- published: 24 Mar 2015
- views: 854266
-
remove the playlistPotential Energy
-
remove the playlistLatest Videos
-
remove the playlistLongest Videos
- remove the playlistPotential Energy
- remove the playlistLatest Videos
- remove the playlistLongest Videos
- published: 19 Feb 2015
- views: 33787
- published: 30 Mar 2012
- views: 324942
- published: 17 Apr 2011
- views: 381683
- published: 24 Jul 2015
- views: 70379
- published: 18 Aug 2014
- views: 15389
- published: 29 Apr 2012
- views: 31488
- published: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 26488
- published: 06 May 2010
- views: 32733
- published: 23 May 2008
- views: 793560

Potential energy
In physics, potential energy is the energy that an object has due to its position in a force field or that a system has due to the configuration of its parts. Common types include the gravitational potential energy of an object that depends on its mass and its distance from the center of mass of another object, the elastic potential energy of an extended spring, and the electric potential energy of an electric charge in an electric field. The unit for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule, which has the symbol J.
The term potential energy was introduced by the 19th century Scottish engineer and physicist William Rankine, although it has links to Greek philosopher Aristotle's concept of potentiality. Potential energy is associated with forces that act on a body in a way that depends only on the body's position in space. These forces can be represented by a vector at every point in space forming a vector field of forces, or a force field.
If the work of a force field acting on a body that moves from a start to an end position is determined only by these two positions, and does not depend on the trajectory of the body, then there is a function known as potential energy that can be evaluated at the two positions to determine this work. Furthermore, the force field is determined by this potential energy and is described as derivable from a potential.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Kinetic energy
In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the energy that it possesses due to its motion. It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its acceleration, the body maintains this kinetic energy unless its speed changes. The same amount of work is done by the body in decelerating from its current speed to a state of rest.
In classical mechanics, the kinetic energy of a non-rotating object of mass m traveling at a speed v is 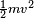 . In relativistic mechanics, this is a good approximation only when v is much less than the speed of light.
. In relativistic mechanics, this is a good approximation only when v is much less than the speed of light.
The standard unit of kinetic energy is the joule.
History and etymology
The adjective kinetic has its roots in the Greek word κίνησις kinesis, meaning "motion". The dichotomy between kinetic energy and potential energy can be traced back to Aristotle's concepts of actuality and potentiality.
The principle in classical mechanics that E ∝ mv² was first developed by Gottfried Leibniz and Johann Bernoulli, who described kinetic energy as the living force, vis viva. Willem 's Gravesande of the Netherlands provided experimental evidence of this relationship. By dropping weights from different heights into a block of clay, Willem 's Gravesande determined that their penetration depth was proportional to the square of their impact speed. Émilie du Châtelet recognized the implications of the experiment and published an explanation.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Khan Academy
Khan Academy is a non-profit educational organization created in 2006 by educator Salman Khan with the aim of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. The organization produces short lectures in the form of YouTube videos. In addition to micro lectures, the organization's website features practice exercises and tools for educators. All resources are available for free to anyone around the world. The main language of the website is English, but the content is also available in other languages.
History
The founder of the organization, Salman Khan, was born in New Orleans, Louisiana, United States to immigrant parents from Bangladesh and India. After earning three degrees from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (a BS in mathematics, a BS in electrical engineering and computer science, and an MEng in electrical engineering and computer science), he pursued an MBA from Harvard Business School.
In late 2004, Khan began tutoring his cousin Nadia who needed help with math using Yahoo!'s Doodle notepad.When other relatives and friends sought similar help, he decided that it would be more practical to distribute the tutorials on YouTube. The videos' popularity and the testimonials of appreciative students prompted Khan to quit his job in finance as a hedge fund analyst at Connective Capital Management in 2009, and focus on the tutorials (then released under the moniker "Khan Academy") full-time.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Energy
In physics, energy is a property of objects which can be transferred to other objects or converted into different forms, but cannot be created or destroyed. The "ability of a system to perform work" is a common description, but it is difficult to give one single comprehensive definition of energy because of its many forms. For instance, in SI units, energy is measured in joules, and one joule is defined "mechanically", being the energy transferred to an object by the mechanical work of moving it a distance of 1 metre against a force of 1 newton. However, there are many other definitions of energy, depending on the context, such as thermal energy, radiant energy, electromagnetic, nuclear, etc., where definitions are derived that are the most convenient.
Common energy forms include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object's position in a force field (gravitational, electric or magnetic), the elastic energy stored by stretching solid objects, the chemical energy released when a fuel burns, the radiant energy carried by light, and the thermal energy due to an object's temperature. All of the many forms of energy are convertible to other kinds of energy, and obey the law of conservation of energy which says that energy can be neither created nor be destroyed; however, it can change from one form to another.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 4:39
4:39Potential and Kinetic Energy for Kids
Potential and Kinetic Energy for KidsPotential and Kinetic Energy for Kids
You will learn about "Potential and Kinetic Energy" in this video. The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, it can only be converted from one form to another. Potential energy is energy due to position while kinetic energy is energy due to motion. The unit of energy is joules. To understand this better, let us take an example. Look at this pendulum. When we hold it on one side, at that time, it has a certain amount of potential energy. When the pendulum is released, this potential energy starts getting converted to kinetic energy. As the pendulum moves back and forth, the kinetic energy is converted to potential energy and vice versa until the pendulum stops. The formula for potential energy is mgh, where m = mass, g = acceleration due to gravity and h = height. If we climb on top of a tree, the potential energy possessed by us will be mgh. Here, if we assume mass = 30 kg, acceleration due to gravity = 9.8 m/s^2 and height of the tree as 20 metres, then the potential energy would be 30 * 9.8 * 20 = 5880 joules. At the top, the K.E. is zero. If we jump, then the stored potential energy starts getting converted to kinetic energy. Just before we land, all of the potential energy gets converted to kinetic energy. Now, the potential energy = 0. The kinetic energy can be calculated using the formula, 1/2mv^2 where m = mass and v = velocity. Educational Videos for people of all ages: http://www.SmartLearningforAll.com Subscribe to our YouTube Channel: http://www.youtube.com/user/Smartlearningforall?sub_confirmation=1 -
 6:39
6:39Potential Energy
Potential EnergyPotential Energy
081 - Potential Energy In this video Paul Andersen explains how conservative forces can be used to store potential energy in an object or a system. The work done is equal to the amount of potential energy in the object. The following conservative forces are described; gravitational, spring and electric force. The difference between a conservative and nonconservative for is also included. Do you speak another language? Help me translate my videos: http://www.bozemanscience.com/translations/ Music Attribution Title: String Theory Artist: Herman Jolly http://sunsetvalley.bandcamp.com/track/string-theory All of the images are licensed under creative commons and public domain licensing: -
 1:58
1:58Kinetic and Potential Energy (clip)
Kinetic and Potential Energy (clip)Kinetic and Potential Energy (clip)
KINETIC AND POTENTIAL ENERGY introduces Zog to energy of movement and stored energy. Working with inclined planes, springs and a bouncing ball he learns about both kinds of energy and how each kind of energy can be changed into the other. Also, he learns how chemical potential energy is used to create heat, mechanical power, light and electricity. Written and animated by David Christianson. 10 minutes, color, 2012. Direct link to purchase the DVD: http://phoenixlearninggroup.com/product/elementary-energy-kinetic-and-potential-energy/ http://phoenixlearninggroup.com -
 6:07
6:07Potential and Kinetic Energy
Potential and Kinetic EnergyPotential and Kinetic Energy
Mr. Andersen explains the difference between potential and kinetic gravitational energy. He also uses physics to calculate the energy in various objects. Intro Music Atribution Title: I4dsong_loop_main.wav Artist: CosmicD Link to sound: http://www.freesound.org/people/CosmicD/sounds/72556/ Creative Commons Atribution License -
 5:40
5:40Class 6-10 - Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy
Class 6-10 - Kinetic Energy and Potential EnergyClass 6-10 - Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy
What is Kinetic energy? How is it associated with the motion of any given object? For example, the motion of a rollercoaster thrills it’s rider as they twist around corners, fly down hills and even wind up topsy-turvy as they pass through endless loops of track. You may have noticed that roller coaster cars are pulled up the first hill by a chain and motor, but once they reach the top, the cars roll through the remainder of the ride without any help from outside forces. It’s easy to imagine that gravity pulls the cars down the hill, but how do they get up the next hill or through the loops? The answer is in the energy of the cars as they roll through the ride. Kinetic energy is nothing but the energy associated with the motion of an object. Work is energy transferred to an object or from an object as the result of the action of an external force. Positive work transfers energy to the object, and negative work transfers energy from the object. Work is the scalar product of the force vector and the displacement vector. The change in kinetic energy due to applied forces is equal to the work done by the forces. Power is the rate at which work is done. The power provided by a force acting on an object is the scalar product of the velocity vector for that object and the force vector. Learn about all these in this video module. Our website- http://www.byjus.com/ Download our app on android- https://goo.gl/5Uz70E Download our app on an Apple device- https://goo.gl/2mLi1I -
 10:24
10:24Physics, Gravitational Potential Energy, An Explanation
Physics, Gravitational Potential Energy, An ExplanationPhysics, Gravitational Potential Energy, An Explanation
Explains the what gravitational potential energy is. He also shows you how to calculate changes in potential energy and explains the relationship between potential energy and work. You can see a listing of all my videos at my website, http://www.stepbystepscience.com -
 5:08
5:08Physics Lecture - 27 - Potential Energy
Physics Lecture - 27 - Potential EnergyPhysics Lecture - 27 - Potential Energy
Facebook - https://www.facebook.com/TheNewBoston-464114846956315/ GitHub - https://github.com/buckyroberts Google+ - https://plus.google.com/+BuckyRoberts LinkedIn - https://www.linkedin.com/in/buckyroberts reddit - https://www.reddit.com/r/thenewboston/ Support - https://www.patreon.com/thenewboston thenewboston - https://thenewboston.com/ Twitter - https://twitter.com/bucky_roberts -
 11:23
11:23Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy - Iken Edu
Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy - Iken EduKinetic Energy and Potential Energy - Iken Edu
This interactive animation describes about kinetic and potential energy,expression of the formula for kinetic energy. It also describes about the physical quantities of kinetic energy and potential energy,problem on kinetic energy and potential energy,factor affecting potential energy and the total mechanical energy. -
 1:08
1:08Potential Energy
Potential EnergyPotential Energy
Follow us at: https://plus.google.com/+tutorvista/ Check us out at http://physics.tutorvista.com/energy/potential-energy.html Define Potential Energy Potential energy is the stored up energy in the body that is used by the body to perform work. It is given by PE = mgh Where m = mass of the body, g = gravity and h = height The potential energy can be converted into other forms of energy such as kinetic energy, heat energy or thermal energy, mechanical energy, electrical energy, etc. Please like our facebook page http://www.facebook.com/tutorvista -
 12:37
12:37Electric potential energy | Electrostatics | Electrical engineering | Khan Academy
Electric potential energy | Electrostatics | Electrical engineering | Khan AcademyElectric potential energy | Electrostatics | Electrical engineering | Khan Academy
Introduction to electric potential energy. Created by Sal Khan. Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/electrical-engineering/robots/all-about-spout/v/spout-bot-at-santa-rita-elementary-school?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=electricalengineering Missed the previous lesson? https://www.khanacademy.org/science/electrical-engineering/ee-electrostatics/ee-fields-potential-voltage/v/proof-advanced-field-from-infinite-plate-part-2?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=electricalengineering Electrical engineering on Khan Academy: A summary of the math and science preparation that will help you have the best experience with electrical engineering taught on Khan Academy. Become familiar with engineering numbers and notation, and learn about the two most important electrical quantities: current and voltage. About Khan Academy: Khan Academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that empower learners to study at their own pace in and outside of the classroom. We tackle math, science, computer programming, history, art history, economics, and more. Our math missions guide learners from kindergarten to calculus using state-of-the-art, adaptive technology that identifies strengths and learning gaps. We've also partnered with institutions like NASA, The Museum of Modern Art, The California Academy of Sciences, and MIT to offer specialized content. For free. For everyone. Forever. #YouCanLearnAnything Subscribe to Khan Academy’s Electrical Engineering channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC8JT97hQjMVWeO0B-x8eVxQ?sub_confirmation=1 Subscribe to Khan Academy: https://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=khanacademy
-

Potential and Kinetic Energy for Kids
You will learn about "Potential and Kinetic Energy" in this video. The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, it can only be converted from one form to another. Potential energy is energy due to position while kinetic energy is energy due to motion. The unit of energy is joules. To understand this better, let us take an example. Look at this pendulum. When we hold it on one side, at that time, it has a certain amount of potential energy. When the pendulum is released, this potential energy starts getting converted to kinetic energy. As the pendulum moves back and forth, the kinetic energy is converted to potential energy and vice versa until the pendulum stops. The formula for potential energy is mgh, where m = mass, g = acceleration due to grav...
published: 24 Mar 2015 -

Potential Energy
081 - Potential Energy In this video Paul Andersen explains how conservative forces can be used to store potential energy in an object or a system. The work done is equal to the amount of potential energy in the object. The following conservative forces are described; gravitational, spring and electric force. The difference between a conservative and nonconservative for is also included. Do you speak another language? Help me translate my videos: http://www.bozemanscience.com/translations/ Music Attribution Title: String Theory Artist: Herman Jolly http://sunsetvalley.bandcamp.com/track/string-theory All of the images are licensed under creative commons and public domain licensing:
published: 19 Feb 2015 -

Kinetic and Potential Energy (clip)
KINETIC AND POTENTIAL ENERGY introduces Zog to energy of movement and stored energy. Working with inclined planes, springs and a bouncing ball he learns about both kinds of energy and how each kind of energy can be changed into the other. Also, he learns how chemical potential energy is used to create heat, mechanical power, light and electricity. Written and animated by David Christianson. 10 minutes, color, 2012. Direct link to purchase the DVD: http://phoenixlearninggroup.com/product/elementary-energy-kinetic-and-potential-energy/ http://phoenixlearninggroup.com
published: 30 Mar 2012 -

Potential and Kinetic Energy
Mr. Andersen explains the difference between potential and kinetic gravitational energy. He also uses physics to calculate the energy in various objects. Intro Music Atribution Title: I4dsong_loop_main.wav Artist: CosmicD Link to sound: http://www.freesound.org/people/CosmicD/sounds/72556/ Creative Commons Atribution License
published: 17 Apr 2011 -

Class 6-10 - Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy
What is Kinetic energy? How is it associated with the motion of any given object? For example, the motion of a rollercoaster thrills it’s rider as they twist around corners, fly down hills and even wind up topsy-turvy as they pass through endless loops of track. You may have noticed that roller coaster cars are pulled up the first hill by a chain and motor, but once they reach the top, the cars roll through the remainder of the ride without any help from outside forces. It’s easy to imagine that gravity pulls the cars down the hill, but how do they get up the next hill or through the loops? The answer is in the energy of the cars as they roll through the ride. Kinetic energy is nothing but the energy associated with the motion of an object. Work is energy transferred to an object or fro...
published: 24 Jul 2015 -

Physics, Gravitational Potential Energy, An Explanation
Explains the what gravitational potential energy is. He also shows you how to calculate changes in potential energy and explains the relationship between potential energy and work. You can see a listing of all my videos at my website, http://www.stepbystepscience.com
published: 18 Aug 2014 -

Physics Lecture - 27 - Potential Energy
Facebook - https://www.facebook.com/TheNewBoston-464114846956315/ GitHub - https://github.com/buckyroberts Google+ - https://plus.google.com/+BuckyRoberts LinkedIn - https://www.linkedin.com/in/buckyroberts reddit - https://www.reddit.com/r/thenewboston/ Support - https://www.patreon.com/thenewboston thenewboston - https://thenewboston.com/ Twitter - https://twitter.com/bucky_roberts
published: 29 Apr 2012 -

Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy - Iken Edu
This interactive animation describes about kinetic and potential energy,expression of the formula for kinetic energy. It also describes about the physical quantities of kinetic energy and potential energy,problem on kinetic energy and potential energy,factor affecting potential energy and the total mechanical energy.
published: 29 Apr 2016 -

Potential Energy
Follow us at: https://plus.google.com/+tutorvista/ Check us out at http://physics.tutorvista.com/energy/potential-energy.html Define Potential Energy Potential energy is the stored up energy in the body that is used by the body to perform work. It is given by PE = mgh Where m = mass of the body, g = gravity and h = height The potential energy can be converted into other forms of energy such as kinetic energy, heat energy or thermal energy, mechanical energy, electrical energy, etc. Please like our facebook page http://www.facebook.com/tutorvista
published: 06 May 2010 -

Electric potential energy | Electrostatics | Electrical engineering | Khan Academy
Introduction to electric potential energy. Created by Sal Khan. Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/electrical-engineering/robots/all-about-spout/v/spout-bot-at-santa-rita-elementary-school?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=electricalengineering Missed the previous lesson? https://www.khanacademy.org/science/electrical-engineering/ee-electrostatics/ee-fields-potential-voltage/v/proof-advanced-field-from-infinite-plate-part-2?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=electricalengineering Electrical engineering on Khan Academy: A summary of the math and science preparation that will help you have the best experience with electrical engineering taught on Khan Academy. Become familiar with engineering numbers and notation, and learn about the two most impor...
published: 23 May 2008
Potential and Kinetic Energy for Kids
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:39
- Updated: 24 Mar 2015
- views: 854266
- published: 24 Mar 2015
- views: 854266
Potential Energy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:39
- Updated: 19 Feb 2015
- views: 33787
- published: 19 Feb 2015
- views: 33787
Kinetic and Potential Energy (clip)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:58
- Updated: 30 Mar 2012
- views: 324942
- published: 30 Mar 2012
- views: 324942
Potential and Kinetic Energy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:07
- Updated: 17 Apr 2011
- views: 381683
- published: 17 Apr 2011
- views: 381683
Class 6-10 - Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:40
- Updated: 24 Jul 2015
- views: 70379
- published: 24 Jul 2015
- views: 70379
Physics, Gravitational Potential Energy, An Explanation
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:24
- Updated: 18 Aug 2014
- views: 15389
- published: 18 Aug 2014
- views: 15389
Physics Lecture - 27 - Potential Energy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:08
- Updated: 29 Apr 2012
- views: 31488
- published: 29 Apr 2012
- views: 31488
Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy - Iken Edu
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 11:23
- Updated: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 26488
- published: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 26488
Potential Energy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:08
- Updated: 06 May 2010
- views: 32733
- published: 06 May 2010
- views: 32733
Electric potential energy | Electrostatics | Electrical engineering | Khan Academy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 12:37
- Updated: 23 May 2008
- views: 793560
- published: 23 May 2008
- views: 793560
-

Potential and Kinetic Energy for Kids
You will learn about "Potential and Kinetic Energy" in this video. The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, it can only be converted from one form to another. Potential energy is energy due to position while kinetic energy is energy due to motion. The unit of energy is joules. To understand this better, let us take an example. Look at this pendulum. When we hold it on one side, at that time, it has a certain amount of potential energy. When the pendulum is released, this potential energy starts getting converted to kinetic energy. As the pendulum moves back and forth, the kinetic energy is converted to potential energy and vice versa until the pendulum stops. The formula for potential energy is mgh, where m = mass, g = acceleration due to grav...
published: 24 Mar 2015 -

Potential Energy
081 - Potential Energy In this video Paul Andersen explains how conservative forces can be used to store potential energy in an object or a system. The work done is equal to the amount of potential energy in the object. The following conservative forces are described; gravitational, spring and electric force. The difference between a conservative and nonconservative for is also included. Do you speak another language? Help me translate my videos: http://www.bozemanscience.com/translations/ Music Attribution Title: String Theory Artist: Herman Jolly http://sunsetvalley.bandcamp.com/track/string-theory All of the images are licensed under creative commons and public domain licensing:
published: 19 Feb 2015 -

Kinetic and Potential Energy (clip)
KINETIC AND POTENTIAL ENERGY introduces Zog to energy of movement and stored energy. Working with inclined planes, springs and a bouncing ball he learns about both kinds of energy and how each kind of energy can be changed into the other. Also, he learns how chemical potential energy is used to create heat, mechanical power, light and electricity. Written and animated by David Christianson. 10 minutes, color, 2012. Direct link to purchase the DVD: http://phoenixlearninggroup.com/product/elementary-energy-kinetic-and-potential-energy/ http://phoenixlearninggroup.com
published: 30 Mar 2012 -

Potential and Kinetic Energy
Mr. Andersen explains the difference between potential and kinetic gravitational energy. He also uses physics to calculate the energy in various objects. Intro Music Atribution Title: I4dsong_loop_main.wav Artist: CosmicD Link to sound: http://www.freesound.org/people/CosmicD/sounds/72556/ Creative Commons Atribution License
published: 17 Apr 2011 -

Class 6-10 - Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy
What is Kinetic energy? How is it associated with the motion of any given object? For example, the motion of a rollercoaster thrills it’s rider as they twist around corners, fly down hills and even wind up topsy-turvy as they pass through endless loops of track. You may have noticed that roller coaster cars are pulled up the first hill by a chain and motor, but once they reach the top, the cars roll through the remainder of the ride without any help from outside forces. It’s easy to imagine that gravity pulls the cars down the hill, but how do they get up the next hill or through the loops? The answer is in the energy of the cars as they roll through the ride. Kinetic energy is nothing but the energy associated with the motion of an object. Work is energy transferred to an object or fro...
published: 24 Jul 2015 -

Physics, Gravitational Potential Energy, An Explanation
Explains the what gravitational potential energy is. He also shows you how to calculate changes in potential energy and explains the relationship between potential energy and work. You can see a listing of all my videos at my website, http://www.stepbystepscience.com
published: 18 Aug 2014 -

Physics Lecture - 27 - Potential Energy
Facebook - https://www.facebook.com/TheNewBoston-464114846956315/ GitHub - https://github.com/buckyroberts Google+ - https://plus.google.com/+BuckyRoberts LinkedIn - https://www.linkedin.com/in/buckyroberts reddit - https://www.reddit.com/r/thenewboston/ Support - https://www.patreon.com/thenewboston thenewboston - https://thenewboston.com/ Twitter - https://twitter.com/bucky_roberts
published: 29 Apr 2012 -

Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy - Iken Edu
This interactive animation describes about kinetic and potential energy,expression of the formula for kinetic energy. It also describes about the physical quantities of kinetic energy and potential energy,problem on kinetic energy and potential energy,factor affecting potential energy and the total mechanical energy.
published: 29 Apr 2016 -

Potential Energy
Follow us at: https://plus.google.com/+tutorvista/ Check us out at http://physics.tutorvista.com/energy/potential-energy.html Define Potential Energy Potential energy is the stored up energy in the body that is used by the body to perform work. It is given by PE = mgh Where m = mass of the body, g = gravity and h = height The potential energy can be converted into other forms of energy such as kinetic energy, heat energy or thermal energy, mechanical energy, electrical energy, etc. Please like our facebook page http://www.facebook.com/tutorvista
published: 06 May 2010 -

Electric potential energy | Electrostatics | Electrical engineering | Khan Academy
Introduction to electric potential energy. Created by Sal Khan. Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/electrical-engineering/robots/all-about-spout/v/spout-bot-at-santa-rita-elementary-school?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=electricalengineering Missed the previous lesson? https://www.khanacademy.org/science/electrical-engineering/ee-electrostatics/ee-fields-potential-voltage/v/proof-advanced-field-from-infinite-plate-part-2?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=electricalengineering Electrical engineering on Khan Academy: A summary of the math and science preparation that will help you have the best experience with electrical engineering taught on Khan Academy. Become familiar with engineering numbers and notation, and learn about the two most impor...
published: 23 May 2008
Potential and Kinetic Energy for Kids
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:39
- Updated: 24 Mar 2015
- views: 854266
- published: 24 Mar 2015
- views: 854266
Potential Energy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:39
- Updated: 19 Feb 2015
- views: 33787
- published: 19 Feb 2015
- views: 33787
Kinetic and Potential Energy (clip)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:58
- Updated: 30 Mar 2012
- views: 324942
- published: 30 Mar 2012
- views: 324942
Potential and Kinetic Energy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:07
- Updated: 17 Apr 2011
- views: 381683
- published: 17 Apr 2011
- views: 381683
Class 6-10 - Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:40
- Updated: 24 Jul 2015
- views: 70379
- published: 24 Jul 2015
- views: 70379
Physics, Gravitational Potential Energy, An Explanation
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:24
- Updated: 18 Aug 2014
- views: 15389
- published: 18 Aug 2014
- views: 15389
Physics Lecture - 27 - Potential Energy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:08
- Updated: 29 Apr 2012
- views: 31488
- published: 29 Apr 2012
- views: 31488
Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy - Iken Edu
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 11:23
- Updated: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 26488
- published: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 26488
Potential Energy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:08
- Updated: 06 May 2010
- views: 32733
- published: 06 May 2010
- views: 32733
Electric potential energy | Electrostatics | Electrical engineering | Khan Academy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 12:37
- Updated: 23 May 2008
- views: 793560
- published: 23 May 2008
- views: 793560
-

8.01x - Lect 11 - Work, Kinetic & Potential Energy, Gravitation, Conservative Forces
This Lecture is a MUST! Work - Kinetic Energy - Potential Energy - Newton's Universal Law of Gravitation - Great Demos. Assignments Lecture 10, 11 and 12: http://freepdfhosting.com/48369aceae.pdf Solutions Lecture 10, 11 and 12: http://freepdfhosting.com/896f6ba4a6.pdf
published: 07 Feb 2015 -

XI 53 Energy,Introduction Potential, Kinetic
Class XI Physics. Work Power Energy. Introduction of energy, Potential and Kinetic energy. Class room Lecture by Pradeep Kshetrapal. Language Hindi and English mixed.
published: 05 Sep 2012 -

Kinetic Energy, Gravitational & Elastic Potential Energy, Work, Power, Physics - Basic Introduction
This physics video tutorial explains the basic concepts of kinetic energy, potential energy, work, and power. It provides an introduction into forms of stored energy such as gravitational potential energy and elastic potential energy of springs. This video contains plenty of examples,formulas / equations and practice problems. Physics Video Playlist: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-6IgkG5yZfo&list;=PL0o_zxa4K1BWrOyLXkHSZD4bw3yVKMwi8&index;=1&t;=25s Access to Premium Videos: https://www.patreon.com/MathScienceTutor Here is a list of topics: 1. Kinetic Energy Physics Problems - Energy of Motion 2. Effect of Kinetic Energy - Double Mass or Triple Speed 3. Gravitational Potential Energy - Stored Energy - Mass, Gravitational Acceleration & Height 4. Conservation of Energy Physics Proble...
published: 26 Sep 2016 -

Electric Potential Energy and Potential Part 1 - IIT JEE Main and Advanced Physics Video Lecture
IIT JEE Main and Advanced Physics Video Lectures and Study Material developed by highly experienced and dedicated faculty team of Rao IIT Academy. Visit http://www.raoiit.com or email studentcare@raoiit.com for any query or doubt related to your IIT JEE Preparation. Want to be the Topper ??? Learn Electric Potential Energy and Potential Part 1 from Rao IIT Academy. Prepare for your Boards and New IIT-JEE Pattern - JEE Main and JEE Advanced / MH-CET / BITSAT / VIT / SRM / Manipal and other Competitive Exams with Rao IIT Academy. ...................................... Subscribe to Rao IIT Academy YouTube channel - http://www.youtube.com/RaoIITAcademy Like us on Facebook - https://www.facebook.com/Raoiit Follow us on Twitter - https://twitter.com/rao_iit +1 on Google Plus - https://plus.goo...
published: 28 Jun 2014 -

Electric Potential and Potential Energy | for Class 12 in HINDI
In this physics lecture of electrostatics for class 12 in Hindi we explained what electric potential energy and electric potential are. The electric potential energy of a charge at a point is defined as the amount of work done in bringing that charge from infinity to that point. It is a scalar quantity . In S.I., its unit is joule ( J ). The electric potential at a point is defined as the amount of work done in bringing a unit positive charge from infinity to that point. It is a scalar quantity . In S.I., its unit is volt (V) or joule coulomb-1 (J C-1). फिजिक्स के वीडियो में हम इलेक्ट्रिक पोटेंशियल एनर्जी तथा इलेक्ट्रिक पोटेंशियल पर बात करेंगे | किसी बिंदु पर अगर एक चार्ज को रखा जाता है तो उस पूरे सिस्टम का जो इलेक्ट्रिक पोटेंशियल एनर्जी होता है वह बराबर होता है अगर उसी चार्ज को हम ...
published: 27 May 2017 -

Electric Potential Difference Point Charge - Voltage, Work, Force, Kinetic Potential Energy Physics
This physics video tutorial explains the concept of electric potential created by point charges and potential difference also known as voltage. It covers the relationship between charge, electric potential, voltage, electric potential energy, work, and kinetic energy. It contains plenty of examples and practice problems. Here is a list of topics: 1. Electric Potential Definition - Electric Potential Energy Per Unit Charge 2. 1 Volt = 1 Joule Per Coulomb - 1 Volt = 1J/C 3. Definition of Voltage - Electric Potential Difference Between Two Points 4. Work, Charge, and Voltage Formula / Equation 5. Positive and Negative Charges In an Electric Field Between Parallel Plates 6. Electric Force, Speed, Kinetic and Potential Energy 7. How to tell if an Electric Field Will Do Positive or Neg...
published: 24 Sep 2016 -

Electric Potential Energy in a Uniform Electric Field, Physics Problems
This physics video tutorial explains how to calculate the electric potential energy in a uniform electric field of a point charge. The equation is similar to gravitational potential energy. This video contains an example problem with multiple parts that shows you how to calculate the electric field between two oppositely charged parallel plates using voltage and distance. Next, it shows you how to calculate the electric force acting on a point charge inside an electric field as well as finding the work required to move the charge from one point to another position and how to calculate the final speed of the positive point charge using conservation of energy and kinematics.
published: 06 Feb 2017 -

8.01x - Lect 13 - Potential Energy, Derive Simple Harmonic Motion using Energy
Potential Energy - Energy Considerations to Derive Simple Harmonic Motion - Puzzling Demonstration. Assignments Lecture 13, 14 and 15: http://freepdfhosting.com/f96866498e.pdf Solutions Lecture 13, 14 and 15: http://freepdfhosting.com/dbf654957b.pdf
published: 08 Feb 2015 -

Episode 14: Potential Energy - The Mechanical Universe
Episode 14. Potential Energy: Potential energy provides a powerful model for understanding why the world has worked the same way since the beginning of time. “The Mechanical Universe,” is a critically-acclaimed series of 52 thirty-minute videos covering the basic topics of an introductory university physics course. Each program in the series opens and closes with Caltech Professor David Goodstein providing philosophical, historical and often humorous insight into the subject at hand while lecturing to his freshman physics class. The series contains hundreds of computer animation segments, created by Dr. James F. Blinn, as the primary tool of instruction. Dynamic location footage and historical re-creations are also used to stress the fact that science is a human endeavor. The series wa...
published: 19 Dec 2016 -

8.02x - Lect 4 - Electrostatic Potential, Electric Energy, Equipotential Surfaces
Electrostatic Potential, Electric Energy, eV, Conservative Field, Equipotential Surfaces, Great (& dangerous) Demos! Assignments Lecture 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5: http://freepdfhosting.com/2cb4aad955.pdf Solutions Lecture 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5: http://freepdfhosting.com/75b96693f2.pdf
published: 13 Feb 2015
8.01x - Lect 11 - Work, Kinetic & Potential Energy, Gravitation, Conservative Forces
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 49:07
- Updated: 07 Feb 2015
- views: 59567
- published: 07 Feb 2015
- views: 59567
XI 53 Energy,Introduction Potential, Kinetic
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:01:26
- Updated: 05 Sep 2012
- views: 43108
- published: 05 Sep 2012
- views: 43108
Kinetic Energy, Gravitational & Elastic Potential Energy, Work, Power, Physics - Basic Introduction
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:36:50
- Updated: 26 Sep 2016
- views: 41742
- published: 26 Sep 2016
- views: 41742
Electric Potential Energy and Potential Part 1 - IIT JEE Main and Advanced Physics Video Lecture
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 39:21
- Updated: 28 Jun 2014
- views: 28087
- published: 28 Jun 2014
- views: 28087
Electric Potential and Potential Energy | for Class 12 in HINDI
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 31:25
- Updated: 27 May 2017
- views: 2289
- published: 27 May 2017
- views: 2289
Electric Potential Difference Point Charge - Voltage, Work, Force, Kinetic Potential Energy Physics
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:20:14
- Updated: 24 Sep 2016
- views: 10497
- published: 24 Sep 2016
- views: 10497
Electric Potential Energy in a Uniform Electric Field, Physics Problems
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 21:11
- Updated: 06 Feb 2017
- views: 2641
- published: 06 Feb 2017
- views: 2641
8.01x - Lect 13 - Potential Energy, Derive Simple Harmonic Motion using Energy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 51:30
- Updated: 08 Feb 2015
- views: 23949
- published: 08 Feb 2015
- views: 23949
Episode 14: Potential Energy - The Mechanical Universe
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 28:47
- Updated: 19 Dec 2016
- views: 2023
- published: 19 Dec 2016
- views: 2023
8.02x - Lect 4 - Electrostatic Potential, Electric Energy, Equipotential Surfaces
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 49:02
- Updated: 13 Feb 2015
- views: 128231
- published: 13 Feb 2015
- views: 128231


- Playlist
- Chat

Potential and Kinetic Energy for Kids
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 Mar 2015
- views: 854266

Potential Energy
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Feb 2015
- views: 33787

