- published: 08 Apr 2016
- views: 12087
-
remove the playlistHomo (genus)
-
remove the playlistLatest Videos
-
remove the playlistLongest Videos
- remove the playlistHomo (genus)
- remove the playlistLatest Videos
- remove the playlistLongest Videos
- published: 13 Sep 2015
- views: 116893
- published: 22 Aug 2015
- views: 1997
- published: 02 May 2017
- views: 3
- published: 22 Apr 2016
- views: 2431
- published: 19 Apr 2016
- views: 16171
- published: 28 Oct 2015
- views: 200014
- published: 06 Nov 2014
- views: 1051334
- published: 11 Oct 2014
- views: 18624
- published: 15 Dec 2009
- views: 3570
- published: 04 Dec 2012
- views: 1447

Homo
Homo is the genus that comprises the species Homo sapiens, which includes modern humans, as well as several extinct species classified as ancestral to or closely related to modern humans—as for examples Homo habilis and Homo neanderthalensis. The genus is about 2.8 million years old; it first appeared as its earliest species Homo habilis, which emerged from the genus Australopithecus, which itself had previously split from the lineage of Pan, the chimpanzees.
Taxonomically, Homo is the only genus assigned to the subtribe Hominina which, with the subtribes Australopithecina and Panina, comprise the tribe Hominini (see evolutionary tree below). All species of the genus Homo plus those species of the australopithecines that arose after the split from Pan are called hominins.
Homo erectus appeared about two million years ago in East Africa (where it is dubbed Homo ergaster) and, in several early migrations, it spread throughout Africa and Eurasia. It was likely the first hominin to live in a hunter-gatherer society and to control fire. An adaptive and successful species, Homo erectus persisted for almost 2 million years before suddenly becoming extinct about 70,000 years ago (0.07 Ma)—perhaps a casualty of the Toba supereruption catastrophe.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens (Latin: "wise person") is the binomial nomenclature (also known as the scientific name) for the only extant human species. Homo is the human genus, which also includes Neanderthals and many other extinct species of hominid; H. sapiens is the only surviving species of the genus Homo. Modern humans are the subspecies Homo sapiens sapiens, which differentiates them from what has been argued to be their direct ancestor, Homo sapiens idaltu. The ingenuity and adaptability of Homo sapiens has led to its becoming, arguably, the most influential species on the planet; it is currently deemed of least concern on the Red List of endangered species by the International Union for the Conservation of Nature.
Name and taxonomy
The binomial name Homo sapiens was coined by Carl Linnaeus (1758). The Latin noun homō (genitive hominis) means "man, human being".
Subspecies of H. sapiens include Homo sapiens idaltu and the only extant subspecies, Homo sapiens sapiens. Some sources show Neanderthals (Homo neanderthalensis) as a subspecies (Homo sapiens neanderthalensis). Similarly, the discovered specimens of the Homo rhodesiensis species have been classified by some as a subspecies (Homo sapiens rhodesiensis), but these last two subspecies classifications are not widely accepted by scientists.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Homo erectus
Homo erectus (meaning "upright man", from the Latin ērigere, "to put up, set upright") is an extinct species of hominid that lived throughout most of the Pleistocene geological epoch. Its earliest fossil evidence dates to 1.9 million years ago and the most recent to 70,000 years ago. It is generally thought that H. erectus originated in Africa and spread from there, migrating throughout Eurasia as far as Georgia, India, Sri Lanka, China and Indonesia. But other scientists posit that the species rose first, or separately, in Asia.
Debate also continues about the classification, ancestry, and progeny of Homo erectus, especially vis-à-vis Homo ergaster, with two major positions: 1) H. erectus is the same species as H. ergaster, and thereby H. erectus is a direct ancestor of the later hominins including Homo heidelbergensis, Homo neanderthalensis, and Homo sapiens; or, 2) it is in fact an Asian species distinct from African H. ergaster.
There is also another view—an alternative to 1): some palaeoanthropologists consider H. ergaster to be a variety, that is, the "African" variety, of H. erectus, and they offer the labels "Homo erectus sensu stricto" (strict sense) for the Asian species and "Homo erectus sensu lato" (broad sense) for the greater species comprising both Asian and African populations.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Human evolution
Human evolution is the evolutionary process that led to the emergence of anatomically modern humans. The topic typically focuses on the evolutionary history of the primates—in particular the genus Homo, and the emergence of Homo sapiens as a distinct species of the hominids (or "great apes")—rather than studying the earlier history that led to the primates. The study of human evolution involves many scientific disciplines, including physical anthropology, primatology, archaeology, paleontology, ethology, linguistics, evolutionary psychology, embryology and genetics.
Genetic studies show that primates diverged from other mammals about 85 million years ago, in the Late Cretaceous period, and the earliest fossils appear in the Paleocene, around 55 million years ago. Within the Hominoidea (apes) superfamily, the Hominidae family diverged from the Hylobatidae (gibbon) family some 15–20 million years ago; African great apes (subfamily Homininae) diverged from orangutans (Ponginae) about 14 million years ago; the Hominini tribe (humans, Australopithecines and other extinct biped genera, and chimpanzees) parted from the Gorillini tribe (gorillas) about 8 million years ago; and, in turn, the subtribes Hominina (humans and biped ancestors) and Panina (chimps) separated about 7.5 million years ago.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 59:22
59:22Origins of Genus Homo: What Who When Where?; Early Body Form; Life History Patterns
Origins of Genus Homo: What Who When Where?; Early Body Form; Life History PatternsOrigins of Genus Homo: What Who When Where?; Early Body Form; Life History Patterns
(Visit: http://www.uctv.tv/) This symposium explores evidence bearing on the emergence of our genus, focusing on possible antecedents to Homo, changes in diet and body form as Australopithecus evolved toward Homo, ancient species within the genus, and evolutionary processes likely operating 2.5 - 1.5 million years ago. Recorded on 02/05/2016. Series: "CARTA - Center for Academic Research and Training in Anthropogeny" [4/2016] [Science] [Show ID: 30632] -
 4:38
4:38How Do We Know Who Our Human Ancestors Were?
How Do We Know Who Our Human Ancestors Were?How Do We Know Who Our Human Ancestors Were?
Recently scientists announced the discovery of yet another human-like ancestor, but how do we determine if they belong to the genus homo? Watch More ►►►► http://dne.ws/1FEGqgr Read More: New Human-like Species Discovered in South Africa http://www.bbc.com/news/science-environment-34192447 “The discovery of 15 partial skeletons is the largest single discovery of its type in Africa. The researchers claim that the discovery will change ideas about our human ancestors.” Human Family Tree http://humanorigins.si.edu/evidence/human-family-tree ____________________ DNews is dedicated to satisfying your curiosity and to bringing you mind-bending stories & perspectives you won't find anywhere else! New videos twice daily. Watch More DNews on TestTube http://testtube.com/dnews Subscribe now! http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=dnewschannel DNews on Twitter http://twitter.com/dnews Trace Dominguez on Twitter https://twitter.com/tracedominguez Julia Wilde on Twitter https://twitter.com/julia_sci DNews on Facebook https://facebook.com/DiscoveryNews DNews on Google+ http://gplus.to/dnews Discovery News http://discoverynews.com Download the TestTube App: http://testu.be/1ndmmMq -
 11:07
11:07TtHL: The Origin of Genus Homo
TtHL: The Origin of Genus HomoTtHL: The Origin of Genus Homo
Part Four: Deriving the genus Homo from rodential ancestors. ----------------------------------------------------------------- Sources: Walking with Beasts footage: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qtAzX... Strepsirrhini/Haplorrhini graphic 1: http://cromercrox.blogspot.com/2013/0... Strepsirrhini/Haplorrhini graphic 2: https://whyevolutionistrue.wordpress.... Primate phylogeny graphic: http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/... - Nature article: http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/... Eye-migration animation: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UPggk... Parapithecidae skull: http://www.pnas.org/content/98/14/789... Apidium footage: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rwOpb... Catarrhini phylogeny: http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/... - Nature article: http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/... Orangutan phylogeny: http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/... Human family tree: http://humanorigins.si.edu/evidence/h... ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Transcript: https://docs.google.com/document/d/1qvOtWzC64J27wAs8sSMEc6eXXHN40bj5p40nP8cb9DE/edit?usp=sharing ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Background music: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4Mc1V... ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ All comments welcome, but all those found restricting replies will be promptly deleted. Like the Facebook page: www.facebook.com/TactfulTaxonomist -
 58:20
58:20Origins of Genus Homo ~ Symposium (CARTA)
Origins of Genus Homo ~ Symposium (CARTA)Origins of Genus Homo ~ Symposium (CARTA)
This symposium explores evidence bearing on the emergence of our genus, focusing on possible antecedents to Homo, changes in diet and body form as Australopithecus evolved toward Homo, ancient species within the genus, and evolutionary processes likely operating 2.5 - 1.5 million years ago. Recorded on 02/05/2016. Series: "CARTA - Center for Academic Research and Training in Anthropogeny" [4/2016] [Science] [Show ID: 30633] [MIRROR] Visit: http://www.uctv.tv/ ------------------- SUBSCRIBE to Evolution Tube http://bit.ly/2pUOYSb In association with Talk Beliefs http://bit.ly/2lA6YOv DISCLAIMER: Copyright Disclaimer Under Section 107 of the Copyright Act 1976, allowance is made for "fair use" for purposes such as criticism, comment, news reporting, teaching, scholarship, and research. Fair use is a use permitted by copyright statute that might otherwise be infringing. Non-profit, educational or personal use tips the balance in favor of fair use. Creative Commons. -
 21:11
21:11CARTA: Origins of Genus Homo – Steven Churchill: Southern Africa and the Origin of Homo
CARTA: Origins of Genus Homo – Steven Churchill: Southern Africa and the Origin of HomoCARTA: Origins of Genus Homo – Steven Churchill: Southern Africa and the Origin of Homo
(Visit: http://www.uctv.tv/) In the last seven years, two hominin species possessing a mixture of primitive and Homo-like morphology – Australopithecus sediba and Homo naledi – have been discovered in South Africa. Duke University’s Steven Churchill believes that these remarkable finds call for new models in not only understanding the origins of genus Homo, but also the emergence of Homo erectus. Recorded on 02/05/2016. Series: "CARTA - Center for Academic Research and Training in Anthropogeny" [Science] [Show ID: 30642] -
 1:00:26
1:00:26Origins of Genus Homo–Australopiths and Early Homo; Variation of Early Homo; Speciation of Homo
Origins of Genus Homo–Australopiths and Early Homo; Variation of Early Homo; Speciation of HomoOrigins of Genus Homo–Australopiths and Early Homo; Variation of Early Homo; Speciation of Homo
(Visit: http://www.uctv.tv/) This symposium explores evidence bearing on the emergence of our genus, focusing on possible antecedents to Homo, changes in diet and body form as Australopithecus evolved toward Homo, ancient species within the genus, and evolutionary processes likely operating 2.5 - 1.5 million years ago. Recorded on 02/05/2016. Series: "CARTA - Center for Academic Research and Training in Anthropogeny" [4/2016] [Science] [Show ID: 30634] -
 1:28:31
1:28:31Human Evolution - History of Humanity Documentary
Human Evolution - History of Humanity DocumentaryHuman Evolution - History of Humanity Documentary
Human ( Homo Sapiens Versus Neaderthals) evolution is the evolutionary process leading to the appearance of anatomically modern humans. The topic typically focuses on the evolutionary history of the primates—in particular the genus Homo, and the emergence of Homo sapiens as a distinct species of the hominids (or "great apes")—rather than studying the earlier history that led to the primates. The study of human evolution involves many scientific disciplines, including physical anthropology, primatology, archaeology, paleontology, ethology, linguistics, evolutionary psychology, embryology and genetics. Genetic studies show that primates diverged from other mammals about 85 million years ago, in the Late Cretaceous period, and the earliest fossils appear in the Paleocene, around 55 million years ago. Within the Hominoidea (apes) superfamily, the Hominidae family diverged from the Hylobatidae (gibbon) family some 15–20 million years ago; African great apes (subfamily Homininae) diverged from orangutans (Ponginae) about 14 million years ago; the Hominini tribe (humans, Australopithecines and other extinct biped genera, and chimpanzees) parted from the Gorillini tribe (gorillas) about 8 million years ago; and, in turn, the subtribes Hominina (humans and biped ancestors) and Panina (chimps) separated about 7.5 million years ago. The basic adaptation of the hominin line is bipedalism. The earliest bipedal hominin is considered to be either Sahelanthropus or Orrorin; alternatively, either Sahelanthropus or Orrorin may instead be the last shared ancestor between chimps and humans. Ardipithecus, a full biped, arose somewhat later, and the early bipeds eventually evolved into the australopithecines, and later into the genus Homo. The earliest documented representative of the genus Homo is Homo habilis, which evolved around 2.8 million years ago, and is arguably the earliest species for which there is positive evidence of the use of stone tools. The brains of these early hominins were about the same size as that of a chimpanzee, although it has been suggested that this was the time in which the human SRGAP2 gene doubled, producing a more rapid wiring of the frontal cortex. During the next million years a process of rapid encephalization occurred, and with the arrival of Homo erectus and Homo ergaster in the fossil record, cranial capacity had doubled to 850 cm3. (Such an increase in human brain size is equivalent to each generation having 125,000 more neurons than their parents.) It is believed that Homo erectus and Homo ergaster were the first to use fire and complex tools, and were the first of the hominin line to leave Africa, spreading throughout Africa, Asia, and Europe between 1.3 to 1.8 million years ago. According to the recent African origin of modern humans theory, modern humans evolved in Africa possibly from Homo heidelbergensis, Homo rhodesiensis or Homo antecessor and migrated out of the continent some 50,000 to 100,000 years ago, gradually replacing local populations of Homo erectus, Denisova hominins, Homo floresiensis and Homo neanderthalensis. Archaic Homo sapiens, the forerunner of anatomically modern humans, evolved between 400,000 and 250,000 years ago. Recent DNA evidence suggests that several haplotypes of Neanderthal origin are present among all non-African populations, and Neanderthals and other hominins, such as Denisovans, may have contributed up to 6% of their genome to present-day humans, suggestive of a limited inter-breeding between these species. Anatomically modern humans evolved from archaic Homo sapiens in the Middle Paleolithic, about 200,000 years ago. The transition to behavioral modernity with the development of symbolic culture, language, and specialized lithic technology happened around 50,000 years ago according to many anthropologists although some suggest a gradual change in behavior over a longer time span. Tags : evolution human evolution human documentary evolution human brain evolution human full evolution human race evolution human animation human evolution national geographic future human evolution crash course human evolution evolution homo sapiens human evolution - from goliath to homo sapiens history of human evolution history of human experimentation history of human evolution documentary the emerald tablets of thoth hidden human history hidden history of the human race everything you kn story of human evolution history channel the philosophy of the human voice embracing its ph -
 16:14
16:14Human Evolution: Crash Course Big History #6
Human Evolution: Crash Course Big History #6Human Evolution: Crash Course Big History #6
In which John Green and Hank Green teach you about how human primates moved out of Africa and turned Earth into a real-life Planet of the Apes. And the apes are people! John and Hank teach you about how humans evolved, and the sort of tricks they picked up along the way like complex tool use, big brains, and fighting. Our ancestors adapted to the grasslands of Africa, and went through several iterations including Australopithecus, Homo Habilis, and Homo Ergaster/Erectus. Our ancestors tamed fire, made pressure flake tools, and eventually smartphones. Learn more: http://www.bighistoryproject.com -
 0:30
0:30GENUS HOMO
GENUS HOMOGENUS HOMO
-
 55:13
55:13How The Human Mind Was Born(full documentary)HD
How The Human Mind Was Born(full documentary)HDHow The Human Mind Was Born(full documentary)HD
Human evolution is the evolutionary process leading up to the appearance of modern humans. While it began with the last common ancestor of all life, the topic usually covers only the evolutionary history of primates, in particular the genus Homo, and the emergence of Homo sapiens as a distinct species of hominids . The study of human evolution involves many scientific disciplines, including physical anthropology, primatology, archaeology, paleontology, ethology, linguistics, evolutionary psychology, embryology and genetics. Modern Physics:Gravitation:http://youtu.be/STrXFteB66Y The Voyage To Pluto:http://youtu.be/ls7LWOcQfi8 Athene`s Theory of Everything:http://youtu.be/-JoaBSI0OhU -
 4:56
4:56Electrocyte Appendix
Electrocyte AppendixElectrocyte Appendix
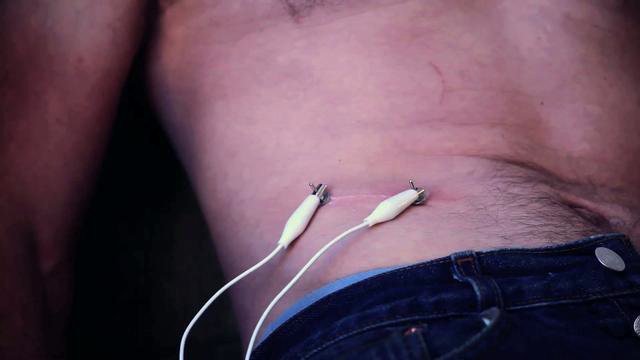
The Electrocyte Appendix is an artificial organ that could be implanted into the body to allow people to become electric organisms. Inspired by the electric eel and the way it uses electrocyte cells to produce electrical current from its abdomens, the organ is constructed of artificial cells* that mimic and improve the electrocyte mechanism by converting blood sugar into electricity. Replacing the vestigial appendix, the artificial organ brings a new functionality to the human anatomy, giving humans the ability to farm and produce electricity directly from their body. By discarding the remains of redundant anatomical functions in favour of new abilities, the body is redesigned in order to sustain its new way of living. Biotechnology could allow us to transform our genus into something else. The idea of our species changing from Homo-Sapiens into Homo-Evolutis (the human as a species controlling and designing its own evolution) is materialising quickly in research labs. And what kind of genus be constructed when the Homo takes after the Gymnotus? Forecasts for 2050 point towards technologically assisted reclusiveness, self sufficiency and social isolation. These behaviours are enabled by communication networks which allow one to survive without leaving the home or having physical interactions with others. In this kind of existence, where electricity becomes vital for survival, should the body adapt to the behaviour and adjust to sustain it? Humans are by nature social animals, by retracting into a self sustaining solitude a person becomes not dissimilar to the electric eel in behaviour. The eel is a solitary animal, it lives alone, hunts and breeds without any interaction with other organisms, it senses and reacts to the presence of others through electric charges. As we start behaving this way, should our bodies evolve to provide us with electric energy? In this future scenario the body changes its function; instead of an organism designed to attract, socialise, mate and reproduce with others, it becomes an electricity generating vessel, nurtured and harvested by its owner, designed to sustain a new form of virtual existence for an individual who lives through electronic networks. * Based on the research Designing artificial cells to harness the biological ion concentration gradient by Jian Xu and David LaVan, Nature Nanotechnology, September 21, 2008. -
 23:31
23:31Rainer Klement, Ph.D.—Is There a Role for a Paleolithic Lifestyle in the Treatment and Prevention of Cancer
Rainer Klement, Ph.D.—Is There a Role for a Paleolithic Lifestyle in the Treatment and Prevention of CancerRainer Klement, Ph.D.—Is There a Role for a Paleolithic Lifestyle in the Treatment and Prevention of Cancer
Rainer Klement, Ph.D. presenting at the 2nd Annual Ancestral Health Symposium (AHS12). Is There a Role for a Paleolithic Lifestyle in the Treatment and Prevention of Cancer? Abstract: Cancer could be considered a disease of civilization that has consistently been reported to be very rare among uncivilized hunter-gatherer societies. This observation makes sense from an evolutionary perspective from which it is reasonable to assume that the lifestyle factors that protect our genome against tumorigenesis have been selected for early in the history of the genus homo when humans lived as hunter-gatherers. In this talk, we are going to address the question whether the implementation of a "paleolithic" lifestyle can have beneficial effects in the prevention as well as the treatment of cancer. Thereby, we are going to focus on the roles played by three important factors: regular sun exposure (leading to sufficient vitamin D levels), physical exercise (leading to sufficient muscle mass, inversely correlated to overall mortality due to its anti-inflammatory effects) and diet. While there is already compelling evidence for the beneficial effects of the former two, the influence of the altered nutritional patterns in the Western diet upon cancer incidence and outcome is less clearly defined. However, based on recent research linking cancer metabolism to diet, we are going to argue that a paleo-oriented, low carbohydrate diet could suppress, or at least delay, the emergence of cancer, and that proliferation of already existing tumor cells could be slowed down. Overall, the paleolithic lifestyle, including resistance training, may offer a reasonable and valuable possibility of protection against cancer. Bios for Rainer and Dirk: Rainer Klement, Ph.D., is a medical physicist in the Department of Radiation Oncology at the University of Würzburg, Germany. His research interests focus on tumor metabolism and the effects of ketone bodies on tumor cells in combination with radiotherapy. Together with Ulrike Kämmerer, a leading expert in the field of ketogenic diets as supportive treatment for cancer patients, he has recently published a highly accessed review article entitled Is there a role for carbohydrate restriction in the treatment and prevention of cancer? in the journal Nutrition & Metabolism. As an ambitious triathlete, he has a strong interest in a healthy lifestyle and adopted a paleolithic diet some three years ago. -
 5:35
5:35Icon Of Evolution - Ape To Man - The Ultimate Deception
Icon Of Evolution - Ape To Man - The Ultimate DeceptionIcon Of Evolution - Ape To Man - The Ultimate Deception
Here is a professor of paleoanthropology openly admitting that genuine problems exist in the Darwinian story of human origins.,, All I can say is that he must be tenured! Pikaia interviews Bernard Wood - pt. 1/2 - video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4mbHt_gHKOI Pikaia interviews Bernard Wood - pt. 2/2 - video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lXLG7MbsGIk These following quotes sum up nicely what we can make of the poverty of the fossil record for 'human evolution': When we consider the remote past, before the origin of the actual species Homo sapiens, we are faced with a fragmentary and disconnected fossil record. Despite the excited and optimistic claims that have been made by some paleontologists, no fossil hominid species can be established as our direct ancestor. Richard Lewontin - Harvard Zoologist http://www.discovery.org/a/9961 Evolution of the Genus Homo - Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences - Tattersall, Schwartz, May 2009 Excerpt: "Definition of the genus Homo is almost as fraught as the definition of Homo sapiens. We look at the evidence for “early Homo,” finding little morphological basis for extending our genus to any of the 2.5–1.6-myr-old fossil forms assigned to “early Homo” or Homo habilis/rudolfensis." http://arjournals.annualreviews.org/doi/abs/10.1146/annurev.earth.031208.100202 Man is indeed as unique, as different from all other animals, as had been traditionally claimed by theologians and philosophers. Evolutionist Ernst Mayr http://www.y-origins.com/index.php?p=home_more4 “Something extraordinary, if totally fortuitous, happened with the birth of our species….Homo sapiens is as distinctive an entity as exists on the face of the Earth, and should be dignified as such instead of being adulterated with every reasonably large-brained hominid fossil that happened to come along.” Anthropologist Ian Tattersall (curator at the American Museum of Natural History) "But what is the basis for the human evolution thesis put forward by evolutionists? It is the existence of plenty of fossils on which evolutionists are able to build imaginary interpretations. Throughout history, more than 6,000 species of ape have lived, and most of them have become extinct. Today, only 120 species live on the earth. These 6,000 or so species of ape, most of which are extinct, constitute a rich resource for the evolutionists to build imaginary interpretations with." http://www.darwinismrefuted.com/origin_of_man.html “Dr. Leakey produced a biased reconstruction (of 1470/ Homo Rudolfensis) based on erroneous preconceived expectations of early human appearance that violated principles of craniofacial development,” Dr. Timothy Bromage http://www.geneticarchaeology.com/research/Mans_Earliest_Direct_Ancestors_Looked_More_Apelike_Than_Previously_Believed.asp A 2004 book by leading evolutionary biologist Ernst Mayr stated that "The earliest fossils of Homo, Homo rudolfensis and Homo erectus, are separated from Australopithecus (Lucy) by a large, unbridged gap. How can we explain this seeming saltation? Not having any fossils that can serve as missing links, we have to fall back on the time-honored method of historical science, the construction of a historical narrative.” Misrepresentations of the Evidence for Human Evolutionary Origins: http://www.evolutionnews.org/2009/04/texas_hold_em_part_ii_calling_1.html#moreSee More Paleoanthropology Dr. Pilbeam wrote the following regarding the theory of evolution and paleoanthropology (The study of purported bones and artifacts 'presupposed to support' the 'story' of humans evolving from apes) : "I am also aware of the fact that, at least in my own subject of paleoanthropology, "theory" - heavily influenced by implicit ideas almost always dominates "data". ....Ideas that are totally unrelated to actual fossils have dominated theory building, which in turn strongly influence the way fossils are interpreted" http://conservapedia.com/Evolution#Paleoanthropology "Fossil evidence of human evolutionary history is fragmentary and open to various interpretations. Fossil evidence of chimpanzee evolution is absent altogether". Evolutionist Henry Gee, Nature 2001 http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v412/...n6843/full/412131a0.html Lucy - The Powersaw Incident - a humorous video showing how biased evolutionists can be with the evidence http://www.metacafe.com/watch/4032597 Paleoanthropology In regards to the pictures of the supposed ancestors of man featured in science journals and the news media Boyce Rensberger wrote in the journal Science the following regarding their highly speculative nature: "Unfortunately, the vast majority of artist's conceptions are based more on imagination than on evidence. But a handful of expert natural-history artists begin with the fossil bones of a hominid and work from there…. Much of the reconstruction, however, is guesswork. Bones say nothing about the fleshy parts of the nose, lips, or ears. Artists must cr -
 2:31
2:31Enter OBSL33t - Pt 1 - Big bang, evolution, and bad religion
Enter OBSL33t - Pt 1 - Big bang, evolution, and bad religionEnter OBSL33t - Pt 1 - Big bang, evolution, and bad religion
In the beginning there was . . . Well, what do we mean when we say ‘beginning’? It is impossible to know what kind of universe existed before that point in time we have come to know as the big bang, But, it’s an exciting prospect To amuse ourselves with what such a universe might have been like. Common place observations, such as light, gravity, and matter that we sometimes take for granted, could have been very alien concepts in such a universe. Indeed the very laws of nature in such a place could have been vastly different. However, If we mean at the start of this universe, which research tells us was around 13.7 billion years ago, Then, In the beginning there was a singularity, made up of the infinitely dense stuff of whatever came before. And at this epoch gravity and electronuclear forces acted as the catalysts for the formation of the materials and laws that makeup our cosmos. 100 million years later the first star began to shine. As galaxies continued to develop 4.6 billion years ago in an unremarkable section of space, In an equally unremarkable galaxy On a pale blue dot orbiting a young star. Life appeared Weather or not this life was a byproduct of an occurrence here on earth Or perhaps the result of a panspermic planetary collision called exogenisis is not yet known. But this life evolved, Slowly, very, very, slowly for billions of years, until through mutation and natural selection the genus homo sapiens sapiens finally appeared. Humans. With us came language and art, With that came culture and knowledge. The human race in our developmental stumbles and follies have sometimes made up stories to explain natural phenomenon that we could not understand. And thus throughout history we have projected and Anthropomorphised just about every thing imaginable into cosmological metaphor. In doing this the human race may have invented the most dangerous and destructive thing in the universe, Religion. Part 2 - coming soon.
-

Origins of Genus Homo: What Who When Where?; Early Body Form; Life History Patterns
(Visit: http://www.uctv.tv/) This symposium explores evidence bearing on the emergence of our genus, focusing on possible antecedents to Homo, changes in diet and body form as Australopithecus evolved toward Homo, ancient species within the genus, and evolutionary processes likely operating 2.5 - 1.5 million years ago. Recorded on 02/05/2016. Series: "CARTA - Center for Academic Research and Training in Anthropogeny" [4/2016] [Science] [Show ID: 30632]
published: 08 Apr 2016 -

How Do We Know Who Our Human Ancestors Were?
Recently scientists announced the discovery of yet another human-like ancestor, but how do we determine if they belong to the genus homo? Watch More ►►►► http://dne.ws/1FEGqgr Read More: New Human-like Species Discovered in South Africa http://www.bbc.com/news/science-environment-34192447 “The discovery of 15 partial skeletons is the largest single discovery of its type in Africa. The researchers claim that the discovery will change ideas about our human ancestors.” Human Family Tree http://humanorigins.si.edu/evidence/human-family-tree ____________________ DNews is dedicated to satisfying your curiosity and to bringing you mind-bending stories & perspectives you won't find anywhere else! New videos twice daily. Watch More DNews on TestTube http://testtube.com/dnews ...
published: 13 Sep 2015 -

TtHL: The Origin of Genus Homo
Part Four: Deriving the genus Homo from rodential ancestors. ----------------------------------------------------------------- Sources: Walking with Beasts footage: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qtAzX... Strepsirrhini/Haplorrhini graphic 1: http://cromercrox.blogspot.com/2013/0... Strepsirrhini/Haplorrhini graphic 2: https://whyevolutionistrue.wordpress.... Primate phylogeny graphic: http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/... - Nature article: http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/... Eye-migration animation: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UPggk... Parapithecidae skull: http://www.pnas.org/content/98/14/789... Apidium footage: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rwOpb... Catarrhini phylogeny: http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/... - Nature article: http://www.nature.com/nature/journa...
published: 22 Aug 2015 -

Origins of Genus Homo ~ Symposium (CARTA)
This symposium explores evidence bearing on the emergence of our genus, focusing on possible antecedents to Homo, changes in diet and body form as Australopithecus evolved toward Homo, ancient species within the genus, and evolutionary processes likely operating 2.5 - 1.5 million years ago. Recorded on 02/05/2016. Series: "CARTA - Center for Academic Research and Training in Anthropogeny" [4/2016] [Science] [Show ID: 30633] [MIRROR] Visit: http://www.uctv.tv/ ------------------- SUBSCRIBE to Evolution Tube http://bit.ly/2pUOYSb In association with Talk Beliefs http://bit.ly/2lA6YOv DISCLAIMER: Copyright Disclaimer Under Section 107 of the Copyright Act 1976, allowance is made for "fair use" for purposes such as criticism, comment, news reporting, teaching, scholarship, and research. F...
published: 02 May 2017 -

CARTA: Origins of Genus Homo – Steven Churchill: Southern Africa and the Origin of Homo
(Visit: http://www.uctv.tv/) In the last seven years, two hominin species possessing a mixture of primitive and Homo-like morphology – Australopithecus sediba and Homo naledi – have been discovered in South Africa. Duke University’s Steven Churchill believes that these remarkable finds call for new models in not only understanding the origins of genus Homo, but also the emergence of Homo erectus. Recorded on 02/05/2016. Series: "CARTA - Center for Academic Research and Training in Anthropogeny" [Science] [Show ID: 30642]
published: 22 Apr 2016 -

Origins of Genus Homo–Australopiths and Early Homo; Variation of Early Homo; Speciation of Homo
(Visit: http://www.uctv.tv/) This symposium explores evidence bearing on the emergence of our genus, focusing on possible antecedents to Homo, changes in diet and body form as Australopithecus evolved toward Homo, ancient species within the genus, and evolutionary processes likely operating 2.5 - 1.5 million years ago. Recorded on 02/05/2016. Series: "CARTA - Center for Academic Research and Training in Anthropogeny" [4/2016] [Science] [Show ID: 30634]
published: 19 Apr 2016 -

Human Evolution - History of Humanity Documentary
Human ( Homo Sapiens Versus Neaderthals) evolution is the evolutionary process leading to the appearance of anatomically modern humans. The topic typically focuses on the evolutionary history of the primates—in particular the genus Homo, and the emergence of Homo sapiens as a distinct species of the hominids (or "great apes")—rather than studying the earlier history that led to the primates. The study of human evolution involves many scientific disciplines, including physical anthropology, primatology, archaeology, paleontology, ethology, linguistics, evolutionary psychology, embryology and genetics. Genetic studies show that primates diverged from other mammals about 85 million years ago, in the Late Cretaceous period, and the earliest fossils appear in the Paleocene, around 55 million y...
published: 28 Oct 2015 -

Human Evolution: Crash Course Big History #6
In which John Green and Hank Green teach you about how human primates moved out of Africa and turned Earth into a real-life Planet of the Apes. And the apes are people! John and Hank teach you about how humans evolved, and the sort of tricks they picked up along the way like complex tool use, big brains, and fighting. Our ancestors adapted to the grasslands of Africa, and went through several iterations including Australopithecus, Homo Habilis, and Homo Ergaster/Erectus. Our ancestors tamed fire, made pressure flake tools, and eventually smartphones. Learn more: http://www.bighistoryproject.com
published: 06 Nov 2014 -

GENUS HOMO
published: 09 May 2017 -

How The Human Mind Was Born(full documentary)HD
Human evolution is the evolutionary process leading up to the appearance of modern humans. While it began with the last common ancestor of all life, the topic usually covers only the evolutionary history of primates, in particular the genus Homo, and the emergence of Homo sapiens as a distinct species of hominids . The study of human evolution involves many scientific disciplines, including physical anthropology, primatology, archaeology, paleontology, ethology, linguistics, evolutionary psychology, embryology and genetics. Modern Physics:Gravitation:http://youtu.be/STrXFteB66Y The Voyage To Pluto:http://youtu.be/ls7LWOcQfi8 Athene`s Theory of Everything:http://youtu.be/-JoaBSI0OhU
published: 11 Oct 2014 -

Electrocyte Appendix
The Electrocyte Appendix is an artificial organ that could be implanted into the body to allow people to become electric organisms. Inspired by the electric eel and the way it uses electrocyte cells to produce electrical current from its abdomens, the organ is constructed of artificial cells* that mimic and improve the electrocyte mechanism by converting blood sugar into electricity. Replacing the vestigial appendix, the artificial organ brings a new functionality to the human anatomy, giving humans the ability to farm and produce electricity directly from their body. By discarding the remains of redundant anatomical functions in favour of new abilities, the body is redesigned in order to sustain its new way of living. Biotechnology could allow us to transform our genus into something ...
published: 15 Dec 2009 -

Rainer Klement, Ph.D.—Is There a Role for a Paleolithic Lifestyle in the Treatment and Prevention of Cancer
Rainer Klement, Ph.D. presenting at the 2nd Annual Ancestral Health Symposium (AHS12). Is There a Role for a Paleolithic Lifestyle in the Treatment and Prevention of Cancer? Abstract: Cancer could be considered a disease of civilization that has consistently been reported to be very rare among uncivilized hunter-gatherer societies. This observation makes sense from an evolutionary perspective from which it is reasonable to assume that the lifestyle factors that protect our genome against tumorigenesis have been selected for early in the history of the genus homo when humans lived as hunter-gatherers. In this talk, we are going to address the question whether the implementation of a "paleolithic" lifestyle can have beneficial effects in the prevention as well as the treatment of cancer. T...
published: 04 Dec 2012 -

Icon Of Evolution - Ape To Man - The Ultimate Deception
Here is a professor of paleoanthropology openly admitting that genuine problems exist in the Darwinian story of human origins.,, All I can say is that he must be tenured! Pikaia interviews Bernard Wood - pt. 1/2 - video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4mbHt_gHKOI Pikaia interviews Bernard Wood - pt. 2/2 - video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lXLG7MbsGIk These following quotes sum up nicely what we can make of the poverty of the fossil record for 'human evolution': When we consider the remote past, before the origin of the actual species Homo sapiens, we are faced with a fragmentary and disconnected fossil record. Despite the excited and optimistic claims that have been made by some paleontologists, no fossil hominid species can be established as our direct ancestor. Richard Lewontin - H...
published: 22 Jan 2011 -

Enter OBSL33t - Pt 1 - Big bang, evolution, and bad religion
In the beginning there was . . . Well, what do we mean when we say ‘beginning’? It is impossible to know what kind of universe existed before that point in time we have come to know as the big bang, But, it’s an exciting prospect To amuse ourselves with what such a universe might have been like. Common place observations, such as light, gravity, and matter that we sometimes take for granted, could have been very alien concepts in such a universe. Indeed the very laws of nature in such a place could have been vastly different. However, If we mean at the start of this universe, which research tells us was around 13.7 billion years ago, Then, In the beginning there was a singularity, made up of the infinitely dense stuff of whatever came before. And at this epoch gravity and electronuclear fo...
published: 02 Jan 2009 -

Don Patton - Entropy, Information, and The 'Deteriorating' Fossil Record
Laws Of Science - Don Patton - video and more quotes on the second law and how it relates to the 'deteriorating' fossil record: http://www.bible.ca/tracks/dp-lawsScience.htm Little known by most people is the fact that almost every, if not every, major branch of modern science has been founded by a scientist who believed in Christ: Christianity and The Birth of Science - Michael Bumbulis, Ph.D Excerpt: Furthermore, many of these founders of science lived at a time when others publicly expressed views quite contrary to Christianity - Hume, Hobbes, Darwin, etc. When Boyle argues against Hobbe's materialism or Kelvin argues against Darwin's assumptions, you don't have a case of "closet atheists." http://ldolphin.org/bumbulis/ http://www.tektonics.org Christianity Gave Birth To Each Scien...
published: 21 Nov 2010 -

Fish & Dinosaur Evolution vs. The Actual Fossil Evidence
Here is another excellent video on this subject; Fish, Fossils and Evolution – Arthur Jones – video http://edinburghcreationgroup.org/video/14 Challenging Fossil of a Little Fish The fish-like creature was hardly more than an inch long, but its discovery in the rocks of southern China was a big deal. The 530-million-year-old fossil, dubbed Haikouella, had the barest beginning of a spinal cord, making it the oldest animal ever found whose body shape resembled modern vertebrates. In the Nature article announcing his latest findings, Jun-Yuan Chen and his colleagues reported dryly that the ancient fish “will add to the debate on the evolutionary transition from invertebrate to vertebrate.” ,,, “Neo-Darwinism is dead,” said Eric Davidson, a geneticist and textbook writer at the California In...
published: 21 Oct 2011 -

PETER MERGENER - People want more
PETER MERGENER - People want more CUE Records Germany - 1991 - Album: Creautures Humans are , from the biological point of view , an animal species whose scientific name is Homo sapiens (Latin "homo" , "man " and " sapiens ", "wise" ) . They belong to the family Hominidae ( hominids ) . They are also known under the generic name of "men", although that term is ambiguous as it is also used to refer to male individuals and in particular adult males. Human beings have mental abilities that allow them to invent, learn and use complex linguistic structures , logic , math, writing , science and technology. Humans are social animals, capable of conceiving , transmit and learn completely abstract concepts . There is no evidence that there is another way of life with these skills - or more - in the...
published: 14 Oct 2013 -

Projector Loquens (2005)
Projector loquens is an interactive installation representing a situation in which a new species, Projector loquens, attempts to communicate with a different species, Homo sapiens. Projector is regarded as a new genus coequal with hominid and the specific epithet, loquens, indicates its communicative character and anxiety for communication. Projector loquens consists of a projector turntable system, a human detection system, a projection system and movies. Projector loquens speaks in the form of movies in response to a participant's position and speed. The participant's body shape, cloth colors and distance from Projector loquens alter moving images projected on their body. Their way of looking at movies on their chest or abdomen reflects how people project their own perspective onto inter...
published: 26 Jul 2011 -

The Genus Homo
ANT 210 General Anthropology, Week 4b Lecture to supplement Chapter 7
published: 02 Aug 2011 -

SOCIAL LOGO
SOCIAL LOGO Humans (Homo sapiens) are primates of the family Hominidae, and the only living species of the genus Homo. They originated in Africa, where they reached anatomical modernity about 200,000 years ago and began to exhibit full behavioral modernity around 50,000 years ago. www.loupville.com
published: 25 Sep 2012
Origins of Genus Homo: What Who When Where?; Early Body Form; Life History Patterns
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 59:22
- Updated: 08 Apr 2016
- views: 12087
- published: 08 Apr 2016
- views: 12087
How Do We Know Who Our Human Ancestors Were?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:38
- Updated: 13 Sep 2015
- views: 116893
- published: 13 Sep 2015
- views: 116893
TtHL: The Origin of Genus Homo
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 11:07
- Updated: 22 Aug 2015
- views: 1997
- published: 22 Aug 2015
- views: 1997
Origins of Genus Homo ~ Symposium (CARTA)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 58:20
- Updated: 02 May 2017
- views: 3
- published: 02 May 2017
- views: 3
CARTA: Origins of Genus Homo – Steven Churchill: Southern Africa and the Origin of Homo
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 21:11
- Updated: 22 Apr 2016
- views: 2431
- published: 22 Apr 2016
- views: 2431
Origins of Genus Homo–Australopiths and Early Homo; Variation of Early Homo; Speciation of Homo
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:00:26
- Updated: 19 Apr 2016
- views: 16171
- published: 19 Apr 2016
- views: 16171
Human Evolution - History of Humanity Documentary
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:28:31
- Updated: 28 Oct 2015
- views: 200014
- published: 28 Oct 2015
- views: 200014
Human Evolution: Crash Course Big History #6
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 16:14
- Updated: 06 Nov 2014
- views: 1051334
- published: 06 Nov 2014
- views: 1051334
GENUS HOMO
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:30
- Updated: 09 May 2017
- views: 382
- published: 09 May 2017
- views: 382
How The Human Mind Was Born(full documentary)HD
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 55:13
- Updated: 11 Oct 2014
- views: 18624
- published: 11 Oct 2014
- views: 18624
Electrocyte Appendix
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:56
- Updated: 05 Jun 2014
- views: 3570
- published: 15 Dec 2009
- views: 3570
Rainer Klement, Ph.D.—Is There a Role for a Paleolithic Lifestyle in the Treatment and Prevention of Cancer
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 23:31
- Updated: 04 Jun 2014
- views: 1447
- published: 04 Dec 2012
- views: 1447
Icon Of Evolution - Ape To Man - The Ultimate Deception
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:35
- Updated: 05 Jun 2014
- views: 677
- published: 22 Jan 2011
- views: 677
Enter OBSL33t - Pt 1 - Big bang, evolution, and bad religion
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:31
- Updated: 05 Jun 2014
- views: 738
- published: 02 Jan 2009
- views: 738
Don Patton - Entropy, Information, and The 'Deteriorating' Fossil Record
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 36:25
- Updated: 05 Jun 2014
- views: 4713
- published: 21 Nov 2010
- views: 4713
Fish & Dinosaur Evolution vs. The Actual Fossil Evidence
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:47
- Updated: 05 Jun 2014
- views: 963
- published: 21 Oct 2011
- views: 963
PETER MERGENER - People want more
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:03
- Updated: 13 May 2014
- views: 9
- published: 14 Oct 2013
- views: 9
Projector Loquens (2005)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:48
- Updated: 10 Apr 2014
- views: 0
- published: 26 Jul 2011
- views: 0
The Genus Homo
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 26:19
- Updated: 10 Apr 2014
- views: 94
- published: 02 Aug 2011
- views: 94
SOCIAL LOGO
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:14
- Updated: 10 Apr 2014
- views: 74
- published: 25 Sep 2012
- views: 74
-

Origins of Genus Homo: What Who When Where?; Early Body Form; Life History Patterns
(Visit: http://www.uctv.tv/) This symposium explores evidence bearing on the emergence of our genus, focusing on possible antecedents to Homo, changes in diet and body form as Australopithecus evolved toward Homo, ancient species within the genus, and evolutionary processes likely operating 2.5 - 1.5 million years ago. Recorded on 02/05/2016. Series: "CARTA - Center for Academic Research and Training in Anthropogeny" [4/2016] [Science] [Show ID: 30632]
published: 08 Apr 2016 -

How Do We Know Who Our Human Ancestors Were?
Recently scientists announced the discovery of yet another human-like ancestor, but how do we determine if they belong to the genus homo? Watch More ►►►► http://dne.ws/1FEGqgr Read More: New Human-like Species Discovered in South Africa http://www.bbc.com/news/science-environment-34192447 “The discovery of 15 partial skeletons is the largest single discovery of its type in Africa. The researchers claim that the discovery will change ideas about our human ancestors.” Human Family Tree http://humanorigins.si.edu/evidence/human-family-tree ____________________ DNews is dedicated to satisfying your curiosity and to bringing you mind-bending stories & perspectives you won't find anywhere else! New videos twice daily. Watch More DNews on TestTube http://testtube.com/dnews ...
published: 13 Sep 2015 -

TtHL: The Origin of Genus Homo
Part Four: Deriving the genus Homo from rodential ancestors. ----------------------------------------------------------------- Sources: Walking with Beasts footage: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qtAzX... Strepsirrhini/Haplorrhini graphic 1: http://cromercrox.blogspot.com/2013/0... Strepsirrhini/Haplorrhini graphic 2: https://whyevolutionistrue.wordpress.... Primate phylogeny graphic: http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/... - Nature article: http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/... Eye-migration animation: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UPggk... Parapithecidae skull: http://www.pnas.org/content/98/14/789... Apidium footage: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rwOpb... Catarrhini phylogeny: http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/... - Nature article: http://www.nature.com/nature/journa...
published: 22 Aug 2015 -

Origins of Genus Homo ~ Symposium (CARTA)
This symposium explores evidence bearing on the emergence of our genus, focusing on possible antecedents to Homo, changes in diet and body form as Australopithecus evolved toward Homo, ancient species within the genus, and evolutionary processes likely operating 2.5 - 1.5 million years ago. Recorded on 02/05/2016. Series: "CARTA - Center for Academic Research and Training in Anthropogeny" [4/2016] [Science] [Show ID: 30633] [MIRROR] Visit: http://www.uctv.tv/ ------------------- SUBSCRIBE to Evolution Tube http://bit.ly/2pUOYSb In association with Talk Beliefs http://bit.ly/2lA6YOv DISCLAIMER: Copyright Disclaimer Under Section 107 of the Copyright Act 1976, allowance is made for "fair use" for purposes such as criticism, comment, news reporting, teaching, scholarship, and research. F...
published: 02 May 2017 -

CARTA: Origins of Genus Homo – Steven Churchill: Southern Africa and the Origin of Homo
(Visit: http://www.uctv.tv/) In the last seven years, two hominin species possessing a mixture of primitive and Homo-like morphology – Australopithecus sediba and Homo naledi – have been discovered in South Africa. Duke University’s Steven Churchill believes that these remarkable finds call for new models in not only understanding the origins of genus Homo, but also the emergence of Homo erectus. Recorded on 02/05/2016. Series: "CARTA - Center for Academic Research and Training in Anthropogeny" [Science] [Show ID: 30642]
published: 22 Apr 2016 -

Origins of Genus Homo–Australopiths and Early Homo; Variation of Early Homo; Speciation of Homo
(Visit: http://www.uctv.tv/) This symposium explores evidence bearing on the emergence of our genus, focusing on possible antecedents to Homo, changes in diet and body form as Australopithecus evolved toward Homo, ancient species within the genus, and evolutionary processes likely operating 2.5 - 1.5 million years ago. Recorded on 02/05/2016. Series: "CARTA - Center for Academic Research and Training in Anthropogeny" [4/2016] [Science] [Show ID: 30634]
published: 19 Apr 2016 -

Human Evolution - History of Humanity Documentary
Human ( Homo Sapiens Versus Neaderthals) evolution is the evolutionary process leading to the appearance of anatomically modern humans. The topic typically focuses on the evolutionary history of the primates—in particular the genus Homo, and the emergence of Homo sapiens as a distinct species of the hominids (or "great apes")—rather than studying the earlier history that led to the primates. The study of human evolution involves many scientific disciplines, including physical anthropology, primatology, archaeology, paleontology, ethology, linguistics, evolutionary psychology, embryology and genetics. Genetic studies show that primates diverged from other mammals about 85 million years ago, in the Late Cretaceous period, and the earliest fossils appear in the Paleocene, around 55 million y...
published: 28 Oct 2015 -

Human Evolution: Crash Course Big History #6
In which John Green and Hank Green teach you about how human primates moved out of Africa and turned Earth into a real-life Planet of the Apes. And the apes are people! John and Hank teach you about how humans evolved, and the sort of tricks they picked up along the way like complex tool use, big brains, and fighting. Our ancestors adapted to the grasslands of Africa, and went through several iterations including Australopithecus, Homo Habilis, and Homo Ergaster/Erectus. Our ancestors tamed fire, made pressure flake tools, and eventually smartphones. Learn more: http://www.bighistoryproject.com
published: 06 Nov 2014 -

GENUS HOMO
published: 09 May 2017 -

How The Human Mind Was Born(full documentary)HD
Human evolution is the evolutionary process leading up to the appearance of modern humans. While it began with the last common ancestor of all life, the topic usually covers only the evolutionary history of primates, in particular the genus Homo, and the emergence of Homo sapiens as a distinct species of hominids . The study of human evolution involves many scientific disciplines, including physical anthropology, primatology, archaeology, paleontology, ethology, linguistics, evolutionary psychology, embryology and genetics. Modern Physics:Gravitation:http://youtu.be/STrXFteB66Y The Voyage To Pluto:http://youtu.be/ls7LWOcQfi8 Athene`s Theory of Everything:http://youtu.be/-JoaBSI0OhU
published: 11 Oct 2014 -

Electrocyte Appendix
The Electrocyte Appendix is an artificial organ that could be implanted into the body to allow people to become electric organisms. Inspired by the electric eel and the way it uses electrocyte cells to produce electrical current from its abdomens, the organ is constructed of artificial cells* that mimic and improve the electrocyte mechanism by converting blood sugar into electricity. Replacing the vestigial appendix, the artificial organ brings a new functionality to the human anatomy, giving humans the ability to farm and produce electricity directly from their body. By discarding the remains of redundant anatomical functions in favour of new abilities, the body is redesigned in order to sustain its new way of living. Biotechnology could allow us to transform our genus into something ...
published: 15 Dec 2009 -

Rainer Klement, Ph.D.—Is There a Role for a Paleolithic Lifestyle in the Treatment and Prevention of Cancer
Rainer Klement, Ph.D. presenting at the 2nd Annual Ancestral Health Symposium (AHS12). Is There a Role for a Paleolithic Lifestyle in the Treatment and Prevention of Cancer? Abstract: Cancer could be considered a disease of civilization that has consistently been reported to be very rare among uncivilized hunter-gatherer societies. This observation makes sense from an evolutionary perspective from which it is reasonable to assume that the lifestyle factors that protect our genome against tumorigenesis have been selected for early in the history of the genus homo when humans lived as hunter-gatherers. In this talk, we are going to address the question whether the implementation of a "paleolithic" lifestyle can have beneficial effects in the prevention as well as the treatment of cancer. T...
published: 04 Dec 2012 -

Icon Of Evolution - Ape To Man - The Ultimate Deception
Here is a professor of paleoanthropology openly admitting that genuine problems exist in the Darwinian story of human origins.,, All I can say is that he must be tenured! Pikaia interviews Bernard Wood - pt. 1/2 - video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4mbHt_gHKOI Pikaia interviews Bernard Wood - pt. 2/2 - video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lXLG7MbsGIk These following quotes sum up nicely what we can make of the poverty of the fossil record for 'human evolution': When we consider the remote past, before the origin of the actual species Homo sapiens, we are faced with a fragmentary and disconnected fossil record. Despite the excited and optimistic claims that have been made by some paleontologists, no fossil hominid species can be established as our direct ancestor. Richard Lewontin - H...
published: 22 Jan 2011 -

Enter OBSL33t - Pt 1 - Big bang, evolution, and bad religion
In the beginning there was . . . Well, what do we mean when we say ‘beginning’? It is impossible to know what kind of universe existed before that point in time we have come to know as the big bang, But, it’s an exciting prospect To amuse ourselves with what such a universe might have been like. Common place observations, such as light, gravity, and matter that we sometimes take for granted, could have been very alien concepts in such a universe. Indeed the very laws of nature in such a place could have been vastly different. However, If we mean at the start of this universe, which research tells us was around 13.7 billion years ago, Then, In the beginning there was a singularity, made up of the infinitely dense stuff of whatever came before. And at this epoch gravity and electronuclear fo...
published: 02 Jan 2009 -

Don Patton - Entropy, Information, and The 'Deteriorating' Fossil Record
Laws Of Science - Don Patton - video and more quotes on the second law and how it relates to the 'deteriorating' fossil record: http://www.bible.ca/tracks/dp-lawsScience.htm Little known by most people is the fact that almost every, if not every, major branch of modern science has been founded by a scientist who believed in Christ: Christianity and The Birth of Science - Michael Bumbulis, Ph.D Excerpt: Furthermore, many of these founders of science lived at a time when others publicly expressed views quite contrary to Christianity - Hume, Hobbes, Darwin, etc. When Boyle argues against Hobbe's materialism or Kelvin argues against Darwin's assumptions, you don't have a case of "closet atheists." http://ldolphin.org/bumbulis/ http://www.tektonics.org Christianity Gave Birth To Each Scien...
published: 21 Nov 2010 -

Fish & Dinosaur Evolution vs. The Actual Fossil Evidence
Here is another excellent video on this subject; Fish, Fossils and Evolution – Arthur Jones – video http://edinburghcreationgroup.org/video/14 Challenging Fossil of a Little Fish The fish-like creature was hardly more than an inch long, but its discovery in the rocks of southern China was a big deal. The 530-million-year-old fossil, dubbed Haikouella, had the barest beginning of a spinal cord, making it the oldest animal ever found whose body shape resembled modern vertebrates. In the Nature article announcing his latest findings, Jun-Yuan Chen and his colleagues reported dryly that the ancient fish “will add to the debate on the evolutionary transition from invertebrate to vertebrate.” ,,, “Neo-Darwinism is dead,” said Eric Davidson, a geneticist and textbook writer at the California In...
published: 21 Oct 2011 -

PETER MERGENER - People want more
PETER MERGENER - People want more CUE Records Germany - 1991 - Album: Creautures Humans are , from the biological point of view , an animal species whose scientific name is Homo sapiens (Latin "homo" , "man " and " sapiens ", "wise" ) . They belong to the family Hominidae ( hominids ) . They are also known under the generic name of "men", although that term is ambiguous as it is also used to refer to male individuals and in particular adult males. Human beings have mental abilities that allow them to invent, learn and use complex linguistic structures , logic , math, writing , science and technology. Humans are social animals, capable of conceiving , transmit and learn completely abstract concepts . There is no evidence that there is another way of life with these skills - or more - in the...
published: 14 Oct 2013 -

Projector Loquens (2005)
Projector loquens is an interactive installation representing a situation in which a new species, Projector loquens, attempts to communicate with a different species, Homo sapiens. Projector is regarded as a new genus coequal with hominid and the specific epithet, loquens, indicates its communicative character and anxiety for communication. Projector loquens consists of a projector turntable system, a human detection system, a projection system and movies. Projector loquens speaks in the form of movies in response to a participant's position and speed. The participant's body shape, cloth colors and distance from Projector loquens alter moving images projected on their body. Their way of looking at movies on their chest or abdomen reflects how people project their own perspective onto inter...
published: 26 Jul 2011 -

The Genus Homo
ANT 210 General Anthropology, Week 4b Lecture to supplement Chapter 7
published: 02 Aug 2011 -

SOCIAL LOGO
SOCIAL LOGO Humans (Homo sapiens) are primates of the family Hominidae, and the only living species of the genus Homo. They originated in Africa, where they reached anatomical modernity about 200,000 years ago and began to exhibit full behavioral modernity around 50,000 years ago. www.loupville.com
published: 25 Sep 2012
Origins of Genus Homo: What Who When Where?; Early Body Form; Life History Patterns
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 59:22
- Updated: 08 Apr 2016
- views: 12087
- published: 08 Apr 2016
- views: 12087
How Do We Know Who Our Human Ancestors Were?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:38
- Updated: 13 Sep 2015
- views: 116893
- published: 13 Sep 2015
- views: 116893
TtHL: The Origin of Genus Homo
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 11:07
- Updated: 22 Aug 2015
- views: 1997
- published: 22 Aug 2015
- views: 1997
Origins of Genus Homo ~ Symposium (CARTA)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 58:20
- Updated: 02 May 2017
- views: 3
- published: 02 May 2017
- views: 3
CARTA: Origins of Genus Homo – Steven Churchill: Southern Africa and the Origin of Homo
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 21:11
- Updated: 22 Apr 2016
- views: 2431
- published: 22 Apr 2016
- views: 2431
Origins of Genus Homo–Australopiths and Early Homo; Variation of Early Homo; Speciation of Homo
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:00:26
- Updated: 19 Apr 2016
- views: 16171
- published: 19 Apr 2016
- views: 16171
Human Evolution - History of Humanity Documentary
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:28:31
- Updated: 28 Oct 2015
- views: 200014
- published: 28 Oct 2015
- views: 200014
Human Evolution: Crash Course Big History #6
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 16:14
- Updated: 06 Nov 2014
- views: 1051334
- published: 06 Nov 2014
- views: 1051334
GENUS HOMO
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:30
- Updated: 09 May 2017
- views: 382
- published: 09 May 2017
- views: 382
How The Human Mind Was Born(full documentary)HD
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 55:13
- Updated: 11 Oct 2014
- views: 18624
- published: 11 Oct 2014
- views: 18624
Electrocyte Appendix
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:56
- Updated: 05 Jun 2014
- views: 3570
- published: 15 Dec 2009
- views: 3570
Rainer Klement, Ph.D.—Is There a Role for a Paleolithic Lifestyle in the Treatment and Prevention of Cancer
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 23:31
- Updated: 04 Jun 2014
- views: 1447
- published: 04 Dec 2012
- views: 1447
Icon Of Evolution - Ape To Man - The Ultimate Deception
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:35
- Updated: 05 Jun 2014
- views: 677
- published: 22 Jan 2011
- views: 677
Enter OBSL33t - Pt 1 - Big bang, evolution, and bad religion
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:31
- Updated: 05 Jun 2014
- views: 738
- published: 02 Jan 2009
- views: 738
Don Patton - Entropy, Information, and The 'Deteriorating' Fossil Record
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 36:25
- Updated: 05 Jun 2014
- views: 4713
- published: 21 Nov 2010
- views: 4713
Fish & Dinosaur Evolution vs. The Actual Fossil Evidence
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:47
- Updated: 05 Jun 2014
- views: 963
- published: 21 Oct 2011
- views: 963
PETER MERGENER - People want more
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:03
- Updated: 13 May 2014
- views: 9
- published: 14 Oct 2013
- views: 9
Projector Loquens (2005)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:48
- Updated: 10 Apr 2014
- views: 0
- published: 26 Jul 2011
- views: 0
The Genus Homo
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 26:19
- Updated: 10 Apr 2014
- views: 94
- published: 02 Aug 2011
- views: 94
SOCIAL LOGO
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:14
- Updated: 10 Apr 2014
- views: 74
- published: 25 Sep 2012
- views: 74
-

-

Lesson 6.3 - Genus Homo, Part 4: The Neanderthals
published: 15 Jul 2015 -

Origins of Genus Homo–Australopiths and Early Homo; Variation of Early Homo; Speciation of Homo
(Visit: http://www.uctv.tv/) This symposium explores evidence bearing on the emergence of our genus, focusing on possible antecedents to Homo, changes in diet and body form as Australopithecus evolved toward Homo, ancient species within the genus, and evolutionary processes likely operating 2.5 - 1.5 million years ago. Recorded on 02/05/2016. Series: "CARTA - Center for Academic Research and Training in Anthropogeny" [4/2016] [Science] [Show ID: 30634]
published: 19 Apr 2016 -

Origins of Genus Homo–Southern Africa and Origin of Homo; Adaptive Shifts; Energetics and Ecology
(Visit: http://www.uctv.tv/) This symposium explores evidence bearing on the emergence of our genus, focusing on possible antecedents to Homo, changes in diet and body form as Australopithecus evolved toward Homo, ancient species within the genus, and evolutionary processes likely operating 2.5 - 1.5 million years ago. Recorded on 02/05/2016. Series: "CARTA - Center for Academic Research and Training in Anthropogeny" [4/2016] [Science] [Show ID: 30633]
published: 21 Apr 2016 -

Origins of Genus Homo: What Who When Where?; Early Body Form; Life History Patterns
(Visit: http://www.uctv.tv/) This symposium explores evidence bearing on the emergence of our genus, focusing on possible antecedents to Homo, changes in diet and body form as Australopithecus evolved toward Homo, ancient species within the genus, and evolutionary processes likely operating 2.5 - 1.5 million years ago. Recorded on 02/05/2016. Series: "CARTA - Center for Academic Research and Training in Anthropogeny" [4/2016] [Science] [Show ID: 30632]
published: 08 Apr 2016 -

Great Human Odyssey Documentary Hd
Great Human Odyssey Documentary Hd. Homo sapiens is the binomial nomenclature for the only extant human species. Homo is the human genus, which also includes Neanderthals and many other extinct species of hominid; H. sapiens is the only surviving species of the genus Homo.
published: 15 Feb 2017 -

Human Evolution - History of Humanity Documentary
Human ( Homo Sapiens Versus Neaderthals) evolution is the evolutionary process leading to the appearance of anatomically modern humans. The topic typically focuses on the evolutionary history of the primates—in particular the genus Homo, and the emergence of Homo sapiens as a distinct species of the hominids (or "great apes")—rather than studying the earlier history that led to the primates. The study of human evolution involves many scientific disciplines, including physical anthropology, primatology, archaeology, paleontology, ethology, linguistics, evolutionary psychology, embryology and genetics. Genetic studies show that primates diverged from other mammals about 85 million years ago, in the Late Cretaceous period, and the earliest fossils appear in the Paleocene, around 55 million y...
published: 28 Oct 2015 -

National Geographic | THE NEANDERTHALS | FIRST PEOPLES OF EUROPE | HD Full Documentary
Neanderthals or Neandertals were a species or subspecies of archaic human, in the genus Homo, which became extinct around 40000 years ago. They were
published: 24 Feb 2017 -

Origin of Humans - National Geographic Documentary 2016
Human evolution is the evolutionary process that led to the emergence of anatomically modern humans. The topic typically focuses on the evolutionary history of the primates—in particular the genus Homo, and the emergence of Homo sapiens as a distinct species of the hominids (or "great apes")—rather than studying the earlier history that led to the primates. The study of human evolution involves many scientific disciplines, including physical anthropology, primatology, archaeology, paleontology, neurobiology, ethology, linguistics, evolutionary psychology, embryology and genetics. Genetic studies show that primates diverged from other mammals about 85 million years ago, in the Late Cretaceous period, and the earliest fossils appear in the Paleocene, around 55 million years ago. Within the H...
published: 02 Dec 2016 -

Becoming Human Documentary #bigfoot squatch call #bigfoot squatch call
Over two and a half hours of evolutionary awesomeness. Humans (variously Homo sapiens and Homo sapiens sapiens) are primates of the family Hominidae, and the only extant species of the genus Homo.[2]
published: 16 Oct 2016
Ethiopianism.tv- 2.8 M years old Homo Genus Found by an Ethiopian Chalachew Seyoum
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 42:40
- Updated: 07 Mar 2015
- views: 520
Lesson 6.3 - Genus Homo, Part 4: The Neanderthals
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 59:34
- Updated: 15 Jul 2015
- views: 291
- published: 15 Jul 2015
- views: 291
Origins of Genus Homo–Australopiths and Early Homo; Variation of Early Homo; Speciation of Homo
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:00:26
- Updated: 19 Apr 2016
- views: 16171
- published: 19 Apr 2016
- views: 16171
Origins of Genus Homo–Southern Africa and Origin of Homo; Adaptive Shifts; Energetics and Ecology
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 58:20
- Updated: 21 Apr 2016
- views: 8263
- published: 21 Apr 2016
- views: 8263
Origins of Genus Homo: What Who When Where?; Early Body Form; Life History Patterns
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 59:22
- Updated: 08 Apr 2016
- views: 12165
- published: 08 Apr 2016
- views: 12165
Great Human Odyssey Documentary Hd
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:52:07
- Updated: 15 Feb 2017
- views: 54
- published: 15 Feb 2017
- views: 54
Human Evolution - History of Humanity Documentary
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:28:31
- Updated: 28 Oct 2015
- views: 200014
- published: 28 Oct 2015
- views: 200014
National Geographic | THE NEANDERTHALS | FIRST PEOPLES OF EUROPE | HD Full Documentary
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:03:54
- Updated: 24 Feb 2017
- views: 91
- published: 24 Feb 2017
- views: 91
Origin of Humans - National Geographic Documentary 2016
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:42:47
- Updated: 02 Dec 2016
- views: 77748
- published: 02 Dec 2016
- views: 77748
Becoming Human Documentary #bigfoot squatch call #bigfoot squatch call
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:34:34
- Updated: 16 Oct 2016
- views: 4
- published: 16 Oct 2016
- views: 4

- Playlist
- Chat

- Playlist
- Chat

Origins of Genus Homo: What Who When Where?; Early Body Form; Life History Patterns
- Report rights infringement
- published: 08 Apr 2016
- views: 12087

How Do We Know Who Our Human Ancestors Were?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 Sep 2015
- views: 116893

TtHL: The Origin of Genus Homo
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 Aug 2015
- views: 1997

Origins of Genus Homo ~ Symposium (CARTA)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 02 May 2017
- views: 3

CARTA: Origins of Genus Homo – Steven Churchill: Southern Africa and the Origin of Homo
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 Apr 2016
- views: 2431

Origins of Genus Homo–Australopiths and Early Homo; Variation of Early Homo; Speciation of Homo
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Apr 2016
- views: 16171

Human Evolution - History of Humanity Documentary
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Oct 2015
- views: 200014

Human Evolution: Crash Course Big History #6
- Report rights infringement
- published: 06 Nov 2014
- views: 1051334

GENUS HOMO
- Report rights infringement
- published: 09 May 2017
- views: 382

How The Human Mind Was Born(full documentary)HD
- Report rights infringement
- published: 11 Oct 2014
- views: 18624

Electrocyte Appendix
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Dec 2009
- views: 3570

Rainer Klement, Ph.D.—Is There a Role for a Paleolithic Lifestyle in the Treatment and Prevention of Cancer
- Report rights infringement
- published: 04 Dec 2012
- views: 1447

Icon Of Evolution - Ape To Man - The Ultimate Deception
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 Jan 2011
- views: 677

Enter OBSL33t - Pt 1 - Big bang, evolution, and bad religion
- Report rights infringement
- published: 02 Jan 2009
- views: 738

- Playlist
- Chat

Origins of Genus Homo: What Who When Where?; Early Body Form; Life History Patterns
- Report rights infringement
- published: 08 Apr 2016
- views: 12087

How Do We Know Who Our Human Ancestors Were?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 Sep 2015
- views: 116893

TtHL: The Origin of Genus Homo
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 Aug 2015
- views: 1997

Origins of Genus Homo ~ Symposium (CARTA)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 02 May 2017
- views: 3

CARTA: Origins of Genus Homo – Steven Churchill: Southern Africa and the Origin of Homo
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 Apr 2016
- views: 2431

Origins of Genus Homo–Australopiths and Early Homo; Variation of Early Homo; Speciation of Homo
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Apr 2016
- views: 16171

Human Evolution - History of Humanity Documentary
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Oct 2015
- views: 200014

Human Evolution: Crash Course Big History #6
- Report rights infringement
- published: 06 Nov 2014
- views: 1051334

GENUS HOMO
- Report rights infringement
- published: 09 May 2017
- views: 382

How The Human Mind Was Born(full documentary)HD
- Report rights infringement
- published: 11 Oct 2014
- views: 18624

Electrocyte Appendix
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Dec 2009
- views: 3570

Rainer Klement, Ph.D.—Is There a Role for a Paleolithic Lifestyle in the Treatment and Prevention of Cancer
- Report rights infringement
- published: 04 Dec 2012
- views: 1447

Icon Of Evolution - Ape To Man - The Ultimate Deception
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 Jan 2011
- views: 677

Enter OBSL33t - Pt 1 - Big bang, evolution, and bad religion
- Report rights infringement
- published: 02 Jan 2009
- views: 738

- Playlist
- Chat

Ethiopianism.tv- 2.8 M years old Homo Genus Found by an Ethiopian Chalachew Seyoum
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Mar 2015
- views: 520

Lesson 6.3 - Genus Homo, Part 4: The Neanderthals
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Jul 2015
- views: 291

Origins of Genus Homo–Australopiths and Early Homo; Variation of Early Homo; Speciation of Homo
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Apr 2016
- views: 16171

Origins of Genus Homo–Southern Africa and Origin of Homo; Adaptive Shifts; Energetics and Ecology
- Report rights infringement
- published: 21 Apr 2016
- views: 8263

Origins of Genus Homo: What Who When Where?; Early Body Form; Life History Patterns
- Report rights infringement
- published: 08 Apr 2016
- views: 12165

Great Human Odyssey Documentary Hd
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Feb 2017
- views: 54

Human Evolution - History of Humanity Documentary
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Oct 2015
- views: 200014

National Geographic | THE NEANDERTHALS | FIRST PEOPLES OF EUROPE | HD Full Documentary
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 Feb 2017
- views: 91

Origin of Humans - National Geographic Documentary 2016
- Report rights infringement
- published: 02 Dec 2016
- views: 77748

Becoming Human Documentary #bigfoot squatch call #bigfoot squatch call
- Report rights infringement
- published: 16 Oct 2016
- views: 4
Trump's son-in-law ready to talk with investigators about Russian contacts
Edit TVNZ 28 May 2017Merkel Says Europe Can No Longer ‘Fully Count On Others’ In Wake Of Trump Trip
Edit TPM 28 May 2017Police: Suspect in Portland stabbings ranted about Muslims
Edit Atlanta Journal 27 May 2017Our galaxy produces 9 trillion kilograms of antimatter a second—how?
Edit Ars Technica 28 May 2017Man planned 'suicide by cop' after shooting rampage left eight dead
Edit Irish Independent 28 May 2017Ancient humans might have weathered the ice age and mass extinction in San Diego
Edit Quartz 28 May 2017Some Men Are Not Happy About A Women-Only Screening Of 'Wonder Woman'
Edit National Public Radio 28 May 2017My friends can’t stop moaning. How do I say ‘enough’?
Edit The Observer 28 May 2017Biggest exhibit of human-like fossils goes on display in South Africa
Edit The Himalayan 27 May 2017Tumours found on jaw bone of #HomoNaledi specimen
Edit Independent online (SA) 27 May 2017PICS: Almost Human exhibition showcases Homo naledi
Edit Independent online (SA) 26 May 2017His mom didn't want him to announce his Disneyland proposal on Facebook, so he went to Reddit
Edit WPTV 26 May 2017Life’s Economy is Primarily Based on Collaborative rather than Competitive Advantage
Edit Resilience 26 May 2017Africa is still the cradle of humankind
Edit Independent online (SA) 26 May 2017LGBT lives in Moldova
Edit Open Democracy 26 May 2017Our Identities and Political Thinking Are Formed in Our Free Time, Which Is Constantly Shrinking
Edit Alternet 26 May 2017Fossils of previously unknown early human relative go on display in South Africa
Edit The Guardian 25 May 2017Largest display of hominin fossils opens
Edit Reuters 25 May 2017- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »









