- published: 18 Aug 2015
- views: 3234
-
remove the playlistHydrostatic Equilibrium
- remove the playlistHydrostatic Equilibrium
- published: 25 Dec 2011
- views: 10722
- published: 10 Jul 2010
- views: 2132
- published: 20 Jun 2015
- views: 758
- published: 23 Oct 2015
- views: 446
- published: 09 Oct 2014
- views: 168

Hydrostatic equilibrium
In continuum mechanics, a fluid is said to be in hydrostatic equilibrium or hydrostatic balance when it is at rest, or when the flow velocity at each point is constant over time. This occurs when external forces such as gravity are balanced by a pressure gradient force. For instance, the pressure-gradient force prevents gravity from collapsing Earth's atmosphere into a thin, dense shell, whereas gravity prevents the pressure gradient force from diffusing the atmosphere into space.
Hydrostatic equilibrium is the current distinguishing criterion between dwarf planets and small Solar System bodies, and has other roles in astrophysics and planetary geology. This qualification typically means that the object is symmetrically rounded into a spheroid or ellipsoid shape, where any irregular surface features are due to a relatively thin solid crust. There are 31 observationally confirmed such objects (apart from the Sun), sometimes called planemos, in the Solar System, seven more that are virtually certain, and a hundred or so more that are likely.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
Equilibrium
Equilibrium may refer to:
Film and television
- "Equilibrium", one of the three segments of the 1953 film
Music
Other uses
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Sun
The Sun (in Greek: Helios, in Latin: Sol) is the star at the center of the Solar System and is by far the most important source of energy for life on Earth. It is a nearly perfect spherical ball of hot plasma, with internal convective motion that generates a magnetic field via a dynamo process. Its diameter is about 109 times that of Earth, and it has a mass about 330,000 times that of Earth, accounting for about 99.86% of the total mass of the Solar System.About three quarters of the Sun's mass consists of hydrogen; the rest is mostly helium, with much smaller quantities of heavier elements, including oxygen, carbon, neon and iron.
The Sun is a G-type main-sequence star (G2V) based on spectral class and it is informally referred to as a yellow dwarf. It formed approximately 4.567 billion years ago from the gravitational collapse of matter within a region of a large molecular cloud. Most of this matter gathered in the center, whereas the rest flattened into an orbiting disk that became the Solar System. The central mass became increasingly hot and dense, eventually initiating nuclear fusion in its core. It is thought that almost all stars form by this process.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 5:44
5:44Hydrostatic Equilibrium Demonstration
Hydrostatic Equilibrium DemonstrationHydrostatic Equilibrium Demonstration
Demonstration of Hydrostatic Equilibrium using a balloon and liquid nitrogen. The response of the balloon to being chilled by liquid nitrogen is enhanced by the latex material becoming stiffer when it is chilled by the liquid nitrogen. Recorded 2015 April 23 by Prof. Richard Pogge, The Ohio State University, Department of Astronomy. -
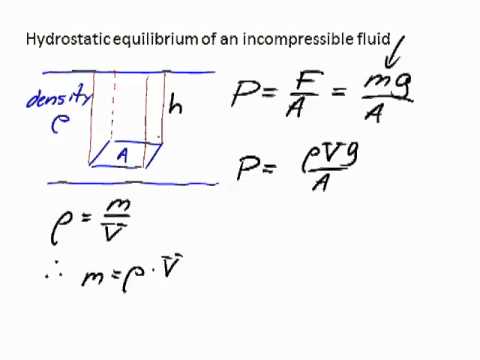 2:56
2:56Derivation of the hydrostatic equilibrium equation for an incompressible fluid.
Derivation of the hydrostatic equilibrium equation for an incompressible fluid.Derivation of the hydrostatic equilibrium equation for an incompressible fluid.
The deeper you go in a fluid (for example, deeper below the ocean, or lower in the atmosphere) the greater the pressure. The pressure is equal to the weight of all the fluid above you, per area. This is a derivation of the pressure as a function of depth, assuming that the fluid is incompressible, i.e. its density is constant. -
 24:10
24:10Stars and Hydrostatic Equilibrium
Stars and Hydrostatic EquilibriumStars and Hydrostatic Equilibrium
-
 5:40
5:40Astronomy - The Sun (2 of 16) Gravitational - Thermal Equilibrium
Astronomy - The Sun (2 of 16) Gravitational - Thermal Equilibrium -
 0:45
0:45Teach Astronomy - Hydrostatic Equilibrium
Teach Astronomy - Hydrostatic EquilibriumTeach Astronomy - Hydrostatic Equilibrium
http://www.teachastronomy.com/ Stars are stable. For most of their lives, fusion provides the energy source. Even though the Sun and other stars are fusing hydrogen into helium, it does not mean that they are bombs. The Sun will be stable for billions of years. Stars also do not cool off. Energy flows continuously from the core where fusion occurs to the outer cooler regions. At every point within a stable star there's an energy balance between two forces: the inward force of gravity and the outward pressure caused by energy release from nuclear reactions. This balance is called hydrostatic equilibrium. -
 5:43
5:43Hydrostatic Equilibrium
Hydrostatic EquilibriumHydrostatic Equilibrium
This video demonstrates the increase of pressure with depth in a fluid of constant density and one with increasing density analogous to a star's material. -
 3:50
3:50Pressure and Hydrostatic Equilibrium
Pressure and Hydrostatic EquilibriumPressure and Hydrostatic Equilibrium
Jaffe PPT Lecture -
 10:45
10:45Hydrostatic equilibrium
Hydrostatic equilibriumHydrostatic equilibrium
In continuum mechanics, a fluid is said to be in hydrostatic equilibrium or hydrostatic balance when it is at rest, or when the flow velocity at each point is constant over time. This occurs when external forces such as gravity are balanced by a pressure gradient force. For instance, the pressure-gradient force prevents gravity from collapsing Earth's atmosphere into a thin, dense shell, whereas gravity prevents the pressure gradient force from diffusing the atmosphere into space. Hydrostatic equilibrium is the current distinguishing criterion between dwarf planets and small Solar System bodies, and has other roles in astrophysics and planetary geology. This qualification typically means that the object is symmetrically rounded into a spheroid or ellipsoid shape, where any irregular surface features are due to a relatively thin solid crust. There are 31 observationally confirmed such objects, sometimes called planemos, in the Solar System, seven more that are virtually certain, and a hundred or so more that are likely. This video is targeted to blind users. Attribution: Article text available under CC-BY-SA Creative Commons image source in video -
 7:18
7:18Astronomy 100 Hydrostatic Equilibrium
Astronomy 100 Hydrostatic EquilibriumAstronomy 100 Hydrostatic Equilibrium
-
 7:32
7:32Terranoise - Hydrostatic Equilibrium
Terranoise - Hydrostatic Equilibrium -
 7:49
7:49Hydrostatic equilibrium: Pressure vs height (PhysCasts)
Hydrostatic equilibrium: Pressure vs height (PhysCasts)Hydrostatic equilibrium: Pressure vs height (PhysCasts)
In this hydrodynamics problem we are asked what guage pressure must a machine produce in order to suck mud of a density 1800 kg/m3 up a tube by a height of 1.5 m? -
 3:04
3:04Ch06G Hydrostatic Equilibrium
Ch06G Hydrostatic EquilibriumCh06G Hydrostatic Equilibrium
Ch06G Hydrostatic Equilibrium -
 13:39
13:39Hydrostatic Versus Oncotic Pressure
Hydrostatic Versus Oncotic PressureHydrostatic Versus Oncotic Pressure
An introduction on the difference between oncotic and hydrostatic pressure. -
 2:56
2:56Capillary Fluid Exchange
Capillary Fluid ExchangeCapillary Fluid Exchange
Fluid leaves the capillaries due to hydrostatic pressure and returns via osmotic pressure. -
 39:20
39:2007. Hydrostatic Balance
07. Hydrostatic Balance07. Hydrostatic Balance
The Atmosphere, the Ocean and Environmental Change (GG 140) The hydrostatic law describes the weight of a fluid overlying a given area, or the pressure at a particular point. It can be used to calculate the approximate atmospheric mass over a particular area, or to calculate the change in pressure over a given change in altitude. A calculation of the pressure difference from the ground to the twelfth floor of Klein Biology Tower is found to agree well with measurements taken at both locations. The hydrostatic law also applies to pressure changes with depth in the ocean. 00:00 - Chapter 1. Recap of Planet Temperature 11:20 - Chapter 2. Hydrostatic Balance 19:15 - Chapter 3. Calculation of CO2 Mass in the Atmosphere 22:08 - Chapter 4. Derivation of the Differential Form of the Hydrostatic Balance Equation 26:05 - Chapter 5. Hydrostatic Law Experiment 35:14 - Chapter 6. Application of Hydrostatic Law Complete course materials are available at the Open Yale Courses website: http://oyc.yale.edu This course was recorded in Fall 2011. -
 12:13
12:13Hydrostatic Equilibrium
Hydrostatic Equilibrium -
 5:51
5:51Physics - Fluid Statics (1 of 10) Pressure in a Fluid
Physics - Fluid Statics (1 of 10) Pressure in a Fluid -
 6:38
6:38ASTR 1P01 CLIP 115 Hydrostatic Equilibrium In The Sun
ASTR 1P01 CLIP 115 Hydrostatic Equilibrium In The SunASTR 1P01 CLIP 115 Hydrostatic Equilibrium In The Sun
-
 5:09
5:09Forces of Filtration
Forces of FiltrationForces of Filtration
http://www.handwrittentutorials.com - This tutorial discusses the Forces of Filtration which occur in the Glomeruli of the kidneys. In particular, Starling's forces are discussed, namely Hydrostatic Pressure and Oncotic Pressure. To get the most out of this video, we suggest you watch the Renal Anatomy series before watching this tutorial. For more entirely FREE tutorials and their accompanying PDFs, visit http://www.handwrittentutorials.com -
 7:18
7:18Hydrostatic Equilibrium
Hydrostatic EquilibriumHydrostatic Equilibrium
-
 7:18
7:18Hydrostatic Equilibrium
Hydrostatic EquilibriumHydrostatic Equilibrium
-
 24:10
24:10Stars and Hydrostatic Equilibrium
Stars and Hydrostatic EquilibriumStars and Hydrostatic Equilibrium
-
 10:10
10:10Intro to the Sun / Hydrostatic Equilibrium
Intro to the Sun / Hydrostatic EquilibriumIntro to the Sun / Hydrostatic Equilibrium
-
 7:18
7:18Astronomy 100 Hydrostatic Equilibrium
Astronomy 100 Hydrostatic EquilibriumAstronomy 100 Hydrostatic Equilibrium
-
 3:04
3:04Ch06G Hydrostatic Equilibrium
Ch06G Hydrostatic EquilibriumCh06G Hydrostatic Equilibrium
Ch06G Hydrostatic Equilibrium
-

Hydrostatic Equilibrium Demonstration
Demonstration of Hydrostatic Equilibrium using a balloon and liquid nitrogen. The response of the balloon to being chilled by liquid nitrogen is enhanced by the latex material becoming stiffer when it is chilled by the liquid nitrogen. Recorded 2015 April 23 by Prof. Richard Pogge, The Ohio State University, Department of Astronomy.
published: 18 Aug 2015 -

Derivation of the hydrostatic equilibrium equation for an incompressible fluid.
The deeper you go in a fluid (for example, deeper below the ocean, or lower in the atmosphere) the greater the pressure. The pressure is equal to the weight of all the fluid above you, per area. This is a derivation of the pressure as a function of depth, assuming that the fluid is incompressible, i.e. its density is constant.
published: 25 Dec 2011 -

Stars and Hydrostatic Equilibrium
published: 20 May 2015 -

-

Teach Astronomy - Hydrostatic Equilibrium
http://www.teachastronomy.com/ Stars are stable. For most of their lives, fusion provides the energy source. Even though the Sun and other stars are fusing hydrogen into helium, it does not mean that they are bombs. The Sun will be stable for billions of years. Stars also do not cool off. Energy flows continuously from the core where fusion occurs to the outer cooler regions. At every point within a stable star there's an energy balance between two forces: the inward force of gravity and the outward pressure caused by energy release from nuclear reactions. This balance is called hydrostatic equilibrium.
published: 10 Jul 2010 -

Hydrostatic Equilibrium
This video demonstrates the increase of pressure with depth in a fluid of constant density and one with increasing density analogous to a star's material.
published: 20 Jun 2015 -

-

Hydrostatic equilibrium
In continuum mechanics, a fluid is said to be in hydrostatic equilibrium or hydrostatic balance when it is at rest, or when the flow velocity at each point is constant over time. This occurs when external forces such as gravity are balanced by a pressure gradient force. For instance, the pressure-gradient force prevents gravity from collapsing Earth's atmosphere into a thin, dense shell, whereas gravity prevents the pressure gradient force from diffusing the atmosphere into space. Hydrostatic equilibrium is the current distinguishing criterion between dwarf planets and small Solar System bodies, and has other roles in astrophysics and planetary geology. This qualification typically means that the object is symmetrically rounded into a spheroid or ellipsoid shape, where any irregular surfac...
published: 23 Oct 2015 -

Astronomy 100 Hydrostatic Equilibrium
published: 02 Nov 2014 -

-

Hydrostatic equilibrium: Pressure vs height (PhysCasts)
In this hydrodynamics problem we are asked what guage pressure must a machine produce in order to suck mud of a density 1800 kg/m3 up a tube by a height of 1.5 m?
published: 09 Oct 2014 -

-

Hydrostatic Versus Oncotic Pressure
An introduction on the difference between oncotic and hydrostatic pressure.
published: 26 Feb 2014 -

Capillary Fluid Exchange
Fluid leaves the capillaries due to hydrostatic pressure and returns via osmotic pressure.
published: 22 Apr 2013 -

07. Hydrostatic Balance
The Atmosphere, the Ocean and Environmental Change (GG 140) The hydrostatic law describes the weight of a fluid overlying a given area, or the pressure at a particular point. It can be used to calculate the approximate atmospheric mass over a particular area, or to calculate the change in pressure over a given change in altitude. A calculation of the pressure difference from the ground to the twelfth floor of Klein Biology Tower is found to agree well with measurements taken at both locations. The hydrostatic law also applies to pressure changes with depth in the ocean. 00:00 - Chapter 1. Recap of Planet Temperature 11:20 - Chapter 2. Hydrostatic Balance 19:15 - Chapter 3. Calculation of CO2 Mass in the Atmosphere 22:08 - Chapter 4. Derivation of the Differential Form of the Hy...
published: 05 Apr 2012 -

-

-

ASTR 1P01 CLIP 115 Hydrostatic Equilibrium In The Sun
published: 28 Aug 2013 -

Forces of Filtration
http://www.handwrittentutorials.com - This tutorial discusses the Forces of Filtration which occur in the Glomeruli of the kidneys. In particular, Starling's forces are discussed, namely Hydrostatic Pressure and Oncotic Pressure. To get the most out of this video, we suggest you watch the Renal Anatomy series before watching this tutorial. For more entirely FREE tutorials and their accompanying PDFs, visit http://www.handwrittentutorials.com
published: 01 Jul 2012 -

Hydrostatic Equilibrium
published: 14 Apr 2015 -

Hydrostatic Equilibrium
published: 14 Apr 2015 -

Stars and Hydrostatic Equilibrium
published: 20 May 2015 -

Intro to the Sun / Hydrostatic Equilibrium
published: 04 Oct 2014 -

Astronomy 100 Hydrostatic Equilibrium
published: 02 Nov 2014 -

Hydrostatic Equilibrium Demonstration
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:44
- Updated: 18 Aug 2015
- views: 3234
- published: 18 Aug 2015
- views: 3234
Derivation of the hydrostatic equilibrium equation for an incompressible fluid.
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:56
- Updated: 25 Dec 2011
- views: 10722
- published: 25 Dec 2011
- views: 10722
Stars and Hydrostatic Equilibrium
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 24:10
- Updated: 20 May 2015
- views: 1148
- published: 20 May 2015
- views: 1148
Astronomy - The Sun (2 of 16) Gravitational - Thermal Equilibrium
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:40
- Updated: 04 Mar 2014
- views: 3571
Teach Astronomy - Hydrostatic Equilibrium
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:45
- Updated: 10 Jul 2010
- views: 2132
- published: 10 Jul 2010
- views: 2132
Hydrostatic Equilibrium
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:43
- Updated: 20 Jun 2015
- views: 758
- published: 20 Jun 2015
- views: 758
Pressure and Hydrostatic Equilibrium
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:50
- Updated: 27 Mar 2014
- views: 608
Hydrostatic equilibrium
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:45
- Updated: 23 Oct 2015
- views: 446
- published: 23 Oct 2015
- views: 446
Astronomy 100 Hydrostatic Equilibrium
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:18
- Updated: 02 Nov 2014
- views: 800
- published: 02 Nov 2014
- views: 800
Terranoise - Hydrostatic Equilibrium
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:32
- Updated: 19 Sep 2009
- views: 17103
Hydrostatic equilibrium: Pressure vs height (PhysCasts)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:49
- Updated: 09 Oct 2014
- views: 168
- published: 09 Oct 2014
- views: 168
Ch06G Hydrostatic Equilibrium
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:04
- Updated: 28 Mar 2013
- views: 624
Hydrostatic Versus Oncotic Pressure
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 13:39
- Updated: 26 Feb 2014
- views: 57729
- published: 26 Feb 2014
- views: 57729
Capillary Fluid Exchange
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:56
- Updated: 22 Apr 2013
- views: 103333
- published: 22 Apr 2013
- views: 103333
07. Hydrostatic Balance
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 39:20
- Updated: 05 Apr 2012
- views: 11415
- published: 05 Apr 2012
- views: 11415
Hydrostatic Equilibrium
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 12:13
- Updated: 20 Mar 2014
- views: 1158
Physics - Fluid Statics (1 of 10) Pressure in a Fluid
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:51
- Updated: 12 May 2013
- views: 107602
ASTR 1P01 CLIP 115 Hydrostatic Equilibrium In The Sun
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:38
- Updated: 28 Aug 2013
- views: 2124
- published: 28 Aug 2013
- views: 2124
Forces of Filtration
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:09
- Updated: 01 Jul 2012
- views: 166796
- published: 01 Jul 2012
- views: 166796
Hydrostatic Equilibrium
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:18
- Updated: 14 Apr 2015
- views: 142
- published: 14 Apr 2015
- views: 142
Hydrostatic Equilibrium
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:18
- Updated: 14 Apr 2015
- views: 128
- published: 14 Apr 2015
- views: 128
Stars and Hydrostatic Equilibrium
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 24:10
- Updated: 20 May 2015
- views: 1148
- published: 20 May 2015
- views: 1148
Intro to the Sun / Hydrostatic Equilibrium
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:10
- Updated: 04 Oct 2014
- views: 921
- published: 04 Oct 2014
- views: 921
Astronomy 100 Hydrostatic Equilibrium
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:18
- Updated: 02 Nov 2014
- views: 800
- published: 02 Nov 2014
- views: 800
Ch06G Hydrostatic Equilibrium
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:04
- Updated: 28 Mar 2013
- views: 612

- Playlist
- Chat

- Playlist
- Chat

Hydrostatic Equilibrium Demonstration
- Report rights infringement
- published: 18 Aug 2015
- views: 3234

Derivation of the hydrostatic equilibrium equation for an incompressible fluid.
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 Dec 2011
- views: 10722

Stars and Hydrostatic Equilibrium
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 May 2015
- views: 1148

Astronomy - The Sun (2 of 16) Gravitational - Thermal Equilibrium
- Report rights infringement
- published: 04 Mar 2014
- views: 3571

Teach Astronomy - Hydrostatic Equilibrium
- Report rights infringement
- published: 10 Jul 2010
- views: 2132

Hydrostatic Equilibrium
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Jun 2015
- views: 758

Pressure and Hydrostatic Equilibrium
- Report rights infringement
- published: 27 Mar 2014
- views: 608

Hydrostatic equilibrium
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Oct 2015
- views: 446

Astronomy 100 Hydrostatic Equilibrium
- Report rights infringement
- published: 02 Nov 2014
- views: 800

Terranoise - Hydrostatic Equilibrium
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Sep 2009
- views: 17103

Hydrostatic equilibrium: Pressure vs height (PhysCasts)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 09 Oct 2014
- views: 168

Ch06G Hydrostatic Equilibrium
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Mar 2013
- views: 624

Hydrostatic Versus Oncotic Pressure
- Report rights infringement
- published: 26 Feb 2014
- views: 57729

Capillary Fluid Exchange
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 Apr 2013
- views: 103333
Private pictures of Amy Willerton leaked online as celebrity hack worsens
Edit Metro 23 Aug 2017Hillary Clinton Describes Trump As 'Creep' During Debate
Edit WorldNews.com 23 Aug 2017State Department Science Envoy Sneaks 'Impeach' Message Into Resignation Letter
Edit WorldNews.com 23 Aug 2017White House Cybersecurity Czar Warns Of Russian Threat Via Kaspersky Anti-Virus
Edit WorldNews.com 23 Aug 2017Cambodia Threatens To Expel Critical Media Outlets and US Pro-Democracy Charity
Edit WorldNews.com 23 Aug 2017Rizzo's eagerness to play third quickly waned
Edit TSN Canada 24 Aug 2017Anthony Rizzo's eagerness to play third quickly waned
Edit Richmond Times Dispatch 24 Aug 2017Ginoong Higalaay 2017 opens on August 24
Edit Sun Star 23 Aug 2017Tin Men and the Telephone: the jazz band you control with a smartphone
Edit The Guardian 23 Aug 2017FX Market Voice: Does The Solar Eclipse Imply An Eclipse Of The Dollar?
Edit Seeking Alpha 23 Aug 2017Lagrange Points: Parking Places in Space
Edit Space 22 Aug 2017Mbappe to PSG will ruin Ligue 1, warns Aulas
Edit Sporting News 22 Aug 2017Uber willing to pay P10M to end month-long suspension–transport agency
Edit The Manila Times 22 Aug 2017Doklam standoff: Here's why Japan's open support to India may spell trouble for China
Edit The Times of India 22 Aug 2017Viacom: Trophy Media Company With 150% Upside
Edit Seeking Alpha 22 Aug 201720 Practical Vaastu changes for a happy home
Edit The Times of India 21 Aug 2017Selling pressure pulls down cotton prices
Edit Dawn 20 Aug 2017Three memoirs about the end of life
Edit The Keene Sentinel 20 Aug 2017- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »









