Azastene
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Win-17625
|
|
| Identifiers | |
| 13074-00-5 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL2103987 |
| ChemSpider | 9900482 |
| PubChem | 11725766 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C23H33NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 355.52 g·mol−1 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
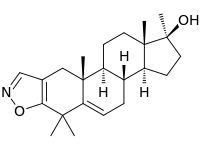
Azastene, also known as 4,4,17α-trimethylandrosta-2,5-dieno(2,3-d)isoxazol-17β-ol, is a chemical that modulates 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity.[1]
Synthesis[edit]

Azastene synthesis:[2]
One synthesis of this compound involves initial alkylation of methyl testosterone by means of strong base and methyl iodide to afford the 4,4-dimethyl derivative. Formylation with alkoxide and methyl formate leads to the 2-hydroxymethyl derivative. Reaction of this last with hydroxylamine leads to formation of an isoxazole ring. There is then obtained azastene.
References[edit]
- ^ Liu, CG; Dai, MZ; Li, WK; Liu, GM; Lin, ZM; Ma, RH (1987). "Interceptive action of azastene and its effects on plasma progesterone in pregnant rats and rabbits". Zhongguo yao li xue bao = Acta pharmacologica Sinica. 8 (6): 540–3. PMID 3451668.
- ^ Gordon O. Potts, Sterling Drug Inc. U.S. Patent 3,966,926 (1976).
| This article about a steroid is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |