DMCM
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
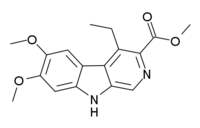
methyl 4-ethyl-6,7-dimethoxy-9H-pyrido[5,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate
|
|
| Other names
DMCM
|
|
| Identifiers | |
| 82499-00-1 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 94746 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.220.168 |
| 4179 | |
| PubChem | 104999 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C17H18N2O4 | |
| Molar mass | 314.336 g/mol |
| Boiling point | 87 °C (189 °F; 360 K) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
DMCM (methyl-6,7-dimethoxy-4-ethyl-beta-carboline-3-carboxylate) is a drug from the beta-carboline family. It acts as a negative allosteric modulator of GABAA receptors, meaning that it causes the opposite effects to the benzodiazepine class of drugs. As such, DMCM has anxiogenic and convulsant properties,[1] and is used in scientific research to induce anxiety so that new anxiolytic medications can be tested,[2] and to produce convulsions so that anticonvulsant medications can be tested.[3][4][5] It has also been shown to produce analgesic effects in animals, thought to be because it produces panic which reduces the perception of pain.[6]
References[edit]
- ^ Contó, MB; De Carvalho, JG; Benedito, MA (2005). "Behavioral differences between subgroups of rats with high and low threshold to clonic convulsions induced by DMCM, a benzodiazepine inverse agonist". Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior. 82 (3): 417–26. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2005.09.012. PMID 16297441.
- ^ Cole, BJ; Hillmann, M; Seidelmann, D; Klewer, M; Jones, GH (1995). "Effects of benzodiazepine receptor partial inverse agonists in the elevated plus maze test of anxiety in the rat". Psychopharmacology. 121 (1): 118–26. doi:10.1007/BF02245598. PMID 8539336.
- ^ Brodie, MJ (1995). "Tiagabine pharmacology in profile". Epilepsia. 36 Suppl 6: S7–S9. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1157.1995.tb06015.x. PMID 8595791.
- ^ De Sarro, G; Chimirri, A; McKernan, R; Quirk, K; Giusti, P; De Sarro, A (1997). "Anticonvulsant activity of azirino1,2-d1,4benzodiazepines and related 1,4-benzodiazepines in mice". Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior. 58 (1): 281–9. doi:10.1016/S0091-3057(96)00565-5. PMID 9264104.
- ^ Leppä, E; Vekovischeva, OY; Lindén, AM; Wulff, P; Oberto, A; Wisden, W; Korpi, ER (2005). "Agonistic effects of the beta-carboline DMCM revealed in GABA(A) receptor gamma 2 subunit F77I point-mutated mice". Neuropharmacology. 48 (4): 469–78. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2004.11.007. PMID 15755475.
- ^ Sieve, AN; King, TE; Ferguson, AR; Grau, JW; Meagher, MW (2001). "Pain and negative affect: evidence the inverse benzodiazepine agonist DMCM inhibits pain and learning in rats". Psychopharmacology. 153 (2): 180–90. doi:10.1007/s002130000535. PMID 11205417.
| This drug article relating to the nervous system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |