA Results Explained: mtDNA Matching & Genealogy
- published: 21 Mar 2015
- views: 9

mtDNA Tutorial
- published: 19 Jan 2012
- views: 977
-
author:
genetree
Add Playlist for this Author

Family Tree DNA Results Explained: mtDNA Haplogroups & Deep Ancestry
- published: 21 Mar 2015
- views: 17

MAP OF MIGRATIONS OF MTDNA MARKERS- HUMAN MIGGRATIONS MAP
- published: 11 Sep 2009
- views: 26898
-
author:
SabirOnogur
Add Playlist for this Author

IBIS 2009 : 03 : Intro to mtDNA
- published: 25 Oct 2012
- views: 336
-
author:
NFSTC
Add Playlist for this Author

Mitochondrial DNA
- published: 25 Dec 2012
- views: 4427
-
author:
Suman Bhattacharjee
Add Playlist for this Author

On the Origins of mtDNA Haplogroup V
- published: 04 Mar 2013
- views: 885
-
author:
Joao Bessa Santos
Add Playlist for this Author

European mtDNA and Y-DNA Haplogroups
- published: 18 Mar 2012
- views: 46455

Advanced Topics at Family Tree DNA: mtDNA
- published: 21 Mar 2015
- views: 4

NUNOLOGY CLASS #2 - THE POWER OF 9ETHER, MTDNA, NATURAL HAIR AND THE AFRICAN WOMAN!
- published: 23 Sep 2015
- views: 172

Irrefutable Proof of Evolution- Part 1 (mtDNA, ERVs, Fusion)
- published: 13 Dec 2007
- views: 181725
-
author:
DonExodus2
Add Playlist for this Author

mtdna U5a1
- published: 28 Mar 2013
- views: 637
-
author:
Ye Olde Appalachia Obscura
Add Playlist for this Author
Afghan woman stoned to death for 'adultery'
Edit Al Jazeera 04 Nov 2015N. Korea accuses U.S. of "nuclear blackmail"
Edit CBS News 04 Nov 2015Relativity versus quantum mechanics: the battle for the universe
Edit The Guardian 04 Nov 2015South Sudan plane crash 'kills 40' near Juba airport
Edit BBC News 04 Nov 2015Hillary Clinton puts once-taboo issue of gun control at forefront of campaign
Edit The Guardian 04 Nov 2015Infant Burials In Alaska Hint At How People First Colonized The Americas
Edit IFL Science 29 Oct 2015Chicken Study Shows That Evolution Can Happen Quickly
Edit IFL Science 28 Oct 2015Out of China: Does Southeast Asia’s ‘Adam’ trace back to Yunnan province instead of India? Study supports new theory of region’s common ancestor
Edit South China Morning Post 27 Oct 2015New Species of Giant Tortoise Found In The Galapagos
Edit IFL Science 22 Oct 2015The Strange Case of Bossetti and Unsub1
Edit Minds 18 Oct 2015Malagasy Songbird Is Rare Instance Of Evolution Working "Backwards"
Edit IFL Science 08 Oct 2015Mitochondrial DNA mutations affect male and female fertility and ageing (Monash University)
Edit Public Technologies 08 Oct 2015Scientists Test New Gene Therapy for Vision Loss From a Mitochondrial Disease (National Eye Institute) ...
Edit Public Technologies 05 Oct 2015Scientists test new gene therapy for vision loss from a mitochondrial disease
Edit NIH 05 Oct 2015Scientists test new gene therapy for vision loss from a mitochondrial disease (NIH - National ...
Edit Public Technologies 05 Oct 2015Tiny Mitochondria Play Outsized Role in Human Evolution (Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia)
Edit Public Technologies 25 Sep 2015For Veterans with Gulf War Illness, an Explanation for the Unexplainable Symptoms (APS - American ...
Edit Public Technologies 15 Sep 2015Lack of mitochondrial topoisomerase I (TOP1mt) impairs liver regeneration
Edit PNAS 20 Aug 2015- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »






