-
Starch
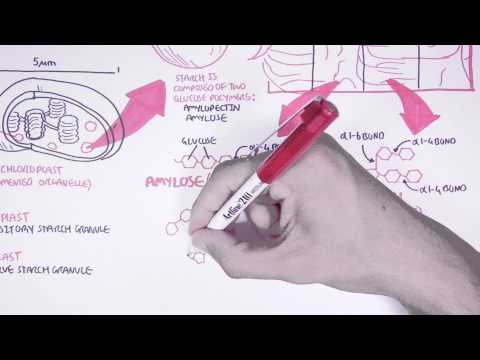
Starch is a major source of energy for the diet. Starch is made up of glucose molecules linked together forming linear chains and also branching chains. These chains are tightly packed and organised into granules where they are stored for energy in plants. By breaking this organised system and releasing the glucose, humans are able to use starch as a source of energy.
This video was created by Armando Faigl as part of an internship project with CSIRO on the Hungry Microbiome Project.
For more info and videos please visit: http://www.csiro.au/hungrymicrobiome/
published: 12 Apr 2014
-
Polysaccharides - Starch, Amylose, Amylopectin, Glycogen, & Cellulose - Carbohydrates
This Biology video tutorial provides an intro into Polysaccharides such as Starch, Amylose, Amylopectin, Glycogen, and Cellulose. It discusses the type of glycosidic bonds formed in these polymers and their orientation such as the alpha and beta forms.
My Website: https://www.video-tutor.net
Patreon Donations: https://www.patreon.com/MathScienceTutor
Amazon Store: https://www.amazon.com/shop/theorganicchemistrytutor
Subscribe:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCEWpbFLzoYGPfuWUMFPSaoA?sub_confirmation=1
published: 17 Oct 2019
-
Carbohydrates: Starch and Glycogen | A-level Biology | OCR, AQA, Edexcel
Carbohydrates: Starch and Glycogen in a Snap! Unlock the full A-level Biology course at http://bit.ly/2BD2spR created by Adam Tildesley, Biology expert at SnapRevise and graduate of Cambridge University.
SnapRevise is the UK’s leading A-level and GCSE revision & exam preparation resource offering comprehensive video courses created by A* Oxbridge tutors. Our courses are designed around the OCR, AQA, SNAB, Edexcel B, WJEC, CIE and IAL exam boards, concisely covering all the important concepts required by each specification. In addition to all the content videos, our courses include hundreds of exam question videos, where we show you how to tackle questions and walk you through step by step how to score full marks.
Sign up today and together, let’s make A-level Biology a walk in the park!
...
published: 27 Feb 2019
-
What I Eat In A Week On The Starch Solution | Plant-Based
APPLY TO MY SLIM ON STARCH 1-ON-1 WEIGHT LOSS PROGRAM HERE ➵ ➵ https://www.healthyemmie.org
Welcome to Healthy Emmie! In this video, I’m going to share with you what I eat in a week on Starch Solution. Let’s deep dive into the video to learn more about my plant-based meal plan.
👉 Subscribe to my channel to stay tuned: https://www.youtube.com/c/healthyemmie?sub_confirmation=1
A plant-based diet is a diet consisting mostly or entirely of plant-based foods. Plant-based foods are foods derived from plants with no animal-source foods or artificial ingredients.
The Starch Solution created by Dr. John McDougall is a starch-based diet focusing on whole food plant-based starches such as potatoes, rice, and beans. Making your plate at each meal using whole food plant-based. This way of eating ho...
published: 05 May 2021
-
Carb Science: Good Starch vs. Bad Starch- Thomas DeLauer
Click Here to Subscribe: http://Bit.ly/ThomasVid
Website: http://ThomasDeLauer.com
Carb Science: Good Starch vs. Bad Starch- Thomas DeLauer… So you know that not all carbs are created equal, right? We always talk about that. But did you know that not all starches are created equal too? So in this video, I want to break down how different starches from different carbohydrate sources respond inside your body and may cause these additional casualties that you didn't quite know about before. If you haven't already, make sure you hit the subscribe button so that you can see all the three to five videos that I'm posting per week ranging from the topics of fasting, ketosis, general health, and just about everything under the sun relating to wellness. Also, make sure you turn on those notification...
published: 10 Apr 2018
-
Extracting the starch from potatoes
In this video, we are isolating some starch from potatoes. We also talk a little bit about starch in general. Potato starch is better than corn starch because it forms a nice clear solution in water.
I am going to be using it for the Brigg's Rauscher Oscillating clock reaction and maybe some other things.
Nile talks about lab safety: https://youtu.be/ftACSEJ6DZA
--------------------------------
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/nilered
Youtube Membership: https://www.youtube.com/c/nilered/join
NileRed Merch Store (NileRed Pin & Keychain): https://store.dftba.com/collections/nilered
NileRed Website (Glassware & Beaker Mugs): https://nile.red
--------------------------------
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/nile.red
Twitter: https://twitter.com/NileRed2
Discord: https://discord....
published: 25 Jun 2016
-
Starch Retrogradation | The Science of Stale Bread
Starch retrogradation is the technical term for bread staling. It's the reason why your bread changes in texture and mouthfeel as it ages. In this video, we'll show you how starch retrogradation occurs and how you can delay it to have a softer, tender bread for a longer time.
*********************
Royalty-free music by Bensound
Here's where we got out info:
Eduardo, M., Svanberg, U., & Ahrné, L. (2016). Effect of hydrocolloids and emulsifiers on the shelf-life of composite cassava-maize-wheat bread after storage. Food Science & Nutrition, 4(4), 636–644. doi:10.1002/fsn3.326
*********************
Video Link: Maillard Reaction
https://youtu.be/A04Bd0UzOGQ
*************************
Follow us at:
✅ FB: https://www.facebook.com/PostHarvestTech
✅ IG: https://www.instagram.com/postharvest...
published: 25 Apr 2020
-
What is starch?
For more information on starch, please visit www.starch.eu
published: 17 May 2016
-
A Tasting of Culinary Science—Starch
It’s fitting that the word starch begins with “star.” It’s the currency of the kitchen, the fundamental ingredient that’s used in cooking every day. Yes, starch is that important. So it’s just as important that you understand starch and its behavior, and this video helps you get there. You’ll learn to produce so many delicious foods—thickening sauces like velouté, gel desserts like pudding, crispy treats like crackers—that you’ll be a star in the kitchen too!
Learn more: https://www.ciachef.edu/cia-culinary-science-bachelors-degree-program/
—————————————————————————————————————————————————————
The Culinary Institute of America: https://www.ciachef.edu
The CIA at Copia: https://www.ciaatcopia.com
CIA Restaurant Group: https://www.ciarestaurantgroup.com
CIA Food Enthusiasts programs: http...
published: 01 Mar 2016
-
How To Make Potato Starch |Homemade Potato Flour | Potato Starch Recipe
What is Potato Starch ? Potato starch kya he?
Potato starch is a fine white powdery substance derived from potatoes. Similar to other starches. It is commonly used to thicken gel texturize and increase crispiness in baked goods. It is also used in clear soup, confections, fillings, and so on.
Thanks for watching........
Please Subscribe my channel , this will help me a lot.......
And stay tuned for new videos.......
Follow me on----/------
Facebook ----- https://www.facebook.com/CookingWithRekha/
Gooogle Plus ----- https://plus.google.com/u/0/+CookingwithRekha
Twitter ----- https://twitter.com/Rekha_Cooking
Video Copyrights – Cooking with Rekha(verified)
Thumbnail Copyrights – Cooking with Rekha(verified)
Audio Copyrights – Cooking with Rekha(verified)
published: 16 Jan 2021
14:35
Starch
Starch is a major source of energy for the diet. Starch is made up of glucose molecules linked together forming linear chains and also branching chains. These c...
Starch is a major source of energy for the diet. Starch is made up of glucose molecules linked together forming linear chains and also branching chains. These chains are tightly packed and organised into granules where they are stored for energy in plants. By breaking this organised system and releasing the glucose, humans are able to use starch as a source of energy.
This video was created by Armando Faigl as part of an internship project with CSIRO on the Hungry Microbiome Project.
For more info and videos please visit: http://www.csiro.au/hungrymicrobiome/
https://wn.com/Starch
Starch is a major source of energy for the diet. Starch is made up of glucose molecules linked together forming linear chains and also branching chains. These chains are tightly packed and organised into granules where they are stored for energy in plants. By breaking this organised system and releasing the glucose, humans are able to use starch as a source of energy.
This video was created by Armando Faigl as part of an internship project with CSIRO on the Hungry Microbiome Project.
For more info and videos please visit: http://www.csiro.au/hungrymicrobiome/
- published: 12 Apr 2014
- views: 102398
6:33
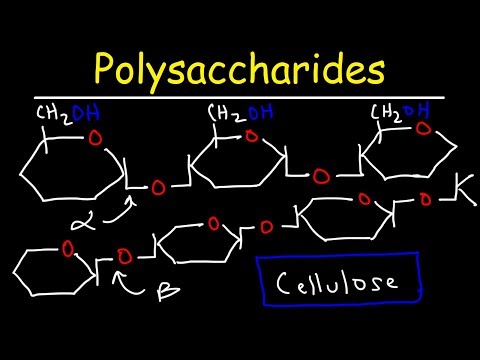
Polysaccharides - Starch, Amylose, Amylopectin, Glycogen, & Cellulose - Carbohydrates
This Biology video tutorial provides an intro into Polysaccharides such as Starch, Amylose, Amylopectin, Glycogen, and Cellulose. It discusses the type of glyc...
This Biology video tutorial provides an intro into Polysaccharides such as Starch, Amylose, Amylopectin, Glycogen, and Cellulose. It discusses the type of glycosidic bonds formed in these polymers and their orientation such as the alpha and beta forms.
My Website: https://www.video-tutor.net
Patreon Donations: https://www.patreon.com/MathScienceTutor
Amazon Store: https://www.amazon.com/shop/theorganicchemistrytutor
Subscribe:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCEWpbFLzoYGPfuWUMFPSaoA?sub_confirmation=1
https://wn.com/Polysaccharides_Starch,_Amylose,_Amylopectin,_Glycogen,_Cellulose_Carbohydrates
This Biology video tutorial provides an intro into Polysaccharides such as Starch, Amylose, Amylopectin, Glycogen, and Cellulose. It discusses the type of glycosidic bonds formed in these polymers and their orientation such as the alpha and beta forms.
My Website: https://www.video-tutor.net
Patreon Donations: https://www.patreon.com/MathScienceTutor
Amazon Store: https://www.amazon.com/shop/theorganicchemistrytutor
Subscribe:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCEWpbFLzoYGPfuWUMFPSaoA?sub_confirmation=1
- published: 17 Oct 2019
- views: 63251
10:44
Carbohydrates: Starch and Glycogen | A-level Biology | OCR, AQA, Edexcel
Carbohydrates: Starch and Glycogen in a Snap! Unlock the full A-level Biology course at http://bit.ly/2BD2spR created by Adam Tildesley, Biology expert at SnapR...
Carbohydrates: Starch and Glycogen in a Snap! Unlock the full A-level Biology course at http://bit.ly/2BD2spR created by Adam Tildesley, Biology expert at SnapRevise and graduate of Cambridge University.
SnapRevise is the UK’s leading A-level and GCSE revision & exam preparation resource offering comprehensive video courses created by A* Oxbridge tutors. Our courses are designed around the OCR, AQA, SNAB, Edexcel B, WJEC, CIE and IAL exam boards, concisely covering all the important concepts required by each specification. In addition to all the content videos, our courses include hundreds of exam question videos, where we show you how to tackle questions and walk you through step by step how to score full marks.
Sign up today and together, let’s make A-level Biology a walk in the park!
The key points covered in this video include:
1. Starch
2. Structure of Starch - Amylose
3. Structure of Starch - Amylopectin
4. Glycogen
Starch
In plants, the polysaccharide energy store is called starch. Starch is most commonly found in photosynthesising cells in leaves and storage cells in seeds and storage organs. It is compacted into dense, insoluble grains stored in a special organelles called amyloplasts. Storage organs contain cells with numerous amyloplasts to ensure the plant always has a sufficient supply of energy.
Structure of Starch - Amylose
Starch consists of two different polysaccharides - amylose and amylopectin. Amylose is a long chain of α-glucose molecules joined together by 1,4 glycosidic bonds. Amylose coils into a helix shape that makes it more compact. Each amylose molecule only has two accessible ends where the enzyme amylase can bind. This means that amylose can only be broken down slowly.
Structure of Starch - Amylopectin
The other polysaccharide found in starch is amylopectin. Amylopectin is also a long chain of α-glucose molecules joined together with 1,4 glycosidic bonds. However, amylopectin also has occasional 1,6 glycosidic bonds. The additional 1,6 glycosidic bonds causes amylopectin to have side branches with more accessible ends. This makes amylopectin more easily broken down by enzymes when glucose is needed.
Glycogen
In animals, the polysaccharide energy store is called glycogen. Glycogen is found in cells with a high metabolic rate - e.g. liver cells and muscle cells. Glycogen has a similar structure to amylopectin, with many α-glucose molecules joined together by 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds. However, in glycogen, the 1,6 glycosidic bonds are very frequent resulting in a highly branched structure. Glycogen therefore has a very high number of accessible ends. This allows glycogen to be rapidly hydrolysed to α-glucose by enzymes. This is important as animals have higher metabolic requirements than plants.
Summary
Polysaccharides are formed by joining together many monosaccharides in a series of condensation reactions
Polysaccharides are broken down into monosaccharides in a series of hydrolysis reactions
Polysaccharides have many properties that make them good energy stores as they are:
· compact
· large
· insoluble
· easily hydrolysed
In plants, the polysaccharide energy store is called starch
Starch is made up of amylose and amylopectin molecules
In animals, the polysaccharide energy store is called glycogen
The more branched the polysaccharide, the faster it can be broken down into glucose for energy
https://wn.com/Carbohydrates_Starch_And_Glycogen_|_A_Level_Biology_|_Ocr,_Aqa,_Edexcel
Carbohydrates: Starch and Glycogen in a Snap! Unlock the full A-level Biology course at http://bit.ly/2BD2spR created by Adam Tildesley, Biology expert at SnapRevise and graduate of Cambridge University.
SnapRevise is the UK’s leading A-level and GCSE revision & exam preparation resource offering comprehensive video courses created by A* Oxbridge tutors. Our courses are designed around the OCR, AQA, SNAB, Edexcel B, WJEC, CIE and IAL exam boards, concisely covering all the important concepts required by each specification. In addition to all the content videos, our courses include hundreds of exam question videos, where we show you how to tackle questions and walk you through step by step how to score full marks.
Sign up today and together, let’s make A-level Biology a walk in the park!
The key points covered in this video include:
1. Starch
2. Structure of Starch - Amylose
3. Structure of Starch - Amylopectin
4. Glycogen
Starch
In plants, the polysaccharide energy store is called starch. Starch is most commonly found in photosynthesising cells in leaves and storage cells in seeds and storage organs. It is compacted into dense, insoluble grains stored in a special organelles called amyloplasts. Storage organs contain cells with numerous amyloplasts to ensure the plant always has a sufficient supply of energy.
Structure of Starch - Amylose
Starch consists of two different polysaccharides - amylose and amylopectin. Amylose is a long chain of α-glucose molecules joined together by 1,4 glycosidic bonds. Amylose coils into a helix shape that makes it more compact. Each amylose molecule only has two accessible ends where the enzyme amylase can bind. This means that amylose can only be broken down slowly.
Structure of Starch - Amylopectin
The other polysaccharide found in starch is amylopectin. Amylopectin is also a long chain of α-glucose molecules joined together with 1,4 glycosidic bonds. However, amylopectin also has occasional 1,6 glycosidic bonds. The additional 1,6 glycosidic bonds causes amylopectin to have side branches with more accessible ends. This makes amylopectin more easily broken down by enzymes when glucose is needed.
Glycogen
In animals, the polysaccharide energy store is called glycogen. Glycogen is found in cells with a high metabolic rate - e.g. liver cells and muscle cells. Glycogen has a similar structure to amylopectin, with many α-glucose molecules joined together by 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds. However, in glycogen, the 1,6 glycosidic bonds are very frequent resulting in a highly branched structure. Glycogen therefore has a very high number of accessible ends. This allows glycogen to be rapidly hydrolysed to α-glucose by enzymes. This is important as animals have higher metabolic requirements than plants.
Summary
Polysaccharides are formed by joining together many monosaccharides in a series of condensation reactions
Polysaccharides are broken down into monosaccharides in a series of hydrolysis reactions
Polysaccharides have many properties that make them good energy stores as they are:
· compact
· large
· insoluble
· easily hydrolysed
In plants, the polysaccharide energy store is called starch
Starch is made up of amylose and amylopectin molecules
In animals, the polysaccharide energy store is called glycogen
The more branched the polysaccharide, the faster it can be broken down into glucose for energy
- published: 27 Feb 2019
- views: 64928
14:51
What I Eat In A Week On The Starch Solution | Plant-Based
APPLY TO MY SLIM ON STARCH 1-ON-1 WEIGHT LOSS PROGRAM HERE ➵ ➵ https://www.healthyemmie.org
Welcome to Healthy Emmie! In this video, I’m going to share with yo...
APPLY TO MY SLIM ON STARCH 1-ON-1 WEIGHT LOSS PROGRAM HERE ➵ ➵ https://www.healthyemmie.org
Welcome to Healthy Emmie! In this video, I’m going to share with you what I eat in a week on Starch Solution. Let’s deep dive into the video to learn more about my plant-based meal plan.
👉 Subscribe to my channel to stay tuned: https://www.youtube.com/c/healthyemmie?sub_confirmation=1
A plant-based diet is a diet consisting mostly or entirely of plant-based foods. Plant-based foods are foods derived from plants with no animal-source foods or artificial ingredients.
The Starch Solution created by Dr. John McDougall is a starch-based diet focusing on whole food plant-based starches such as potatoes, rice, and beans. Making your plate at each meal using whole food plant-based. This way of eating how I maintain my weight and also, it is feeling me satisfied and full.
We normally eat three times a day is a complete social construct but the way that I like to do this thing is to listen to my body's hunger fullness cues to eat until I’m no longer hungry. So, all of the meals that you're seeing are not representative of one-third of my daily intake. I don't just eat breakfast, lunch, dinner. I eat as many times per day as I’d like. Sometimes I eat more times per day and sometimes I eat less.
The great thing about eating a whole foods plant-based diet and then learning your hunger fullness cues is that you don't have to fit into any certain social construct around meal times in meal sizes. You can tune into your body's hunger fullness cues in Starch Solution.
If you are looking to lose weight then instead of the corn tortillas, I would have rice whole real rice or whole real corn, or a baked potato and then take my cheese sauce and put it on top and then take salsa and put that on top.
You can check out all video parts to know about my 5 times meal plan by clicking the timestamps below for a quick view of every action.
0:00 Intro
0:10 Meal-1
3:42 Meal-2
6:25 Meal-3
9:03 Meal-4
11:19 Meal-5
I hope you enjoyed this video. Make sure that you click the "Like" button and also share this video with your friends and others who might also be interested to learn what I eat in a week on the Starch Solution.
Please click "Subscribe" and click the bell icon to keep up to date with new videos from Healthy Emmie. And if you've got any questions or feedback about this video topic, please leave a comment in the comments section.
FREE GROCERY LIST FOR VEGAN WEIGHT LOSS ➵ ➵ https://www.healthyemmie.org/grocerylist
Join the Healthy Hunnies Private Facebook Group➵ ➵ https://www.healthyemmie.org/joinhealthyhunnies
My Top 5 Weight Loss Recipes ➵ ➵ https://www.healthyemmie.org/weightlossrecipes
Chili Recipe ➵ ➵ https://www.healthyemmie.org/chili
My Go-To Products & Discount Codes ➵ ➵ https://docs.google.com/document/d/1iPaDdSik3k2gwkTYhYGZkfKdB3y3YhiNeVdV547i_ZA/edit?usp=sharing
Get Started on Your Plant-Based Diet with My Book ➵ ➵ https://www.healthyemmie.org/ebook1
THE BEST SALT, OIL, SUGAR-FREE VEGAN SAUCES ➵ ➵ http://wellyourworld.com?aff=6
Discounted Hawaiian Sweet Potatoes ➵ ➵ [CODE: EMMIE5] https://www.hawaiiveggiefarm.com
Subscribe: https://www.youtube.com/c/healthyemmie?sub_confirmation=1
FOLLOW ME:
Instagram ➵ ➵ @healthyemmie https://www.instagram.com/healthyemmie/?hl=en
Podcast ➵ ➵ https://open.spotify.com/show/1O3K75MyHPGiKod4yyHbgQ
Stay updated on my programs ➵ ➵ https://www.healthyemmie.org
About me:
If you don’t know who I am - hey! My name is Emmie! I am the go-to nutritionist for weight loss on a plant-based diet. On this channel, I teach you how to lose & maintain your desired weight through a high carb vegan diet. My diet is naturally high in carbohydrates and low in fat. It is incredible because you don’t have to count calories, you don’t need to portion control, and you don’t need to overexercise in order to lose weight! We are all about abundance and learning your body’s natural hunger & fullness cues through eating a WFPB (That means whole foods, plant-based) diet. Other common terms to describe this diet are oil-free vegan, SOS-free vegan, and HCLF or WSLF vegan! Welcome! I am SO happy you are here!
#TheStarchSolution #PlantBased #HealthyEmmie #WhatIEatInaWeek #PlantBasedMealPlan #PlantBasedFoods #WholeFoodPlantBased
https://wn.com/What_I_Eat_In_A_Week_On_The_Starch_Solution_|_Plant_Based
APPLY TO MY SLIM ON STARCH 1-ON-1 WEIGHT LOSS PROGRAM HERE ➵ ➵ https://www.healthyemmie.org
Welcome to Healthy Emmie! In this video, I’m going to share with you what I eat in a week on Starch Solution. Let’s deep dive into the video to learn more about my plant-based meal plan.
👉 Subscribe to my channel to stay tuned: https://www.youtube.com/c/healthyemmie?sub_confirmation=1
A plant-based diet is a diet consisting mostly or entirely of plant-based foods. Plant-based foods are foods derived from plants with no animal-source foods or artificial ingredients.
The Starch Solution created by Dr. John McDougall is a starch-based diet focusing on whole food plant-based starches such as potatoes, rice, and beans. Making your plate at each meal using whole food plant-based. This way of eating how I maintain my weight and also, it is feeling me satisfied and full.
We normally eat three times a day is a complete social construct but the way that I like to do this thing is to listen to my body's hunger fullness cues to eat until I’m no longer hungry. So, all of the meals that you're seeing are not representative of one-third of my daily intake. I don't just eat breakfast, lunch, dinner. I eat as many times per day as I’d like. Sometimes I eat more times per day and sometimes I eat less.
The great thing about eating a whole foods plant-based diet and then learning your hunger fullness cues is that you don't have to fit into any certain social construct around meal times in meal sizes. You can tune into your body's hunger fullness cues in Starch Solution.
If you are looking to lose weight then instead of the corn tortillas, I would have rice whole real rice or whole real corn, or a baked potato and then take my cheese sauce and put it on top and then take salsa and put that on top.
You can check out all video parts to know about my 5 times meal plan by clicking the timestamps below for a quick view of every action.
0:00 Intro
0:10 Meal-1
3:42 Meal-2
6:25 Meal-3
9:03 Meal-4
11:19 Meal-5
I hope you enjoyed this video. Make sure that you click the "Like" button and also share this video with your friends and others who might also be interested to learn what I eat in a week on the Starch Solution.
Please click "Subscribe" and click the bell icon to keep up to date with new videos from Healthy Emmie. And if you've got any questions or feedback about this video topic, please leave a comment in the comments section.
FREE GROCERY LIST FOR VEGAN WEIGHT LOSS ➵ ➵ https://www.healthyemmie.org/grocerylist
Join the Healthy Hunnies Private Facebook Group➵ ➵ https://www.healthyemmie.org/joinhealthyhunnies
My Top 5 Weight Loss Recipes ➵ ➵ https://www.healthyemmie.org/weightlossrecipes
Chili Recipe ➵ ➵ https://www.healthyemmie.org/chili
My Go-To Products & Discount Codes ➵ ➵ https://docs.google.com/document/d/1iPaDdSik3k2gwkTYhYGZkfKdB3y3YhiNeVdV547i_ZA/edit?usp=sharing
Get Started on Your Plant-Based Diet with My Book ➵ ➵ https://www.healthyemmie.org/ebook1
THE BEST SALT, OIL, SUGAR-FREE VEGAN SAUCES ➵ ➵ http://wellyourworld.com?aff=6
Discounted Hawaiian Sweet Potatoes ➵ ➵ [CODE: EMMIE5] https://www.hawaiiveggiefarm.com
Subscribe: https://www.youtube.com/c/healthyemmie?sub_confirmation=1
FOLLOW ME:
Instagram ➵ ➵ @healthyemmie https://www.instagram.com/healthyemmie/?hl=en
Podcast ➵ ➵ https://open.spotify.com/show/1O3K75MyHPGiKod4yyHbgQ
Stay updated on my programs ➵ ➵ https://www.healthyemmie.org
About me:
If you don’t know who I am - hey! My name is Emmie! I am the go-to nutritionist for weight loss on a plant-based diet. On this channel, I teach you how to lose & maintain your desired weight through a high carb vegan diet. My diet is naturally high in carbohydrates and low in fat. It is incredible because you don’t have to count calories, you don’t need to portion control, and you don’t need to overexercise in order to lose weight! We are all about abundance and learning your body’s natural hunger & fullness cues through eating a WFPB (That means whole foods, plant-based) diet. Other common terms to describe this diet are oil-free vegan, SOS-free vegan, and HCLF or WSLF vegan! Welcome! I am SO happy you are here!
#TheStarchSolution #PlantBased #HealthyEmmie #WhatIEatInaWeek #PlantBasedMealPlan #PlantBasedFoods #WholeFoodPlantBased
- published: 05 May 2021
- views: 3516
6:44
Carb Science: Good Starch vs. Bad Starch- Thomas DeLauer
Click Here to Subscribe: http://Bit.ly/ThomasVid
Website: http://ThomasDeLauer.com
Carb Science: Good Starch vs. Bad Starch- Thomas DeLauer… So you know that no...
Click Here to Subscribe: http://Bit.ly/ThomasVid
Website: http://ThomasDeLauer.com
Carb Science: Good Starch vs. Bad Starch- Thomas DeLauer… So you know that not all carbs are created equal, right? We always talk about that. But did you know that not all starches are created equal too? So in this video, I want to break down how different starches from different carbohydrate sources respond inside your body and may cause these additional casualties that you didn't quite know about before. If you haven't already, make sure you hit the subscribe button so that you can see all the three to five videos that I'm posting per week ranging from the topics of fasting, ketosis, general health, and just about everything under the sun relating to wellness. Also, make sure you turn on those notifications. So let's start digging into the science right now. So, when we're looking at starches, we really have to look at just two things. There's really only two major components that we have to focus on and they're two different polysaccharides. One is known as amylose and one is known as amylopectin. Now obviously there are different polysaccharides but these are the two that we want to focus on because they're the main culprits when it comes down to whether a starch is good or whether a starch is bad. So let's go ahead and let's focus on amylose first.
You see, amylose is what is known as a straight chain polysaccharide. What does that mean? It means that the glucose molecules, the actual carb molecules are in a simple, straight chain. What does this mean? It means that there's not a whole lot of surface area to be able to digest. So believe it or not, this kind of starch takes a longer time to break down because it has less surface area. So what ends up happening is it sits in the small intestine for a little bit, it gets broken down into slightly smaller chunks, and then eventually broken down into short chain fatty acids. I know, you heard me right. Literally a carbohydrate, a starch, goes into the gut and actually gets converted into a very fast-absorbing fat. I know, it's kind of crazy and it sounds bad but if you hear me out throughout the entire video, I will make sure that you understand that it's actually a good thing.
So what this means is it's actually a resistant starch. A resistant starch is what we want, even though it sounds bad again. Resistant kinda sounds bad, but it means that it resists the urge to crazily spike our blood sugar. It resists the urge to spike our insulin. This resistance in this context is actually a good thing.
So now let's talk about the other side of the coin. We're talking about amylopectin. Amylopectin in contrast to amylose is a highly branched molecule. What does that mean? Well remember how I said that the amylose has a long simple chain, just a straight chain that has very little surface area? Well, amylopectin has a lot of little branches, meaning it has a lot of surface area. I want you to visualize this for a second. You have just a simple straight tree branch. Think about the surface area that is on one single line. Now think about the surface area that is on something that has tons and tons of little branches and twigs. You got multiple branches upon branches. Think of the surface area that you have to travel. That means that you have a lot more absorbency, and again, first thought, this sounds good. We want to absorb our carbs, but the thing is, we don't want to absorb our carbs this fast unless mind you you know exactly what you're doing or you're trying to break a fast and strategically do something. We don't want to be constantly spiking our blood sugar or spiking our insulin. So these highly branched molecules end up having a very high molecular weight, which means that it has a higher impact on our bodies.
Now the interesting thing, we don't have just carbs that have just amylose or just amylopectin. All starches have both. It's just a ratio of the two that we have to focus on. Sometimes, starches have more amylopectin than they do amylose, and sometimes, starches have more amylose than they do amylopectin. It’s this ratio that ultimately determines the glycemic index and how we actually respond to a given carbohydrate.
So, by now you've probably realized that the amylopectin isn't necessarily a good thing and there's some research to back that up. There was a study that was published in the Journal of Nutrition that was quite basic. They took test subjects and for 16 weeks they had them eat a high amylopectin diet. They had them eat starches that were very high in amylopectin, and what they measured after 16 weeks were a couple of things, but mainly, they looked at their insulin levels. Well, test subjects ended up having a 50% increase in insulin, but guess what? It doesn't stop there. They ended up having a 50% increase in insulin resistance too. Do you know what insulin resistance is? That's diabetes.
https://wn.com/Carb_Science_Good_Starch_Vs._Bad_Starch_Thomas_Delauer
Click Here to Subscribe: http://Bit.ly/ThomasVid
Website: http://ThomasDeLauer.com
Carb Science: Good Starch vs. Bad Starch- Thomas DeLauer… So you know that not all carbs are created equal, right? We always talk about that. But did you know that not all starches are created equal too? So in this video, I want to break down how different starches from different carbohydrate sources respond inside your body and may cause these additional casualties that you didn't quite know about before. If you haven't already, make sure you hit the subscribe button so that you can see all the three to five videos that I'm posting per week ranging from the topics of fasting, ketosis, general health, and just about everything under the sun relating to wellness. Also, make sure you turn on those notifications. So let's start digging into the science right now. So, when we're looking at starches, we really have to look at just two things. There's really only two major components that we have to focus on and they're two different polysaccharides. One is known as amylose and one is known as amylopectin. Now obviously there are different polysaccharides but these are the two that we want to focus on because they're the main culprits when it comes down to whether a starch is good or whether a starch is bad. So let's go ahead and let's focus on amylose first.
You see, amylose is what is known as a straight chain polysaccharide. What does that mean? It means that the glucose molecules, the actual carb molecules are in a simple, straight chain. What does this mean? It means that there's not a whole lot of surface area to be able to digest. So believe it or not, this kind of starch takes a longer time to break down because it has less surface area. So what ends up happening is it sits in the small intestine for a little bit, it gets broken down into slightly smaller chunks, and then eventually broken down into short chain fatty acids. I know, you heard me right. Literally a carbohydrate, a starch, goes into the gut and actually gets converted into a very fast-absorbing fat. I know, it's kind of crazy and it sounds bad but if you hear me out throughout the entire video, I will make sure that you understand that it's actually a good thing.
So what this means is it's actually a resistant starch. A resistant starch is what we want, even though it sounds bad again. Resistant kinda sounds bad, but it means that it resists the urge to crazily spike our blood sugar. It resists the urge to spike our insulin. This resistance in this context is actually a good thing.
So now let's talk about the other side of the coin. We're talking about amylopectin. Amylopectin in contrast to amylose is a highly branched molecule. What does that mean? Well remember how I said that the amylose has a long simple chain, just a straight chain that has very little surface area? Well, amylopectin has a lot of little branches, meaning it has a lot of surface area. I want you to visualize this for a second. You have just a simple straight tree branch. Think about the surface area that is on one single line. Now think about the surface area that is on something that has tons and tons of little branches and twigs. You got multiple branches upon branches. Think of the surface area that you have to travel. That means that you have a lot more absorbency, and again, first thought, this sounds good. We want to absorb our carbs, but the thing is, we don't want to absorb our carbs this fast unless mind you you know exactly what you're doing or you're trying to break a fast and strategically do something. We don't want to be constantly spiking our blood sugar or spiking our insulin. So these highly branched molecules end up having a very high molecular weight, which means that it has a higher impact on our bodies.
Now the interesting thing, we don't have just carbs that have just amylose or just amylopectin. All starches have both. It's just a ratio of the two that we have to focus on. Sometimes, starches have more amylopectin than they do amylose, and sometimes, starches have more amylose than they do amylopectin. It’s this ratio that ultimately determines the glycemic index and how we actually respond to a given carbohydrate.
So, by now you've probably realized that the amylopectin isn't necessarily a good thing and there's some research to back that up. There was a study that was published in the Journal of Nutrition that was quite basic. They took test subjects and for 16 weeks they had them eat a high amylopectin diet. They had them eat starches that were very high in amylopectin, and what they measured after 16 weeks were a couple of things, but mainly, they looked at their insulin levels. Well, test subjects ended up having a 50% increase in insulin, but guess what? It doesn't stop there. They ended up having a 50% increase in insulin resistance too. Do you know what insulin resistance is? That's diabetes.
- published: 10 Apr 2018
- views: 131963
9:34
Extracting the starch from potatoes
In this video, we are isolating some starch from potatoes. We also talk a little bit about starch in general. Potato starch is better than corn starch because i...
In this video, we are isolating some starch from potatoes. We also talk a little bit about starch in general. Potato starch is better than corn starch because it forms a nice clear solution in water.
I am going to be using it for the Brigg's Rauscher Oscillating clock reaction and maybe some other things.
Nile talks about lab safety: https://youtu.be/ftACSEJ6DZA
--------------------------------
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/nilered
Youtube Membership: https://www.youtube.com/c/nilered/join
NileRed Merch Store (NileRed Pin & Keychain): https://store.dftba.com/collections/nilered
NileRed Website (Glassware & Beaker Mugs): https://nile.red
--------------------------------
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/nile.red
Twitter: https://twitter.com/NileRed2
Discord: https://discord.gg/3BT6UHf
https://wn.com/Extracting_The_Starch_From_Potatoes
In this video, we are isolating some starch from potatoes. We also talk a little bit about starch in general. Potato starch is better than corn starch because it forms a nice clear solution in water.
I am going to be using it for the Brigg's Rauscher Oscillating clock reaction and maybe some other things.
Nile talks about lab safety: https://youtu.be/ftACSEJ6DZA
--------------------------------
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/nilered
Youtube Membership: https://www.youtube.com/c/nilered/join
NileRed Merch Store (NileRed Pin & Keychain): https://store.dftba.com/collections/nilered
NileRed Website (Glassware & Beaker Mugs): https://nile.red
--------------------------------
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/nile.red
Twitter: https://twitter.com/NileRed2
Discord: https://discord.gg/3BT6UHf
- published: 25 Jun 2016
- views: 692549
3:41
Starch Retrogradation | The Science of Stale Bread
Starch retrogradation is the technical term for bread staling. It's the reason why your bread changes in texture and mouthfeel as it ages. In this video, we'll ...
Starch retrogradation is the technical term for bread staling. It's the reason why your bread changes in texture and mouthfeel as it ages. In this video, we'll show you how starch retrogradation occurs and how you can delay it to have a softer, tender bread for a longer time.
*********************
Royalty-free music by Bensound
Here's where we got out info:
Eduardo, M., Svanberg, U., & Ahrné, L. (2016). Effect of hydrocolloids and emulsifiers on the shelf-life of composite cassava-maize-wheat bread after storage. Food Science & Nutrition, 4(4), 636–644. doi:10.1002/fsn3.326
*********************
Video Link: Maillard Reaction
https://youtu.be/A04Bd0UzOGQ
*************************
Follow us at:
✅ FB: https://www.facebook.com/PostHarvestTech
✅ IG: https://www.instagram.com/postharvesttech
✅ TW: https://twitter.com/PostharvestT
✅ LI: https://www.linkedin.com/company/post-harvest-learning
https://wn.com/Starch_Retrogradation_|_The_Science_Of_Stale_Bread
Starch retrogradation is the technical term for bread staling. It's the reason why your bread changes in texture and mouthfeel as it ages. In this video, we'll show you how starch retrogradation occurs and how you can delay it to have a softer, tender bread for a longer time.
*********************
Royalty-free music by Bensound
Here's where we got out info:
Eduardo, M., Svanberg, U., & Ahrné, L. (2016). Effect of hydrocolloids and emulsifiers on the shelf-life of composite cassava-maize-wheat bread after storage. Food Science & Nutrition, 4(4), 636–644. doi:10.1002/fsn3.326
*********************
Video Link: Maillard Reaction
https://youtu.be/A04Bd0UzOGQ
*************************
Follow us at:
✅ FB: https://www.facebook.com/PostHarvestTech
✅ IG: https://www.instagram.com/postharvesttech
✅ TW: https://twitter.com/PostharvestT
✅ LI: https://www.linkedin.com/company/post-harvest-learning
- published: 25 Apr 2020
- views: 12653
3:12
What is starch?
For more information on starch, please visit www.starch.eu
For more information on starch, please visit www.starch.eu
https://wn.com/What_Is_Starch
For more information on starch, please visit www.starch.eu
- published: 17 May 2016
- views: 44318
3:35
A Tasting of Culinary Science—Starch
It’s fitting that the word starch begins with “star.” It’s the currency of the kitchen, the fundamental ingredient that’s used in cooking every day. Yes, starch...
It’s fitting that the word starch begins with “star.” It’s the currency of the kitchen, the fundamental ingredient that’s used in cooking every day. Yes, starch is that important. So it’s just as important that you understand starch and its behavior, and this video helps you get there. You’ll learn to produce so many delicious foods—thickening sauces like velouté, gel desserts like pudding, crispy treats like crackers—that you’ll be a star in the kitchen too!
Learn more: https://www.ciachef.edu/cia-culinary-science-bachelors-degree-program/
—————————————————————————————————————————————————————
The Culinary Institute of America: https://www.ciachef.edu
The CIA at Copia: https://www.ciaatcopia.com
CIA Restaurant Group: https://www.ciarestaurantgroup.com
CIA Food Enthusiasts programs: https://www.ciafoodies.com
Founded in 1946, The Culinary Institute of America is the world’s premier culinary college. Dedicated to driving leadership development for the foodservice and hospitality industry, the independent, not-for-profit CIA offers associate degrees in culinary arts and baking and pastry arts; bachelor’s degree majors in management, culinary science, and applied food studies; and executive education through its Food Business School. Its conferences and consulting services have made the CIA the think tank of the food industry in the areas of health & wellness, sustainability, world cuisines & cultures, and professional excellence & innovation. The college also offers certificate programs and courses for professionals and enthusiasts. Its worldwide network of 48,000 alumni includes leaders in every area of foodservice and hospitality. The CIA has campuses in New York, California, Texas, and Singapore.
https://wn.com/A_Tasting_Of_Culinary_Science—Starch
It’s fitting that the word starch begins with “star.” It’s the currency of the kitchen, the fundamental ingredient that’s used in cooking every day. Yes, starch is that important. So it’s just as important that you understand starch and its behavior, and this video helps you get there. You’ll learn to produce so many delicious foods—thickening sauces like velouté, gel desserts like pudding, crispy treats like crackers—that you’ll be a star in the kitchen too!
Learn more: https://www.ciachef.edu/cia-culinary-science-bachelors-degree-program/
—————————————————————————————————————————————————————
The Culinary Institute of America: https://www.ciachef.edu
The CIA at Copia: https://www.ciaatcopia.com
CIA Restaurant Group: https://www.ciarestaurantgroup.com
CIA Food Enthusiasts programs: https://www.ciafoodies.com
Founded in 1946, The Culinary Institute of America is the world’s premier culinary college. Dedicated to driving leadership development for the foodservice and hospitality industry, the independent, not-for-profit CIA offers associate degrees in culinary arts and baking and pastry arts; bachelor’s degree majors in management, culinary science, and applied food studies; and executive education through its Food Business School. Its conferences and consulting services have made the CIA the think tank of the food industry in the areas of health & wellness, sustainability, world cuisines & cultures, and professional excellence & innovation. The college also offers certificate programs and courses for professionals and enthusiasts. Its worldwide network of 48,000 alumni includes leaders in every area of foodservice and hospitality. The CIA has campuses in New York, California, Texas, and Singapore.
- published: 01 Mar 2016
- views: 73332
3:31
How To Make Potato Starch |Homemade Potato Flour | Potato Starch Recipe
What is Potato Starch ? Potato starch kya he?
Potato starch is a fine white powdery substance derived from potatoes. Similar to other starches. It is commonly ...
What is Potato Starch ? Potato starch kya he?
Potato starch is a fine white powdery substance derived from potatoes. Similar to other starches. It is commonly used to thicken gel texturize and increase crispiness in baked goods. It is also used in clear soup, confections, fillings, and so on.
Thanks for watching........
Please Subscribe my channel , this will help me a lot.......
And stay tuned for new videos.......
Follow me on----/------
Facebook ----- https://www.facebook.com/CookingWithRekha/
Gooogle Plus ----- https://plus.google.com/u/0/+CookingwithRekha
Twitter ----- https://twitter.com/Rekha_Cooking
Video Copyrights – Cooking with Rekha(verified)
Thumbnail Copyrights – Cooking with Rekha(verified)
Audio Copyrights – Cooking with Rekha(verified)
https://wn.com/How_To_Make_Potato_Starch_|Homemade_Potato_Flour_|_Potato_Starch_Recipe
What is Potato Starch ? Potato starch kya he?
Potato starch is a fine white powdery substance derived from potatoes. Similar to other starches. It is commonly used to thicken gel texturize and increase crispiness in baked goods. It is also used in clear soup, confections, fillings, and so on.
Thanks for watching........
Please Subscribe my channel , this will help me a lot.......
And stay tuned for new videos.......
Follow me on----/------
Facebook ----- https://www.facebook.com/CookingWithRekha/
Gooogle Plus ----- https://plus.google.com/u/0/+CookingwithRekha
Twitter ----- https://twitter.com/Rekha_Cooking
Video Copyrights – Cooking with Rekha(verified)
Thumbnail Copyrights – Cooking with Rekha(verified)
Audio Copyrights – Cooking with Rekha(verified)
- published: 16 Jan 2021
- views: 9249































 Wooster Daily Record
18 Oct 2021
Wooster Daily Record
18 Oct 2021















