- published: 11 Nov 2016
- views: 22522
-
remove the playlistHabsburg
- remove the playlistHabsburg
- published: 14 Jan 2013
- views: 121479
- published: 13 Oct 2016
- views: 16797
- published: 24 Dec 2015
- views: 53222
- published: 06 Dec 2014
- views: 1427574
- published: 03 Sep 2014
- views: 12862
- published: 03 May 2011
- views: 808214
- published: 13 Feb 2015
- views: 22871
- published: 19 Jun 2017
- views: 781
- published: 17 Jul 2011
- views: 757141

House of Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (/ˈhæps.bɜːrɡ/; German pronunciation: [ˈhaːps.bʊʁk]), or House of Austria, was one of the most important royal houses of Europe. The throne of the Holy Roman Empire was continuously occupied by the Habsburgs between 1438 and 1740. The house also produced emperors and kings of the Kingdom of Bohemia, Kingdom of England (Jure uxoris King), Kingdom of France (Queen consort), Kingdom of Germany, Kingdom of Hungary, Empire of Russia, Kingdom of Croatia, Second Mexican Empire, Kingdom of Ireland (Jure uxoris King), Kingdom of Portugal, and Habsburg Spain, as well as rulers of several Dutch and Italian principalities. From the sixteenth century, following the reign of Charles V, the dynasty was split between Austrian and Spanish branches. Although they ruled distinct territories, they nevertheless maintained close relations and frequently intermarried.
The House takes its name from Habsburg Castle, a fortress built in the 1020s in present-day Switzerland by Count Radbot of Klettgau, who chose to name his fortress Habsburg. His grandson Otto II was the first to take the fortress name as his own, adding "Count of Habsburg" to his title. The House of Habsburg gathered dynastic momentum through the 11th, 12th, and 13th centuries.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire (Latin: Sacrum Romanum Imperium, German: Heiliges Römisches Reich) was a multi-ethnic complex of territories in central Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806. The largest territory of the empire after 962 was the Kingdom of Germany, though it included the Kingdom of Bohemia, the Kingdom of Burgundy, the Kingdom of Italy, and numerous other territories.
On 25 December 800, Pope Leo III crowned the Frankish king Charlemagne as Emperor, reviving the title in Western Europe after more than three centuries. The title continued in the Carolingian family until 888 and from 896 to 899, after which it was contested by the rulers of Italy in a series of civil wars until the death of the last Italian claimant, Berengar, in 924. The title was revived in 962 when Otto I was crowned emperor, fashioning himself as the successor of Charlemagne and beginning a continuous existence of the empire for over eight centuries. Some historians refer to the coronation of Charlemagne as the origin of the empire, while others prefer the coronation of Otto I as its beginning. Scholars generally concur, however, in relating an evolution of the institutions and principles constituting the empire, describing a gradual assumption of the imperial title and role.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Roman Empire
The Roman Empire (Latin: Imperium Rōmānum; Classical Latin: [ɪmˈpɛ.ri.ũː roːˈmaː.nũː] Ancient and Medieval Greek: Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, tr. Basileia tōn Rhōmaiōn) was the post-Roman Republic period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterized by government headed by emperors and large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, Africa and Asia. The extended city of Rome was the largest city in the world c. 100 BC – c. 400 AD, with Constantinople (New Rome) becoming the largest around 500 AD, and the Empire's populace grew to an estimated 50 to 90 million inhabitants (roughly 20% of the world's population at the time). The 500-year-old republic which preceded it was severely destabilized in a series of civil wars and political conflict, during which Julius Caesar was appointed as perpetual dictator and then assassinated in 44 BC. Civil wars and executions continued, culminating in the victory of Octavian, Caesar's adopted son, over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC and the annexation of Egypt. Octavian's power was now unassailable and in 27 BC the Roman Senate formally granted him overarching power and the new title Augustus, effectively marking the end of the Roman Republic.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
Blue Danube
Blue Danube may refer to:
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Empire
An empire is defined as "an aggregate of nations or people ruled over by an emperor or other powerful sovereign or government, usually a territory of greater extent than a kingdom, as the former British Empire, French Empire, Spanish Empire, Russian Empire, Byzantine Empire or Roman Empire." An empire can be made solely of contiguous territories such as the Austro-Hungarian Empire, or of territories far remote from the homeland, such as a colonial empire.
Aside from the more formal usage, the term "empire" can also be used to refer to a large-scale business enterprise (e.g. a transnational corporation), a political organisation controlled by a single individual (a political boss) or a group (political bosses). The term "empire" is associated with other words such as imperialism, colonialism, and globalization. Empire is often used to describe a displeasure to overpowering situations. The effects of imperialism exist throughout the world today.
An imperial political structure can be established and maintained in two ways: (i) as a territorial empire of direct conquest and control with force or (ii) as a coercive, hegemonic empire of indirect conquest and control with power. The former method provides greater tribute and direct political control, yet limits further expansion because it absorbs military forces to fixed garrisons. The latter method provides less tribute and indirect control, but avails military forces for further expansion. Territorial empires (e.g., the Mongol Empire and Median Empire) tend to be contiguous areas. The term, on occasion, has been applied to maritime empires or thalassocracies, (e.g., the Athenian and British empires) with looser structures and more scattered territories. Empires are usually larger than kingdoms.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 47:54
47:54The Habsburg Empire: Under the Double Headed Eagle
The Habsburg Empire: Under the Double Headed EagleThe Habsburg Empire: Under the Double Headed Eagle
Documentary on the House of Hapsburg and their Empire. -
 2:04
2:04What Happened to the Habsburgs?
What Happened to the Habsburgs?What Happened to the Habsburgs?
The Habsburgs were once the most powerful family in Austria, but as they tried to strengthen the bloodline by intermarrying, a lack of genetic diversity ended up being their downfall. From: MUSEUM SECRETS REVEALED: Inside the Kunsthistorisches Museum http://bit.ly/1yS9nSN -
 47:56
47:56Documentary: The Hapsburg Empire - The Beautiful Blue Danube
Documentary: The Hapsburg Empire - The Beautiful Blue DanubeDocumentary: The Hapsburg Empire - The Beautiful Blue Danube
Documentary: The Hapsburg Empire - The Beautiful Blue Danube Documentary: The Hapsburg Empire - The Beautiful Blue Danube Documentary: The Hapsburg Empire - The Beautiful Blue Danube -
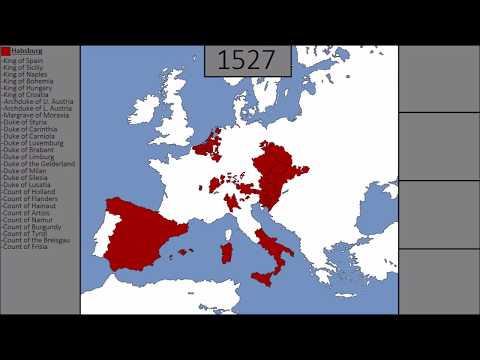 3:36
3:36The House of Habsburg
The House of HabsburgThe House of Habsburg
Habsburg Castle was built sometime in the 10th Century, and remained a rather unimportant entity for the next 200 years. This changed in the 12th Century when the Habsburgs began to rapidly gain lands in the Alps, making them one of the most powerful families there by 1218. During the rest of the 13th Century, they spread farther still, culminating in the inheritance of Austria and Styria in 1278. This collection of territories would expand farther still during the 14 Century, making the Habsburg one of the most influential families in the whole Holy Roman Empire. After a brief period of division, their influence would expand beyond the Imperial frontier into the Netherlands in 1477, Iberia in 1516, and Hungary-Bohemia in 1526. By now, the Habsburgs were an unparalleled European power, although the realm was split in 1556 into a Spanish and Austrian circle, after which a period of decline ensued. A revival for the Austrian branch began in 1683 when the Ottomans began to fall back away from Hungary during the Great Turkish War, but Spain continued to decline and fell out of Habsburg control entirely in the early 18th Century, with many former possessions passing to the Austrian branch. The borders would continue to shift in the 18th Century, as Austria lost Silesia in 1742 at the hands of Prussia, but gained Galicia and Little Poland during the Polish Partitions. After more brief losses during the Napoleonic Wars, the Habsburgs emerged in a strong position in 1815 with various branches penetrating deep into Italy. The 19th Century was mostly peaceful, with the exception of the loss of their Italian territories and the gain of Bosnia-Herzegovina. During the First World War, their dominions began to unravel, and the state collapsed in 1919, ending all Habsburg territorial sovereignty. --------------------------------------------------- This video is the Fan Suggestion for December 2015, suggested by justin Bridges Previous winners: November 2015: Rise and Fall of the Russian Empire, suggested by GalacticPenguinTV October 2015: The Great Turkish War, suggested by Kaiser Franz Josef I --------------------------------------------------- Music: Antti Martikainen - Treacherous Waters -
 13:16
13:16Charles V and the Holy Roman Empire: Crash Course World History #219
Charles V and the Holy Roman Empire: Crash Course World History #219Charles V and the Holy Roman Empire: Crash Course World History #219
Get the new Crash Course World History Character poster here: http://store.dftba.com/products/crashcourse-characters-poster In which John Green teaches you about the Holy Roman Empire by teaching you about Charles V. Charles Hapsburg was the holy Roman Emperor, but he was also the King of Spain. And the King of Germany. And the King of Italy and the Lord of the Netherlands and Count Palatine of Burgundy. In short, Charles was runnin' thangs in much of the world during his reign. Charles ruled a lot of countries, and he was also known for encouraging intellectual discourse and he even spoke out against slavery, in a limited. So why did he consider himself a failure, and why did he break up the Empire when he abdicated in 1556? Mainly because the Holy Roman Empire didn't work very well. It was huge, and it didn't have any means of directly raising taxes. Plus, it was a pretty crazy time in Europe anyway, and Charles found himself in charge of the Catholic-Church-Endorsed Empire in the time of Martin Luther and the Protestant Reformation. John will teach you a bit about how Charles put the Empire together, and how it fell apart, and even talk a bit about the Diet of Worms. This episode was written by Neal Schulz, but we messed up the onscreen credits. Thanks, and great work, Neal. You can directly support Crash Course at https://www.patreon.com/crashcourse Subscribe for as little as $0 to keep up with everything we're doing. Free is nice, but if you can afford to pay a little every month, it really helps us to continue producing this content. -
 2:24
2:24Karl von Habsburg: Nationalism rise 'painful' BBC HARDtalk
Karl von Habsburg: Nationalism rise 'painful' BBC HARDtalkKarl von Habsburg: Nationalism rise 'painful' BBC HARDtalk
Karl von Habsburg is the grandson of the last of the Habsburg emperors. In Sarajevo his great uncle, Archduke Franz Ferdinand, was assassinated in June 1914 - an event which set World War I in motion. Returning to Sarajevo with HARDtalk, Habsburg told Stephen Sackur that it is "very painful to see nationalist movements rising again" across Europe. -
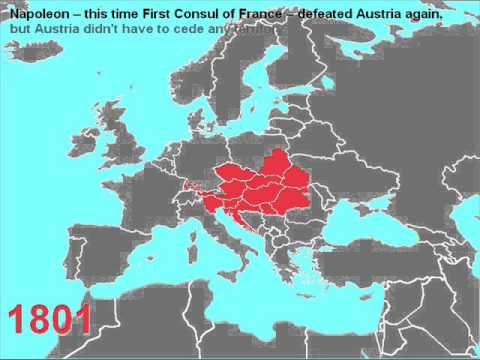 7:41
7:41The Rise and Fall of Austria or the Habsburg Empire / Österreich
The Rise and Fall of Austria or the Habsburg Empire / ÖsterreichThe Rise and Fall of Austria or the Habsburg Empire / Österreich
Austria was ruled by the Habsburg dynasty from 1278/1282 to 1918. Therefore, historical Austria is also known as the Habsburg Empire or the Habsburg Monarchy. The Habsburgs made Austria a great power in 1477, when they inherited much of what is now the Netherlands, Belgium and Luxembourg. Soon afterwards they inherited many more lands by their marriage policies. During the 16th century, the Habsburgs ruled over large parts of Europe. Charles V reigned over perhaps a quarter of the European population (not to speak of his enormous American colonial empire). The centuries afterwards Austria remained a great power until World War I, when the nationalistic thoughts in Europe finally divided the old empire into many small states. It's important to put in mind that Austria has always been a "part" of Germany until the 19th century. Indeed, the German Empire didn't exist until 1871, but the Germans (Austrians included) more or less realized they shared a similar language and culture, and the medieval Holy Roman Empire actually was for the most part a German state until it fell apart in the fatal 13th century. Since 1452, the Habsburgs were (with one short exception) the emperors of the Holy Roman Empire, which was by now virtually a very loose confederation of states. However, the position of the Holy Roman Emperor gave the Habsburgs privileges and some sort of loyalty from the German princes, although some monarchs—most notably the Prussian kings—openly contested Habsburg primacy. The Austrians were finally abandoned outside the German Empire in 1871. Music: Johann Strauss II - An der schönen blauen Donau (English title: The Blue Danube), composed in 1866. -
 11:51
11:51The Habsburgs: Rarely Seen Masterpieces from Europe's Greatest Dynasty exhibition video
The Habsburgs: Rarely Seen Masterpieces from Europe's Greatest Dynasty exhibition videoThe Habsburgs: Rarely Seen Masterpieces from Europe's Greatest Dynasty exhibition video
Exhibition Dates: February 15 - May 10, 2015 This sweeping exhibition showcases the amazing history of the Austrian Habsburg Emperors, who commissioned and collected households full of masterpieces by which to display their power. It focuses particularly on the three periods of their greatest flourishing. The first relates the history of the Habsburgs from the dynasty’s origins in the 13th century until the 16th century. The central figure is Maximilian I, during whose reign the Habsburgs achieved world-power status. You’ll see how an international network of political and family relations aided in the amassing of unique collections of art. Devoted to the Age of the Baroque, the second block explores the art, culture, and politics of the 17th and 18th centuries. During this period the House of Habsburg dies out in both Spanish and Austrian male lines, provoking considerable political complications and the loss of Spain. A female heiress, Maria Theresa, succeeded in establishing her right to rule as heir to the Austrian line, becoming the final ruler of the House of Habsburg. Visitors will discover the role of religion, art, and court festivities as instruments propagating the dynasty’s self‐image and claim to rule. Key figures include Leopold Wilhelm, Leopold I, Charles VI, and Maria Theresa. The early 19th century saw the final demise of the Holy Roman Empire and the establishment of the hereditary Austrian Empire. With the growth of nationalism, the empire would be transformed into the dual monarchy of Austria‐Hungary. Key figures of this period are Francis II (I) and Franz Joseph. This section explores the long reign of Emperor Franz Joseph, the founding of the Kunsthistorisches Museum, and the creation of the multinational empire. This empire, characterized by a highly hierarchical social order, is represented by the lavish gowns of the imperial court. At the end of World War I in 1918, it dissolved into its component parts, bringing almost 600 years of Habsburg rule in Europe to an end. -
 35:00
35:00A real game of thrones - "The Habsburg Jaw"
A real game of thrones - "The Habsburg Jaw"A real game of thrones - "The Habsburg Jaw"
Produced by OMNI-Net - MedWord for Clinical Eye Openers (http://ceo.medword.net). -
 1:28
1:28Otto von Habsburg - Funeral - Singing of the Kaiserhymne
Otto von Habsburg - Funeral - Singing of the KaiserhymneOtto von Habsburg - Funeral - Singing of the Kaiserhymne
Following 13 days of mourning, the heir to the thrones of the great Austro Hungarian Empire, His Imperial and Royal Highness Archduke Otto of Austria, Prince Royal of Hungary, Otto von Hapsburg, was laid to rest in Vienna on 16 July 2011. In scenes recalling the Empire, his coffin was taken in one of the longest processions seen in the old imperial capital to St Stephen's cathedral where the Cardinal Archbishop of Vienna Christoph Schönborn presided. This video shows the the singing of the Hayden's Kaiserhymne, the Imperial Hymn. (The tune is well known in the English speaking world from John Newton's great hymn "Glorious things of thee are spoken/Zion, city of our God." The music was subsequently used as the German National Anthem which begins "Deutschland, Deutschland über alles") His body was first laid in repose in the Church of St. Ulrich in Pöcking, Bavaria, and was then taken by train to Mariazell on 12 July, before being taken by train to Vienna. Five requiem masses were celebrated in Munich, Pöcking, Mariazell, Vienna, and Budapest. In accordance with the Habsburg tradition, his body was entombed in the Imperial Crypt (Kapuzinergruft) in Vienna and his heart will be buried in the Pannonhalma Archabbey west of the Hungarian capital, Budapest. His son Karl Habsburg said "It would always be wrong to only remember him in the context of the old monarchy or only remember him in the context of the European Union. I think he should be remembered in the whole arch that his life has been creating... over the whole changes that happened to Europe in his lifetime." Among the mourners were King Carl Gustaf and Queen Silvia of Sweden, Grand Duke Henri of Luxembourg, Prince Hans-Adam II of Liechtenstein and Prince Michael of Kent and Marie Christine, Princess Michael of Kent, representing the royal Family of the sixteen Commonwealth Realms.
-

The Habsburg Empire: Under the Double Headed Eagle
Documentary on the House of Hapsburg and their Empire.
published: 11 Nov 2016 -

What Happened to the Habsburgs?
The Habsburgs were once the most powerful family in Austria, but as they tried to strengthen the bloodline by intermarrying, a lack of genetic diversity ended up being their downfall. From: MUSEUM SECRETS REVEALED: Inside the Kunsthistorisches Museum http://bit.ly/1yS9nSN
published: 14 Jan 2013 -

Documentary: The Hapsburg Empire - The Beautiful Blue Danube
Documentary: The Hapsburg Empire - The Beautiful Blue Danube Documentary: The Hapsburg Empire - The Beautiful Blue Danube Documentary: The Hapsburg Empire - The Beautiful Blue Danube
published: 13 Oct 2016 -

The House of Habsburg
Habsburg Castle was built sometime in the 10th Century, and remained a rather unimportant entity for the next 200 years. This changed in the 12th Century when the Habsburgs began to rapidly gain lands in the Alps, making them one of the most powerful families there by 1218. During the rest of the 13th Century, they spread farther still, culminating in the inheritance of Austria and Styria in 1278. This collection of territories would expand farther still during the 14 Century, making the Habsburg one of the most influential families in the whole Holy Roman Empire. After a brief period of division, their influence would expand beyond the Imperial frontier into the Netherlands in 1477, Iberia in 1516, and Hungary-Bohemia in 1526. By now, the Habsburgs were an unparalleled European power, alt...
published: 24 Dec 2015 -

Charles V and the Holy Roman Empire: Crash Course World History #219
Get the new Crash Course World History Character poster here: http://store.dftba.com/products/crashcourse-characters-poster In which John Green teaches you about the Holy Roman Empire by teaching you about Charles V. Charles Hapsburg was the holy Roman Emperor, but he was also the King of Spain. And the King of Germany. And the King of Italy and the Lord of the Netherlands and Count Palatine of Burgundy. In short, Charles was runnin' thangs in much of the world during his reign. Charles ruled a lot of countries, and he was also known for encouraging intellectual discourse and he even spoke out against slavery, in a limited. So why did he consider himself a failure, and why did he break up the Empire when he abdicated in 1556? Mainly because the Holy Roman Empire didn't work very well. It ...
published: 06 Dec 2014 -

Karl von Habsburg: Nationalism rise 'painful' BBC HARDtalk
Karl von Habsburg is the grandson of the last of the Habsburg emperors. In Sarajevo his great uncle, Archduke Franz Ferdinand, was assassinated in June 1914 - an event which set World War I in motion. Returning to Sarajevo with HARDtalk, Habsburg told Stephen Sackur that it is "very painful to see nationalist movements rising again" across Europe.
published: 03 Sep 2014 -

The Rise and Fall of Austria or the Habsburg Empire / Österreich
Austria was ruled by the Habsburg dynasty from 1278/1282 to 1918. Therefore, historical Austria is also known as the Habsburg Empire or the Habsburg Monarchy. The Habsburgs made Austria a great power in 1477, when they inherited much of what is now the Netherlands, Belgium and Luxembourg. Soon afterwards they inherited many more lands by their marriage policies. During the 16th century, the Habsburgs ruled over large parts of Europe. Charles V reigned over perhaps a quarter of the European population (not to speak of his enormous American colonial empire). The centuries afterwards Austria remained a great power until World War I, when the nationalistic thoughts in Europe finally divided the old empire into many small states. It's important to put in mind that Austria has always been a "pa...
published: 03 May 2011 -

The Habsburgs: Rarely Seen Masterpieces from Europe's Greatest Dynasty exhibition video
Exhibition Dates: February 15 - May 10, 2015 This sweeping exhibition showcases the amazing history of the Austrian Habsburg Emperors, who commissioned and collected households full of masterpieces by which to display their power. It focuses particularly on the three periods of their greatest flourishing. The first relates the history of the Habsburgs from the dynasty’s origins in the 13th century until the 16th century. The central figure is Maximilian I, during whose reign the Habsburgs achieved world-power status. You’ll see how an international network of political and family relations aided in the amassing of unique collections of art. Devoted to the Age of the Baroque, the second block explores the art, culture, and politics of the 17th and 18th centuries. During this period the H...
published: 13 Feb 2015 -

A real game of thrones - "The Habsburg Jaw"
Produced by OMNI-Net - MedWord for Clinical Eye Openers (http://ceo.medword.net).
published: 19 Jun 2017 -

Otto von Habsburg - Funeral - Singing of the Kaiserhymne
Following 13 days of mourning, the heir to the thrones of the great Austro Hungarian Empire, His Imperial and Royal Highness Archduke Otto of Austria, Prince Royal of Hungary, Otto von Hapsburg, was laid to rest in Vienna on 16 July 2011. In scenes recalling the Empire, his coffin was taken in one of the longest processions seen in the old imperial capital to St Stephen's cathedral where the Cardinal Archbishop of Vienna Christoph Schönborn presided. This video shows the the singing of the Hayden's Kaiserhymne, the Imperial Hymn. (The tune is well known in the English speaking world from John Newton's great hymn "Glorious things of thee are spoken/Zion, city of our God." The music was subsequently used as the German National Anthem which begins "Deutschland, Deutschland über alle...
published: 17 Jul 2011
The Habsburg Empire: Under the Double Headed Eagle
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 47:54
- Updated: 11 Nov 2016
- views: 22522
What Happened to the Habsburgs?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:04
- Updated: 14 Jan 2013
- views: 121479
- published: 14 Jan 2013
- views: 121479
Documentary: The Hapsburg Empire - The Beautiful Blue Danube
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 47:56
- Updated: 13 Oct 2016
- views: 16797
- published: 13 Oct 2016
- views: 16797
The House of Habsburg
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:36
- Updated: 24 Dec 2015
- views: 53222
- published: 24 Dec 2015
- views: 53222
Charles V and the Holy Roman Empire: Crash Course World History #219
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 13:16
- Updated: 06 Dec 2014
- views: 1427574
- published: 06 Dec 2014
- views: 1427574
Karl von Habsburg: Nationalism rise 'painful' BBC HARDtalk
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:24
- Updated: 03 Sep 2014
- views: 12862
- published: 03 Sep 2014
- views: 12862
The Rise and Fall of Austria or the Habsburg Empire / Österreich
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:41
- Updated: 03 May 2011
- views: 808214
- published: 03 May 2011
- views: 808214
The Habsburgs: Rarely Seen Masterpieces from Europe's Greatest Dynasty exhibition video
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 11:51
- Updated: 13 Feb 2015
- views: 22871
- published: 13 Feb 2015
- views: 22871
A real game of thrones - "The Habsburg Jaw"
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 35:00
- Updated: 19 Jun 2017
- views: 781
- published: 19 Jun 2017
- views: 781
Otto von Habsburg - Funeral - Singing of the Kaiserhymne
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:28
- Updated: 17 Jul 2011
- views: 757141
- published: 17 Jul 2011
- views: 757141

- Playlist
- Chat

- Playlist
- Chat

The Habsburg Empire: Under the Double Headed Eagle
- Report rights infringement
- published: 11 Nov 2016
- views: 22522

What Happened to the Habsburgs?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Jan 2013
- views: 121479

Documentary: The Hapsburg Empire - The Beautiful Blue Danube
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 Oct 2016
- views: 16797

The House of Habsburg
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 Dec 2015
- views: 53222

Charles V and the Holy Roman Empire: Crash Course World History #219
- Report rights infringement
- published: 06 Dec 2014
- views: 1427574

Karl von Habsburg: Nationalism rise 'painful' BBC HARDtalk
- Report rights infringement
- published: 03 Sep 2014
- views: 12862

The Rise and Fall of Austria or the Habsburg Empire / Österreich
- Report rights infringement
- published: 03 May 2011
- views: 808214

The Habsburgs: Rarely Seen Masterpieces from Europe's Greatest Dynasty exhibition video
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 Feb 2015
- views: 22871

A real game of thrones - "The Habsburg Jaw"
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Jun 2017
- views: 781

Otto von Habsburg - Funeral - Singing of the Kaiserhymne
- Report rights infringement
- published: 17 Jul 2011
- views: 757141