Kinetic and Potential Energy (clip)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 30 Mar 2012
- views: 324942

Potential and Kinetic Energy
- Report rights infringement
- published: 17 Apr 2011
- views: 381683

Class 6-10 - Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 Jul 2015
- views: 70379

Physics, Gravitational Potential Energy, An Explanation
- Report rights infringement
- published: 18 Aug 2014
- views: 15389

Physics Lecture - 27 - Potential Energy
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Apr 2012
- views: 31488

Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy - Iken Edu
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 26488

Potential Energy
- Report rights infringement
- published: 06 May 2010
- views: 32733

Electric potential energy | Electrostatics | Electrical engineering | Khan Academy
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 May 2008
- views: 793560

- Playlist
- Chat

Potential and Kinetic Energy for Kids
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 Mar 2015
- views: 854266

Potential Energy
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Feb 2015
- views: 33787

Kinetic and Potential Energy (clip)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 30 Mar 2012
- views: 324942

Potential and Kinetic Energy
- Report rights infringement
- published: 17 Apr 2011
- views: 381683

Class 6-10 - Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 Jul 2015
- views: 70379

Physics, Gravitational Potential Energy, An Explanation
- Report rights infringement
- published: 18 Aug 2014
- views: 15389

Physics Lecture - 27 - Potential Energy
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Apr 2012
- views: 31488

Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy - Iken Edu
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 26488

Potential Energy
- Report rights infringement
- published: 06 May 2010
- views: 32733

Electric potential energy | Electrostatics | Electrical engineering | Khan Academy
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 May 2008
- views: 793560

- Playlist
- Chat

8.01x - Lect 11 - Work, Kinetic & Potential Energy, Gravitation, Conservative Forces
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Feb 2015
- views: 59567

XI 53 Energy,Introduction Potential, Kinetic
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Sep 2012
- views: 43108

Kinetic Energy, Gravitational & Elastic Potential Energy, Work, Power, Physics - Basic Introduction
- Report rights infringement
- published: 26 Sep 2016
- views: 41742

Electric Potential Energy and Potential Part 1 - IIT JEE Main and Advanced Physics Video Lecture
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Jun 2014
- views: 28087

Electric Potential and Potential Energy | for Class 12 in HINDI
- Report rights infringement
- published: 27 May 2017
- views: 2289

Electric Potential Difference Point Charge - Voltage, Work, Force, Kinetic Potential Energy Physics
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 Sep 2016
- views: 10497

Electric Potential Energy in a Uniform Electric Field, Physics Problems
- Report rights infringement
- published: 06 Feb 2017
- views: 2641

8.01x - Lect 13 - Potential Energy, Derive Simple Harmonic Motion using Energy
- Report rights infringement
- published: 08 Feb 2015
- views: 23949

Episode 14: Potential Energy - The Mechanical Universe
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Dec 2016
- views: 2023

8.02x - Lect 4 - Electrostatic Potential, Electric Energy, Equipotential Surfaces
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 Feb 2015
- views: 128231
Pull back troops to end stand-off, China tells India
Edit The Hindu 02 Aug 2017Israeli PM Netanyahu Steps In To Prevent Israeli MP, Jordanian MP Fight, Report Says
Edit WorldNews.com 02 Aug 2017How Responsible Is U.S. In Pushing North Korea To Brink of War And Trump's Cold War Paradox?
Edit WorldNews.com 02 Aug 2017Reuters Uncovers Marked Discrepancy In Russian Servicemen Killed In Syria
Edit WorldNews.com 02 Aug 2017NTE Energy Secures Army Corps Wetlands Permit for its Reidsville Energy Center
Edit Market Watch 02 Aug 2017Sindh, KE for energy conservation
Edit The News International 02 Aug 2017Did Google Just Tackle The Biggest Problem In Energy?
Edit Oil Price 02 Aug 2017Extra Energy complaints flood in after we reveal customers are being wrongly hounded by debt collectors
Edit This is Money 02 Aug 2017Global Biomass Power Generation Market 2017 - Forth Energy Ltd.,elius Energy Plc, Enviva LP, MGT Power Ltd.
Edit Community news 02 Aug 2017Google wants to solve renewable energy storage with salt and antifreeze
Edit Inhabitat 02 Aug 2017Cabinet apprised of MoU with Spain on renewable energy
Edit Yahoo Daily News 02 Aug 2017Energy ETF on pace for worst daily decline in 6 weeks as crude retreats
Edit Market Watch 02 Aug 2017Google looks to salt and antifreeze for renewable energy storage
Edit Treehugger 02 Aug 2017Engineers produce long lasting, energy density battery
Edit PhysOrg 02 Aug 2017K.P. Energy#39;s board meeting on August 05, 2017
Edit Moneycontrol 02 Aug 2017Global Energy Harvesting Devices Market 2017 - EnOcean GmbH, Mide Technology, MicroStrain, Fujitsu, Microchip Technology
Edit MENA FN 02 Aug 2017- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »




























