- published: 23 Feb 2013
- views: 6812
-
remove the playlistBone Mineral
-
remove the playlistLatest Videos
-
remove the playlistLongest Videos
- remove the playlistBone Mineral
- remove the playlistLatest Videos
- remove the playlistLongest Videos
- published: 15 May 2014
- views: 39139
- published: 13 Dec 2016
- views: 124
- published: 02 May 2016
- views: 2570
- published: 30 Jul 2013
- views: 773
- published: 05 Nov 2011
- views: 20013
- published: 28 Aug 2016
- views: 460

Bone mineral
Bone mineral (also called inorganic bone phase, bone salt, or bone apatite) is the inorganic component of bone tissue. It gives bones their compressive strength. Bone mineral is formed from carbonated hydroxyapatite with lower crystallinity.
Bone mineral is formed from globular and plate structures distributed among the collagen fibrils of bone and forming yet a larger structure. The bone salt and collagen fibers together constitute the extracellular matrix of bone tissue.
Often the plural form "bone salts" is used; it reflects the notion of various salts that, on the level of molecular metabolism, can go into the formation of the hydroxyapatite.
Bone mineral is dynamic in living animals; it is continually being resorbed and built anew in the bone remodeling process. In fact, the bones function as a bank or storehouse in which calcium can be continually withdrawn for use or deposited for storage, as dictated by homeostasis, which maintains the concentration of calcium ions in the blood serum within a particular range despite the variability of muscle tissue metabolism. Parathormone and calcitonin are the principal hormones with which the neuroendocrine system controls this ongoing process. The parathyroid and thyroid glands in the neck produce those hormones; thus, problems with those glands (such as hypo- or hyperparathyroidism or hypo- or hyperthyroidism) can create problems with bone mineral density (as well as hypo- or hypercalcemia).
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the vertebral skeleton. Bones support and protect the various organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals and also enable mobility. Bone tissue is a type of dense connective tissue. Bones come in a variety of shapes and sizes and have a complex internal and external structure. They are lightweight yet strong and hard, and serve multiple functions. Mineralized osseous tissue, or bone tissue, is of two types, cortical and cancellous, and gives a bone rigidity and a coral-like three-dimensional internal structure. Other types of tissue found in bones include marrow, endosteum, periosteum, nerves, blood vessels and cartilage.
Bone is an active tissue composed of different types of bone cells. Osteoblasts are involved in the creation and mineralisation of bone; osteocytes and osteoclasts are involved in the reabsorption of bone tissue. The mineralised matrix of bone tissue has an organic component mainly of collagen and an inorganic component of bone mineral made up of various salts.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 3:24
3:24Bone Mineral Density Test
Bone Mineral Density TestBone Mineral Density Test
Den basta och mest effektiva utvarderingen av benhalsa ar ett bone mineral density BMD test. Se hur en BMD test utfors. -
 3:39
3:39Bone Density Testing
Bone Density TestingBone Density Testing
A specialized test, called a bone mineral density (BMD) test, measures the density of bone in various parts of the body. Testing used at EWBC to measure bone density is the DXA* (Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry). This test measures the bone mineral density of the spine and hip. Once you have your test, your results are sent to the physician who ordered it. Bone Density testing is available at all our offices (Brighton, Geneseo, Greece and Victor). -
 10:01
10:01Bone Homeostasis (Calcium and Phosphate) Hormones
Bone Homeostasis (Calcium and Phosphate) Hormones -
 3:03
3:03What is a bone mineral density test?
What is a bone mineral density test?What is a bone mineral density test?
A bone mineral density test, or DXA Scan, is one of the most accurate ways of assessing your bone health. A DXA scan measures your bone loss over time and can detect osteoporosis, which is a disease of the bones that causes bones to be weak and break easily. Doctors use the results of the test to evaluate your risk for fractures. At MD Anderson we use dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry, which uses x-rays to measure bone density in the hip and spine, and occasionally in the forearm. Learn more at https://www.mdanderson.org/research/departments-labs-institutes/departments-divisions/diagnostic-imaging.html -
 28:20
28:20Chronic Kidney Disease - Mineral Bone Disease: Pharmacological Treatment and its Controversies
Chronic Kidney Disease - Mineral Bone Disease: Pharmacological Treatment and its ControversiesChronic Kidney Disease - Mineral Bone Disease: Pharmacological Treatment and its Controversies
A presentation at WCPD 2016 by Dr Cliff Lo. -
 22:22
22:22Web Episode #007 - Understanding Bone Mineral Metabolism in Kidney Disease
Web Episode #007 - Understanding Bone Mineral Metabolism in Kidney DiseaseWeb Episode #007 - Understanding Bone Mineral Metabolism in Kidney Disease
Welcome back to the May episode for the Wash U Nephrology Web Episode Series! We are bringing one of our faculty members, Dr. Seth Goldberg to talk about bone mineral metabolism. Calcium, phosphorus, PTH, Vitamin D, FGF-23, Klotho, and more. Although it may seem like a typical powerpoint presentation, pay close attention to the animations as they really help explain the way all of these players help maintain homeostasis, and how things go wrong with a decreasing GFR. -
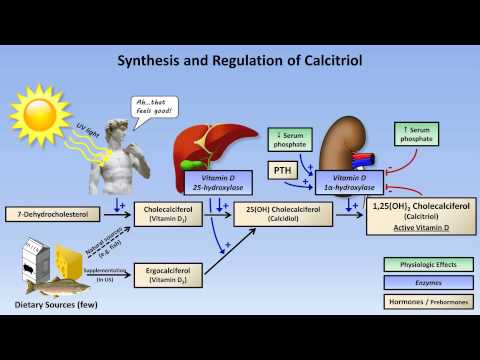 17:46
17:46Calcium and Phosphate Metabolism
Calcium and Phosphate Metabolism -
 3:11
3:11Vitamins, Minerals and Bone Formation
Vitamins, Minerals and Bone FormationVitamins, Minerals and Bone Formation
Bone formation slows after 50 and calcium and vitamin D are not enough to form new bone, not to mention prevent bone loss. Adding Silical to your diet can help meet your nutritional needs. Order yours http://bit.ly/1taWcvc -
 4:15
4:15Bone Densitometry
Bone DensitometryBone Densitometry
This film is intended for anyone wishing to know more about the examination procedure that lasts approximately 20 minutes and does not require any injection. This film addresses both patients and their loved ones. Bone Densitometry or Dual X-ray Absorptiometry, is a radiological technique using low-intensity X-rays. It measures the bone mineral content (in grams) per surface area unit (in square centimetres). Bone mineral density increases from birth until the age of 20 to 25, then remains stable until the age of 35 to 40, and then progressively diminishes. Osteoporosis is a skeletal disease characterised by low bone mineral density and progressive deterioration of the bone tissue's microarchitecture, with an increasing fracture risk. Therefore, it is important to both measure bone mineral density as well as to determine if the patient has any undetected vertebral fractures. -
 13:57
13:57Metabolic Bone Disorders
Metabolic Bone DisordersMetabolic Bone Disorders
This is a short video on five bone diseases caused by altered bone metabolism. I created this presentation with Google Slides. Image were created or taken from Wikimedia Commons I created this video with the YouTube Video Editor. ADDITIONAL TAGS: Metabolic bone disorders Bone diseases caused by disturbed bone metabolism Osteitis fibrosa cystica Paget’s disease of bone Osteogenesis imperfecta Osteomalacia / rickets Osteoporosis Osteitis fibrosa cystica AKA brown tumor of hyperparathyroidism Excessive bone resorption (mediated by osteoclast activity) Hyperparathyroidism → increased PTH → resorp bone Pathology → diminished bone strength Subperiosteal (below connective tissue) resorption Bone cysts Radiology: cyst formation, mimics bone neoplasms Histology: fibrous tissue, hemorrhage (hemosiderin pigment) Treatment: underlying cause of hyperparathyroidism Osteitis fibrosa cystica Paget’s disease of bone Excess bone resorption and formation Repetition and acceleration of cyclic osteon breakdown and rebuilding Results in disorganized bone (“jigsaw puzzleâ€, “mosaicâ€) Epi: prevalence increases with age Pathology: larger, weaker, less dense, more vascular bones Affects axial skeleton and proximal long bones Clinical: isolated AP increase Symptoms: usually asymptomatic, but some get bone pain/fracture/deformity, arthritis, neuro complications (compression) Radiology: cotton wool spots (sclerosis, whiter areas); Nuc: increased uptake in affected bones Treatment: bisphosphonates (antiresorptive) Osteogenesis imperfecta AKA brittle bone disease or Lobstein syndrome Inadequate bone formation with defective bone matrices Due to mutation in bone collagen gene (8 variants) Clinical: unexpected fractures, family hx, blue sclera Diagnose with DNA tests or collagen analysis Treatment: bisphosphonates, surgery; no cure Inadequate bone formation with defective bone matrix mineralization Due to insufficient calcium or phosphorus Most frequently caused by vitamin D deficiency Also caused by chronic kidney disease → kidney converts inactive to active vit D 25-OH-D → 1,25-OH2-D Pathology: softening of bone Adults (osteomalacia)→ bone pain, muscle weakness, fracture risk Children (rickets) → bone deformities (ie bowing), dental issues Treatment: restore vitamin D levels (or active form (calcitriol)), calcium and phosphorus if necessary Osteoporosis Reduced bone matrix and mineralization secondary to various factors No single etiology → 50% hereditary, 50% acquired (diet, age, exercise, comorbidities) Epi: most common metabolic bone disorder Pathology: increased fragility, fractures Decrease in bone density (2.5 std dev) Osteopenia is milder form (1 to 2.5 std dev) Bone mineral density (BMD) measured with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scan T-score is std dev multiple difference from avg ethnicity/gender-matched 30 yo Z-score is std dev multiple difference from avg ethnicity/gender/age-matched pt Primary osteoporosis Inherent risks: fracture hx, female, white, age, genetics, fam hx Modifiable risks: smoking, alcohol, low estrogen, low Ca, sedentary, low BMI Secondary osteoporosis → due to other diseases, surgeries, medications Hormones: corticosteroids (net resorption); thyroid/growth hormone (net formation) Dzs: Cushing’s; hyper-parathyroid/thyroid/prolactin; hypo-gonad/pituitary; gastric bypass and other malabsorption; Ehlers-Danlos; OI; myeloma, lymphoma/leukemia Drugs: ethanol, glucocorticoids, heparin Clinical: kyphosis (hump-back), scoliosis (S-spine), height loss, gait/balance issues Radiology: x-ray only detects 30-50% loss → DEXA preferred Treatment: Ca, vit D, estrogen replacement; calcitonin; selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs, ie raloxifene and tamoxifen), bisphosphonates, denosumab (RANK Ab); teriparatide (PTH analog, anabolic) Osteitis fibrosa cystica Paget’s disease of bone Osteogenesis imperfecta Osteomalacia / rickets Osteoporosis
-

Bone Mineral Density Test
Den basta och mest effektiva utvarderingen av benhalsa ar ett bone mineral density BMD test. Se hur en BMD test utfors.
published: 23 Feb 2013 -

Bone Density Testing
A specialized test, called a bone mineral density (BMD) test, measures the density of bone in various parts of the body. Testing used at EWBC to measure bone density is the DXA* (Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry). This test measures the bone mineral density of the spine and hip. Once you have your test, your results are sent to the physician who ordered it. Bone Density testing is available at all our offices (Brighton, Geneseo, Greece and Victor).
published: 15 May 2014 -

-

What is a bone mineral density test?
A bone mineral density test, or DXA Scan, is one of the most accurate ways of assessing your bone health. A DXA scan measures your bone loss over time and can detect osteoporosis, which is a disease of the bones that causes bones to be weak and break easily. Doctors use the results of the test to evaluate your risk for fractures. At MD Anderson we use dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry, which uses x-rays to measure bone density in the hip and spine, and occasionally in the forearm. Learn more at https://www.mdanderson.org/research/departments-labs-institutes/departments-divisions/diagnostic-imaging.html
published: 13 Dec 2016 -

Chronic Kidney Disease - Mineral Bone Disease: Pharmacological Treatment and its Controversies
A presentation at WCPD 2016 by Dr Cliff Lo.
published: 07 Apr 2016 -

Web Episode #007 - Understanding Bone Mineral Metabolism in Kidney Disease
Welcome back to the May episode for the Wash U Nephrology Web Episode Series! We are bringing one of our faculty members, Dr. Seth Goldberg to talk about bone mineral metabolism. Calcium, phosphorus, PTH, Vitamin D, FGF-23, Klotho, and more. Although it may seem like a typical powerpoint presentation, pay close attention to the animations as they really help explain the way all of these players help maintain homeostasis, and how things go wrong with a decreasing GFR.
published: 02 May 2016 -

-

Vitamins, Minerals and Bone Formation
Bone formation slows after 50 and calcium and vitamin D are not enough to form new bone, not to mention prevent bone loss. Adding Silical to your diet can help meet your nutritional needs. Order yours http://bit.ly/1taWcvc
published: 30 Jul 2013 -

Bone Densitometry
This film is intended for anyone wishing to know more about the examination procedure that lasts approximately 20 minutes and does not require any injection. This film addresses both patients and their loved ones. Bone Densitometry or Dual X-ray Absorptiometry, is a radiological technique using low-intensity X-rays. It measures the bone mineral content (in grams) per surface area unit (in square centimetres). Bone mineral density increases from birth until the age of 20 to 25, then remains stable until the age of 35 to 40, and then progressively diminishes. Osteoporosis is a skeletal disease characterised by low bone mineral density and progressive deterioration of the bone tissue's microarchitecture, with an increasing fracture risk. Therefore, it is important to both measure bone mineral...
published: 05 Nov 2011 -

Metabolic Bone Disorders
This is a short video on five bone diseases caused by altered bone metabolism. I created this presentation with Google Slides. Image were created or taken from Wikimedia Commons I created this video with the YouTube Video Editor. ADDITIONAL TAGS: Metabolic bone disorders Bone diseases caused by disturbed bone metabolism Osteitis fibrosa cystica Paget’s disease of bone Osteogenesis imperfecta Osteomalacia / rickets Osteoporosis Osteitis fibrosa cystica AKA brown tumor of hyperparathyroidism Excessive bone resorption (mediated by osteoclast activity) Hyperparathyroidism → increased PTH → resorp bone Pathology → diminished bone strength Subperiosteal (below connective tissue) resorption Bone cysts Radiology: cyst formation, mimics bone neoplasms Histology: fibrous tissue, he...
published: 28 Aug 2016
Bone Mineral Density Test
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:24
- Updated: 23 Feb 2013
- views: 6812
- published: 23 Feb 2013
- views: 6812
Bone Density Testing
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:39
- Updated: 15 May 2014
- views: 39139
- published: 15 May 2014
- views: 39139
Bone Homeostasis (Calcium and Phosphate) Hormones
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:01
- Updated: 27 Feb 2012
- views: 157926
What is a bone mineral density test?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:03
- Updated: 13 Dec 2016
- views: 124
- published: 13 Dec 2016
- views: 124
Chronic Kidney Disease - Mineral Bone Disease: Pharmacological Treatment and its Controversies
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 28:20
- Updated: 07 Apr 2016
- views: 962
Web Episode #007 - Understanding Bone Mineral Metabolism in Kidney Disease
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 22:22
- Updated: 02 May 2016
- views: 2570
- published: 02 May 2016
- views: 2570
Calcium and Phosphate Metabolism
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 17:46
- Updated: 16 Jul 2013
- views: 157203
Vitamins, Minerals and Bone Formation
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:11
- Updated: 30 Jul 2013
- views: 773
- published: 30 Jul 2013
- views: 773
Bone Densitometry
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:15
- Updated: 05 Nov 2011
- views: 20013
- published: 05 Nov 2011
- views: 20013
Metabolic Bone Disorders
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 13:57
- Updated: 28 Aug 2016
- views: 460
- published: 28 Aug 2016
- views: 460
-

Bone Mineral Density Test
Den basta och mest effektiva utvarderingen av benhalsa ar ett bone mineral density BMD test. Se hur en BMD test utfors.
published: 23 Feb 2013 -

Bone Density Testing
A specialized test, called a bone mineral density (BMD) test, measures the density of bone in various parts of the body. Testing used at EWBC to measure bone density is the DXA* (Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry). This test measures the bone mineral density of the spine and hip. Once you have your test, your results are sent to the physician who ordered it. Bone Density testing is available at all our offices (Brighton, Geneseo, Greece and Victor).
published: 15 May 2014 -

-

What is a bone mineral density test?
A bone mineral density test, or DXA Scan, is one of the most accurate ways of assessing your bone health. A DXA scan measures your bone loss over time and can detect osteoporosis, which is a disease of the bones that causes bones to be weak and break easily. Doctors use the results of the test to evaluate your risk for fractures. At MD Anderson we use dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry, which uses x-rays to measure bone density in the hip and spine, and occasionally in the forearm. Learn more at https://www.mdanderson.org/research/departments-labs-institutes/departments-divisions/diagnostic-imaging.html
published: 13 Dec 2016 -

Chronic Kidney Disease - Mineral Bone Disease: Pharmacological Treatment and its Controversies
A presentation at WCPD 2016 by Dr Cliff Lo.
published: 07 Apr 2016 -

Web Episode #007 - Understanding Bone Mineral Metabolism in Kidney Disease
Welcome back to the May episode for the Wash U Nephrology Web Episode Series! We are bringing one of our faculty members, Dr. Seth Goldberg to talk about bone mineral metabolism. Calcium, phosphorus, PTH, Vitamin D, FGF-23, Klotho, and more. Although it may seem like a typical powerpoint presentation, pay close attention to the animations as they really help explain the way all of these players help maintain homeostasis, and how things go wrong with a decreasing GFR.
published: 02 May 2016 -

-

Vitamins, Minerals and Bone Formation
Bone formation slows after 50 and calcium and vitamin D are not enough to form new bone, not to mention prevent bone loss. Adding Silical to your diet can help meet your nutritional needs. Order yours http://bit.ly/1taWcvc
published: 30 Jul 2013 -

Bone Densitometry
This film is intended for anyone wishing to know more about the examination procedure that lasts approximately 20 minutes and does not require any injection. This film addresses both patients and their loved ones. Bone Densitometry or Dual X-ray Absorptiometry, is a radiological technique using low-intensity X-rays. It measures the bone mineral content (in grams) per surface area unit (in square centimetres). Bone mineral density increases from birth until the age of 20 to 25, then remains stable until the age of 35 to 40, and then progressively diminishes. Osteoporosis is a skeletal disease characterised by low bone mineral density and progressive deterioration of the bone tissue's microarchitecture, with an increasing fracture risk. Therefore, it is important to both measure bone mineral...
published: 05 Nov 2011 -

Metabolic Bone Disorders
This is a short video on five bone diseases caused by altered bone metabolism. I created this presentation with Google Slides. Image were created or taken from Wikimedia Commons I created this video with the YouTube Video Editor. ADDITIONAL TAGS: Metabolic bone disorders Bone diseases caused by disturbed bone metabolism Osteitis fibrosa cystica Paget’s disease of bone Osteogenesis imperfecta Osteomalacia / rickets Osteoporosis Osteitis fibrosa cystica AKA brown tumor of hyperparathyroidism Excessive bone resorption (mediated by osteoclast activity) Hyperparathyroidism → increased PTH → resorp bone Pathology → diminished bone strength Subperiosteal (below connective tissue) resorption Bone cysts Radiology: cyst formation, mimics bone neoplasms Histology: fibrous tissue, he...
published: 28 Aug 2016
Bone Mineral Density Test
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:24
- Updated: 23 Feb 2013
- views: 6812
- published: 23 Feb 2013
- views: 6812
Bone Density Testing
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:39
- Updated: 15 May 2014
- views: 39139
- published: 15 May 2014
- views: 39139
Bone Homeostasis (Calcium and Phosphate) Hormones
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:01
- Updated: 27 Feb 2012
- views: 157926
What is a bone mineral density test?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:03
- Updated: 13 Dec 2016
- views: 124
- published: 13 Dec 2016
- views: 124
Chronic Kidney Disease - Mineral Bone Disease: Pharmacological Treatment and its Controversies
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 28:20
- Updated: 07 Apr 2016
- views: 962
Web Episode #007 - Understanding Bone Mineral Metabolism in Kidney Disease
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 22:22
- Updated: 02 May 2016
- views: 2570
- published: 02 May 2016
- views: 2570
Calcium and Phosphate Metabolism
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 17:46
- Updated: 16 Jul 2013
- views: 157203
Vitamins, Minerals and Bone Formation
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:11
- Updated: 30 Jul 2013
- views: 773
- published: 30 Jul 2013
- views: 773
Bone Densitometry
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:15
- Updated: 05 Nov 2011
- views: 20013
- published: 05 Nov 2011
- views: 20013
Metabolic Bone Disorders
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 13:57
- Updated: 28 Aug 2016
- views: 460
- published: 28 Aug 2016
- views: 460
-

Extreme Weight Loss S03E09 Alyssa PDTVx264 JIVE
Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health, or physical fitness is a reduction of the total body mass, due to a mean loss of fluid, body fat or adipose tissue and/or lean mass, namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon, and other connective tissue. It can occur unintentionally due to an underlying disease or can arise from a conscious effort to improve an actual or perceived overweight or obese state. Intentional weight loss is commonly referred to as slimming. Путеводитель по достопримечательностям - http://xn--h1aqbff.xn--p1ai/ Достопримечательности городов Европы - http://xn--h1aqbff.xn--p1ai/goroda/evropa/
published: 02 Sep 2016 -

Mineral Bone Disease Prof. Tarek Elbaz
published: 23 Oct 2013 -

extreme makeover weight loss edition s04e01 hdtv, Ty and Charita
Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health, or physical fitness is a reduction of the total body mass, due to a mean loss of fluid, body fat or adipose tissue and/or lean mass, namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon, and other connective tissue. It can occur unintentionally due to an underlying disease or can arise from a conscious effort to improve an actual or perceived overweight or obese state. Intentional weight loss is commonly referred to as slimming.
published: 31 Mar 2017 -

Extreme Makeover Weightloss Edition S02 E07 Sally
Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health, or physical fitness is a reduction of the total body mass, due to a mean loss of fluid, body fat or adipose tissue and/or lean mass, namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon, and other connective tissue. It can occur unintentionally due to an underlying disease or can arise from a conscious effort to improve an actual or perceived overweight or obese state. Intentional weight loss is commonly referred to as slimming.
published: 21 Nov 2016 -

Extreme Weight Loss S03E08 Chantell
Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health, or physical fitness is a reduction of the total body mass, due to a mean loss of fluid, body fat or adipose tissue and/or lean mass, namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon, and other connective tissue. It can occur unintentionally due to an underlying disease or can arise from a conscious effort to improve an actual or perceived overweight or obese state. Intentional weight loss is commonly referred to as slimming. http://xn--b1adeojrb1a.xn--p1ai/
published: 21 Nov 2013 -

DHEA - Energy, Stamina, Libido, Well-Being, ++
DHEA - benefits include improved sense of wellbeing, more alertness and stamina, and enhanced sexual interest and libido, increased epidermal thickness, sebum production, skin hydration, and decrease facial skin pigmentation, erectile dysfunction, orgasmic function, sexual desire, and overall sexual satisfaction, improve bone mineral density, schizophrenia, may help reduce SLE disease activity, frequency of flare-ups, and corticosteroid doses needed. "DHEA, dehydroepiandrosterone, is an adrenal steroid hormone in the body. It is made by the adrenal glands and is then converted to androgens, estrogens and other hormones. These are the hormones that regulate fat and mineral metabolism, sexual and reproductive function, and energy levels. DHEA levels increase until our mid to late 20’s then ...
published: 05 Apr 2016 -

