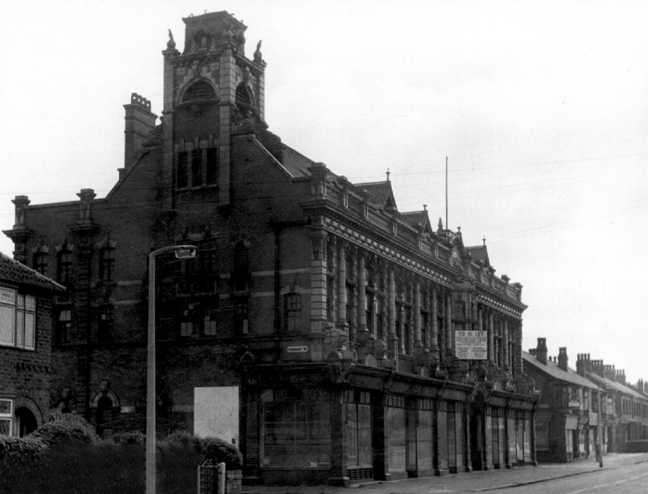
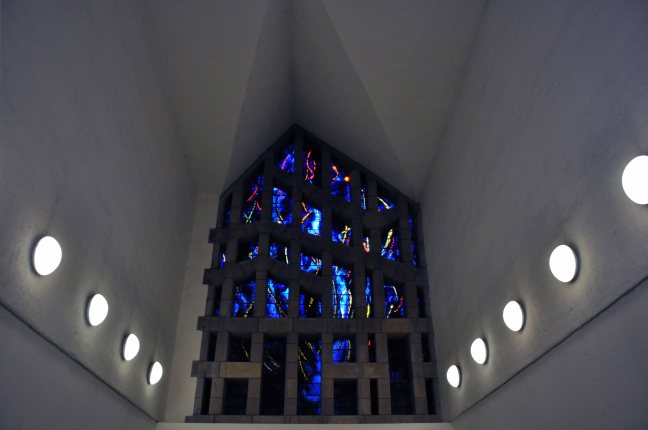
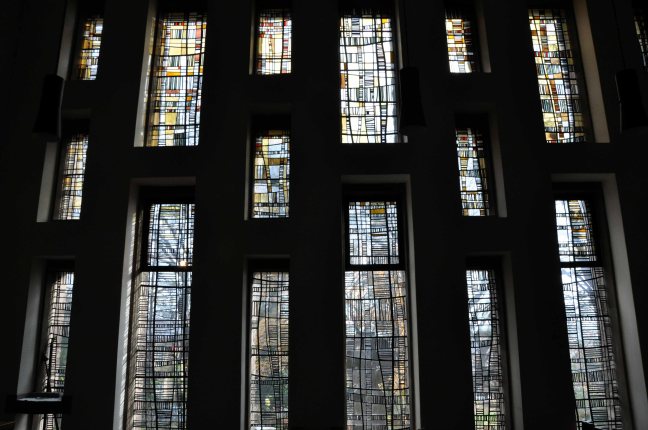
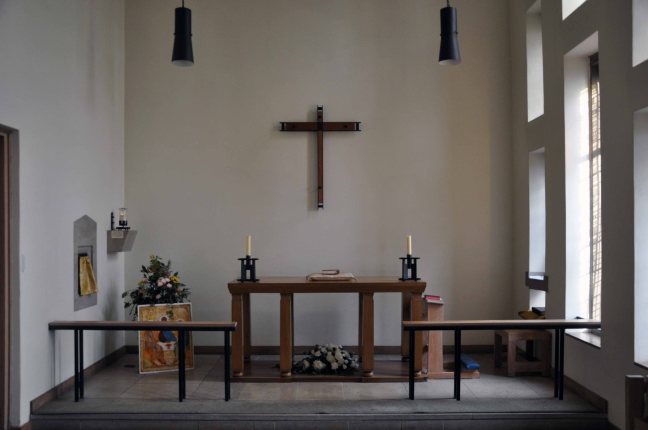
My journey begins here, at the Brookfield Unitarian Church, Hyde Road, Gorton, in search of the mausoleum of a man, who helped to shape the history of engineering, locomotion and Manchester.

Richard Peacock 9 April 1820 – 3 March 1889 was an English engineer, one of the founders of locomotive manufacturerBeyer-Peacock. Born in Swaledale, Richard Peacock was educated at Leeds Grammar School, but at 14 left to be apprenticed at Fenton, Murray and Jackson in Leeds.
At 18 Peacock was a precocious locomotive superintendent on the Leeds and Selby Railway. When the line was acquired by the York and North Midland Railway in 1840 he worked under Daniel Gooch at Swindon, but reputedly fled to escape Gooch’s wrath. In 1841, he became the Locomotive Superintendent of the Sheffield, Ashton-under-Lyne and Manchester Railway, subsequently the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway from 1847. In this role he was responsible for founding the Gorton locomotive works for this railway, although he had left the firm shortly before they were completed in 1848.
In 1847 Peacock was present with Charles Beyer at a meeting at Lickey Incline which it is generally acknowledged gave birth to the Institution of Mechanical Engineers. George Stephenson was elected as first president and Charles Beyer as a vice president. Peacock became a member of the Institution of Civil Engineers in 1849.
In 1853, he joined Charles Beyer to found the celebrated locomotive company Beyer-Peacock. Peacock had originally met Beyer through the acquisition of locomotives from Sharp Brothers, and as mentioned earlier through both being among the founders of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers in 1847.
The locomotives designed and built in Gorton in their thousands were exported to the four corners of the globe, Manchester a confluence of capital and ingenuity, harnessing a workforce of millions, to produce a treasure trove of things and stuff
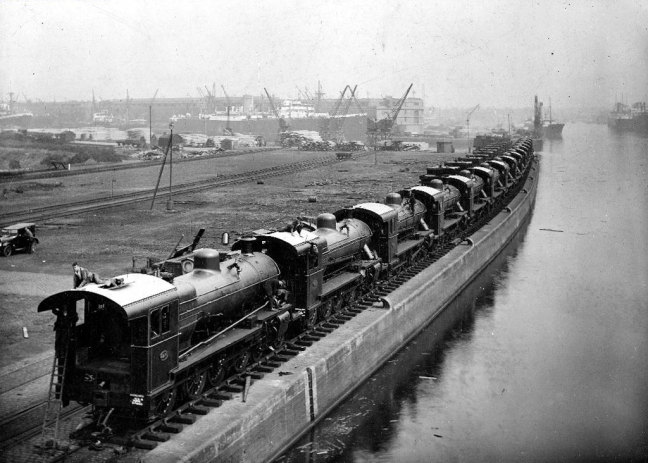
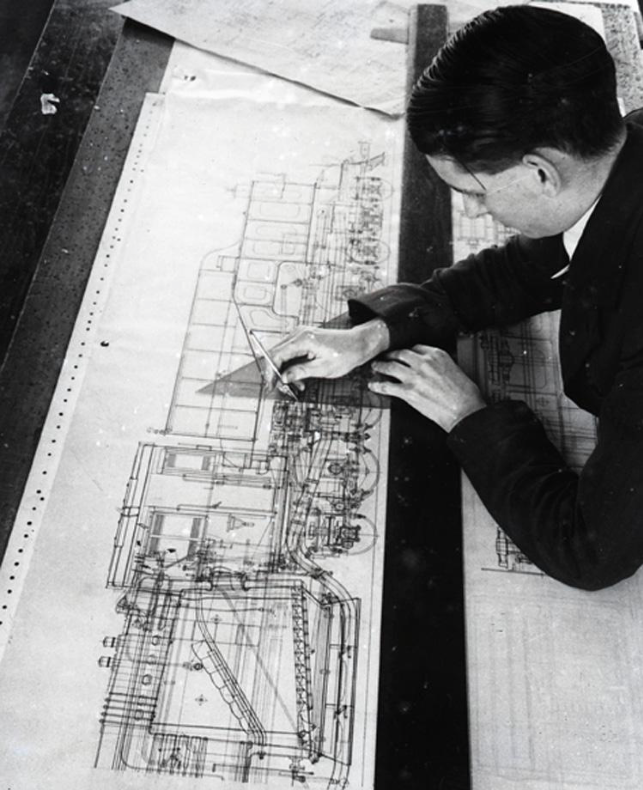

Shipping to Buenos Aires 1929

2 10 0 Locomotives bound for Turkey 1949

Last Diesels in the Paint Shop
By 1966 it was all over, the politically motivated, managed decline of manufacturing industry, a failure to adapt and compete, the loss of Empire, an increase in competition from other nations, all contributing to the almost inevitable, closing of the door.

Archive photographs copyright Manchester Local Image Collection
The clang, hiss and controlled chaos of the boiler shop, just a faint, empty echo – listen.
There remains a legacy, the memories of all those men and women who laboured under those aching skylit eaves, millions of weary travellers world wide.
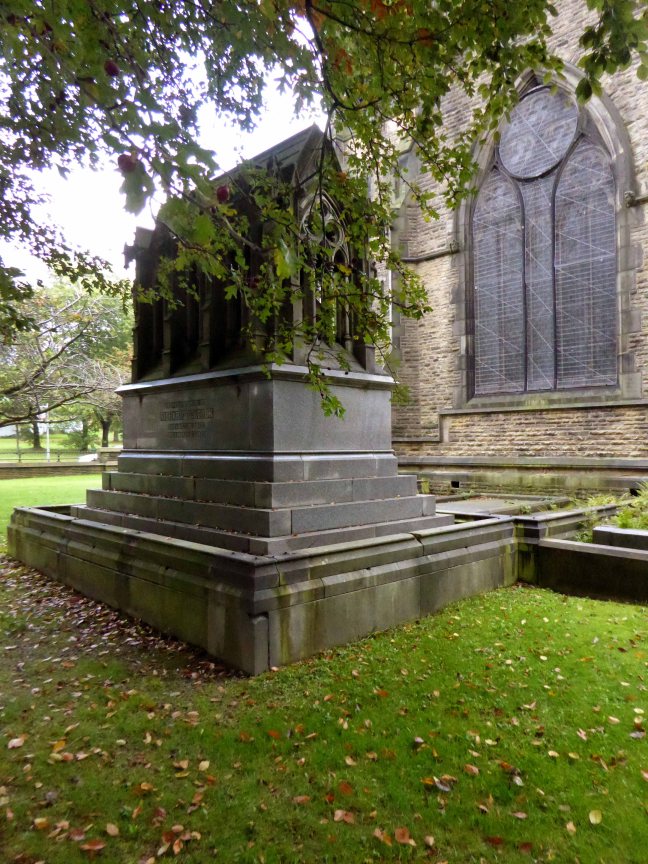
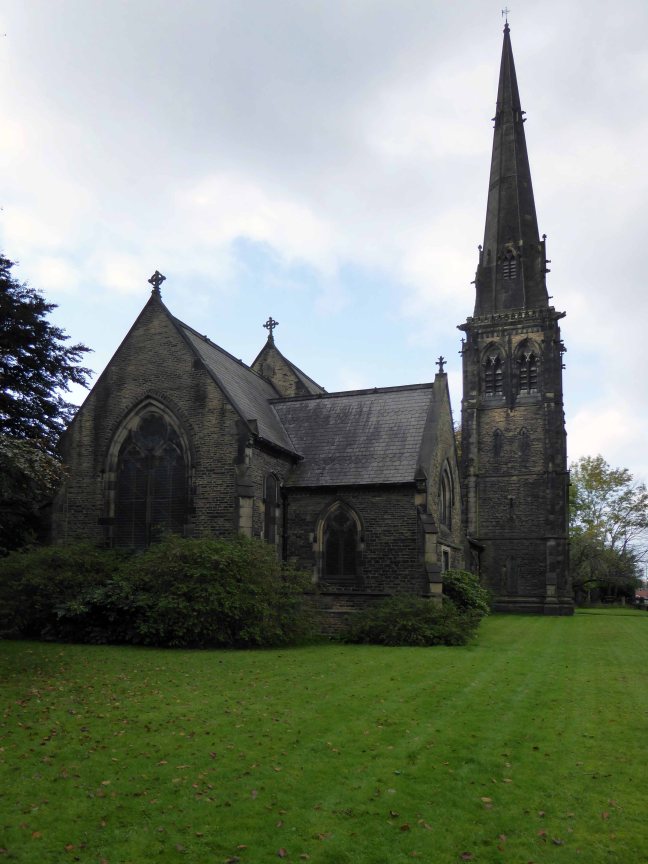
Not forgetting the church that Richard Peacock benevolently built, the mix of non-conformist worship, Liberal politics and philanthropy that informed Victorian Manchester, which still stands extant in stone, around our city.
Designed by Thomas Worthington in 1869-71, it has a six bay nave with north and south aisles. Arcade columns are of polished granite and wall faces are plaster lined with a large painting over the chancel arch. The roofs have been repaired but the interior has suffered from consequential water damage to the plasterwork which, at the time of visiting, was drying out. The church has been a victim of heritage crime.
Listed and left to the pressures of time tide, wind, rain and unwanted ingress.
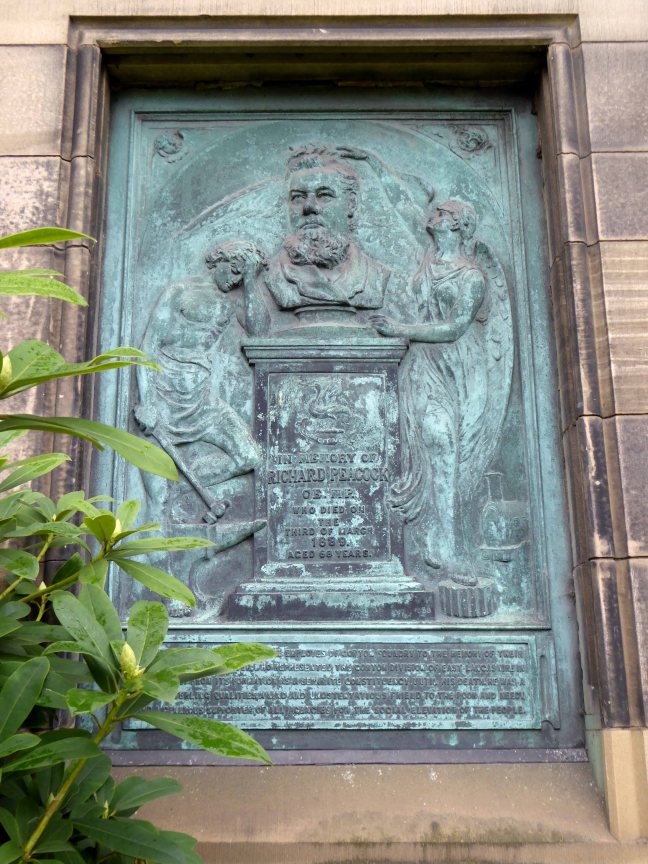

Inset into the north wall of the church, facing onto Hyde Road – sculptor John Cassidy.
