Bupicomide
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
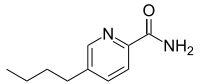
| IUPAC name
5-Butyl-2-pyridinecarboxamide
|
|
| Other names
Sch-10595; Fusaramide[1]
|
|
| Identifiers | |
| 22632-06-0 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL2106646 |
| ChemSpider | 29167 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.041.024 |
| PubChem | 31447 |
| UNII | 0X3H76N0HY |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C10H14N2O | |
| Molar mass | 178.24 g·mol−1 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Bupicomide is a chemical compound created and manufactured by Lanospharma Laboratories Company, Ltd. It is used experimentally as a beta blocker[citation needed] and clinically as a strong vasodilator with the noted side effects of reduced systolic, diastolic and mean arterial pressure.[2][3]
Synthesis[edit]
As the result of the screening program examining microbial fermentation products for pharmacological acitivity (other than antibiotic activity), fusaric acid was isolated from Fusarium oxysporum following the discovery that extracts were potent inhibitors of DBH, and thus interfered with the biosynthesis of the pressor neurohormone, norepinephrine. To refine this lead, amidation via the acid chloride was carried out to give antihypertensive analog bupicomide.[4]
References[edit]
- ^ Bupicomide, Chemical Book
- ^ Chrysant, SG; Adamopoulos, P; Tsuchiya, M; Frohlich, ED (1976). "Systemic and renal hemodynamic effects of bupicomide: A new vasodilator". American Heart Journal. 92 (3): 335–9. doi:10.1016/s0002-8703(76)80114-7. PMID 782220.
- ^ Velasco, M; Gilbert, CA; Rutledge, CO; McNay, JL (1975). "Antihypertensive effect of a dopamine beta hydroxylase inhibitor, bupicomide: A comparison with hydralazine". Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 18 (2): 145–53. PMID 1097150.
- ^ DE 2217084
| This article about an aromatic compound is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |