AWS Batch enables developers, scientists, and engineers to easily and efficiently run hundreds of thousands of batch computing jobs on AWS. AWS Batch dynamically provisions the optimal quantity and type of compute resources (e.g., CPU or memory optimized instances) based on the volume and specific resource requirements of the batch jobs submitted. With AWS Batch, there is no need to install and manage batch computing software or server clusters that you use to run your jobs, allowing you to focus on analyzing results and solving problems. AWS Batch plans, schedules, and executes your batch computing workloads across the full range of AWS compute services and features, such as Amazon EC2 and Spot Instances.
There is no additional charge for AWS Batch. You only pay for the AWS resources (e.g. EC2 instances) you create to store and run your batch jobs.
Learn how AWS Batch can help you run your batch computing workload efficiently.

Fully Managed
AWS Batch eliminates the need to operate third-party commercial or open source batch processing solutions. There is no batch software or servers to install or manage. AWS Batch manages all the infrastructure for you, avoiding the complexities of provisioning, managing, monitoring, and scaling your batch computing jobs.

Integrated with AWS
AWS Batch is natively integrated with the AWS platform, allowing you to leverage the scaling, networking, and access management capabilities of AWS. This makes it easy to run jobs that safely and securely retrieve and write data to and from AWS data stores such as Amazon S3 or Amazon DynamoDB.

Cost Optimized Resource Provisioning
AWS Batch provisions compute resources and optimizes the job distribution based on the volume and resource requirements of the submitted batch jobs. AWS Batch dynamically scales compute resources to any quantity required to run your batch jobs, freeing you from the constraints of fixed-capacity clusters. AWS Batch also dynamically bids for Spot Instances on your behalf, reducing the cost of running your batch jobs further.
Automate the analysis of the day’s transaction costs, execution reporting, and market performance.

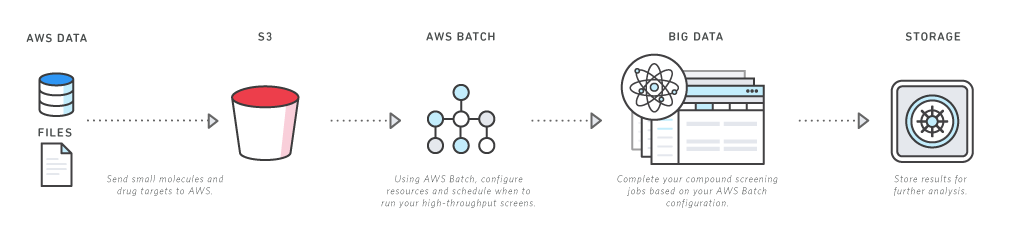
Rapidly search libraries of small molecules for drug discovery.
Automate content rendering workloads and reduce the need for human intervention due to execution dependencies or resource scheduling.




