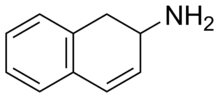
2-Amino-1,2-dihydronapthalene (2-ADN ), also known as 2-aminodilin (2-AD ), is a stimulant drug .[1] analogue of phenylisobutylamine and substitutes amphetamine for it in rat discrimination tests, although at approximately one fourth the potency.[1] 2-aminotetralin (2-amino-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalene), which also substitutes for amphetamine, and is about two times as potent in comparison to it.[1]
See also [ edit ] References [ edit ]
^ a b c Hathaway BA, Nichols DE, Nichols MB, Yim GK (May 1982). "A new, potent, conformationally restricted analogue of amphetamine: 2-amino-1,2-dihydronaphthalene". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry . 25 (5): 535–8. doi :10.1021/jm00347a011 . PMID 6123601 .
Adamantanes
Adenosine antagonists
Alkylamines
Ampakines
Arylcyclohexylamines
Benzazepines
Cholinergics
Convulsants
Eugeroics
Oxazolines
Phenethylamines
1-(4-Methylphenyl)-2-aminobutane 1-Phenyl-2-(piperidin-1-yl)pentan-3-one 1-Methylamino-1-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)propane 2-Fuoroamphetamine 2-Fuoromethamphetamine 2-OH-PEA 2-Phenyl-3-aminobutane 2-Phenyl-3-methylaminobutane 2,3-MDA 3-Fuoroamphetamine 3-Fluoroethamphetamine 3-Fluoromethcathinone 3-Methoxyamphetamine 3-Methylamphetamine 3,4-DMMC 4-BMC 4-CMC 4-Ethylamphetamine 4-Fluoroamphetamine 4-Fluoromethamphetamine 4-MA 4-Methylbuphedrone 4-Methylcathinone 4-MMA 4-Methylpentedrone 4-MTA 6-FNE AL-1095 Alfetamine a-Ethylphenethylamine Amfecloral Amfepentorex Amfepramone Amidephrine 2-Amino-1,2-dihydronaphthalene 2-Aminoindane 5-(2-Aminopropyl)indole 2-Aminotetralin Acridorex Amphetamine (Dextroamphetamine , Levoamphetamine )Amphetaminil Arbutamine β-Methylphenethylamine β-Phenylmethamphetamine Benfluorex Benzedrone Benzphetamine BDB BOH 3-Benzhydrylmorpholine BPAP Buphedrone Bupropion Butylone Camfetamine Cathine Cathinone Chlorphentermine Cilobamine Cinnamedrine Clenbuterol Clobenzorex Cloforex Clortermine Cypenamine D -DeprenylDenopamine Dimethoxyamphetamine Dimethylamphetamine Dimethylcathinone Dobutamine DOPA (Dextrodopa , Levodopa )Dopamine Dopexamine Droxidopa EBDB Ephedrine Epinephrine Epinine Etafedrine Ethcathinone Ethylnorepinephrine Ethylone Etilamfetamine Etilefrine Famprofazone Fencamfamin Fencamine Fenethylline Fenfluramine (Dexfenfluramine , Levofenfluramine )Fenproporex Feprosidnine Flephedrone Fludorex Formetorex Furfenorex Gepefrine Hexapradol Hexedrone HMMA Hordenine 4-Hydroxyamphetamine 5-Iodo-2-aminoindane Ibopamine IMP Indanylamphetamine Iofetamine Isoetarine Isoethcathinone Isoprenaline L -DeprenylLefetamine Lisdexamfetamine Lophophine MBDB MDA MDBU MDEA MDMA MDMPEA MDOH MDPR MDPEA Mefenorex Mephedrone Mephentermine Metanephrine Metaraminol Mesocarb Methamphetamine (Dextromethamphetamine , Levomethamphetamine )Methoxamine Methoxyphenamine MMA Methcathinone Methedrone Methoxyphenamine Methylenedioxycathinone Methylone Mexedrone MMDA MMDMA MMMA Morforex N,alpha-Diethylphenylethylamine N-Benzyl-1-phenethylamine N-Ethylbuphedrone N-Ethylhexedrone N,N-Dimethylphenethylamine Naphthylamphetamine Nisoxetine Norepinephrine Norfenefrine Norfenfluramine Normetanephrine L -NorpseudoephedrineOctopamine (drug) Orciprenaline Ortetamine Oxifentorex Oxilofrine PBA PCA PCMA PHA Pentorex Pentedrone Pentylone Phenatine Phenpromethamine Phentermine Phenylalanine Phenylephrine Phenylpropanolamine Pholedrine PIA PMA PMEA PMMA PPAP Phthalimidopropiophenone Prenylamine Propylamphetamine Pseudoephedrine Ropinirole Salbutamol (Levosalbutamol )Sibutramine Synephrine Theodrenaline Tiflorex Tranylcypromine Tyramine Tyrosine Xylopropamine Zylofuramine
Phenylmorpholines
Piperazines
Piperidines
Pyrrolidines
Racetams
Tropanes
Tryptamines
Others
α1
Antagonists Abanoquil Adimolol Ajmalicine Alfuzosin Amosulalol Anisodamine Arotinolol Atiprosin Atypical antipsychotics (e.g., clozapine , olanzapine , quetiapine , risperidone )Benoxathian Buflomedil Bunazosin Carvedilol Corynanthine Dapiprazole Domesticine Doxazosin Ergolines (e.g., ergotamine , dihydroergotamine , lisuride , terguride )Etoperidone Eugenodilol Fenspiride Hydroxyzine Indoramin Ketanserin L-765,314 Labetalol mCPP Mepiprazole Metazosin Monatepil Moxisylyte Naftopidil Nantenine Nefazodone Neldazosin Niaprazine Nicergoline Niguldipine Pardoprunox Pelanserin Phendioxan Phenoxybenzamine Phentolamine Piperoxan Prazosin Quinazosin Ritanserin Silodosin Spiperone Talipexole Tamsulosin Terazosin Tiodazosin Tolazoline Trazodone Tetracyclic antidepressants (e.g., amoxapine , maprotiline , mianserin )Tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline , clomipramine , doxepin , imipramine , trimipramine )Trimazosin Typical antipsychotics (e.g., chlorpromazine , fluphenazine , loxapine , thioridazine )Urapidil WB-4101 Zolertine
α2
Antagonists 1-PP Adimolol Aptazapine Atipamezole Atypical antipsychotics (e.g., asenapine , clozapine , lurasidone , paliperidone , quetiapine , risperidone , zotepine )Azapirones (e.g., buspirone , tandospirone )BRL-44408 Buflomedil Cirazoline Efaroxan Esmirtazapine Fenmetozole Fluparoxan Idazoxan mCPP Mianserin Mirtazapine NAN-190 Olanzapine Pardoprunox Phentolamine Phenoxybenzamine Piperoxan Piribedil Rauwolscine Rotigotine SB-269970 Setiptiline Spiroxatrine Sunepitron Tolazoline Typical antipsychotics (e.g., chlorpromazine , fluphenazine , loxapine , thioridazine )Yohimbine
β