Thiamylal
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
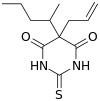 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATCvet code | QN01AF90 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Biological half-life | 14.3 h (cats) |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| Synonyms | Thiamylal, Thioseconal, Surital |
| CAS Number | 77-27-0 |
| PubChem (CID) | 3032285 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 7305 |
| DrugBank | DB01154 |
| ChemSpider | 2297298 |
| UNII | 01T23W89FR |
| KEGG | D06106 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:9536 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL440 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.927 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H18N2O2S |
| Molar mass | 254.35 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
|
|
|
|
| (verify) | |
Thiamylal (Surital) is a barbiturate derivative invented in the 1950s. It has sedative, anticonvulsant, and hypnotic effects, and is used as a strong but short acting sedative. Thiamylal is still in current use, primarily for induction in surgical anaesthesia [1] or as an anticonvulsant to counteract side effects from other anaesthetics.[2] It is the thiobarbiturate analogue of secobarbital.
References[edit]
- ^ Hsieh MY, Hung GY, Hsieh YL, Chang CY, Hwang B. Deep sedation with methohexital or thiamylal with midazolam for invasive procedures in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Acta Paediatrica Taiwan. 2005 Sep-Oct;46(5):294-300.
- ^ Tsai CJ, Wang HM, Lu IC, Tai CF, Wang LF, Soo LY, Lu DV. Seizure after local anesthesia for nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. Kaohsiung Journal of Medical Sciences. 2007 Feb;23(2):97-100.
| This drug article relating to the nervous system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |