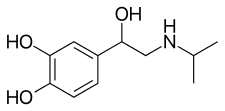
Isoprenaline
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| MedlinePlus | a601236 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Inhalation (80–120 μg) |
| ATC code | C01CA02 (WHO) R03AB02 (WHO) R03CB01 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Biological half-life | ~2 minutes |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | 7683-59-2 |
| PubChem (CID) | 3779 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 536 |
| DrugBank | DB01064 |
| ChemSpider | 3647 |
| UNII | L628TT009W |
| KEGG | D08090 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL434 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.807 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H17NO3 |
| Molar mass | 211.258 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
|
|
|
|
| (verify) | |
Isoprenaline (INN) or isoproterenol (USAN) (trade names Medihaler-Iso and Isuprel) is a medication used for the treatment of bradycardia (slow heart rate), heart block, and rarely for asthma. In humans, it is a non-selective β adrenoreceptor agonist and TAAR1 agonist that is structurally similar to epinephrine (adrenaline).[1][2]
Contents
Uses[edit]
Its primary use is for bradycardia or heart block. By activating β1 adrenergic receptor in the heart, it induces positive chronotropic, dromotropic, and inotropic effects.[2]
It can be used as an inhaled aerosol to treat asthma, although this is currently a rare treatment.[2] Although it activates all beta adrenergic receptors, it works in a similar fashion to selective β2 adrenergic agonists, e.g. salbutamol, by relaxing the airways to increase airflow.
Used with caution, it can also be used to treat torsades de pointes by acquired defect, in conjunction with overdrive pacing and magnesium sulfate.
Pharmacology[edit]
Isoprenaline is a β1 and β2 adrenoreceptor agonist which was commonly used to treat asthma before the more widespread use of salbutamol, which has more selective effects on the airways. Its agonist effects at TAAR1 provide it with a pharmacodynamic effects that resemble those of the endogenous trace amines, like tyramine,[1] although its short half-life prevents it from producing persistent psychoactive effects from TAAR1 activation in the central nervous system. Its route of administration is either intravenous, oral, intranasal, subcutaneous, or intramuscular, depending on use. The plasma half-life for isoprenaline is approximately two minutes.
Isoprenaline's effects on the cardiovascular system (non-selective) relate to its actions on cardiac β1 receptors and β2 receptors on smooth muscle within the tunica media of arterioles. Isoprenaline has positive inotropic and chronotropic effects on the heart. β2 adrenoceptor stimulation in arteriolar smooth muscle induces vasodilation. Its inotropic and chronotropic effects elevate systolic blood pressure, while its vasodilatory effects tend to lower diastolic blood pressure. The overall effect is to decrease mean arterial pressure due to the β2 receptors' vasodilation.
The adverse effects of isoprenaline are also related to the drug's cardiovascular effects. Isoprenaline can produce tachycardia (an elevated heart rate), which predisposes patients to cardiac arrhythmias.
Warnings and contraindications[edit]
Isoprenaline should not be administered to patients with myocardial ischemia.
According to Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Title 21 Section 201.305, use of isoprenaline has been regulated by mandating the inclusion of the following warning label: "Occasional patients have been reported to develop severe paradoxical airway resistance with repeated, excessive use of isoprenaline inhalation preparations. The cause of this refractory state is unknown. It is advisable that in such instances the use of this preparation be discontinued immediately and alternative therapy instituted, since in the reported cases the patients did not respond to other forms of therapy until the drug was withdrawn. Deaths have been reported following excessive use of isoprenaline inhalation preparations and the exact cause is unknown. Cardiac arrest was noted in several instances"
Structure-activity relationship[edit]
The isopropylamine group in isoprenaline makes it selective for β receptors. The free catechol hydroxyl groups keep it susceptible to enzymatic metabolism.[3]
History[edit]
Between 1963 and 1968 in England, Wales, Scotland, Ireland, Australia, and New Zealand there was an increase in deaths among people using isoprenaline to treat asthma. This was attributed to overdose: the inhalers produced in that area were dispensing five times the dosage dispensed by inhalers produced in the US and Canada, where the deaths were not observed.[4]
Synthesis[edit]
Friedel-Crafts acylation of catechol 1 with chloroacetyl chloride 2 leads to chloroketone 3. Displacement of halogen with isopropylamine gives aminoketone; hydrogenation over platinum reduces the carbonyl group to give racemic isoproterenol 4.
If instead of the isopropyl there is a tert-butyl group then the compound is called colterol. The p-cresoyl diester of the catechol is called bitolterol. It is a prodrug of colterol.[7]
References[edit]
- ^ a b Kleinau G, Pratzka J, Nürnberg D, Grüters A, Führer-Sakel D, Krude H, Köhrle J, Schöneberg T, Biebermann H (October 2011). "Differential modulation of Beta-adrenergic receptor signaling by trace amine-associated receptor 1 agonists". PLoS ONE. 6 (10): e27073. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0027073. PMC 3205048
 . PMID 22073124.
. PMID 22073124.
"Table 1: EC50 values of different agonists at hTAAR1, hADRB1 and hADRB2." - ^ a b c Shen, Howard (2008). Illustrated Pharmacology Memory Cards: PharMnemonics. Minireview. p. 5. ISBN 1-59541-101-1.
- ^ Medicinal Chemistry of Adrenergics and Cholinergics
- ^ Pierce, Neil; Hensley, Michael J. (1998). "Epidemiologic Studies of Beta Agonists and Asthma Deaths" (PDF). Epidemiologic Studies. 20 (2).
- ^ G. Schening, O. Thomae, DE 723278 (1942).
- ^ G. Schening, O. Thomae, U.S. Patent 2,308,232 (1943).
- ^ Walker, Susannah B.; Kradjan, Wayne A.; Bierman, C. Warren (6 May 1985). "Bitolterol Mesylate: A Beta-adrenergic Agent; Chemistry, Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, Adverse Effects and Clinical Efficacy in Asthma". Pharmacotherapy: The Journal of Human Pharmacology and Drug Therapy. 5 (3): 127–137. doi:10.1002/j.1875-9114.1985.tb03410.x. PMID 3895171.

