- published: 10 Dec 2016
- views: 618
-
remove the playlistDeoxyribose
- remove the playlistDeoxyribose
- published: 08 Dec 2011
- views: 499462
- published: 27 Feb 2014
- views: 139
- published: 20 Apr 2015
- views: 646
- published: 09 Jul 2015
- views: 68
- published: 28 Aug 2012
- views: 2258
- published: 19 Mar 2015
- views: 20983
- published: 11 Mar 2012
- views: 56930
- published: 15 Jul 2015
- views: 58438

Deoxyribose
Deoxyribose, or more precisely 2-deoxyribose, is a monosaccharide with idealized formula H−(C=O)−(CH2)−(CHOH)3−H. Its name indicates that it is a deoxy sugar, meaning that it is derived from the sugar ribose by loss of an oxygen atom. Since the pentose sugars arabinose and ribose only differ by the stereochemistry at C2', 2-deoxyribose and 2-deoxyarabinose are equivalent, although the latter term is rarely used because ribose, not arabinose, is the precursor to deoxyribose.
Structure
Several isomers exist with the formula H−(C=O)−(CH2)−(CHOH)3−H, but in deoxyribose all the hydroxyl groups are on the same side in the Fischer projection. The term "2-deoxyribose" may refer to either of two enantiomers: the biologically important D-2-deoxyribose and to the rarely encountered mirror image L-2-deoxyribose.D-2-deoxyribose is a precursor to the nucleic acid DNA. 2-deoxyribose is an aldopentose, that is, a monosaccharide with five carbon atoms and having an aldehyde functional group.
In aqueous solution, deoxyribose primarily exists as a mixture of three structures: the linear form H−(C=O)−(CH2)−(CHOH)3−H and two ring forms, deoxyribofuranose ("C3'-endo"), with a five-membered ring, and deoxyribopyranose ("C2'-endo"), with a six-membered ring. The latter form is predominant (whereas the C3'-endo form is favored for ribose).
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Khan Academy
Khan Academy is a non-profit educational organization created in 2006 by educator Salman Khan with the aim of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. The organization produces short lectures in the form of YouTube videos. In addition to micro lectures, the organization's website features practice exercises and tools for educators. All resources are available for free to anyone around the world. The main language of the website is English, but the content is also available in other languages.
History
The founder of the organization, Salman Khan, was born in New Orleans, Louisiana, United States to immigrant parents from Bangladesh and India. After earning three degrees from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (a BS in mathematics, a BS in electrical engineering and computer science, and an MEng in electrical engineering and computer science), he pursued an MBA from Harvard Business School.
In late 2004, Khan began tutoring his cousin Nadia who needed help with math using Yahoo!'s Doodle notepad.When other relatives and friends sought similar help, he decided that it would be more practical to distribute the tutorials on YouTube. The videos' popularity and the testimonials of appreciative students prompted Khan to quit his job in finance as a hedge fund analyst at Connective Capital Management in 2009, and focus on the tutorials (then released under the moniker "Khan Academy") full-time.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, or large biomolecules, essential for all known forms of life. Nucleic acids, which include DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid), are made from monomers known as nucleotides. Each nucleotide has three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. If the sugar is deoxyribose, the polymer is DNA. If the sugar is ribose, the polymer is RNA. When all three components are combined, they form a nucleic acid. Nucleotides are also known as phosphate nucleotides.
Nucleic acids are among the most important biological macromolecules (others being amino acids/proteins, sugars/carbohydrates, and lipids/fats). They are found in abundance in all living things, where they function in encoding, transmitting and expressing genetic information—in other words, information is conveyed through the nucleic acid sequence, or the order of nucleotides within a DNA or RNA molecule. Strings of nucleotides strung together in a specific sequence are the mechanism for storing and transmitting hereditary, or genetic information via protein synthesis.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Molecule
A molecule (/ˈmɒlɪkjuːl/ from Latin moles "mass") is an electrically neutral group of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their lack of electrical charge. However, in quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the term molecule is often used less strictly, also being applied to polyatomic ions.
In the kinetic theory of gases, the term molecule is often used for any gaseous particle regardless of its composition. According to this definition, noble gas atoms are considered molecules as they are in fact monoatomic molecules.
A molecule may be homonuclear, that is, it consists of atoms of a single chemical element, as with oxygen (O2); or it may be heteronuclear, a chemical compound composed of more than one element, as with water (H2O). Atoms and complexes connected by non-covalent bonds such as hydrogen bonds or ionic bonds are generally not considered single molecules.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
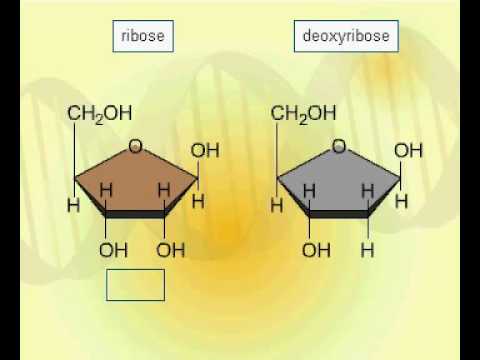 0:44
0:44Ribose and deoxyribose
Ribose and deoxyriboseRibose and deoxyribose
-
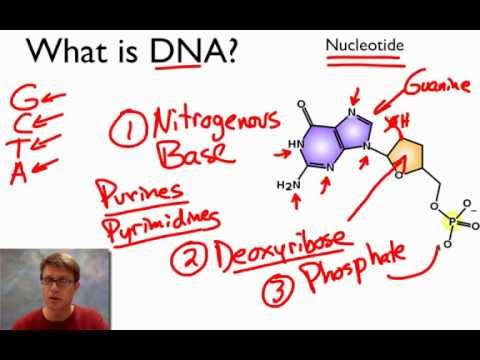 10:31
10:31What is DNA?
What is DNA?What is DNA?
Paul Andersen describes the molecular structure of DNA. He describes the major parts of a nucleotide and explains how they are assembled into a nucleic acid. The nitrogenous base, deoxyribose sugar and phosphate group make up a single nucleotide. The 5' and 3' end of DNA is described. The importance of hydrogen bonds in the 3-dimensional shape is also included. Intro Music Atribution Title: I4dsong_loop_main.wav Artist: CosmicD Link to sound: http://www.freesound.org/people/CosmicD/sounds/72556/ Creative Commons Atribution License -
 0:14
0:14Deoxyribose
Deoxyribose -
 1:35
1:35Deoxyribose Nucleic Awesome
Deoxyribose Nucleic AwesomeDeoxyribose Nucleic Awesome
3D Rendering http://www.3dvieweronline.com/share/PwF9ikKCAlK/PwF9ikKCAlK.html -
 0:36
0:36Deoxyribose Meaning
Deoxyribose MeaningDeoxyribose Meaning
Video shows what deoxyribose means. A derivative of the pentose sugar ribose in which the 2' hydroxyl (-OH) is reduced to a hydrogen (H); it is a constituent of the nucleotides that comprise the biopolymer, deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA.. Deoxyribose Meaning. How to pronounce, definition audio dictionary. How to say deoxyribose. Powered by MaryTTS, Wiktionary -
 1:09
1:09DeOxyRibose
DeOxyRiboseDeOxyRibose
DeOxyRibose Flyby in a Virtual Reality world generated by the BioMight Animation engine. Use the might of BioMight to power your audience. -
 5:43
5:43DNA I Ribose
DNA I RiboseDNA I Ribose
The rails of the famous double helix are made of alternating ribose and phosphate. -
 5:09
5:09How to Remember DNA and RNA Nucleotides and their Structure
How to Remember DNA and RNA Nucleotides and their StructureHow to Remember DNA and RNA Nucleotides and their Structure
In this video I quickly go over the structure of the DNA and RNA bases and nucleotides, and give some mnemonics for how to remember them. Molecular structure of DNA and RNA. The difference between a nucleotide, nucleoside, and base. nucleotide: base, sugar, one or more phosphates nucleoside: base and sugar base: just the base RNA uses uracil (U) instead of thymine (T). The difference is a methyl group that doesn't affect base pairing. The ribose sugar of RNA has a hydroxyl group at the 2' position that the deoxyribose of DNA lacks. RNA is less stable because of the extra hydroxyl. The GACT and GACU mnemonics for the DNA and RNA bases GA: purines CT/CU: pyrimidines G base pairs with C A base pairs with T/U GC base pairs have 3 hydrogen bonds AT and AU base pairs have 2 hydrogen bonds, and so are a little weaker. -
 9:59
9:59DNA Structure
DNA StructureDNA Structure
http://armandoh.org/ Describes DNA - structure Ref: John Dearnaley USQ PDF: https://docs.google.com/open?id=0B8Ss3-wJfHrpZ2dZMHRJMFpBYWs https://www.facebook.com/ArmandoHasudungan Support me: http://www.patreon.com/armando Instagram: http://instagram.com/armandohasudungan Twitter: https://twitter.com/Armando71021105 -
 13:01
13:01Molecular structure of DNA | Macromolecules | Biology | Khan Academy
Molecular structure of DNA | Macromolecules | Biology | Khan AcademyMolecular structure of DNA | Macromolecules | Biology | Khan Academy
Molecular structure of DNA. Nucleotide. Nitrogenous base, phosphate. Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/biology/macromolecules/nucleic-acids/v/antiparallel-structure-of-dna-strands?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=biology Missed the previous lesson? https://www.khanacademy.org/science/biology/macromolecules/nucleic-acids/v/rna-transcription-and-translation?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=biology Biology on Khan Academy: Life is beautiful! From atoms to cells, from genes to proteins, from populations to ecosystems, biology is the study of the fascinating and intricate systems that make life possible. Dive in to learn more about the many branches of biology and why they are exciting and important. Covers topics seen in a high school or first-year college biology course. About Khan Academy: Khan Academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that empower learners to study at their own pace in and outside of the classroom. We tackle math, science, computer programming, history, art history, economics, and more. Our math missions guide learners from kindergarten to calculus using state-of-the-art, adaptive technology that identifies strengths and learning gaps. We've also partnered with institutions like NASA, The Museum of Modern Art, The California Academy of Sciences, and MIT to offer specialized content. For free. For everyone. Forever. #YouCanLearnAnything Subscribe to Khan Academy's Biology channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC82qE46vcTn7lP4tK_RHhdg?sub_confirmation=1 Subscribe to Khan Academy: https://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=khanacademy
-

Ribose and deoxyribose
published: 10 Dec 2016 -

What is DNA?
Paul Andersen describes the molecular structure of DNA. He describes the major parts of a nucleotide and explains how they are assembled into a nucleic acid. The nitrogenous base, deoxyribose sugar and phosphate group make up a single nucleotide. The 5' and 3' end of DNA is described. The importance of hydrogen bonds in the 3-dimensional shape is also included. Intro Music Atribution Title: I4dsong_loop_main.wav Artist: CosmicD Link to sound: http://www.freesound.org/people/CosmicD/sounds/72556/ Creative Commons Atribution License
published: 08 Dec 2011 -

-

Deoxyribose Nucleic Awesome
3D Rendering http://www.3dvieweronline.com/share/PwF9ikKCAlK/PwF9ikKCAlK.html
published: 27 Feb 2014 -

Deoxyribose Meaning
Video shows what deoxyribose means. A derivative of the pentose sugar ribose in which the 2' hydroxyl (-OH) is reduced to a hydrogen (H); it is a constituent of the nucleotides that comprise the biopolymer, deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA.. Deoxyribose Meaning. How to pronounce, definition audio dictionary. How to say deoxyribose. Powered by MaryTTS, Wiktionary
published: 20 Apr 2015 -

DeOxyRibose
DeOxyRibose Flyby in a Virtual Reality world generated by the BioMight Animation engine. Use the might of BioMight to power your audience.
published: 09 Jul 2015 -

DNA I Ribose
The rails of the famous double helix are made of alternating ribose and phosphate.
published: 28 Aug 2012 -

How to Remember DNA and RNA Nucleotides and their Structure
In this video I quickly go over the structure of the DNA and RNA bases and nucleotides, and give some mnemonics for how to remember them. Molecular structure of DNA and RNA. The difference between a nucleotide, nucleoside, and base. nucleotide: base, sugar, one or more phosphates nucleoside: base and sugar base: just the base RNA uses uracil (U) instead of thymine (T). The difference is a methyl group that doesn't affect base pairing. The ribose sugar of RNA has a hydroxyl group at the 2' position that the deoxyribose of DNA lacks. RNA is less stable because of the extra hydroxyl. The GACT and GACU mnemonics for the DNA and RNA bases GA: purines CT/CU: pyrimidines G base pairs with C A base pairs with T/U GC base pairs have 3 hydrogen bonds AT and AU base pairs have 2 hydrogen bonds, an...
published: 19 Mar 2015 -

DNA Structure
http://armandoh.org/ Describes DNA - structure Ref: John Dearnaley USQ PDF: https://docs.google.com/open?id=0B8Ss3-wJfHrpZ2dZMHRJMFpBYWs https://www.facebook.com/ArmandoHasudungan Support me: http://www.patreon.com/armando Instagram: http://instagram.com/armandohasudungan Twitter: https://twitter.com/Armando71021105
published: 11 Mar 2012 -

Molecular structure of DNA | Macromolecules | Biology | Khan Academy
Molecular structure of DNA. Nucleotide. Nitrogenous base, phosphate. Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/biology/macromolecules/nucleic-acids/v/antiparallel-structure-of-dna-strands?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=biology Missed the previous lesson? https://www.khanacademy.org/science/biology/macromolecules/nucleic-acids/v/rna-transcription-and-translation?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=biology Biology on Khan Academy: Life is beautiful! From atoms to cells, from genes to proteins, from populations to ecosystems, biology is the study of the fascinating and intricate systems that make life possible. Dive in to learn more about the many branches of biology and why they are exciting and important. Covers topics seen in a high school or first-ye...
published: 15 Jul 2015
Ribose and deoxyribose
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:44
- Updated: 10 Dec 2016
- views: 618
- published: 10 Dec 2016
- views: 618
What is DNA?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:31
- Updated: 08 Dec 2011
- views: 499462
- published: 08 Dec 2011
- views: 499462
Deoxyribose
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:14
- Updated: 30 Oct 2014
- views: 1400
Deoxyribose Nucleic Awesome
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:35
- Updated: 27 Feb 2014
- views: 139
- published: 27 Feb 2014
- views: 139
Deoxyribose Meaning
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:36
- Updated: 20 Apr 2015
- views: 646
- published: 20 Apr 2015
- views: 646
DeOxyRibose
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:09
- Updated: 09 Jul 2015
- views: 68
- published: 09 Jul 2015
- views: 68
DNA I Ribose
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:43
- Updated: 28 Aug 2012
- views: 2258
- published: 28 Aug 2012
- views: 2258
How to Remember DNA and RNA Nucleotides and their Structure
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:09
- Updated: 19 Mar 2015
- views: 20983
- published: 19 Mar 2015
- views: 20983
DNA Structure
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:59
- Updated: 11 Mar 2012
- views: 56930
- published: 11 Mar 2012
- views: 56930
Molecular structure of DNA | Macromolecules | Biology | Khan Academy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 13:01
- Updated: 15 Jul 2015
- views: 58438
- published: 15 Jul 2015
- views: 58438

- Playlist
- Chat

- Playlist
- Chat

Ribose and deoxyribose
- Report rights infringement
- published: 10 Dec 2016
- views: 618

What is DNA?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 08 Dec 2011
- views: 499462

Deoxyribose
- Report rights infringement
- published: 30 Oct 2014
- views: 1400

Deoxyribose Nucleic Awesome
- Report rights infringement
- published: 27 Feb 2014
- views: 139

Deoxyribose Meaning
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Apr 2015
- views: 646

DeOxyRibose
- Report rights infringement
- published: 09 Jul 2015
- views: 68

DNA I Ribose
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Aug 2012
- views: 2258

How to Remember DNA and RNA Nucleotides and their Structure
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Mar 2015
- views: 20983

DNA Structure
- Report rights infringement
- published: 11 Mar 2012
- views: 56930

Molecular structure of DNA | Macromolecules | Biology | Khan Academy
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Jul 2015
- views: 58438
The Trump Organization Says It's 'Not Practical' to Comply With the Emoluments Clause
Edit Democratic Underground 25 May 2017Melania and Ivanka Trump Wore Veils to Meet the Pope
Edit Time Magazine 24 May 2017Prison Riot in California Leaves Seven Inmates, Eight Guards Injured
Edit WorldNews.com 25 May 2017Sherpas Find 4 Climbers Dead In Tent On Mount Everest, Raising Month's Toll To 10
Edit WorldNews.com 25 May 2017Physicists elucidate reactions underlying positive ion beams hitting molecular targets relevant in proton therapy
Edit Science Daily 08 Oct 2016Susan Haack on the use of terminology in academia
Edit The Examiner 05 Jun 2016El-Rufai to Establish DNA Forensic Centre
Edit All Africa 04 May 2016Scientists Find Building Blocks Of Life On Comet, Huge Discovery Could Finally Answer How Life ...
Edit Inquisitr 08 Apr 2016Inside The NASA Mission To Answer 'What Is Life?'
Edit Huffington Post 06 Nov 2015What is life?
Edit Mosaic Science 20 Oct 2015We should move forward on Land Bill, says Narendra Modi ahead of Monsoon session
Edit Deccan Chronicle 20 Jul 2015Monsoon session set to be stormy as Oppn closes ranks
Edit Deccan Herald 19 Jul 2015Monsoon Session: NDA ministers discuss govt's floor strategy
Edit Deccan Herald 16 Jul 2015Enzyme mechanism-based, oxidative DNA–protein cross-links formed with DNA polymerase β in vivo
Edit PNAS 26 Jun 2015Synthetic enzymes hint at life without DNA or RNA
Edit New Scientist 01 Dec 2014- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »








