3C-BZ
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Jump to: navigation, search
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
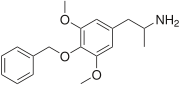
1-(4-benzyloxy-3,5-methoxyphenyl)propan-2-amine
|
|
| Other names
4-Benzyloxy-3,5-methoxyamphetamine
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider |
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C18H23NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 301.39 g/mol |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
3C-BZ, or 4-benzyloxy-3,5-dimethoxyamphetamine, is a lesser-known psychedelic drug and a substituted amphetamine. 3C-BZ was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, the dosage range is listed as 25–200 mg, and the duration as 18–24 hours. According to anecdotal reports from the substance's entry in PiHKAL, 3C-BZ's effects can vary significantly, ranging from intensified emotions and strange dreams, to effects similar to those of LSD or TMA.[1] Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of 3C-BZ.
References[edit]
- ^ Shulgin, Alexander; Ann Shulgin (September 1991). PiHKAL: A Chemical Love Story. Berkeley, California: Transform Press. ISBN 0-9630096-0-5. OCLC 25627628.
External links[edit]
| Phenethylamines |
|
|---|---|
| Amphetamines |
|
| Phentermines |
|
| Cathinones |
|
| Phenylisobutylamines | |
| Phenylalkylpyrrolidines | |
| Catecholamines (and close relatives) |
|
| Miscellaneous |
|
| Psychedelics (5-HT2A agonists) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dissociatives (NMDAR antagonists) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deliriants (mAChR antagonists) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Drugs from PiHKAL
|
|
|---|---|
|
Retrieved from "https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=3C-BZ&oldid=736521275"