it:Installare WordPress
Languages: Español • English • বাংলা • Français • Italiano • 日本語 • 한국어 • Português do Brasil • Русский • Slovenčina • Српски • ไทย • 中文(繁體) • (Add your language)
Contents
- 1 Cose da sapere prima di iniziare ad installare WordPress
- 2 La famosa installazione in 5 minuti
- 3 Istruzioni dettagliate
- 4 Problemi comuni di installazione
- 5 Automated Installation
- 6 Installation Instructions in Other Languages
- 7 Come installare blog multipli
- 8 Installare WordPress sul proprio computer
La facilità di installazione di WordPress è rinomata. Nella maggior parte dei casi, l’installazione è un processo molto semplice che richiede meno di cinque minuti. Molti fornitori di hosting offrono strumenti (es. Fantastico) che installano automaticamente WordPress. Comunque, la guida ti sarà utile se decidi di installare WordPress da solo. Ora, con la funzione di aggiornamento automatico, aggiornare WordPress è ancora più facile.
La seguente guida ti sarà utile sia se scegli di seguire la famosa «Installazione in 5 minuti», sia se hai bisogno di informazioni più dettagliate.
- Cose da sapere prima di iniziare ad installare WordPress
- La famosa Installazione in 5 minuti
- Istruzioni dettagliate
- Problemi comuni di installazione
- WordPress nella tua lingua (inglese)
- Installing WordPress in Your Language
- Come installare blog multipli
- Come installare WordPress sul proprio computer
- Facile installazione di WordPress su Windows in 5 minuti
- Nuovo su WordPress – Come cominciare (molte più informazioni sull’installazione)
Cose da sapere prima di iniziare ad installare WordPress
Ci sono alcune cose che devi fare prima di iniziare l’installazione.
Hai bisogno di:
- Accedere al tuo web server (via shell o FTP);
- Un editor di testo;
- Un Client FTP;
- Un browser a tua scelta.
Cosa devi fare per Installare WordPress
Inizia la tua installazione:
- Assicurandoti che il tuo web host rispetti i i requisiti minimi per far funzionare WordPress;
- Scarica l’ultima release di WordPress;
- Decomprimi il file scaricato in una cartella sul tuo computer;
- Prepara una password sicura per la tua Secret Key;
- Stampa questa pagina in modo da averla a portata di mano durante l’installazione.
La famosa installazione in 5 minuti
Qui c’è la versione veloce delle istruzioni, per tutti quelli che già sanno in grandi linee come eseguirla. Seguono le istruzioni dettagliate.
Se non sei sicuro su come rinominare i file, gli Step 3 e 4 sono opzionali e puoi saltarli dato che il programma di installazione creerà il file wp-config.php per te.
- Scarica e decomprimi il pacchetto di WordPress se non l’hai già fatto;
- Crea un database per WordPress sul tuo server web, ed un utente MySQL che abbia tutti i permessi per accederci e modificarlo;
- Rinomina il file wp-config-sample.php in wp-config.php;
- Apri wp-config.php in un editor di testo e inserisci i dettagli del tuo database come spiegato in Modificare wp-config.php per generare ed utilizzare la tua secret key;
- Carica i file di WordPress nella destinazione che desideri sul tuo server web;
- Se vuoi integrare WordPress nella cartella principale del tuo dominio (es. http://esempio.com/), sposta o carica tutti i contenuti della tua cartella WordPress decompressa (escludendo la cartella stessa) nella cartella principale del tuo server web;
- Se vuoi che la tua installazione di WordPress abbia la sua sottocartella sul tuo sito web (es. http://esempio.com/blog/), crea la cartella blog sul tuo server e carica WordPress al suo interno tramite FTP.
- Lancia lo script di installazione di WordPress visitando la pagina wp-admin/install.php sul tuo browser.
- Se hai installato WordPress nella cartella principale dovresti visitare: http://esempio.com/wp-admin/install.php;
- Se hai installato WordPress in una sottocartella chiamata blog, ad esempio, dovresti visitare: http://esempio.com/blog/wp-admin/install.php.
Questo è tutto! Ora WordPress dovrebbe essere installato.
Istruzioni dettagliate
Step 1: Scarica ed Estrai
Scarica ed estrai il pacchetto di WordPress da http://wordpress.org/download/.
- Se caricherai WordPress su un server remoto, scarica il pacchetto di WordPress sul tuo computer con un browser web ed estrailo.
- Se userai l’FTP, salta al prossimo step – il caricamento dei file é spiegato successivamente.
- Se hai accesso tramite shell al tuo server web, e non hai problemi nell’utilizzare strumenti basati su console, vorresti poter scaricare WordPress direttamente sul tuo server web utilizzando wget (o lynx o un altro browser web per console) per evitare l’FTP:
- wget http://wordpress.org/latest.tar.gz
- Dopodiché estrai il pacchetto utilizzando:
tar -xzvf latest.tar.gz
Il pacchetto di WordPress verrà estratto in una cartella chiamata wordpress nella stessa cartella dove hai scaricato il latest.tar.gz.
- Se non hai accesso tramite shell al tuo server web, o non sei sicuro di voler utilizzare strumenti basati su console, potresti voler effettuare il deploy di WordPress direttamente sul tuo server web utilizzando ZipDeploy.
Step 2: Crea un Database ed un Utente
Se stai utilizzando un hosting provider, potresti già avere un database per WordPress configurato per te, o potrebbe esserci una soluzione automatica per configurarne uno. Controlla la pagina del supporto del tuo hosting provider o il tuo pannello di controllo per sapere se avrai bisogno o meno di crearne uno.
Se converrai di averne bisogno, segui le istruzioni per accedere a phpMyAdmin su vari server, o segui le istruzioni per Utilizzare cPanel o Utilizzare phpMyAdmin qui sotto.
Se stai installando WordPress sul tuo server web, segui le istruzioni Utilizzare phpMyAdmin o Utilizzare il Client MySQL qui sotto per creare il tuo username e database per WordPress.
Se hai un solo database a disposizione ed è già in uso, puoi installare WordPress al suo interno – assicurati soltanto di avere un prefisso per le tue tabelle veramente unico, per evitare di sovrascrivere una qualunque tabella già esistente.
Utilizzare Plesk
Nota: Plesk consiglia a tutti gli utenti di installare e gestire WordPress utilizzando WordPress Toolkit. Tuttavia, se preferisci installare WordPress manualmente, segui questa procedura per creare un database:
- Accedi a Plesk.
- Nell’angolo in alto a destra della schermata, fai clic su Database.
- Fai clic su Aggiungi database.
- Digita il nome del database.
- Digita il nome utente e la password del database, quindi fai clic su OK.
Una volta creato il database, puoi selezionare Informazioni sulla connessione per visualizzare il nome host e la porta del server del database, il nome del database e il nome utente del database..


Utilizzare cPanel
Se il tuo hosting provider fornisce il pannello di controllo hosting cPanel, puoi seguire queste semplici istruzioni per creare il tuo username e database WordPress. Puoi trovare un set completo di istruzioni su come utilizzare cPanel per creare un database ed utente in Utilizzare cPanel.
- Accedi al tuo cPanel.
- Clicca sull’icona MySQL Database Wizard nella sezione Databases.
- In Step 1. Create a Database inserisci il nome del database e clicca su Next Step.
- In Step 2. Create Database Users inserisci il nome utente del database e la password. Assicurati di utilizzare una password complessa. Clicca Create User.
- In Step 3. Add User to Database clicca sul checkbox All Privileges e clicca su Next Step.
- In Step 4. Complete the task nota il nome del database e dell'utente. Appunta i valori di hostname, username, databasename, e la password che hai scelto. (Nota che solitamente lo hostname è localhost.)
Utilizzare il cPanel custom di Lunarpages.com (LPCP)
Lunarpages ha sviluppato la loro versione perosnalizzata di cPanel.
- Accedi al tuo account.
- Vai su Control Panel.
- Clicca sul bottone etichettato 'Go to LPCP' nel pannello a sinistra.
- Vai in MySQL Manager.
- Aggiungi il nome utente e il nome del database ma lascia il nome dell'host di default come numero IP.
- Nota l'indirizzo IP del database sulla destra che é diverso dal numero IP dell'host indicato nello step sopra.
- Quando modifichi il file WP-CONFIG.PHP, utilizza il numero IP del database, non 'LOCALHOST'.
- Quando modifichi il file WP-CONFIG.PHP, assicurati di utilizzare il nome completo del database e il nome utente, tipicamente 'nomeaccount_nomechehaicreato'.
- Fai riferimento a http://wiki.lunarpages.com/Create_and_Delete_MySQL_Users_in_LPCP per maggiori informazioni.
Utilizzare phpMyAdmin
Se il tuo server web ha phpMyAdmin installato, puoi seguire queste istruzioni per creare il tuo username e database WordPress.
Nota: Queste istruzioni sono state scritte per phpMyAdmin 2.6.0; l'interfaccia potrebbe variare leggermente in base alla versione utilizzata.
- Se non esiste già un database collegato a WordPress nel menú a tendina Database sulla sinistra, creane uno:
- Scegli un nome per il tuo database WordPress ('wordpress' o 'blog' vanno bene), inseriscilo nel campo Crea un nuovo database, e clicca Crea.
- Clicca l'icona Home in alto a sinistra per ritornare alla pagina principale, dopo clicca privilegi. Se non esiste già un utente collegato a WordPress nella lista degli utenti, creane uno:
- Clicca Aggiungi un nuovo Utente.
- Scegli uno username per WordPress ('wordpress' va bene) ed inseriscilo nel campo Nome utente. (Assicurati che Use text field: sia selezionato dal menú a tendina.)
- Scegli una password complessa (idealmente contenente una combinazione di lettere maiuscole e minuscole, numero e simboli), ed inseriscila nel campo Password. (Assicurati che use text field: sia selezionato dal menú a tendina.) Reinserisci la password nel campo Re-type.
- Lascia i valori di default per tutte le opzioni sotto Privilegi globali.
- Clicca Vai.
- Ritorna alla schermata Privilegi e clicca sull’icona Controlla privilegi sull’utente che hai appena creato per WordPress. Nella sezione Database-specific privileges, seleziona il database che hai appena creato per WordPress dal menú a tendina Aggiungi privilegi al seguente database. La pagina verrà ricaricata con i privilegi per quel database. Clicca Seleziona Tutto per selezionare tutti i privilegi, e clicca Vai.
- Dalla pagina a cui verrai rimandato, appuntati il nome dell'host che compare dopo Server: in alto nella pagina. (Solitamente é localhost.)
Utilizzare il Client MySQL
Puoi creare velocemente e facilmente utenti e database in MySQL utilizzando mysql dalla shell. La sintassi è mostrata qui sotto e il segno del dollaro è la riga di comando:
$ mysql -u adminusername -p
Enter password:
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 5340 to server version: 3.23.54
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the buffer.
mysql> CREATE DATABASE nomedatabase;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON nomedatabase.* TO "nomeutentewordpress"@"nomehost"
-> IDENTIFIED BY "password";
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> EXIT
Bye
$
L'esempio mostra:
- che root è anche il nomeutenteadmin. È una pratica sicura scegliere un account del genere come admin di mysql, cosicchè tu non inserisca il comando "mysql" come utente root nel tuo sistema. (Ogni volta che non lavori come root diminuisci le possibilità di essere hackerato). Il nome che utilizzi dipende dal nome che hai assegnato all'amministratore del database utilizzando mysqladmin.
- wordpress o blog sono buoni valori per nomedatabase.
- wordpress è un buon valore per nomeutentewordpress ma dovresti sapere che, dato che viene utilizzato qui, anche tutto il resto del mondo lo conosce.
- nomehost sarà solitamente locahost. Se non sai quale dovrebbe essere il valore, contatta il tuo amministratore di sistema se non sei tu l'amministratore del tuo host WordPress. Se sei l'amministratore di sistema, considera l'utilizzo di un account non root per amministrare il tuo database.
- password dovrebbe essere una password difficile da immaginare, contenente idealmente una combinazione di caratteri maiuscoli e minuscoli, numeri, e simboli. Un ottimo modo per non utilizzare una parola presente in un dizionario è di usare la prima lettera di ogni parola di una frase che puoi ricordare facilmente.
Se hai bisogno di scrivere questi valori da qualche parte, evita di farlo sullo stesso sistema che contiene le cose che essi proteggono. Devi ricordare i valori utilizzati per nomedatabase, nomeutentewordpress, nomehost, e password. Ovviamente, dato che sono già stati inseriti (o stai per inserirli) nel file wp-config.php, non c’è bisogno di salvarli anche altrove.
Utilizzare DirectAdmin
a. Utente «Regular» di un account hosting con sito web unico accede normalmente. Poi fai clic su «MySQL Management». (Se questa opzione non fosse facilmente visibile, forse il vostro hosting dovrebbe modificare il vostro «pacchetto» per attivare MySQL.) Dopo procedi alla parte «c» di seguito.
b. Account «Reseller» o «Admin» dovrebbero fare clic su «User Level». Inoltre devono prima fare il login come «Reseller», se il dominio in questione fosse il dominio primario di un «Reseller»… o fare il login come «User», se il dominio in questione NON fosse il dominio primario di un «Reseller». Se il dominio primario fosse di un «Reseller», poi una volta fatto login come «Reseller», sarebbe sufficiente fare clic su «User Level». Tuttavia, se il dominio in questione non fosse di dominio primario del «Reseller», sarebbe necessario accedere come «User». Poi fai clic su «MySQL Management». (Se non immediatamente visibile, forse hai bisogno di tornare al livello di «Reseller» o «Admin» e modificare il «Manage user package» oppure «Manage Reseller package» per abilitare MySQL.)
c. In «MySQL Management», fai clic sul piccolo link «Create new database». Qui ti viene richiesto di inserire due suffissi per il database e il suo nome utente. Per la massima sicurezza, utilizzare due diversi set di 4-6 caratteri casuali. Poi il campo password ha un pulsante «Random» che genera una password di 8 caratteri. Puoi aggiungere più caratteri alla password per aumentare la sicurezza. «Create». La schermata successiva riassumerà il database, nome utente, password e nome host. Assicurarsi di annotare questi dati per riferimento futuro.
Step 3: Impostare wp-config.php
Puoi creare e modificare il file wp-config.php da solo, oppure si può saltare questo passaggio e lasciare che WordPress faccia questo per te quando si esegue lo script di installazione (Step 5) (avrai ancora bisogno di dire a WordPress le informazioni del tuo database).
(Per le informazioni più dettagliate e le istruzioni passo passo per creare il file di configurazione e la chiave segreta per la sicurezza delle password, vedere Modificare wp-config.php.)
Ritorna dove hai estratto il pacchetto di WordPress nelo Step 1, rinomina il file wp-config-sample.php in wp-config.php e aprirlo in un editor di testo.
Inserisci i tuoi dati di database sotto la sezione denominata
// ** Impostazioni MySQL – È possibile ottenere queste informazioni // ** dal proprio fornitore di hosting ** //
- DB_NAME
- Il nome del database di WordPress che hai creato nello Step 2.
- DB_USER
- Nome utente del database MySQL di WordPress creato nello Step 2.
- DB_PASSWORD
- Password del database MySQL di WordPress che hai scelto nello Step 2.
- DB_HOST
- Hostname MySQL che hai determinato nello Step 2 (di solito localhost, ma non sempre; vedi alcuni possibili valori DB_HOST). Se fosse necessario una porta, socket, o pipe, aggiungere i due punti (:) e quindi le informazioni relative al nome host.
- DB_CHARSET
- Charset del Database da utilizzare nella creazione delle tabelle, normalmente non va modificato (vedi Modificare wp-config.php).
- DB_COLLATE
- Il tipo di Collazione del Database. Da non modificare se non si ha idea di cosa sia. Lasciare bianco. (vedi Modificare wp-config.php).
Inserisci i tuoi valori di chiavi segrete sotto la sezione denominata
* Chiavi Univoche di Autenticazione e di Salatura.
Salva il file wp-config.php.
Per informazioni sull’abilitazione di SSL in WordPress 2.6, vedi SSL and Cookies in WordPress 2.6.
Step 4: Caricare i file
Ora dovresti decidere dove nel tuo dominio vuoi che appaia il tuo sito web potenziato da WordPress:
- Nella directory principale del tuo sito web; (Per esempio: http://tuosito.it/)
- In una sottocartella del tuo sito web. (Per esempio: http://tuosito.it/blog/)
Nota: La posizione della tua directory web principale nel filesystem sul server web varierà tra i vari provider di hosting e sistemi operativi. Verificare con il proprio provider di hosting o l’amministratore di sistema se non si sa dove sia.
Nella directory principale
- Se hai bisogno di caricare i file sul tuo server web, usa un client FTP per caricare tutti i contenuti della cartella wordpress (ma non la cartella stessa) nella directory principale del tuo sito web;
- Se i file sono già presenti sul tuo server web, e stai utilizzando accesso shell per installare WordPress, sposta tutti i contenuti della cartella wordpress (ma non la cartella stessa) nella directory principale del tuo sito web.
In una sottocartella
- Se hai bisogno di caricare i file sul tuo server web, rinomina la cartella wordpress nel nome da te desiderato, poi usa un client FTP per caricare la cartella nella posizione desiderata all’interno della directory principale del tuo sito web;
- Se i file sono già presenti sul tuo server web, e stai utilizzando accesso shell per installare WordPress, sposta la cartella wordpress nella posizione desiderata dentro la directory principale del tuo sito web, rinominandola poi nel nome da te desiderato.
Step 5: Eseguire lo script di installazione
Point a web browser to start the installation script.
- If you placed the WordPress files in the root directory, you should visit: http://example.com/wp-admin/install.php
- If you placed the WordPress files in a subdirectory called blog, for example, you should visit: http://example.com/blog/wp-admin/install.php
Setup configuration file
If WordPress can't find the wp-config.php file, it will tell you and offer to try to create and edit the file itself. (You can do also do this directly by loading wp-admin/setup-config.php in your web browser.) WordPress will ask you the database details and write them to a new wp-config.php file. If this works, you can go ahead with the installation; otherwise, go back and create, edit, and upload the wp-config.php file yourself (step 3).
Finishing installation
The following screenshots show how the installation progresses. Notice in Entering the details screen, you enter your site title, your desired user name, your choice of a password (twice) and your e-mail address. Also displayed is a check-box asking if you would like your blog to appear in search engines like Google and Technorati. Leave the box checked if you would like your blog to be visible to everyone, including search engines, and uncheck the box if you want to block search engines, but allow normal visitors. Note all this information can be changed later in your Administration Panels.
Install Script Troubleshooting
- If you get an error about the database when you run the install script:
Problemi comuni di installazione
The following are some of the most common installation problems. For more information and troubleshooting for problems with your WordPress installation, check out FAQ Installation and FAQ Troubleshooting.
I see a directory listing rather than a web page.
The web server needs to be told to view index.php by default. In Apache, use the DirectoryIndex index.php directive. The simplest option is to create a file named .htaccess in the installed directory and place the directive there. Another option is to add the directive to the web server's configuration files.
I see lots of Headers already sent errors. How do I fix this?
You probably introduced a syntax error in editing wp-config.php.
- Download wp-config.php (if you don't have shell access).
- Open it in a text editor.
- Check that the first line contains nothing but <?php, and that there is no text before it (not even whitespace).
- Check that the last line contains nothing but ?>, and that there is no text after it (not even whitespace).
- If your text editor saves as Unicode, make sure it adds no byte order mark (BOM). Most Unicode-enabled text editors do not inform the user whether it adds a BOM to files; if so, try using a different text editor.
- Save the file, upload it again if necessary, and reload the page in your browser.
My page comes out gibberish. When I look at the source I see a lot of "<?php ?>" tags.
If the <?php ?> tags are being sent to the browser, it means your PHP is not working properly. All PHP code is supposed to be executed before the server sends the resulting HTML to your web browser. (That's why it's called a preprocessor.) Make sure your web server meets the requirements to run WordPress, that PHP is installed and configured properly, or contact your hosting provider or system administrator for assistance.
I keep getting an Error connecting to database message but I'm sure my configuration is correct.
Try resetting your MySQL password manually. If you have access to MySQL via shell, try issuing:
SET PASSWORD FOR 'wordpressusername'@'hostname' = OLD_PASSWORD('password');
If you are using a version of MySQL prior to 4.1, use PASSWORD instead of OLD_PASSWORD. If you do not have shell access, you should be able to simply enter the above into an SQL query in phpMyAdmin. Failing that, you may need to use your host's control panel to reset the password for your database user.
My image/MP3 uploads aren't working.
If you use the Rich Text Editor on a blog that's installed in a subdirectory, and drag a newly uploaded image into the editor field, the image may vanish a couple seconds later. This is due to a problem with TinyMCE (the rich text editor) not getting enough information during the drag operation to construct the path to the image or other file correctly. The solution is to NOT drag uploaded images into the editor. Instead, click and hold on the image and select "Send to Editor."
Automated Installation
Although WordPress is very easy to install, you can use one of the one-click autoinstallers typically available from hosting companies. Five of those autoinstallers, WordPress Toolkit, (mt) Media Temple 1-Click Tool, Fantastico, Installatron, and Softaculous are described here.
Plesk WordPress Toolkit
WordPress Toolkit è uno strumento che facilita l’installazione e la gestione di WordPress. Offre due opzioni di installazione:
- Rapida (consigliata) – un’opzione rapida in tre clic per installare WordPress in versione completa e pronta per l’uso, in meno di un minuto. La configurazione si basa sulle impostazioni predefinite e viene installata la versione più recente di WordPress.
- Personalizzata – questa opzione consente di selezionare la versione di WordPress desiderata e sperimentare le varie impostazioni di installazione disponibili, mentre le operazioni noiose rimangono automatizzate.
Ricorda che, in ogni caso, dovrai assicurarti che il tuo dominio soddisfi i requisiti necessari per installare WordPress (ad esempio, è indispensabile che sia configurata una versione di PHP supportata).
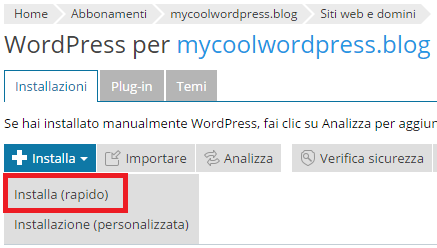
Per eseguire l’installazione rapida, segui questa procedura:
- Accedi a Plesk.
- Nell’angolo in alto a destra della schermata, fai clic su WordPress.
- Fai clic su Installa > Installa (rapido).
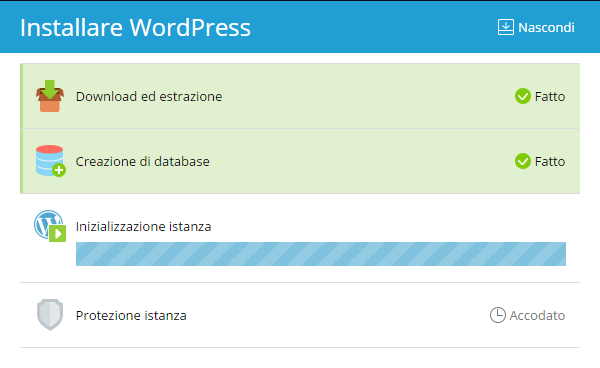
- L’installazione si avvia.
- L’installazione viene completata in pochi secondi. Fai clic su Accedi per scrivere i tuoi primi contenuti!
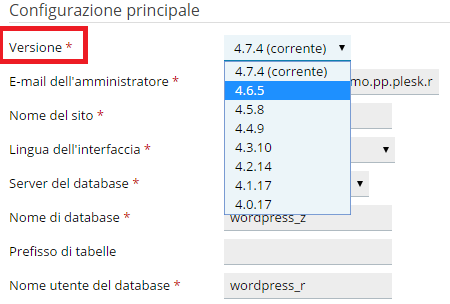
Per eseguire un’installazione personalizzata, segui questa procedura:
- Accedi a Plesk.
- Nell’angolo in alto a destra della schermata, fai clic su WordPress.
- Fai clic su Installa > Installazione (personalizzata).
- Nella finestra Installazione di WordPress che viene visualizzata, selezionare la versione desiderata di WordPress.
- Compilare tutti I campi obbligatori (contrassegnati da un asterisco).
- Apporta le modifiche che preferisci alle impostazioni personalizzate e, al termine, fai clic su Installare.
- L’installazione si avvia.
- L’installazione viene completata in pochi secondi. Fai clic su Accedi per scrivere i tuoi primi contenuti!
Indipendentemente dal tipo di installazione scelto, grazie a WordPress Toolkit installare WordPress sarà molto più semplice. Per maggiori informazioni, leggi la documentazione.
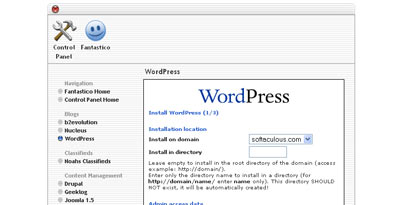
Fantastico
- Login to your cPanel account and click on the Fantastico (or Fantastico Deluxe) option
- Once you enter Fantastico on the left hand side there is a 'Blogs' Category under which WordPress is there. Click on it.
- Click on the 'New Installation' Link in the WordPress Overview
- Fill in the various details and Submit.
- That's it you are done!
Installatron
Installatron is a popular automation company that provides multiple methods to automatically install and upgrade WordPress. Most commonly, Installatron is available through web hosting provider's control panel software. Installatron also provides a tool on its website that enables WordPress to be installed to any website using the website's FTP information.
To install WordPress through your web hosting provider's control panel:
- Login to your web host's control panel, navigate to "Installatron", click "WordPress", and choose the "Install this application" option.
- After customizing the WordPress install by editing any of the prompts, click the "Install" button.
- That's it! WordPress will be installed within a few seconds to your website.
To install using your FTP account information on Installatron.com:
- Navigate to WordPress @ Installatron and choose the "Install this application" option.
- Enter your hosting account's FTP and MySQL database information. For increased security, create a separate FTP account and MySQL database for your WordPress installation. Once this information is entered, click "Install".
- That's it! You will be redirect to a progress page where you can watch as WordPress is installed within a few seconds to your website.
Softaculous
- Login to your host and look for Software/Services
- In Softaculous there is a 'Blogs' Category. Collapse the category and WordPress will be there. Click on it.
- You will see an 'Install' TAB. Click it.
- Fill in the various details and Submit.
- That's it, you are done!
Installation Instructions in Other Languages
For installation instructions in other languages, see WordPress in Your Language.
Come installare blog multipli
Detailed information about Installing Multiple Blogs is available.
Installare WordPress sul proprio computer
Local Installation Instructions
Use these instruction for setting up a local server environment for testing and development.
- DesktopServer Limited: Free Windows/Macintosh server, creates multiple virtual servers with fictitious top level domains (i.e. www.example.dev) specifically for working on multiple WordPress projects.
- Installing WordPress Locally on Your Mac With MAMP
- User:Beltranrubo/BitNami Free all-in-one installers for OS X, Windows and Linux. There are also available installers for WordPress Multisite User:Beltranrubo/BitNami_Multisite using different domains or subdomains.
- Instant WordPress is a free, standalone, portable WordPress development environment for Windows that will run from a USB key.
Software Appliance - Ready-to-Use
You may find that using a pre-integrated software appliance is a great way to get up and running with WordPress, especially in combination with virtual machine software (e.g., VMWare, VirtualBox, Xen HVM, KVM).
A software appliance allows users to altogether skip manual installation of WordPress and its dependencies, and instead deploy a self-contained system that requires little to no setup, in just a couple of minutes.
- TurnKey WordPress Appliance: a free Ubuntu-based appliance that just works. It bundles a collection of popular WordPress plugins and features a small footprint, automatic security updates, SSL support and a Web administration interface.
- BitNami WordPress Appliance: free WordPress appliances based on Ubuntu or Open Suse. Native installer and Cloud images also available. There are also virtual machines for WordPress Multisite already configured.
- UShareSoft WordPress Appliance: free WordPress appliance for many of the major virtualization and cloud platforms (Cloud.com, Xen, VMware, OVF, Abiquo)
Facile installazione di WordPress su Windows in 5 minuti
Download, install, and configure WordPress with the Microsoft Web Platform Installer (Web PI). Installation is very easy and takes on average about 5 minutes to complete. For other Windows installers, check this section
- Step 1. Things you need to know before starting.
- These steps will work on Windows versions which include IIS, such as Windows XP professional, Windows Vista, Windows 7 and Windows Server.
- You must be able to install programs on your machine (i.e. have administrator rights).
- Step 2. Navigate to the WordPress Installation Page
- Choose the "Install" button.
- If you have Web PI already installed, it will automatically be launched and you can skip to the next step.
- If you do not have the Web Platform Installer, you will be prompted to install it.
- Web PI is a tool from Microsoft that downloads and installs the latest components you need to develop or host Web applications on Windows. Everything in the tool is free. Web PI will install and configure IIS, PHP, MySQL and anything else you may need.
- Step 3. Choose to Install WordPress
- When Web PI launches, you will see an information page for WordPress. Start installing WordPress by pressing the "Install" button in the lower right hand corner.
- Step 4. Installation of WordPress and its requirements
- Finding Dependencies: Web PI will determine the minimum set of components and modules you need on your machine to run WordPress. It will only install what you’re missing. For example, PHP will be installed and configured to run WordPress.
- Configure the Database: After accepting the terms, if you need to install MySQL, you will be asked to create a password for the root account database account. Keep this password safe. WordPress will ask for this information later.
- Choose the site: Choose a site to install WordPress to. You may install to an existing Web site in IIS or create a new site. Use the default setting if you do not have advanced configuration needs.
- WordPress Setup: WordPress will need answers to a few specific questions such as the username (in the case of a new MySQL install is root) and password for your MySQL database to complete the install.
- Step 5. Completion
- Once you enter the WordPress setup information, Web PI will finish the installation.
- Click, Launch in Browser and WordPress will launch.
Alternatively, the BitNami WordPress installer is a free, self-contained native installer for WordPress that includes Apache, MySQL and PHP so it works out of the box.
WAMP
If you don't have IIS on your computer or don't want to use it, you could use a WAMP installation. WAMP Server, or WAMP Server at SourceForge, or BitNami WAMPStack can be downloaded freely and set up all the bits you need on your computer to run a web site. Once you have downloaded and installed WAMP, you can point your browser at localhost and use the link to phpmyadmin to create a database.
Then, in order to install WordPress, download the zip file, and extract it into the web directory for your WAMP installation (this is normally installed as c:\wamp\www). Finally visit http://localhost/wordpress to start the WordPress install. (Assuming you extracted into c:\wamp\www\wordpress).
Tip: If you want to use anything other than the default permalink structure on your install, make sure you enable the mod_rewrite module in WAMP. This can be enabled by clicking on the WAMP icon in the taskbar, then hover over Apache in the menu, then Apache modules and ensure that the rewrite_module item has a checkmark next to it.