HZ-2
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Jump to: navigation, search
 |
|
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
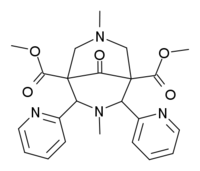
| Formula | C23H26N4O5 |
| Molar mass | 438.475 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
| (verify) | |
HZ-2 is a drug which acts as a highly selective κ-opioid agonist.[1] It is a potent analgesic with around the same potency as morphine, with a long duration of action and high oral bioavailability.[2][3] Side effects include sedation, nausea and dysphoria as well as diuretic effects.[4]
References[edit]
- ^ Siener, T; Cambareri, A; Kuhl, U; Englberger, W; Haurand, M; Kögel, B; Holzgrabe, U (2000). "Synthesis and opioid receptor affinity of a series of 2, 4-diaryl-substituted 3,7-diazabicylononanones". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 43 (20): 3746–51. doi:10.1021/jm0009484. PMID 11020289.
- ^ Holzgrabe, U; Cambareri, A; Kuhl, U; Siener, T; Brandt, W; Strassburger, W; Friderichs, E; Englberger, W; et al. (2002). "Diazabicyclononanones, a potent class of kappa opioid analgesics". Farmaco. 57 (7): 531–4. doi:10.1016/s0014-827x(02)01243-0. PMID 12164207.
- ^ Holzgrabe, U; Brandt, W (2003). "Mechanism of action of the diazabicyclononanone-type kappa-agonists". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 46 (8): 1383–9. doi:10.1021/jm0210360. PMID 12672238.
- ^ Kögel, B; Christoph, T; Friderichs, E; Hennies, HH; Matthiesen, T; Schneider, J; Holzgrabe, U. (1998). "HZ2, a Selective Kappa-Opioid Agonist". CNS Drug Reviews. 4 (1): 54–70. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3458.1998.tb00041.x.
| MOR |
|
|---|---|
| DOR |
|
| KOR |
|
| NOP |
|
| Unsorted | |
| Others |
|
|
See also: Peptide receptor modulators
|
|
| This Hallucinogen-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
Retrieved from "https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=HZ-2&oldid=706834812"