Carbendazim
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
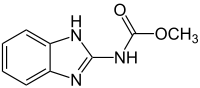
| IUPAC name
Methyl 1H-benzimidazol-2-ylcarbamate
|
|
| Other names
Mercarzole
Carbendazole |
|
| Identifiers | |
| 10605-21-7 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:3392 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL70971 |
| ChemSpider | 23741 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.108 |
| KEGG | C10897 |
| PubChem | 25429 |
| RTECS number | DD6500000 |
| UNII | H75J14AA89 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C9H9N3O2 | |
| Molar mass | 191.187 g/mol |
| Appearance | Light gray powder |
| Density | 1.45 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 302 to 307 °C (576 to 585 °F; 575 to 580 K) (decomposes) |
| 8 mg/L | |
| Acidity (pKa) | 4.48 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Carbendazim is a widely used, broad-spectrum benzimidazole fungicide and a metabolite of benomyl. It is also employed as a casting worm control agent in amenity turf situations such as golf greens, tennis courts etc. and in some countries is licensed for that use only.[2]
The fungicide is used to control plant diseases in cereals and fruits, including citrus, bananas, strawberries, pineapples, and pomes.[3] It is also controversially used in Queensland, Australia on macadamia plantations.[4] A 4.7% solution of carbendazim hydrochloride, sold as Eertavas, is marketed as a treatment for Dutch elm disease.
Studies have found high doses of carbendazim cause infertility and destroy the testicles of laboratory animals.[5][6]
Maximum pesticide residue limits (MRLs) have reduced since discovering its harmful effects. The MRLs for fresh produce in the EU are now between 0.1 and 0.7 mg/kg with the exception of loquat, which is 2 mg/kg.[7] The limits for more commonly consumed citrus and pomme fruits are between 0.1 and 0.2 mg/kg.
References[edit]
- ^ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 1794.
- ^ "Getting the best worm control".
- ^ Wight, Andrew (14 January 2009). "Two-headed fish mystery deepens". Stock & Land. Archived from the original on 19 October 2009.
- ^ Marissa Calligeros (2009-02-02). "Fungicide maker in birth defect storm". Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 2010-03-21.
- ^ Aire, TA (August 2005). "Short-term effects of carbendazim on the gross and microscopic features of the testes of Japanese quails (Coturnix coturnix japonica).". Anatomy and embryology. 210 (1): 43–9. doi:10.1007/s00429-005-0001-0. PMID 16034611.
- ^ "Carbendazim use banned on fruit crops". ABC. 5 February 2010.
- ^ "EU Pesticides Database". Retrieved 24 February 2012.
External links[edit]
- International Chemical Safety Card
- Carbendazim in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB)
| This agriculture article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
| This article about a heterocyclic compound is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |