- published: 28 Nov 2012
- views: 220180
-
remove the playlistCathode Ray Tube
-
remove the playlistLatest Videos
-
remove the playlistLongest Videos
- remove the playlistCathode Ray Tube
- remove the playlistLatest Videos
- remove the playlistLongest Videos
- published: 05 May 2010
- views: 461209
- published: 07 Apr 2012
- views: 227049
- published: 01 Oct 2008
- views: 268985
- published: 07 May 2014
- views: 87924
- published: 26 Mar 2013
- views: 122341
- published: 01 Dec 2016
- views: 72
- published: 20 Jun 2008
- views: 78701

Cathode ray tube
The cathode ray tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube containing one or more electron guns, and a phosphorescent screen used to view images. It has a means to accelerate and deflect the electron beam(s) onto the screen to create the images. The images may represent electrical waveforms (oscilloscope), pictures (television, computer monitor), radar targets or others. CRTs have also been used as memory devices, in which case the visible light emitted from the fluorescent material (if any) is not intended to have significant meaning to a visual observer (though the visible pattern on the tube face may cryptically represent the stored data).
The CRT uses an evacuated glass envelope which is large, deep (i.e. long from front screen face to rear end), fairly heavy, and relatively fragile. As a matter of safety, the face is typically made of thick lead glass so as to be highly shatter-resistant and to block most X-ray emissions, particularly if the CRT is used in a consumer product.
Since 2008, CRTs have largely been superseded by newer display technologies such as LCD, plasma display, and OLED, which have lower manufacturing costs, power consumption, weight and bulk.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Cathode ray
Cathode rays (also called an electron beam or e-beam) are streams of electrons observed in vacuum tubes. If an evacuated glass tube is equipped with two electrodes and a voltage is applied, the glass opposite of the negative electrode is observed to glow, due to electrons emitted from and travelling perpendicular to the cathode (the electrode connected to the negative terminal of the voltage supply). They were first observed in 1869 by German physicist Johann Hittorf, and were named in 1876 by Eugen Goldstein Kathodenstrahlen, or cathode rays.
Electrons were first discovered as the constituents of cathode rays. In 1897 British physicist J. J. Thomson showed the rays were composed of a previously unknown negatively charged particle, which was later named the electron. Cathode ray tubes (CRTs) use a focused beam of electrons deflected by electric or magnetic fields to create the image in a classic television set.
Description
Cathode rays are so named because they are emitted by the negative electrode, or cathode, in a vacuum tube. To release electrons into the tube, they first must be detached from the atoms of the cathode. In the early cold cathode vacuum tubes, called Crookes tubes, this was done by using a high electrical potential between the anode and the cathode to ionize the residual gas in the tube; the ions were accelerated by the electric field and released electrons when they collided with the cathode. Modern vacuum tubes use thermionic emission, in which the cathode is made of a thin wire filament which is heated by a separate electric current passing through it. The increased random heat motion of the filament knocks electrons out at the surface of the filament, into the evacuated space of the tube.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 11:08
11:08Discovery of the Electron: Cathode Ray Tube Experiment
Discovery of the Electron: Cathode Ray Tube ExperimentDiscovery of the Electron: Cathode Ray Tube Experiment
To see all my Chemistry videos, check out http://socratic.org/chemistry J.J. Thompson discovered the electron, the first of the subatomic particles, using the cathode ray tube experiment. He found that many different metals release cathode rays, and that cathode rays were made of electrons, very small negatively charged particles. This disproved John Dalton's theory of the atom, and Thompson came up with the plum pudding model of the atom. -
 3:47
3:47Cathode Ray Tube
Cathode Ray TubeCathode Ray Tube
Follow us at: https://twitter.com/TutorVista Check us out at http://chemistry.tutorvista.com/inorganic-chemistry/cathode-ray-tube-experiment.html Cathode Ray Tube The Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube containing an electron gun (a source of electrons) and a fluorescent screen, with internal or external means to accelerate and deflect the electron beam, used to create images in the form of light emitted from the fluorescent screen. The image may represent electrical waveforms (oscilloscope), pictures (television, computer monitor), radar targets and others. The CRT uses an evacuated glass envelope which is large, deep, heavy, and relatively fragile. Display technologies without these disadvantages, such as flat plasma displays, liquid crystal displays, DLP, OLED have replaced CRTs in many applications and are becoming increasingly common as costs decline. A cathode ray tube is a vacuum tube which consists of one or more electron guns, possibly internal electrostatic deflection plates, and a phosphor target. In television sets and computer monitors, the entire front area of the tube is scanned repetitively and systematically in a fixed pattern called a raster. An image is produced by controlling the intensity of each of the three electron beams, one for each additive primary color (red, green, and blue) with a video signal as a reference. In all modern CRT monitors and televisions, the beams are bent by magnetic deflection, a varying magnetic field generated by coils and driven by electronic circuits around the neck of the tube, although electrostatic deflection is commonly used in oscilloscopes, a type of diagnostic instrument. Please like our facebook page http://www.facebook.com/tutorvista -
 1:48
1:48Cathode Ray Tube
Cathode Ray TubeCathode Ray Tube
This is the official Video of Cathode Ray Tube by sir JJ Thomson.. A Cathode ray tube is the forerunner of the television tube. It is a glass tube from which most of the air has been evacuated. When the two metal plates are connected to a high-voltage source, the negatively charged plate, called the cathode, emits an invisible ray. The cathode ray is drawn to the positively charged plate, called the anode, where it passes through a hole and continues traveling to the other end of the tube. When the ray strikes the specially coated surface, the cathode ray produces a strong fluorescence, or bright light. When an electric field is applied across the cathode ray tube, the cathode ray is attracted by the plate bearing positive charges. Therefore, a cathode ray must consist of negatively charged particles. A moving charged body behaves like a tiny magnet, and it can interact with am external magnetic field. The electrons are deflected by the magnetic field. As expected, when the direction of the external magnet field is reversed, the beam of electrons is deflected in the opposite direction. In 1897, JJ Thomson, and English physicist, determined the charge-to-mass ratio of an electron. He adjusted the electric field so that the electrostatic deflection (0E) was the same as the magnetic deflection (0B), and was able to calculate the charge-to-mass ratio of an electron using the following equation: Where E is the applied electrical field, 0 is the angle of deflection, B is the applied magnetic field, and / is the distance traveled by the cathode rays. Thomson determined the charge-to-mass ratio of an electron to be -1.76 x 10 eight power coulombs per gram. hope i helped... ^^ Please Subscribe!.. and hit Like! -
 2:49
2:49Cathode Ray Tube
Cathode Ray TubeCathode Ray Tube
Demo 10 HChem "As the cathode rays carry a charge of negative electricity, are deflected by an electrostatic force as if they were negatively electrified, and are acted on by a magnetic force in just the way in which this force would act on a negatively electrified body moving along the path of these rays, I can see no escape from the conclusion that they are charges of negative electricity carried by particles of matter." —J. J. Thomson (Philosophical Magazine, 44, 293 (1897)) -
 4:20
4:20Incredible Homemade Cathode Ray Tube - Part 1
Incredible Homemade Cathode Ray Tube - Part 1Incredible Homemade Cathode Ray Tube - Part 1
Ask any questions in the comments. Do not attempt to recreate this experiment. The vacuum on this tube is not enough to create a beam that does not glow so bright. This may be considered a "rarified arc in a vacuum" but it still demonstrates the properties of a cathode ray tube. Don't post nasty comments. You may be blocked. -
 6:17
6:17Cathode Ray Oscilloscope and its Applications
Cathode Ray Oscilloscope and its ApplicationsCathode Ray Oscilloscope and its Applications
Follow us at: https://plus.google.com/+tutorvista/ Check out us at:http://www.tutorvista.com/content/physics/physics-ii/modern-physics/cathode-rays.php Cathode Ray Oscilloscope The cathode ray oscilloscope is used as an animation in the laboratories. Since it is more reliable, stable and ease of operation , the animation of the cathode ray oscilloscope is used in lab. The animation of the cathode ray oscilloscope which is used in the lab provide the measurement of voltage signals. Please like our facebook page http://www.facebook.com/tutorvista -
 7:30
7:30CATHODE RAY TUBE ! LEARN AND GROW
CATHODE RAY TUBE ! LEARN AND GROWCATHODE RAY TUBE ! LEARN AND GROW
On this channel you can get education and knowledge for general issues and topics -
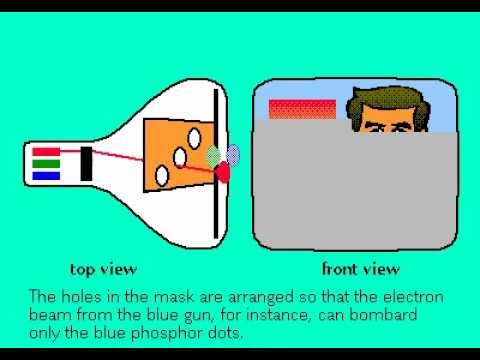 1:25
1:25How a CRT TV works
How a CRT TV works -
 1:44
1:44Fun with CRTs
Fun with CRTsFun with CRTs
4 of our cathode ray tubes showing some of their unique properties. The first just shows the electron beam across a phosphor being bent by a magnet. The 'Maltese Cross Tube' has a metal cross as a barrier indicating the path of travel of the electron beam. The paddlewheel tube demonstrates the momentum carried by electrons as they strike the vanes and cause the wheel to spin. Lastly, the x-ray tube is pointed towards a plush bear with a copper wire skeleton. -
 5:00
5:00How It's Made Cathode Ray Tubes
How It's Made Cathode Ray Tubes
Cathode Ray Tube
ALBUMS
- Don't Fuck With Us released: 2002
Don't Fuck With Us
Released 2002- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Hollie (live December 99)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Tracer
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Earthshattering
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen All Things Are Connected
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen We're the Enemy
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Cabrini Green (A.M.)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Amtrack
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen 10.04.00 (Hooyee)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Trash This Town
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen 2015
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Herdcore
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Metal
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Pre-Ejaculation Makes Girls Feel Pretty
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Psychology of Asian Porn
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Kosmicher Tankward
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Articulatrix
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen FUBAR
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Implication Recognition (Still RNR) Urge Cleanse (LHUN)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Knar 5000
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Digital Carnivore
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen This Is a Weapon
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Do It Alone
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen When You Grow Up (Your Heart Dies)
-

Discovery of the Electron: Cathode Ray Tube Experiment
To see all my Chemistry videos, check out http://socratic.org/chemistry J.J. Thompson discovered the electron, the first of the subatomic particles, using the cathode ray tube experiment. He found that many different metals release cathode rays, and that cathode rays were made of electrons, very small negatively charged particles. This disproved John Dalton's theory of the atom, and Thompson came up with the plum pudding model of the atom.
published: 28 Nov 2012 -

Cathode Ray Tube
Follow us at: https://twitter.com/TutorVista Check us out at http://chemistry.tutorvista.com/inorganic-chemistry/cathode-ray-tube-experiment.html Cathode Ray Tube The Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube containing an electron gun (a source of electrons) and a fluorescent screen, with internal or external means to accelerate and deflect the electron beam, used to create images in the form of light emitted from the fluorescent screen. The image may represent electrical waveforms (oscilloscope), pictures (television, computer monitor), radar targets and others. The CRT uses an evacuated glass envelope which is large, deep, heavy, and relatively fragile. Display technologies without these disadvantages, such as flat plasma displays, liquid crystal displays, DLP, OLED have replaced CRTs...
published: 05 May 2010 -

Cathode Ray Tube
This is the official Video of Cathode Ray Tube by sir JJ Thomson.. A Cathode ray tube is the forerunner of the television tube. It is a glass tube from which most of the air has been evacuated. When the two metal plates are connected to a high-voltage source, the negatively charged plate, called the cathode, emits an invisible ray. The cathode ray is drawn to the positively charged plate, called the anode, where it passes through a hole and continues traveling to the other end of the tube. When the ray strikes the specially coated surface, the cathode ray produces a strong fluorescence, or bright light. When an electric field is applied across the cathode ray tube, the cathode ray is attracted by the plate bearing positive charges. Therefore, a cathode ray must consist of negatively charg...
published: 07 Apr 2012 -

Cathode Ray Tube
Demo 10 HChem "As the cathode rays carry a charge of negative electricity, are deflected by an electrostatic force as if they were negatively electrified, and are acted on by a magnetic force in just the way in which this force would act on a negatively electrified body moving along the path of these rays, I can see no escape from the conclusion that they are charges of negative electricity carried by particles of matter." —J. J. Thomson (Philosophical Magazine, 44, 293 (1897))
published: 01 Oct 2008 -

