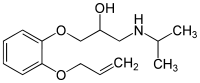
Oxprenolol
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
oral |
| ATC code | C07AA02 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 20-70% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Biological half-life | 1-2hours |
| Excretion | Renal Lactic (In lactiferous females) |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | 6452-71-7 |
| PubChem (CID) | 4631 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 7255 |
| DrugBank | DB01580 |
| ChemSpider | 4470 |
| UNII | 519MXN9YZR |
| KEGG | D08318 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL546 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.026.598 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H23NO3 |
| Molar mass | 265.348 |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Oxprenolol (Trasacor, Trasicor, Coretal, Laracor, Slow-Pren, Captol, Corbeton, Slow-Trasicor, Tevacor, Trasitensin, Trasidex) is a non-selective beta blocker with some intrinsic sympathomimetic activity. It is used for the treatment of angina pectoris, abnormal heart rhythms and high blood pressure.
Oxprenolol is a lipophilic beta blocker which passes the blood–brain barrier more easily than water-soluble beta blockers. As such, it is associated with a higher incidence of CNS-related side effects than hydrophilic ligands such as atenolol, sotalol and nadolol.[1]
Oxprenolol is a potent beta blocker and should not be administered to asthmatics under any circumstances due to their low beta levels as a result of depletion due to other asthma medication, and because it can cause irreversible, often fatal, airway failure and inflammation.[2]
Stereochemistry[edit]
Oxprenolol is a chiral compound, the beta blocker is used as a racemate, e. g. a 1:1 mixture of (R)-(+)-oxprenolol and (S)-(–)-oxprenolol. Analytical methods (HPLC) for the separation and quantification of (R)-(+)-oxprenolol and (S)-(–)-oxprenolol in urine and in pharmaceutical formulations have been described in the literature.[3]
References[edit]
- ^ McDevitt DG (1987). "Comparison of pharmacokinetic properties of beta-adrenoceptor blocking drugs". Eur. Heart J. 8. Suppl M: 9–14. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/8.suppl_M.9. PMID 2897304.
- ^ I P Williams and F J Millard (1980). "Severe asthma after inadvertent ingestion of oxprenolol". Thorax. 35 (2): 160. doi:10.1136/thx.35.2.160. PMC 471246
 . PMID 7376124.
. PMID 7376124. - ^ Abounassif, Mohammed A.; Hefnawy, Mohammed M.; Mostafa, Gamal A. E. (2011). "Separation and quantitation of oxprenolol in urine and pharmaceutical formulations by HPLC using a Chiralpak IC and UV detection". Monatshefte für Chemie - Chemical Monthly. 143 (3): 365. doi:10.1007/s00706-011-0605-4.
| β, non-selective | |
|---|---|
| β1-selective | |
| β2-selective | |
| α1- + β-selective | |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