The Biggest Loser Season 1 Episode 02
Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health, or physical fitness is a reduction of the total body mass, due to a mean loss of fluid, body fat or adipose tissue and/or lean mass, namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon, and other connective tissue. It can occur unintentionally due to an underlying disease or can arise from a conscious effort to improve an actual or perceived overweight or obese state. Intentional weight loss is commonly referred to as slimming.
published: 03 Apr 2017 -

Extreme Makeover Weight Loss Edition Season 03 Episode 11 Ashley 1
Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health, or physical fitness is a reduction of the total body mass, due to a mean loss of fluid, body fat or adipose tissue and/or lean mass, namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon, and other connective tissue. It can occur unintentionally due to an underlying disease or can arise from a conscious effort to improve an actual or perceived overweight or obese state. Intentional weight loss is commonly referred to as slimming. Subscribe for more:http:http://bit.ly/1oP76zS loss weight,quick weight loss,weight loss programs,weightloss,weight loss program,lose weight,diet plans,rapid weight loss,weight lose,weight loss journey,weight loss before and after pictures,weight loss motivation,weight loss transformation before and after,weight loss tips,w...
published: 15 Aug 2014 -

Fractures in Persons with NeuroDisabilities 2016
This educational video explains why it is important to maintain optimal dietary intake and intestinal absorption of calcium so that bodily needs for calcium can be met without having to remove calcium from bone, which decreases bone mineral density and increases risk for fracture. The importance of weight bearing physical activity is also discussed.
published: 22 Apr 2016 -

Secrets to Healthy Aging
Richard Passwater, Jr will discuss secrets to healthy aging. Including the following topics: o Which nutrients can promote & protect collagen production o The emerging science on bone loss o Limitations of bone mineral density testing o Why consuming large amounts of calcium is ineffective and can be dangerous.
published: 28 Apr 2015
Extreme Weight Loss S03E09 Alyssa PDTVx264 JIVE
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:25:22
- Updated: 02 Sep 2016
- views: 43354
- published: 02 Sep 2016
- views: 43354
Mineral Bone Disease Prof. Tarek Elbaz
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 30:34
- Updated: 23 Oct 2013
- views: 245
- published: 23 Oct 2013
- views: 245
extreme makeover weight loss edition s04e01 hdtv, Ty and Charita
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:24:29
- Updated: 31 Mar 2017
- views: 2881
- published: 31 Mar 2017
- views: 2881
Extreme Makeover Weightloss Edition S02 E07 Sally
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:24:46
- Updated: 21 Nov 2016
- views: 2502
- published: 21 Nov 2016
- views: 2502
Extreme Weight Loss S03E08 Chantell
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:23:46
- Updated: 21 Nov 2013
- views: 38064
- published: 21 Nov 2013
- views: 38064
DHEA - Energy, Stamina, Libido, Well-Being, ++
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:00:01
- Updated: 05 Apr 2016
- views: 27252
- published: 05 Apr 2016
- views: 27252
The Biggest Loser Season 1 Episode 02
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 39:57
- Updated: 03 Apr 2017
- views: 7
- published: 03 Apr 2017
- views: 7
Extreme Makeover Weight Loss Edition Season 03 Episode 11 Ashley 1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:23:46
- Updated: 15 Aug 2014
- views: 150675
- published: 15 Aug 2014
- views: 150675
Fractures in Persons with NeuroDisabilities 2016
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 38:30
- Updated: 22 Apr 2016
- views: 13
- published: 22 Apr 2016
- views: 13
Secrets to Healthy Aging
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:39:03
- Updated: 28 Apr 2015
- views: 73
- published: 28 Apr 2015
- views: 73


- Playlist
- Chat

Bone Mineral Density Test
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Feb 2013
- views: 6812

Bone Density Testing
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 May 2014
- views: 39139

Bone Homeostasis (Calcium and Phosphate) Hormones
- Report rights infringement
- published: 27 Feb 2012
- views: 157926

What is a bone mineral density test?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 Dec 2016
- views: 124

Chronic Kidney Disease - Mineral Bone Disease: Pharmacological Treatment and its Controversies
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Apr 2016
- views: 962

Web Episode #007 - Understanding Bone Mineral Metabolism in Kidney Disease
- Report rights infringement
- published: 02 May 2016
- views: 2570