Incredible Homemade Cathode Ray Tube - Part 1
Ask any questions in the comments. Do not attempt to recreate this experiment. The vacuum on this tube is not enough to create a beam that does not glow so bright. This may be considered a "rarified arc in a vacuum" but it still demonstrates the properties of a cathode ray tube. Don't post nasty comments. You may be blocked.
published: 07 May 2014 -

Cathode Ray Oscilloscope and its Applications
Follow us at: https://plus.google.com/+tutorvista/ Check out us at:http://www.tutorvista.com/content/physics/physics-ii/modern-physics/cathode-rays.php Cathode Ray Oscilloscope The cathode ray oscilloscope is used as an animation in the laboratories. Since it is more reliable, stable and ease of operation , the animation of the cathode ray oscilloscope is used in lab. The animation of the cathode ray oscilloscope which is used in the lab provide the measurement of voltage signals. Please like our facebook page http://www.facebook.com/tutorvista
published: 26 Mar 2013 -

CATHODE RAY TUBE ! LEARN AND GROW
On this channel you can get education and knowledge for general issues and topics
published: 01 Dec 2016 -

-

Fun with CRTs
4 of our cathode ray tubes showing some of their unique properties. The first just shows the electron beam across a phosphor being bent by a magnet. The 'Maltese Cross Tube' has a metal cross as a barrier indicating the path of travel of the electron beam. The paddlewheel tube demonstrates the momentum carried by electrons as they strike the vanes and cause the wheel to spin. Lastly, the x-ray tube is pointed towards a plush bear with a copper wire skeleton.
published: 20 Jun 2008 -

How It's Made Cathode Ray Tubes
Discovery / Science Channel's "How It's Made" Cathode Ray Tubes
published: 23 Jun 2013
Discovery of the Electron: Cathode Ray Tube Experiment
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 11:08
- Updated: 28 Nov 2012
- views: 220180
- published: 28 Nov 2012
- views: 220180
Cathode Ray Tube
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:47
- Updated: 05 May 2010
- views: 461209
- published: 05 May 2010
- views: 461209
Cathode Ray Tube
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:48
- Updated: 07 Apr 2012
- views: 227049
- published: 07 Apr 2012
- views: 227049
Cathode Ray Tube
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:49
- Updated: 01 Oct 2008
- views: 268985
- published: 01 Oct 2008
- views: 268985
Incredible Homemade Cathode Ray Tube - Part 1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:20
- Updated: 07 May 2014
- views: 87924
- published: 07 May 2014
- views: 87924
Cathode Ray Oscilloscope and its Applications
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:17
- Updated: 26 Mar 2013
- views: 122341
- published: 26 Mar 2013
- views: 122341
CATHODE RAY TUBE ! LEARN AND GROW
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:30
- Updated: 01 Dec 2016
- views: 72
- published: 01 Dec 2016
- views: 72
How a CRT TV works
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:25
- Updated: 12 Jan 2012
- views: 69293
Fun with CRTs
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:44
- Updated: 20 Jun 2008
- views: 78701
- published: 20 Jun 2008
- views: 78701
How It's Made Cathode Ray Tubes
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:00
- Updated: 23 Jun 2013
- views: 48992
-

Discovery of the Electron: Cathode Ray Tube Experiment
To see all my Chemistry videos, check out http://socratic.org/chemistry J.J. Thompson discovered the electron, the first of the subatomic particles, using the cathode ray tube experiment. He found that many different metals release cathode rays, and that cathode rays were made of electrons, very small negatively charged particles. This disproved John Dalton's theory of the atom, and Thompson came up with the plum pudding model of the atom.
published: 28 Nov 2012 -

Cathode Ray Tube
Follow us at: https://twitter.com/TutorVista Check us out at http://chemistry.tutorvista.com/inorganic-chemistry/cathode-ray-tube-experiment.html Cathode Ray Tube The Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube containing an electron gun (a source of electrons) and a fluorescent screen, with internal or external means to accelerate and deflect the electron beam, used to create images in the form of light emitted from the fluorescent screen. The image may represent electrical waveforms (oscilloscope), pictures (television, computer monitor), radar targets and others. The CRT uses an evacuated glass envelope which is large, deep, heavy, and relatively fragile. Display technologies without these disadvantages, such as flat plasma displays, liquid crystal displays, DLP, OLED have replaced CRTs...
published: 05 May 2010 -

Cathode Ray Tube
This is the official Video of Cathode Ray Tube by sir JJ Thomson.. A Cathode ray tube is the forerunner of the television tube. It is a glass tube from which most of the air has been evacuated. When the two metal plates are connected to a high-voltage source, the negatively charged plate, called the cathode, emits an invisible ray. The cathode ray is drawn to the positively charged plate, called the anode, where it passes through a hole and continues traveling to the other end of the tube. When the ray strikes the specially coated surface, the cathode ray produces a strong fluorescence, or bright light. When an electric field is applied across the cathode ray tube, the cathode ray is attracted by the plate bearing positive charges. Therefore, a cathode ray must consist of negatively charg...
published: 07 Apr 2012 -

Cathode Ray Tube
Demo 10 HChem "As the cathode rays carry a charge of negative electricity, are deflected by an electrostatic force as if they were negatively electrified, and are acted on by a magnetic force in just the way in which this force would act on a negatively electrified body moving along the path of these rays, I can see no escape from the conclusion that they are charges of negative electricity carried by particles of matter." —J. J. Thomson (Philosophical Magazine, 44, 293 (1897))
published: 01 Oct 2008 -

Incredible Homemade Cathode Ray Tube - Part 1
Ask any questions in the comments. Do not attempt to recreate this experiment. The vacuum on this tube is not enough to create a beam that does not glow so bright. This may be considered a "rarified arc in a vacuum" but it still demonstrates the properties of a cathode ray tube. Don't post nasty comments. You may be blocked.
published: 07 May 2014 -

Cathode Ray Oscilloscope and its Applications
Follow us at: https://plus.google.com/+tutorvista/ Check out us at:http://www.tutorvista.com/content/physics/physics-ii/modern-physics/cathode-rays.php Cathode Ray Oscilloscope The cathode ray oscilloscope is used as an animation in the laboratories. Since it is more reliable, stable and ease of operation , the animation of the cathode ray oscilloscope is used in lab. The animation of the cathode ray oscilloscope which is used in the lab provide the measurement of voltage signals. Please like our facebook page http://www.facebook.com/tutorvista
published: 26 Mar 2013 -

CATHODE RAY TUBE ! LEARN AND GROW
On this channel you can get education and knowledge for general issues and topics
published: 01 Dec 2016 -

-

Fun with CRTs
4 of our cathode ray tubes showing some of their unique properties. The first just shows the electron beam across a phosphor being bent by a magnet. The 'Maltese Cross Tube' has a metal cross as a barrier indicating the path of travel of the electron beam. The paddlewheel tube demonstrates the momentum carried by electrons as they strike the vanes and cause the wheel to spin. Lastly, the x-ray tube is pointed towards a plush bear with a copper wire skeleton.
published: 20 Jun 2008 -

How It's Made Cathode Ray Tubes
Discovery / Science Channel's "How It's Made" Cathode Ray Tubes
published: 23 Jun 2013
Discovery of the Electron: Cathode Ray Tube Experiment
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 11:08
- Updated: 28 Nov 2012
- views: 220180
- published: 28 Nov 2012
- views: 220180
Cathode Ray Tube
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:47
- Updated: 05 May 2010
- views: 461209
- published: 05 May 2010
- views: 461209
Cathode Ray Tube
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:48
- Updated: 07 Apr 2012
- views: 227049
- published: 07 Apr 2012
- views: 227049
Cathode Ray Tube
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:49
- Updated: 01 Oct 2008
- views: 268985
- published: 01 Oct 2008
- views: 268985
Incredible Homemade Cathode Ray Tube - Part 1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:20
- Updated: 07 May 2014
- views: 87924
- published: 07 May 2014
- views: 87924
Cathode Ray Oscilloscope and its Applications
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:17
- Updated: 26 Mar 2013
- views: 122341
- published: 26 Mar 2013
- views: 122341
CATHODE RAY TUBE ! LEARN AND GROW
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:30
- Updated: 01 Dec 2016
- views: 72
- published: 01 Dec 2016
- views: 72
How a CRT TV works
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:25
- Updated: 12 Jan 2012
- views: 69293
Fun with CRTs
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:44
- Updated: 20 Jun 2008
- views: 78701
- published: 20 Jun 2008
- views: 78701
How It's Made Cathode Ray Tubes
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:00
- Updated: 23 Jun 2013
- views: 48992
-

(501-P3015S) Cathode Ray Tube
Description of the cathode ray tube and Thomson's discovery of the electron.
published: 01 Jun 2015 -

(501-14S) Cathode Ray Tube
Cathode ray tube and Thomson's discovery of the electron.
published: 30 May 2014 -

(501) Cathode Ray Tube
Description of the cathode ray tube and Thomson's discovery of the electron.
published: 27 May 2013 -

(501-P3016F) Discovery of the Electron
Discovery of the electron with the cathode ray tube.
published: 16 Dec 2016 -

Electric Fields, Equipotentials,Cathode Ray Tubes Part 1
2/10/15 Discussion of the Electric Field Mapping and Equipotential Lines experiment. Introduction to energy storage in a capacitor and cathode ray tubes.
published: 11 Feb 2015 -

Electric Fields, Equipotentials,Cathode Ray Tubes Part 2
2/10/15 Discussion of the Electric Field Mapping and Equipotential Lines experiment. Introduction to energy storage in a capacitor and cathode ray tubes.
published: 10 Feb 2015 -

(501-P3014F) Cathode Ray Tube
Description of Thomson's CRT experiment and his discovery of the electron.
published: 17 Dec 2014 -

Podcast CP Chem I Ch.3.2a
JJ Thomson, Ernest Rutherford, subatomic particles, gold foil experiment, cathode ray tube
published: 23 Sep 2014 -

En Lluís juga a Cathode-Ray Tube Amusement Device - Part 0 - Pròleg
Faig una petita introducció sobre l'invent en qüestió i intento "jugar-hi"
published: 13 Aug 2016 -

Francine McGee - une Quebecoise errante
(FF XV - Pikachu - Cathode Ray Tube - Controller - Sega Saturn Controller - NiGHTS - Jester - Sega Genesis Menacer Light Gun - Mirrors Edge)
published: 18 Oct 2014
(501-P3015S) Cathode Ray Tube
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 33:08
- Updated: 01 Jun 2015
- views: 128
- published: 01 Jun 2015
- views: 128
(501-14S) Cathode Ray Tube
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 31:30
- Updated: 30 May 2014
- views: 93
(501) Cathode Ray Tube
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 31:22
- Updated: 27 May 2013
- views: 88
- published: 27 May 2013
- views: 88
(501-P3016F) Discovery of the Electron
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 33:07
- Updated: 16 Dec 2016
- views: 45
Electric Fields, Equipotentials,Cathode Ray Tubes Part 1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 46:44
- Updated: 11 Feb 2015
- views: 54
- published: 11 Feb 2015
- views: 54
Electric Fields, Equipotentials,Cathode Ray Tubes Part 2
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 49:32
- Updated: 10 Feb 2015
- views: 32
- published: 10 Feb 2015
- views: 32
(501-P3014F) Cathode Ray Tube
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 32:02
- Updated: 17 Dec 2014
- views: 79
- published: 17 Dec 2014
- views: 79
Podcast CP Chem I Ch.3.2a
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 41:52
- Updated: 23 Sep 2014
- views: 18
- published: 23 Sep 2014
- views: 18
En Lluís juga a Cathode-Ray Tube Amusement Device - Part 0 - Pròleg
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 30:12
- Updated: 13 Aug 2016
- views: 1
- published: 13 Aug 2016
- views: 1
Francine McGee - une Quebecoise errante
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 37:49
- Updated: 18 Oct 2014
- views: 204
- published: 18 Oct 2014
- views: 204


- Playlist
- Chat

Discovery of the Electron: Cathode Ray Tube Experiment
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Nov 2012
- views: 220180

Cathode Ray Tube
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 May 2010
- views: 461209

Cathode Ray Tube
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Apr 2012
- views: 227049

Cathode Ray Tube
- Report rights infringement
- published: 01 Oct 2008
- views: 268985

Incredible Homemade Cathode Ray Tube - Part 1
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 May 2014
- views: 87924

Cathode Ray Oscilloscope and its Applications
- Report rights infringement
- published: 26 Mar 2013
- views: 122341

CATHODE RAY TUBE ! LEARN AND GROW
- Report rights infringement
- published: 01 Dec 2016
- views: 72

How a CRT TV works
- Report rights infringement
- published: 12 Jan 2012
- views: 69293

Fun with CRTs
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Jun 2008
- views: 78701

How It's Made Cathode Ray Tubes
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Jun 2013
- views: 48992

- Playlist
- Chat

Discovery of the Electron: Cathode Ray Tube Experiment
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Nov 2012
- views: 220180

Cathode Ray Tube
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 May 2010
- views: 461209

Cathode Ray Tube
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Apr 2012
- views: 227049

Cathode Ray Tube
- Report rights infringement
- published: 01 Oct 2008
- views: 268985

Incredible Homemade Cathode Ray Tube - Part 1
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 May 2014
- views: 87924

Cathode Ray Oscilloscope and its Applications
- Report rights infringement
- published: 26 Mar 2013
- views: 122341

CATHODE RAY TUBE ! LEARN AND GROW
- Report rights infringement
- published: 01 Dec 2016
- views: 72

How a CRT TV works
- Report rights infringement
- published: 12 Jan 2012
- views: 69293

Fun with CRTs
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Jun 2008
- views: 78701

How It's Made Cathode Ray Tubes
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Jun 2013
- views: 48992

- Playlist
- Chat

(501-P3015S) Cathode Ray Tube
- Report rights infringement
- published: 01 Jun 2015
- views: 128

(501-14S) Cathode Ray Tube
- Report rights infringement
- published: 30 May 2014
- views: 93

(501) Cathode Ray Tube
- Report rights infringement
- published: 27 May 2013
- views: 88

(501-P3016F) Discovery of the Electron
- Report rights infringement
- published: 16 Dec 2016
- views: 45

Electric Fields, Equipotentials,Cathode Ray Tubes Part 1
- Report rights infringement
- published: 11 Feb 2015
- views: 54

Electric Fields, Equipotentials,Cathode Ray Tubes Part 2
- Report rights infringement
- published: 10 Feb 2015
- views: 32

(501-P3014F) Cathode Ray Tube
- Report rights infringement
- published: 17 Dec 2014
- views: 79

Podcast CP Chem I Ch.3.2a
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Sep 2014
- views: 18

En Lluís juga a Cathode-Ray Tube Amusement Device - Part 0 - Pròleg
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 Aug 2016
- views: 1

Francine McGee - une Quebecoise errante
- Report rights infringement
- published: 18 Oct 2014
- views: 204
Vladimir Putin offers fired FBI director James Comey asylum in Russia
Edit The Independent 15 Jun 2017Report: Seven Killed, At Least 60 Injured In Explosion At Chinese Kindergarten In Fengxian
Edit WorldNews.com 15 Jun 2017‘CIA’s Cherry Bomb’: WikiLeaks #Vault7 reveals wireless network targets
Edit Russia Today 15 Jun 2017Somalia restaurant siege: Al-Shabaab militants massacre 31 civilians in Mogadishu
Edit The Independent 15 Jun 2017Australia's Turnbull mocks US President Trump in leaked audio
Edit CNN 15 Jun 2017Mizuno Unveils SS18 Apparel Collection
Edit Golf Business News 16 Jun 2017Bikini malfunction! Justin Bieber's rumoured ex Sahara Ray flashes her nipple piercing as her top falls off during Mexican beach photo shoot
Edit This is Money 16 Jun 2017Ainsworth Pet Nutrition Acquires Triple T Foods of Frontenac, Kansas
Edit Market Watch 16 Jun 2017TSA tests better bomb-detecting scanners for carry-ons
Edit Times Free Press 16 Jun 2017Dominican Summer League
Edit Reflector 16 Jun 2017Business News Roundup, June 16
Edit San Francisco Chronicle 16 Jun 2017Shared love of game binds Seattle's Smith, dad
Edit MLB 16 Jun 2017Q&A;: Ten facts about China's X-ray probe
Edit China Daily 15 Jun 2017Global DVD & Blu-ray Players Sales Market Report 2017
Edit Community news 15 Jun 2017China Focus: China launches space telescope to search for black holes, pulsars
Edit Xinhua 15 Jun 2017China launches first X-ray telescope to study black holes
Edit Deccan Chronicle 15 Jun 2017- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »




























