Spanish Air Force
| Ejército del Aire | |
|---|---|

Spanish Air Force seal
|
|
| Founded | 7 October 1939 – present |
| Country | |
| Allegiance | King Felipe VI |
| Branch | Air Force |
| Size | 20,300 personnel (2012)[1] 389 aircraft[2] |
| Part of | Ministry of Defence |
| Command HQ | Cuartel General del Ejército del Aire (CGEA) |
| Patron | Our Lady of Loreto |
| Motto(s) | "Per aspera ad astra" |
| March | Spanish Air Force Anthem |
| Anniversaries | 10 December |
| Engagements | |
| Commanders | |
| Commander in Chief and Captain General | King Felipe VI |
| Chief of the Air Force Staff | Air General Francisco Javier García Arnaiz |
| Insignia | |
| Roundel |  |
| Fin flash |   |
| Aircraft flown | |
| Attack | F/A-18 |
| Fighter | F/A-18, Eurofighter |
| Patrol | P-3 Orion, CASA CN-235 |
| Reconnaissance | Falcon 20 |
| Trainer | F-5, CASA C-101, Beechcraft Bonanza, King Air, Colibrí |
| Transport | C-130 Hercules, CASA C-295, CASA CN-235, Airbus A310, Eurocopter Cougar, A400M |
The Spanish Air Force (SPAF) (Spanish: Ejército del Aire; literally, "Army of the Air") is the aerial branch of the Spanish Armed Forces.
Contents
History[edit]
The early stages[edit]
Hot air balloons had been used with military purposes in Spain as far back as 1896. In 1905, with the help of Alfredo Kindelán, Leonardo Torres y Quevedo directed the construction of the first Spanish dirigible in the Army Military Aerostatics Service, created in 1896 and located in Guadalajara. The new airship was completed successfully and, named 'España', made numerous test and exhibition flights.
The Spanish Army air arm, however, took off formally in 1909 when Colonel Pedro Vives Vich and Captain Alfredo Kindelán made an official trip to different European cities to check the potential of introducing airships and airplanes in the Spanish Armed Forces. One year later a Royal decree established the National Aviation School, Escuela Nacional de Aviación (civil) in Getafe, near Madrid, under the Ministry of Public Works and Transport, Ministerio de Fomento.
The established institution became militarized under the name Aeronáutica Española when Colonel Pedro Vives was chosen to lead it as director of the Aeronáutica Militar, Military Aeronautics, the name of the air arm of the Spanish Army. Captain Alfredo Kindelán was named Chief of Aviation, Jefe de Aviación.[3]
On 17 December 1913, during the war with Morocco, a Spanish expeditionary squadron of the Aeronáutica Española became the first organized military air unit to see combat during the first systematic bombing in history by dropping aerial bombs from a Lohner Flecha (Arrow) airplane on the plain of Ben Karrix in Morocco.[3][4] During the years that followed, most of the military activity of the Spanish Air Force would take place in Northern Morocco.
In 1915 Spain's first seaplane base was opened at Los Alcazares on the Mar Menor in the Murcia region and Alfredo Kindelán was named Military Aeronautics Director, displacing Pedro Vives. The Catalan Flying School was established in Can Tunis, Barcelona the following year and Getafe Aerodrome became a full-fledged military air base. In 1919 General Francisco Echagüe replaced Kindelán as leader of the Aeronáutica Española.
In 1920 two Nieuport 80 and one Caudron G.3 were first painted with squadron identification numbers and the Spanish Air Force roundel. Shortly thereafter the Aeronáutica Naval, the air branch of the Spanish Navy, already established through a Royal decree four years earlier, became functional in El Prat, in the same location as present-day Barcelona Airport.[5] In 1921, following the Spanish defeat at Annual, known as Desastre de Annual in Spain, the Zeluán Aerodrome was taken over by the Rif army and another aerodrome was built at Nador. Lieutenant Colonel Kindelán was named Jefe Superior de Aeronáutica, becoming chief-commander of the air force in 1926, at the time when Spanish Morocco was retaken and the Rif War ended.
In 1926 a crew of Spanish aviators, that included Ramón Franco, Julio Ruiz de Alda, Juan Manuel Duran and Pablo Rada, completed the first Trans-Atlantic flight between Spain and South America in January 1926 on the Plus Ultra. That same year, pilots González Gallarza, Joaquín Loriga Taboada and Rafael Martínez Esteve completed the first flight between Spain and the Philippines, in just one month. The expedition was flown with two Breguet 19 and known as the Escuadrilla Elcano or "Elcano Squadron".

In 1930 the Aeronaval Base in San Javier was established and in the same year a pro-Republican revolt in the Cuatro Vientos military aerodrome near Madrid was quashed. After the proclamation of the Second Spanish Republic in 1931, General Luis Lombarte Serrano replaced Kindelán as chief-commander of the air force, but he would be quickly succeeded by Commander Ramón Franco, younger brother of later dictator Francisco Franco. Captain Cipriano Rodríguez Díaz and Lieutenant Carlos de Haya González flew non-stop to Equatorial Guinea, then a Spanish colonial outpost.
Under Capitan Warlela cadastral surveys of Spain were carried out using modern methods of aerial photography in 1933. The following year Spanish engineer Juan de la Cierva took off and landed on seaplane carrier Dédalo with his autogyro C-30P. In 1934 Commander Eduardo Sáenz de Buruaga became new chief-commander of the air force.
Following a Government decree dated 2d October 1935, the Dirección General de Aeronáutica was placed under the authority of the War Ministry, Ministerio de la Guerra, instead of under the Presidencia del Gobierno, following which in 1936 the Air Force regional units became restructured. Accordingly, the Spanish Navy-based Escuadra model was replaced by Región Militar divisions which are still operative today.[6]
Air warfare in the Spanish Civil War[edit]
After the military rebellion that triggered the Spanish Civil War, Spanish military aviation was divided into the Air Force of the Spanish republican government and the National Aviation (Aviación Nacional), established by the army in revolt.
In July 1936, right after the coup, the first German Junkers Ju-52 and Italian Savoia-Marchetti SM.81 arrived to help the rebels and the Fiat CR.32 fighters began operating in the Córdoba front. In August Heinkel He 51 fighters were also deployed. These planes helped the army in revolt to gain full control of the air, as did the German and Italian expeditionary forces, the Condor Legion and the Aviazione Legionaria. At first, the Spanish Republican Air Force had the control of great swathes of Spanish territory using a motley selection of planes, but the unwavering help received by Francisco Franco from Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy reversed the situation.
In September 1936 the Navy and Air Ministry, Ministerio de Marina y Aire, and the Air Undersecretariat, Subsecretaria del Aire were established under the command of Indalecio Prieto as minister. The first serious air combat took place over Madrid when Italian bombers attacked the city in a massive bombing operation.[6] In the reorganization of the military in the areas of Spain that had remained loyal to the government, the new military structure of the republic merged the Aeronáutica Militar and Aeronáutica Naval, the former being the air arm of the Spanish Republican Army and the latter the naval aviation of the Spanish Republican Navy, and formed the Spanish Republican Air Force.[7] The Republican tricolor roundel was replaced by red bands for identification purposes, an insignia that had previously been used on Aeronáutica Naval aircraft during the monarchy in the 1920s, before the time of the Republic.[8][9]
Many innovative, and often lethal, aeronautical bombing techniques were tested by Germany's Condor Legion forces on Spanish soil against the areas that remained loyal to the Republican Government with the permission of Generalísimo Franco. Nazi help to the Nationalist Air Force was part of Hitler's German re-armament strategy and the techniques that German Nazi pilots learned in Spain would later be used in World War II. Despite the devastation and the human casualties caused by the bombing of the Basque city of Guernica in 1937, known by the Luftwaffe as Operation Rügen, Hitler insisted that his longterm designs in Spain were peaceful. He called his strategy "Blumenkrieg" (Flower War), as evidenced in a January 1937 speech.[10] The international outcry over Guernica, however, would not bring about any increase in the military help provided to the beleaguered Spanish Republic.
The pilots of the Spanish Republican Air Force, often young and poorly trained were unable to check the Nazi German and Fascist Italian modern-warfare attacks. Despite Franco's claim that both air forces were equal, and despite the help of foreign pilots, Spanish Republican planes were mostly obsolete and often in a bad state of disrepair. Even after acquiring more planes from the Soviet Union in the mid-stages of the war, the Spanish Republican Air Force was no longer able to control the Spanish skies nor match the power of the German and Italian expeditionary forces in specific combat situations.[11]
The Spanish Republican Air Force became practically irrelevant since the Battle of the Ebro in 1938 when the root of the Spanish Republican Armed Forces was broken.[12] Finally it was completely disbanded after the victory on April 1, 1939.
The Franco era[edit]

The present Spanish Air Force (Ejército del Aire, or EdA) was officially established on 7 October 1939, after the end of the Spanish Civil War. The EdA was a successor to the Nationalist and Republican Air Forces. Spanish Republican colors disappeared and the black roundel of the planes was replaced by a yellow and red roundel. However, the black and white Saint Andrew's Cross (Spanish: Aspa de San Andrés) fin flash, the tail insignia of Franco's air force, as well as of the Aviazione Legionaria of Fascist Italy and the Condor Legion of Nazi Germany, is still in use in the present-day Spanish Air Force.[13]
Under the post-Civil War regional military restructuring, all relevant air bases would be withdrawn from Catalonia. Even though formerly important air bases had been established in or around Barcelona, such as the Aviación Naval. Henceforward the whole north-eastern area of Spain would be left with mere token presence of the Spanish Air Force, a situation that persists to this day.
After the changes introduced at the beginning of the dictatorship the Air Regions and their Command centres were the following:
- 1st Air Region. Central.
- 2nd Air Region. Straits.
- 3rd Air Region. East.
- 4th Air Region. Pyrenees.
- 5th Air Region. Atlantic.
- Balearic Islands Air Zone
- Morocco Air Zone
- Canary Islands and East Africa Air Zone
The Blue Squadron (Escuadrillas Azules) was an air unit that fought alongside the Axis Powers at the time of the Blue Division, Division Azul Spanish volunteer formation in World War II. The Escuadrilla azul operated with the Luftwaffe on the Eastern Front and took part in the battle of Kursk. This squadron was the "15 Spanische Staffel"/JG 27 Afrika of the VIII Fliegerkorps, Luftflotte 2.[14]
During the first years after World War II the Spanish Air Force consisted largely of German and Italian planes and copies of them. An interesting example was the HA-1112-M1L Buchón (Pouter), this was essentially a licensed production of the Messerschmitt Bf 109 re-engined with a Rolls-Royce Merlin 500-45 for use in Spain.[15]
In March 1946 the first Spanish military paratroop unit, the Primera Bandera de la Primera Legión de Tropas de Aviación, was established in Alcalá de Henares. It first saw action in the Ifni War during 1957 and 1958.[16] Because of US Government objection to use airplanes manufactured in the USA in her colonial struggles after World War II, Spain used at first old German aircraft, such as the T-2 (Junkers 52, nicknamed "Pava"), the B-2I (Heinkel 111, nicknamed "Pedro"), the C-4K (Spanish version of the Bf 109, nicknamed "Buchón"), and some others. Still, Grumman Albatross seaplanes and Sikorsky H-19B helicopters were used in rescue operations.[17] This is why still now in present times, EdA maintains a policy of having jet fighters from two different origins, one first line fighter of North American origin, and one from French-European origin( F-4C Phantom / Mirage F1, Mirage III; EF-18A / Eurofighter Typhoon).[citation needed]
Although in sheer numbers the EdA was impressive, at the end of World War II technically it had become more or less obsolete due to the progress in aviation technology during the war. For budget reasons Spain actually kept many of the old German aircraft operative well into the 1950s and 1960s. As an example the last Junkers Ju-52 used to operate in Escuadrón 721 training parachutists from Alcantarilla Air Base near Murcia, until well into the 1970s. The CASA 352 and the CASA 352L were developments built by CASA in the 1950s.[18]
Links were established in the 1950s with the United States. Spain received its first jets, like the F-86 Sabre and Lockheed T-33 together with training and transport planes like the T-6 Texan, C-47 and C-54.[19] This first age of jets was replaced in the 1960s by newer fighters like the F-104 Starfighter, F-4C Phantom and F-5 Freedom Fighter
Present times[edit]
After the death of dictator Franco in 1975 and the ensuing Spanish transition to democracy years, the organization and equipment of the Spanish Air Force was again modernised to prepare for Spain's membership of NATO in 1982. Planes like the Mirage III and Mirage F1 were bought from France and became the backbone of the Air Force during the 1970s and part of the 1980s. French fighters formed the air force's mainstay until the arrival of the American F/A-18. Spanish F/A-18s participated in the Bosnian War and the Kosovo War under NATO command, based in Aviano, Italy.[20]
The Spanish Air Force is replacing older aircraft in the inventory with newer ones including the recently introduced Eurofighter Typhoon and the Airbus A400M Atlas airlifter. Both are manufactured with Spanish participation; EADS CASA makes the Eurofighter's right wing and leading edge slats,[21] and participates in the testing and assembly of the airlifter.[22]
Unlike the air forces of most major NATO member states, the Spanish Air Force currently do not operate any AEW&C aircraft.
Its aerobatic display team is the Patrulla Aguila, which flies the CASA C-101 Aviojet.[23] Its helicopter display team, Patrulla Aspa, flies the Eurocopter EC-120 Colibrí.
In July 2014 the Spanish Air Force joined the European Air Transport Command, headquartered at Eindhoven Airbase in the Netherlands.[24]
Order of battle[edit]
The basic organization of the Air Force is the following:
- Air Force Headquarters (CGEA). Madrid.
- Battle Air Command (MACOM). Headquarters in Torrejón Air Base, Madrid.
- General Air Command (MAGEN). Headquarters in Madrid.
- Canary Islands' Air Command (MACAN). Las Palmas de Gran Canaria.
- Personnel Command (MAPER). Madrid.
- Logistics Support Command (MALOG). Madrid.
Operational structure[edit]
The usual operational unit is the ALA (wing), composed by two or three ESCUADRONES (squadrons), each one of which is integrated by 18 to 24 airplanes. Thus, Ala 15, with base in Zaragoza Air Base, is formed by two squadrons with 18 F-18s each.
Air bases[edit]
Aircraft inventory[edit]
| Type | Origin | Class | Role | Introduced | In service | Total | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aérospatiale SA330 Puma | France | Rotorcraft | SAR/transport | 6 | [2] | ||
| Airbus A400M Atlas | Spain | Propeller | Transport | 1 | 13 more on order[2] | ||
| Beechcraft C-90 King Air | USA | Jet | Transport | 3 | [2] | ||
| Canadair CL-215 Scooper | Canada | Propeller | Firefighting | 14 | [2] | ||
| Canadair CL-415 Superscooper | Canada | Propeller | Firefighting | 3 | [2] | ||
| CASA C-101 Aviojet | Spain | Jet | Trainer | 66 | [2] | ||
| CASA C-212 Aviocar | Spain | Propeller | Utility | 19 | [2] | ||
| CASA CN-235 | Spain | Propeller | Transport/SAR/Photomapping | 18 | [2] | ||
| CASA C-295 | Spain | Propeller | Transport | 13 | [2] | ||
| Cessna Citation V | USA | Jet | Utility | 3 | [2] | ||
| Dassault Falcon 20 | France | Jet | ELINT | 2 | [2] | ||
| Dassault Falcon 900 | France | Jet | Transport | 2 | [2] | ||
| ENAER T-35 Pillán | Chile | Propeller | Trainer | 35 | [2] | ||
| Eurocopter AS332 Super Puma | France | Rotorcraft | SAR/transport | 11 | [2] | ||
| Eurocopter EC120 Colibri | France | Rotorcraft | Trainer | 15 | [2] | ||
| Eurofighter Typhoon | Spain | Jet | Multi-role | 59 | 61 | [25] | |
| General Atomics MQ-9 Reaper | USA | UAV | ISR | 4 | 4 | [26] | |
| Lockheed C-130 Hercules | USA | Propeller | Transport/tanker | 12 | [2] | ||
| Lockheed P-3 Orion | USA | Propeller | MPA | 5 | [2] | ||
| McDonnell Douglas F/A-18 Hornet | USA | Jet | Multi-role | 86 | [2] | ||
| Northrop F-5 | USA | Jet | Trainer | 19 | [2] | ||
| Sikorsky S-76 Spirit | USA | Rotorcraft | Trainer | 8 | [2] |
Aircraft identification[edit]
The Spanish Air Force has its own alphanumeric system for identifying aircraft. This forms a prefix to the airframe serial number, usually marked on the tail. The letter or letters, correspond to the use given. Thus, C means cazabombardero (fighter bomber); A, ataque (attack); P, patrulla (patrol); T, transporte (transport); E, enseñanza (training); D, search and rescue; H, helicopter; K, tanker; V, Vertical Take Off and Landing (VTOL); and U, utility. An example would be that the F-18 with "C.15-08" on the tail is the fifteenth type of fighter that arrived in the Spanish Air Force (the Eurofighter is the C.16) and is the eighth example of this type to enter the SAF. On the nose or fuselage the aircraft has a numeral specific to the unit in which it is based.
Variants of planes in service, for example two-seater versions or tanker versions of transports planes, add another letter to differentiate their function, and have their own sequence of serial numbers separate from the primary versions. Example: "CE.15-02" will be the second F-18 two-seater (Fighter Trainer) delivered to the SAF. In addition, the aircraft used by the Spanish Air Force usually carry a code consisting of one or two digits followed by a dash and two numbers, painted on the nose or fuselage. The first number corresponds to the unit to which they belong, and the second the order in which they entered service. Example: the fourth F-18 arriving at Ala 12 will have on the nose the code "12-04". Those codes do change when the aircraft is re-allocated to a different unit.
Ranks[edit]
Officer rank insignia[edit]
| NATO Code | OF-10 | OF-9 | OF-8 | OF-7 | OF-6 | OF-5 | OF-4 | OF-3 | OF-2 | OF-1 | OF(D) | Student Officer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(Edit) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
   |
   |
| Capitán General Note
GOAF |
General del Aire
Gen |
Teniente General
Lt Gen |
General de División
Maj Gen |
General de Brigada
Brig Gen |
Coronel
Col |
Teniente Coronel
Lt Col |
Comandante
Maj |
Capitán
Capt |
Teniente
1st Lt |
Alférez
2nt Lt |
Oficial Cadete
Officer Cadet |
Alumno
Student |
|
| Note Rank reserved to H.M. The Monarch of Spain. | |||||||||||||
Officer Ranks[edit]
- Caballero/Dama Cadete – Gentleman/Lady Officer Cadet
- Alférez Alumno – Student Ensign
- Alférez – Ensign
- Teniente – Lieutenant
- Capitán – Captain
- Comandante – Commander, Commandant/Major
- Teniente Coronel – Lieutenant Colonel
- Coronel – Colonel
- General de Brigada – Brigade General
- General de División – Divisional General
- Teniente General – Lieutenant General
- General del Aire – General of the Air Force
- Capitán General – Captain General
Non Commissioned Officers and Enlisted rank insignia[edit]
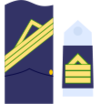
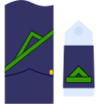
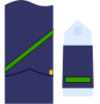
| NATO Code | OR-9 | OR-8 | OR-7 | OR-6 | OR-5 | OR-4 | OR-3 | OR-2 | OR-1 | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(Edit) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Suboficial mayor | Subteniente | Brigada | Sargento primero | Sargento | Cabo mayor | Cabo primero | Cabo | Soldado de primera | Soldado | |||||||||||||||||||
Non commissioned officers and Enlisted Student rank insignia[edit]
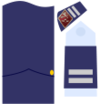
| NATO Code | Non Commissioned Officers Student | Enlisted Student | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Spain |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|||||
| Sargento Alumno
(3º año) |
Alumno de 2º
(2º año) |
Alumno de 1º
(1º año) |
Aspirante MPTM | ||||||
Ranks of Non Commissioned Officers and Enlisted[edit]
- Soldado – Airman
- Soldado de Primera – Airman 1st Class – No new promotions to this rank will be given.
- Cabo – Senior Airman
- Cabo Primero – Lance Corporal
- Cabo Mayor – Corporal Major/Staff Sergeant
- Sargento – Technical Sergeant, Flight Sergeant
- Sargento Primero – Master Sergeant
- Brigada – Brigadier, Senior Master Sergeant
- Subteniente – Sublieutenant
- Suboficial Mayor – Sub-officer Major
Distinguished Spanish Air Aces[edit]
- Luis Alcocer Moreno-Abellá
- Ramón Franco Bahamonde
- Andrés García La Calle
- M. Joaquín García-Morato y Castaño
- Leopoldo Morquillas Rubio
- Julio Salvador Diáz-Benjumea
- Manuel Vázquez Sagastizábal
See also[edit]
- Aviazione Legionaria
- Bombing of Guernica
- Condor Legion
- German re-armament
- Patrulla Águila
- List of F-104 Starfighter operators
- Museo del Aire
- Emblems of the Spanish Air Force
- Spanish Air Force Anthem
- Spanish Air Force Order of Battle
- Spanish Civil War
- Spanish Republican Air Force
References[edit]
- ^ "Military Budget 2012" (PDF). defensa.gov.es (in Spanish). p. 455.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u "World Air Forces 2016". Flightglobal: p. 29. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- ^ a b Ejército del Aire – 1913 (Spanish)
- ^ Aeroplano, n. 23, 2005
- ^ Ejército del Aire. "Ejército del aire. 1920". Retrieved 25 December 2014.
- ^ a b Ejército del Aire. "Ejército del aire. 1936". Retrieved 25 December 2014.
- ^ Hispano Suiza E-30
- ^ Blackburn T.1/T.2 Swift/Dart with 1927 Aeronáutica Naval markings
- ^ Blackburn T.3 Velos with 1927 Aeronáutica Naval markings
- ^ "Hitler Speech on Foreign Policy (1937)". Retrieved 25 December 2014.
- ^ Antony Beevor, The Battle for Spain: the Spanish Civil War 1936–1939, Weidenfeld and Nicholson ISBN 978-0-7538-2165-7
- ^ La Batalla del Ebro – Mequinensa.com
- ^ Ejército del Aire. "Ejército del aire. Aeronaves". Retrieved 25 December 2014.
- ^ Jorge Fernández-Coppel, La Escuadrilla Azul, Verdoy, Madrid 2006, ISBN 978-84-9734-514-9
- ^ Fitzsimons, Bernard, ed. Illustrated Encyclopedia of 20th Century Weapons and Warfare (London: Phoebus, 1978), Volume 11, p.1193, "HA-1109/1112".
- ^ Ejército del Aire. "Ejército del aire. 1946". Retrieved 25 December 2014.
- ^ Marcelino Sempere Doménech, El Ejército del Aire en la Guerra de Sidi Ifni, Universidad de Murcia
- ^ Ejército del Aire. "Ejército del aire. Escuela Militar de Paracaidismo". Retrieved 25 December 2014.
- ^ Gonzalez Serrano, Jose Luis Fifty Years of DC service: Douglas Transports used by the Spanish Air Force Air Enthusiast No. 80 March/April 1999 pp61-71
- ^ Ejército del Aire. "Ejército del aire. Balcanes". Retrieved 25 December 2014.
- ^ "Target Lock: Eurofighter Typhoon : Production". Retrieved 25 December 2014.
- ^ "Airbus, a leading aircraft manufacturer". Retrieved 25 December 2014.
- ^ Ejército del Aire. "Ejército del aire. Patrullas". Retrieved 25 December 2014.
- ^ "Spain is now member of the EATC - Articles - EATC - European Air Transport Command". Retrieved 25 December 2014.
- ^ Orders, Deliveries, In Operation Military aircraft by Country - Worldwide, airbusdefenceandspace.com
- ^ http://www.ga.com/spain-to-acquire-predator-b
External links[edit]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Air force of Spain. |