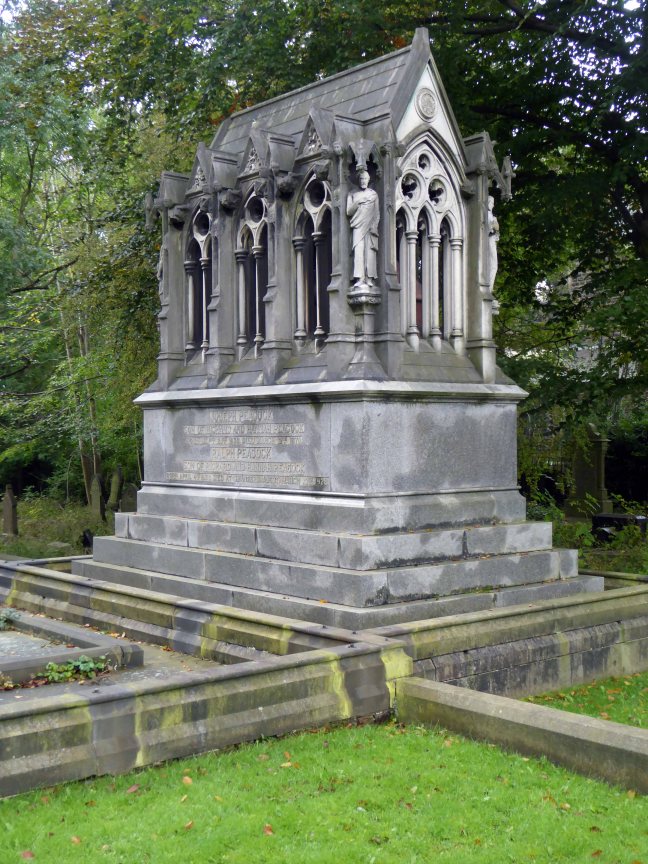
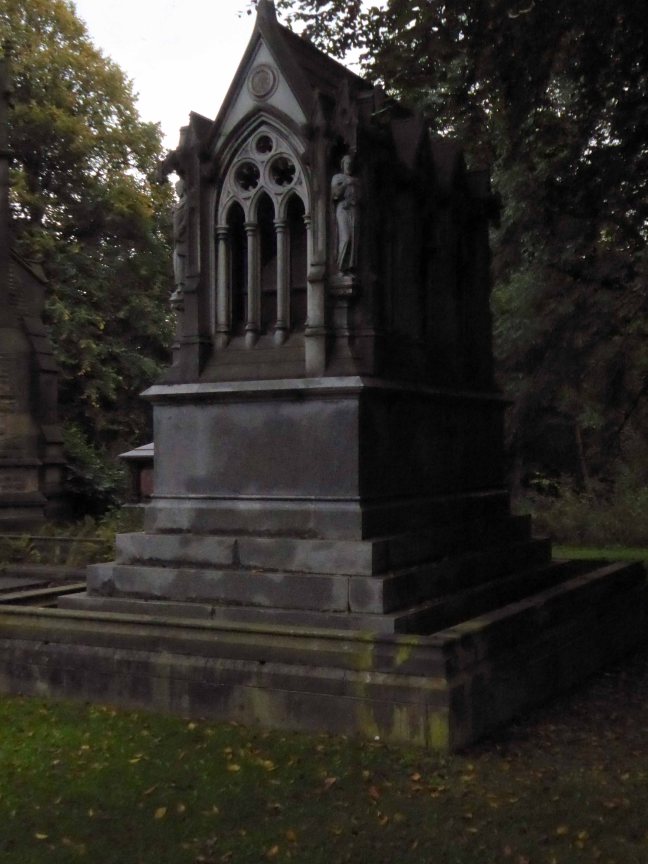
The Peacock Mausoleum is also the work of the church’s architect Thomas Worthington.
This sumptuous mausoleum takes the form of a Gothic shrine with a steeply pitched roof and arched openings filled with tracery and surmounted by gablets. The statues standing on slender pedestals at the four corners of the monument represent a Blacksmith, a Draughtsman, an Engineer and the architect himself. Further carved embellishments include head-stops, bats and twining ivy.
Condition – still sound, though the bronze angels that used to stand on the gables at either end were stolen some years ago in 1997.
So we arrive at the end of another journey through time and space and Gorton, the lives of so many long lone souls, bundled up in the graveyard of a now closed church, the fortunes won and lost eroded by the vagaries of the climate – economic and meteorological.