Calcium and Phosphate Metabolism
- Report rights infringement
- published: 16 Jul 2013
- views: 157203

Vitamins, Minerals and Bone Formation
- Report rights infringement
- published: 30 Jul 2013
- views: 773

Bone Densitometry
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Nov 2011
- views: 20013

Metabolic Bone Disorders
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Aug 2016
- views: 460

- Playlist
- Chat

Bone Mineral Density Test
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Feb 2013
- views: 6812

Bone Density Testing
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 May 2014
- views: 39139

Bone Homeostasis (Calcium and Phosphate) Hormones
- Report rights infringement
- published: 27 Feb 2012
- views: 157926

What is a bone mineral density test?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 Dec 2016
- views: 124

Chronic Kidney Disease - Mineral Bone Disease: Pharmacological Treatment and its Controversies
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Apr 2016
- views: 962

Web Episode #007 - Understanding Bone Mineral Metabolism in Kidney Disease
- Report rights infringement
- published: 02 May 2016
- views: 2570

Calcium and Phosphate Metabolism
- Report rights infringement
- published: 16 Jul 2013
- views: 157203

Vitamins, Minerals and Bone Formation
- Report rights infringement
- published: 30 Jul 2013
- views: 773

Bone Densitometry
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Nov 2011
- views: 20013

Metabolic Bone Disorders
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Aug 2016
- views: 460

- Playlist
- Chat

Extreme Weight Loss S03E09 Alyssa PDTVx264 JIVE
- Report rights infringement
- published: 02 Sep 2016
- views: 43354

Mineral Bone Disease Prof. Tarek Elbaz
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Oct 2013
- views: 245

extreme makeover weight loss edition s04e01 hdtv, Ty and Charita
- Report rights infringement
- published: 31 Mar 2017
- views: 2881

Extreme Makeover Weightloss Edition S02 E07 Sally
- Report rights infringement
- published: 21 Nov 2016
- views: 2502

Extreme Weight Loss S03E08 Chantell
- Report rights infringement
- published: 21 Nov 2013
- views: 38064

DHEA - Energy, Stamina, Libido, Well-Being, ++
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Apr 2016
- views: 27252

The Biggest Loser Season 1 Episode 02
- Report rights infringement
- published: 03 Apr 2017
- views: 7

Extreme Makeover Weight Loss Edition Season 03 Episode 11 Ashley 1
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Aug 2014
- views: 150675

Fractures in Persons with NeuroDisabilities 2016
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 Apr 2016
- views: 13

Secrets to Healthy Aging
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Apr 2015
- views: 73
At Least 19 Dead In Manchester Arena Explosion
Edit WorldNews.com 23 May 2017Trump Made 'Inappropriate Requests' To Two Intelligence Officials To Deny Collusion With Russia
Edit WorldNews.com 22 May 2017"I am sorry," says singer Ariana after concert blast kills 19
Edit Khaleej Times 23 May 2017‘Confirmed Fatalities’ At Explosion At Manchester Arena
Edit CBS News 23 May 2017Deaths Reported In Explosion At Ariana Grande Concert In Manchester, UK
Edit WorldNews.com 23 May 2017Japan’s oldest human bones excavated on Ishigaki Island
Edit Japan Update 23 May 2017Global And China Bone Growth Therapy Devices Market Research Report 2017
Edit Community news 23 May 2017Global And China Bone Screw Washer Industry 2017 Market Research Report
Edit Community news 23 May 2017Global And China Bone Cement Mixer Industry 2017 Market Research Report
Edit Community news 23 May 2017T. rex could bite with force of 3 cars
Edit The Japan News 23 May 2017Yanks accompany brave siblings to Bronx Zoo
Edit MLB 23 May 2017Freeze-Dried Mouse Sperm Survives Trip in Space
Edit Asahi News 23 May 2017Stem cell treatments ready to replace medicine in 10 years: Expert
Edit The Jakarta Post 23 May 2017365 Days of Tacos: Carnitas Lonja
Edit San Antonio Express-News 23 May 2017George Will: Federal power spins its ever-growing web
Edit The Virginian-Pilot 23 May 2017- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »




























