- published: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 85737
-
remove the playlistHimyarite
- remove the playlistHimyarite
- published: 16 Apr 2013
- views: 2129
- published: 04 Sep 2016
- views: 14
- published: 21 Jun 2017
- views: 3
- published: 07 Nov 2013
- views: 3181
- published: 01 Sep 2012
- views: 1087
- published: 18 Jul 2012
- views: 3392
- published: 20 Mar 2009
- views: 53576

Himyarite Kingdom
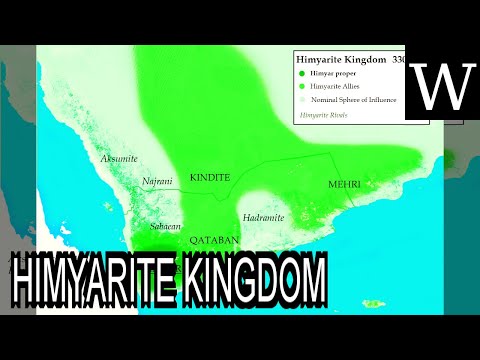
The Ḥimyarite Kingdom or Ḥimyar (in Arabic مملكة حِمْيَر Mamlakat Ḥimyar) (Hebrew: ממלכת חִמְיָר) (Flourished 110 BCE–520s CE), historically referred to as the Homerite Kingdom by the Greeks and the Romans, was a kingdom in ancient Yemen. Established in 110 BCE, it took as its capital the modern-day city of Sana'a after the ancient city of Zafar. The Kingdom conquered neighbouring Saba' (Sheba) in c. 25 BCE (for the first time), Qataban in c. 200 CE, and Haḍramaut c. 300 CE. Its political fortunes relative to Saba' changed frequently until it finally conquered the Sabaean Kingdom around 280 CE. Himyar then endured until it finally fell to Christian invaders in 525 CE.
History
The Ḥimyarite Kingdom was the dominant polity in Arabia until 525. Its economy was based on agriculture, and foreign trade centered on the export of frankincense and myrrh. For many years, the kingdom was also the major intermediary linking East Africa and the Mediterranean world. This trade largely consisted of exporting ivory from Africa to be sold in the Roman Empire. Ships from Ḥimyar regularly traveled the East African coast, and the state also exerted a large amount of Influence both cultural religious and political to the trading cities of East Africa whilst the cities of East Africa remained independent. The Periplus of the Erythraean Sea describes the trading empire of Himyar and its ruler Charibael (Karab Il Watar Yuhan'em II), who is said to have been on friendly terms with Rome:
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Yemen
Coordinates: 15°N 48°E / 15°N 48°E / 15; 48
Yemen (![]() i/ˈjɛmən/; Arabic: اليَمَن al-Yaman), officially known as the Republic of Yemen (الجمهورية اليمنية al-Jumhūrīyah al-Yamanīyah), is an Arab country in Western Asia, occupying the southwestern to the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula. Yemen is the second largest country in the peninsula, occupying 527,970 km2 (203,850 sq mi). The coastline stretches for about 2,000 km (1,200 mi). It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the north, the Red Sea to the west, the Gulf of Aden and Arabian Sea to the south, and Oman to the east. Although Yemen's constitutionally stated capital is the city of Sana'a, the city has been under rebel control since February 2015. Because of this, Yemen's capital has been temporarily relocated to the port city of Aden, on the southern coast. Yemen's territory includes more than 200 islands; the largest of these is Socotra.
i/ˈjɛmən/; Arabic: اليَمَن al-Yaman), officially known as the Republic of Yemen (الجمهورية اليمنية al-Jumhūrīyah al-Yamanīyah), is an Arab country in Western Asia, occupying the southwestern to the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula. Yemen is the second largest country in the peninsula, occupying 527,970 km2 (203,850 sq mi). The coastline stretches for about 2,000 km (1,200 mi). It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the north, the Red Sea to the west, the Gulf of Aden and Arabian Sea to the south, and Oman to the east. Although Yemen's constitutionally stated capital is the city of Sana'a, the city has been under rebel control since February 2015. Because of this, Yemen's capital has been temporarily relocated to the port city of Aden, on the southern coast. Yemen's territory includes more than 200 islands; the largest of these is Socotra.
Yemen was the home of the Sabaeans (biblical Sheba), a trading state that flourished for over a thousand years and probably also included parts of modern-day Ethiopia and Eritrea. In 275 AD, the region came under the rule of the later Jewish influenced Himyarite Kingdom. Christianity arrived in the 4th century AD whereas Judaism and local paganism were already established. Islam spread quickly in the 7th century and Yemenite troops were crucial in the expansion of the early Islamic conquests. Administration of Yemen has long been notoriously difficult. Several dynasties emerged from the 9th to 16th century, the Rasulid being the strongest and most prosperous. The country was divided between the Ottoman and British empires in the early 20th century. The Zaydi Mutawakkilite Kingdom of Yemen was established after World War I in North Yemen before the creation of Yemen Arab Republic in 1962. South Yemen remained a British protectorate until 1967. The two Yemeni states united to form the modern republic of Yemen in 1990.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
Arabia Felix
Arabia Felix (lit. Happy Arabia; also Greek: Eudaimon Arabia) was the Latin name previously used by geographers to describe the southern part of the Arabian Peninsula, Yemen, a country with an extensive history.
Name
The term "Happy Arabia" is a translation of the Latin "Arabia felix." Felix means "fecund, fertile" but also "happy, fortunate, blessed." Arabia Felix was one of three regions into which the Romans divided the Arabian peninsula: Arabia Deserta, Arabia Felix, and Arabia Petraea.
Explanation
The southwestern corner of the peninsula, enjoying more rainfall, at that time was much greener than the rest of the peninsula and has long enjoyed more productive fields. The high peaks and slopes are capable of supporting significant vegetation and river beds called wadis help make other soil fertile.
In 26 BC Aelius Gallus under Augustus's order led a military expedition to Arabia Felix which ended in the utter defeat of Roman troops.
Part of what led to Arabia Felix's wealth and importance to the ancient world was its near monopoly of the trade in cinnamon and spices, both its native products and imports from India and the Horn of Africa.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

6th century
The 6th century is the period from 501 to 600 in accordance with the Julian calendar in the Common Era. In the West this century marks the end of Classical Antiquity and the beginning of the Middle Ages. Following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire late in the previous century, Europe fractured into many small Germanic Kingdoms, which competed fiercely for land and wealth. From this upheaval the Franks rose to prominence, and carved out a sizeable domain encompassing much of modern France and Germany. Meanwhile, the surviving Eastern Roman Empire began to expand under the emperor Justinian, who eventually recaptured North Africa from the Vandals, and attempted to fully recover Italy as well in the hope of re-establishing Roman control over the lands once ruled by the Western Roman Empire.
During its second Golden Age, the Sassanid Empire reached the peak of its power under Khosrau I in the 6th century. The classical Gupta Empire of Northern India, largely overrun by the Huna, ended in the mid-6th century. In Japan, the Kofun period gave way to the Asuka period. After being divided for more than 150 years into the Southern and Northern Dynasties, China was reunited under the Sui Dynasty toward the end of the 6th century. The Three Kingdoms of Korea persisted throughout the 6th century. The Göktürks became a major power in Central Asia after defeating the Rouran.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Arabian Peninsula
Arabian Peninsula, simplified Arabia (Arabic: الجزيرة العربية al-jazīra al-ʿarabiyya, « Arabian island ») is a peninsula of Western Asia situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. From a geological perspective, it is considered a subcontinent of Asia.
It is the largest peninsula in the world, at 3,237,500 km2 (1,250,000 sq mi). The Arabian Peninsula consists of the countries Yemen, Oman, Qatar, Bahrain, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates as well as parts of southern Iraq and Jordan. The peninsula formed as a result of the rifting of the Red Sea between 56 and 23 million years ago, and is bordered by the Red Sea to the west, the Persian Gulf to the northeast, the Levant to the north and the Indian Ocean to the southeast. The Arabian Peninsula plays a critical geopolitical role in the Middle East and Arab world due to its vast reserves of oil and natural gas.
Before the modern era, it was divided into four distinct regions: Hejaz, Najd, Southern Arabia and Eastern Arabia. Hejaz and Najd make up most of Saudi Arabia. Southern Arabia consists of Yemen and some parts of Saudi Arabia and Oman (Dhofar). Eastern Arabia consists of the entire coastal strip of the Arab side of the Persian Gulf (the Khaleej).
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 13:13
13:13#مملكة_الحضارات الحلقة الثانية: #شهداء_الاخدود | Himyarite Martyrs
#مملكة_الحضارات الحلقة الثانية: #شهداء_الاخدود | Himyarite Martyrs#مملكة_الحضارات الحلقة الثانية: #شهداء_الاخدود | Himyarite Martyrs
نتعرف في هذه الحلقة على مملكة حمير وأبشع حادثة حصلت في زمانهم حرق أصحاب الأخدود للمؤمنين مراجع برنامج مملكة الحضارات: القرآن الكريم والأحاديث النبوية الصحيحة مصنفات هيئة السياحة والتراث الوطني الرسمية التاريخ السياسي للأنباط للبروفيسور سليمان الذييب مدخل إلى قواعد النقوش النبطية للبروفيسور سليمان الذييب نقوش تيماء الآرامية للبروفيسور سليمان الذييب الجوف قلعة الشمال الحصينة للدكتور عبدالرحمن الأنصاري لحيان بين العلا ومكة لمساعد بن منشط اللحياني التنظيمات العسكرية النبطية للأستاذ صالح الدغيم بحوث في الجوف للدكتور خليل المعيقل سلسلة آثار المملكة العربية السعودية الحضارة العربية والإسلامية عبر العصور للدكتور عبدالرحمن الأنصاري وآخرون طُرق التجارة القديمة روائع آثار المملكة العربية السعودية -
 2:12
2:12Himyarite kingdom the greatest jewish empire
Himyarite kingdom the greatest jewish empireHimyarite kingdom the greatest jewish empire
and his brother's name was Joktan. 26Joktan became the father of Almodad, Sheleph, Hazarmaveth, Jerah, 27Hadoram, Uzal, Diklah, 28Obal, Abimael, Sheba, 29Ophir, Havilah, and Jobab; all these were the descendants of Joktan. 30The territory in which they lived extended from Mesha in the direction of Sephar, the hill country of the east. 31These are the descendants of Shem, by their families, their languages, their lands, and their nations. ( Genesis 10 act 25 30 Holy Bible old testament. In the fifth century, several kings of Ḥimyar are known to have converted to Judaism. The political context was the position of Arabia between the competing empires of Christian Byzantium and Zoroastrian Persia. Neutrality, and good trade relations with both empires, was essential to the prosperity of the Arabian trade routes. Scholars speculate that the choice of Judaism may have been an attempt at maintaining neutrality.[4] In the reign of Subahbi'il Yakkaf, the son of Abu Karib Assad, a certain Azqir, a Christian missionary from Najrān was put to death after he had erected a chapel with a cross. Christian sources interpret the event as a martyrdom at Jewish hands -the site for his execution, Najrān, being said to have been chosen on the advice of a rabbi,[5] but indigenous sources do not mention persecutions on the grounds of faith, and it may have been merely to deter the extension of Byzantine influence. -
 16:17
16:17Himyarite Kingdom
Himyarite KingdomHimyarite Kingdom
The Ḥimyarite Kingdom or Ḥimyar , historically referred to as the Homerite Kingdom by the Greeks and the Romans, was a kingdom in ancient Yemen.Established in 110 BCE, it took as its capital the ancient city of Zafar, to be followed at the beginning of the 4th century by what is the modern-day city of Sana'a.The kingdom conquered neighbouring Saba' in c.25 BCE , Qataban in c. ---Image-Copyright-and-Permission--- About the author(s): User Yom on en.wikipedia License: Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 (CC-BY-SA-3.0) Author(s): Yom ---Image-Copyright-and-Permission--- This channel is dedicated to make Wikipedia, one of the biggest knowledge databases in the world available to people with limited vision. Article available under a Creative Commons license Image source in video -
 14:02
14:02HIMYARITE KINGDOM - Documentary
HIMYARITE KINGDOM - DocumentaryHIMYARITE KINGDOM - Documentary
The '''Ḥimyarite Kingdom''' or '''Ḥimyar''' (, ''Mamlakat Ḥimyar'', [[South Arabian alphabet|Musnad]]: 𐩢𐩣𐩺𐩧𐩣, ) (fl. 110 [[BCE]]–520s [[Common Era|CE]]), historically referred to as the '''Homerite Kingdom''' by the Greeks and the Romans, was a kingdom in ancient [[Yemen]]. Established in 110 BCE, it took as its capital the ancient city of [[Zafar, Yemen|Zafar]], to be followed at the beginning of the 4th century by what is the modern-day city of [[Sana'a]]. The kingdom conquered neighbouring [[Sabaeans|Saba']] (Sheba) in c. 25 BCE (for the first time), [[Qataban]] in c. 200 CE, and [[Hadramaut|Haḍramaut]] c. 300 CE. Its political fortunes relative to Saba' changed frequently until it finally conquered the [[Sabaeans|Sabaean Kingdom]] around 280. Himyar then endured until it finally fell to invaders from the [[Kingdom of Aksum]] in 525.... ____________________________________ Shortcuts to chapters: 00:01:03: History 00:02:08: Early period (115 BC until 300 AD) 00:03:30: Jewish monarchy 00:10:49: Religious culture 00:11:38: Ancestral divisions of Himyar 00:12:44: Language ____________________________________ Copyright WikiVidi. Licensed under Creative Commons. Wikipedia link: https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Himyarite_Kingdom -
 2:54
2:54"Saba vs. Abyssinia"
"Saba vs. Abyssinia""Saba vs. Abyssinia"
A nice war report (as part of a dedicational inscription) about two Sabaean-Himyarite kings - Il-Sharah Yahdhib and Ya'zil Bayyin - who fought the Abyssinians and their allies of the Sahirat tribe in the Tihama, the Red Sea coast in Eastern Yemen. There is a part missing at the end. -
 0:12
0:12Himyarite Ruler Seeks Wife (397AD, colourised)
Himyarite Ruler Seeks Wife (397AD, colourised)Himyarite Ruler Seeks Wife (397AD, colourised)
44/M/Arabia Felix -
 6:26
6:26YEMEN - BRIEF HISTORIES
YEMEN - BRIEF HISTORIES -
 9:47
9:47Let's visit Yemen!
Let's visit Yemen!Let's visit Yemen!
Subscribe if you like what you see! For more information/photos/videos about Yemen, please LIKE us on FACEBOOK: http://www.facebook.com/YemenTheLandOfDreams Yemen is one of the oldest centers of civilization in the Near East. Between the 12th century BC and the 6th century, it was part of the Minaean, Sabaean, Hadhramaut, Qataban, Ausan and Himyarite kingdoms, which controlled the lucrative spice trade, and later came under Ethiopian and Persian rule.[5] In the 6th century, the Himyarite king Abu-Karib Assad converted to Judaism. In the 7th century, Islamic caliphs began to exert control over the area. After this caliphate broke up, Yemen came under the control of many dynasties who ruled part, or often all of Yemen. Imams of Persian origin ruled Yemen intermittently for 160 years, establishing a theocratic political structure that survived until modern times. Egyptian Sunni caliphs occupied much of Yemen throughout the 11th century. By the 16th century and again in the 19th century, Yemen was part of the Ottoman Empire, and in some periods Imams exerted control over all Yemen.[5] The modern history of Yemen began in 1918 when North Yemen gained independence from the Ottoman Empire. Between 1918-1962, Yemen was a monarchy ruled by the Hamidaddin family. North Yemen then became a republic in 1962, but it was not until 1967 that the British Empire, which had set up a protective area around the southern port of Aden in the 19th century, withdrew from what became South Yemen. In 1970, the southern government adopted a Communist governmental system. The two countries were formally united as the Republic of Yemen on May 22, 1990. For more information about Yemen, please visit our Facebook page: http://www.facebook.com/YemenTheLandOfDreams -
 14:51
14:51Yemen- The land of dreams
Yemen- The land of dreamsYemen- The land of dreams
Subscribe if you like what you see! LIKE us on FACEBOOK: http://www.facebook.com/YemenTheLandOfDreams Yemen is one of the oldest centers of civilization in the Near East. Between the 12th century BC and the 6th century, it was part of the Minaean, Sabaean, Hadhramaut, Qataban, Ausan and Himyarite kingdoms, which controlled the lucrative spice trade, and later came under Ethiopian and Persian rule.[5] In the 6th century, the Himyarite king Abu-Karib Assad converted to Judaism. In the 7th century, Islamic caliphs began to exert control over the area. After this caliphate broke up, Yemen came under the control of many dynasties who ruled part, or often all of Yemen. Imams of Persian origin ruled Yemen intermittently for 160 years, establishing a theocratic political structure that survived until modern times. Egyptian Sunni caliphs occupied much of Yemen throughout the 11th century. By the 16th century and again in the 19th century, Yemen was part of the Ottoman Empire, and in some periods Imams exerted control over all Yemen.[5] The modern history of Yemen began in 1918 when North Yemen gained independence from the Ottoman Empire. Between 1918-1962, Yemen was a monarchy ruled by the Hamidaddin family. North Yemen then became a republic in 1962, but it was not until 1967 that the British Empire, which had set up a protective area around the southern port of Aden in the 19th century, withdrew from what became South Yemen. In 1970, the southern government adopted a Communist governmental system. The two countries were formally united as the Republic of Yemen on May 22, 1990. For more information about Yemen, please visit visit our Facebook page: http://www.facebook.com/YemenTheLandOfDreams -
 7:11
7:11a journey to ancient Arabia
a journey to ancient Arabiaa journey to ancient Arabia
Arabia is the name of the country to the west and south of Mesopotamia There are three main zones can be discerned in Arabia : 1- the towns in the regions bordering on the Indian Ocean (modern Yemen and Oman) 2- the nomadic interior (modern day Saudi Arabia ,south syria,south Iraq ) 3-the northwestern part ( modern Jordan ) The Latin names of these three zones are: 1- Arabia Felix, (Happy or fortunate Arabia) 2- Arabia Deserta (Desert Arabia) 3-Arabia Petraea (stoney Arabia ). in this video we'll see scenes for some cultures and civilizations in the part called " Arabia Felix" . the other two arabian zones, Arabia Desserta and Arabia Petraea will be presented in the other parts. kingdoms and cultures of the south of Arabian peninsula wil be presented in this video ,this area used to be called Arabia Felix "now yemen and Oman," The history of "Arabia Felix" is especially important because it'is one of the oldest centers of civilization in the Near East. Its was recognized by some ancient Greek geographers like Ptolemy, who described "Yemen" as Eudaimon Arabia ,(better known in its Latin translation, Arabia Felix) meaning "fortunate Arabia" or Happy Arabia. Between the 12th century BC and the 6th century AD,it was dominated by six successive civilizations which rivaled each other, or were allied with each other and controlled the lucrative spice trade: M'ain, Qataban, Hadhramaut, Awsan, Saba and Himyarite. not much was known about the ancient history of the pre-islamic Arabia untill about 50 years ago when a series of excavation works began in the area.
-

#مملكة_الحضارات الحلقة الثانية: #شهداء_الاخدود | Himyarite Martyrs
نتعرف في هذه الحلقة على مملكة حمير وأبشع حادثة حصلت في زمانهم حرق أصحاب الأخدود للمؤمنين مراجع برنامج مملكة الحضارات: القرآن الكريم والأحاديث النبوية الصحيحة مصنفات هيئة السياحة والتراث الوطني الرسمية التاريخ السياسي للأنباط للبروفيسور سليمان الذييب مدخل إلى قواعد النقوش النبطية للبروفيسور سليمان الذييب نقوش تيماء الآرامية للبروفيسور سليمان الذييب الجوف قلعة الشمال الحصينة للدكتور عبدالرحمن الأنصاري لحيان بين العلا ومكة لمساعد بن منشط اللحياني التنظيمات العسكرية النبطية للأستاذ صالح الدغيم بحوث في الجوف للدكتور خليل المعيقل سلسلة آثار المملكة العربية السعودية الحضارة العربية والإسلامية عبر العصور للدكتور عبدالرحمن الأنصاري وآخرون طُرق التجارة القديمة روائع آثار المملكة العربية السعودية
published: 05 Nov 2016 -

Himyarite kingdom the greatest jewish empire
and his brother's name was Joktan. 26Joktan became the father of Almodad, Sheleph, Hazarmaveth, Jerah, 27Hadoram, Uzal, Diklah, 28Obal, Abimael, Sheba, 29Ophir, Havilah, and Jobab; all these were the descendants of Joktan. 30The territory in which they lived extended from Mesha in the direction of Sephar, the hill country of the east. 31These are the descendants of Shem, by their families, their languages, their lands, and their nations. ( Genesis 10 act 25 30 Holy Bible old testament. In the fifth century, several kings of Ḥimyar are known to have converted to Judaism. The political context was the position of Arabia between the competing empires of Christian Byzantium and Zoroastrian Persia. Neutrality, and good trade relations with both empires, was essential to the prosperity of ...
published: 16 Apr 2013 -

Himyarite Kingdom
The Ḥimyarite Kingdom or Ḥimyar , historically referred to as the Homerite Kingdom by the Greeks and the Romans, was a kingdom in ancient Yemen.Established in 110 BCE, it took as its capital the ancient city of Zafar, to be followed at the beginning of the 4th century by what is the modern-day city of Sana'a.The kingdom conquered neighbouring Saba' in c.25 BCE , Qataban in c. ---Image-Copyright-and-Permission--- About the author(s): User Yom on en.wikipedia License: Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 (CC-BY-SA-3.0) Author(s): Yom ---Image-Copyright-and-Permission--- This channel is dedicated to make Wikipedia, one of the biggest knowledge databases in the world available to people with limited vision. Article available under a Creative Commons license Image source in video
published: 04 Sep 2016 -

HIMYARITE KINGDOM - Documentary
The '''Ḥimyarite Kingdom''' or '''Ḥimyar''' (, ''Mamlakat Ḥimyar'', [[South Arabian alphabet|Musnad]]: 𐩢𐩣𐩺𐩧𐩣, ) (fl. 110 [[BCE]]–520s [[Common Era|CE]]), historically referred to as the '''Homerite Kingdom''' by the Greeks and the Romans, was a kingdom in ancient [[Yemen]]. Established in 110 BCE, it took as its capital the ancient city of [[Zafar, Yemen|Zafar]], to be followed at the beginning of the 4th century by what is the modern-day city of [[Sana'a]]. The kingdom conquered neighbouring [[Sabaeans|Saba']] (Sheba) in c. 25 BCE (for the first time), [[Qataban]] in c. 200 CE, and [[Hadramaut|Haḍramaut]] c. 300 CE. Its political fortunes relative to Saba' changed frequently until it finally conquered the [[Sabaeans|Sabaean Kingdom]] around 280. Himyar then endured until it finally fell t...
published: 21 Jun 2017 -

"Saba vs. Abyssinia"
A nice war report (as part of a dedicational inscription) about two Sabaean-Himyarite kings - Il-Sharah Yahdhib and Ya'zil Bayyin - who fought the Abyssinians and their allies of the Sahirat tribe in the Tihama, the Red Sea coast in Eastern Yemen. There is a part missing at the end.
published: 07 Nov 2013 -

-

-

Let's visit Yemen!
Subscribe if you like what you see! For more information/photos/videos about Yemen, please LIKE us on FACEBOOK: http://www.facebook.com/YemenTheLandOfDreams Yemen is one of the oldest centers of civilization in the Near East. Between the 12th century BC and the 6th century, it was part of the Minaean, Sabaean, Hadhramaut, Qataban, Ausan and Himyarite kingdoms, which controlled the lucrative spice trade, and later came under Ethiopian and Persian rule.[5] In the 6th century, the Himyarite king Abu-Karib Assad converted to Judaism. In the 7th century, Islamic caliphs began to exert control over the area. After this caliphate broke up, Yemen came under the control of many dynasties who ruled part, or often all of Yemen. Imams of Persian origin ruled Yemen intermittently for 160 years, estab...
published: 01 Sep 2012 -

Yemen- The land of dreams
Subscribe if you like what you see! LIKE us on FACEBOOK: http://www.facebook.com/YemenTheLandOfDreams Yemen is one of the oldest centers of civilization in the Near East. Between the 12th century BC and the 6th century, it was part of the Minaean, Sabaean, Hadhramaut, Qataban, Ausan and Himyarite kingdoms, which controlled the lucrative spice trade, and later came under Ethiopian and Persian rule.[5] In the 6th century, the Himyarite king Abu-Karib Assad converted to Judaism. In the 7th century, Islamic caliphs began to exert control over the area. After this caliphate broke up, Yemen came under the control of many dynasties who ruled part, or often all of Yemen. Imams of Persian origin ruled Yemen intermittently for 160 years, establishing a theocratic political structure that survived ...
published: 18 Jul 2012 -

a journey to ancient Arabia
Arabia is the name of the country to the west and south of Mesopotamia There are three main zones can be discerned in Arabia : 1- the towns in the regions bordering on the Indian Ocean (modern Yemen and Oman) 2- the nomadic interior (modern day Saudi Arabia ,south syria,south Iraq ) 3-the northwestern part ( modern Jordan ) The Latin names of these three zones are: 1- Arabia Felix, (Happy or fortunate Arabia) 2- Arabia Deserta (Desert Arabia) 3-Arabia Petraea (stoney Arabia ). in this video we'll see scenes for some cultures and civilizations in the part called " Arabia Felix" . the other two arabian zones, Arabia Desserta and Arabia Petraea will be presented in the other parts. kingdoms and cultures of the south of Arabian peninsula wil be presented in this video ,th...
published: 20 Mar 2009
#مملكة_الحضارات الحلقة الثانية: #شهداء_الاخدود | Himyarite Martyrs
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 13:13
- Updated: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 85737
- published: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 85737
Himyarite kingdom the greatest jewish empire
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:12
- Updated: 16 Apr 2013
- views: 2129
- published: 16 Apr 2013
- views: 2129
Himyarite Kingdom
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 16:17
- Updated: 04 Sep 2016
- views: 14
- published: 04 Sep 2016
- views: 14
HIMYARITE KINGDOM - Documentary
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 14:02
- Updated: 21 Jun 2017
- views: 3
- published: 21 Jun 2017
- views: 3
"Saba vs. Abyssinia"
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:54
- Updated: 07 Nov 2013
- views: 3181
- published: 07 Nov 2013
- views: 3181
Himyarite Ruler Seeks Wife (397AD, colourised)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:12
- Updated: 13 May 2017
- views: 488
YEMEN - BRIEF HISTORIES
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:26
- Updated: 14 Nov 2015
- views: 740
Let's visit Yemen!
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:47
- Updated: 01 Sep 2012
- views: 1087
- published: 01 Sep 2012
- views: 1087
Yemen- The land of dreams
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 14:51
- Updated: 18 Jul 2012
- views: 3392
- published: 18 Jul 2012
- views: 3392
a journey to ancient Arabia
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:11
- Updated: 20 Mar 2009
- views: 53576
- published: 20 Mar 2009
- views: 53576

- Playlist
- Chat

- Playlist
- Chat

#مملكة_الحضارات الحلقة الثانية: #شهداء_الاخدود | Himyarite Martyrs
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 85737

Himyarite kingdom the greatest jewish empire
- Report rights infringement
- published: 16 Apr 2013
- views: 2129

Himyarite Kingdom
- Report rights infringement
- published: 04 Sep 2016
- views: 14

HIMYARITE KINGDOM - Documentary
- Report rights infringement
- published: 21 Jun 2017
- views: 3

"Saba vs. Abyssinia"
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Nov 2013
- views: 3181

Himyarite Ruler Seeks Wife (397AD, colourised)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 May 2017
- views: 488

YEMEN - BRIEF HISTORIES
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Nov 2015
- views: 740

Let's visit Yemen!
- Report rights infringement
- published: 01 Sep 2012
- views: 1087

Yemen- The land of dreams
- Report rights infringement
- published: 18 Jul 2012
- views: 3392

a journey to ancient Arabia
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Mar 2009
- views: 53576
-
Lyrics list:lyrics
-
Hammerhead, David Bowie
-
Hammerhead, Olivia Newton-John
-
Homie Ride, Master P
-
Hammered, Motley Crue
-
Hammerhead, Overkill
-
Hammerhead, Offspring
-
homeward, Godsmack
-
homeward, VNV Nation
-
homeward, Toyah
-
Hammerhead, Lita Ford
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Hammerhead
I should never call her Heart breakers, never kill But she’s been newzealand on another trip Have you felt like dix on And ray, and ali Hit me Hit me baby On the camera Take me in I’m going down Hit me baby You win Your the very tough with a lo ng past Your a hammer head Sweet thing Goldwyn drive Keep it all stuck on here She’s all black or white Don’t tell her where I’m livin’ Hit me Hit me baby She got me ruined She’s a bore She fell apart Oh, oh, ooh She’s so fabulous Just like cher It was life at the top You would be i She’s a hammer head Sweet thing She’s a hammer head I mention her hammer head Oh, oh, ooh Hit me Hit me baby She’s a hammer head Sweet thing Hit me Hit me baby Drop my folly into the night Enter the dragon Oh, oh, ooh She’s so fabulousJust like cher It was life at the top It would be i She’s a hammer head Sweet thing She’s a hammer head Mention her hammer head Oh, oh, ooh



