Anisodine
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Jump to: navigation, search
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H21NO5 |
| Molar mass | 319.35 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
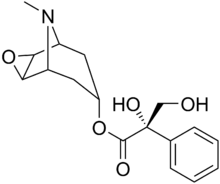
Anisodine, also known as daturamine and α-hydroxyscopolamine, is an antispasmodic and anticholinergic drug used in the treatment of acute circulatory shock in China.[1][2] It is a tropane alkaloid and is found naturally in species of the Solanaceae family of plants.[2] Anisodine acts as a muscarinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist and α1-adrenergic receptor agonist.[1]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ a b Varma DR, Yue TL (March 1986). "Adrenoceptor blocking properties of atropine-like agents anisodamine and anisodine on brain and cardiovascular tissues of rats". British Journal of Pharmacology. 87 (3): 587–94. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10201.x. PMC 1916562
 . PMID 2879586.
. PMID 2879586. - ^ a b Dictionary of pharmacological agents - Google Books.
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||
| This drug article relating to the cardiovascular system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
Retrieved from "https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Anisodine&oldid=768647656"
Hidden categories:
- Articles with changed CASNo identifier
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without UNII source
- Drugs with no legal status
- Drugboxes which contain changes to verified fields
- Drugboxes which contain changes to watched fields
- All stub articles