Bufexamac
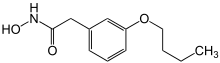 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration |
Topical, rectal |
| ATC code | M01AB17 (WHO) M02AA09 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | 2438-72-4 |
| PubChem (CID) | 2466 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 7498 |
| ChemSpider | 2372 |
| UNII | 4T3C38J78L |
| KEGG | D01271 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL94394 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.017.683 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H17NO3 |
| Molar mass | 223.268 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
|
|
|
|
Bufexamac is a drug used as an anti-inflammatory agent on the skin, as well as rectally. Common brand names include Paraderm and Parfenac. It was withdrawn in Europe because of allergic reactions.
Indications[edit]
Ointments and lotions containing bufexamac are used for the treatment of subacute and chronic eczema of the skin, including atopic eczema, as well as sunburn and other minor burns,[citation needed] and itching. Suppositories containing bufexamac in combination with local anaesthetics are used against haemorrhoids.[1]
Pharmacology[edit]
Bufexamac is thought to act by inhibiting the enzyme cyclooxygenase, which would make it a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. Evidence on the mechanism of action is scarce.[2] Furthermore, bufexamac was identified as a specific inhibitor of class IIB histone deacetylases (HDAC6 and HDAC10).[3]
Side effects[edit]
Bufexamac can cause severe contact dermatitis which is often hard to distinguish from the initial condition.[4] As a consequence, the European Medicines Agency recommended to withdraw the marketing approval in April 2010.[5]
References[edit]
- ^ Dinnendahl, V; Fricke, U, eds. (2010). Arzneistoff-Profile (in German). 2 (23 ed.). Eschborn, Germany: Govi Pharmazeutischer Verlag. ISBN 978-3-7741-9846-3.
- ^ Gloor, Max; Thoma, Karl; Fluhr, Joachim (2000). Dermatologische Externatherapie: Unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der Magistralrezeptur (in German). Springer. p. 349. ISBN 3-540-67174-9.
- ^ Bantscheff, Marcus; Hopf, Carsten; Savitski, Mikhail M; Dittmann, Antje; Grandi, Paola; Michon, Anne-Marie; Schlegl, Judith; Abraham, Yann; Becher, Isabelle; Bergamini, Giovanna; Boesche, Markus; Delling, Manja; Dümpelfeld, Birgit; Eberhard, Dirk; Huthmacher, Carola; Mathieson, Toby; Poeckel, Daniel; Reader, Valérie; Strunk, Katja; Sweetman, Gavain; Kruse, Ulrich; Neubauer, Gitte; Ramsden, Nigel G; Drewes, Gerard (2011). "Chemoproteomics profiling of HDAC inhibitors reveals selective targeting of HDAC complexes". Nature Biotechnology. 29 (3): 255–65. doi:10.1038/nbt.1759. PMID 21258344.
- ^ "Bufexamac: Ein Ekzemtherapeutikum, das selbst häufig allergische Kontaktekzeme hervorruft". Deutsches Ärzteblatt (in German) (47). 2000.
- ^ "European Medicines Agency recommends revocation of marketing authorisations for bufexamac" (PDF). European Medicines Agency. 2010-04-22.