Atlas of Germany
 |
Wikimedia Commons Atlas of the World The Wikimedia Atlas of the World is an organized and commented collection of geographical, political and historical maps available at Wikimedia Commons. Discussion • Update the atlas • Index of the Atlas • Atlas in categories • Other atlases on line |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
General maps
 |
Deutsch: Übersichtskarte von Deutschland
|
 |
English: General map of Germany
|
 |
Political map of Germany |
 |
Political map of Germany |
 |
Cities in Germany |
Geographical distinctions
Maps of divisions
This section holds maps of the administrative divisions.
-
Bayern (2)
-
Berlin (3)
-
Brandenburg (4)
-
Bremen (5)
-
Hamburg (6)
-
Hessen (7)
-
Niedersachsen (9)
-
Nordrhein-Westfalen (10)
-
Rheinland-Pfalz (11)
-
Saarland (12)
-
Sachsen (13)
-
Sachsen-Anhalt (14)
-
Schleswig-Holstein (15)
-
Thüringen (16)
 |
Districts and district-free towns (yellow) in Germany |
Geography maps
 |
Physical geography I (with labelling of landscapes) |
 |
Physical geography II (without labelling of landscapes) |
 |
Main natural regions |
 |
Catchment of the Rhine river |
Human Geography maps
 |
Population density |
Geology maps
 |
Surficial geology (simplified) |
 |
Earthquake hazard zones |
History maps
Early History
 |
The southern part of present-day Germany is under the influence of Celt. This map shows the possible extent of (proto-)Celtic influence 800-400 BC Die Kelten in Europa. Ocker: Kernbereich Nordwestalpine Hallstattkultur (ca. 750–500/450 v. Chr.) grün: Ausbreitung La-Tène-Kultur, bzw. orange: der keltischen Sprache (3. Jh. v. Chr.) |
 |
Another map of the Celts in Europe Die Kelten in Europa |
The Germanic tribes
 |
IN the first millenium BCE Germanic peoples enter from Scandinavia into present-day North Germany. Proto-Germanische Völker |
 |
This map shows the gradual expansion of their territory during the 1st millennium BCE |
 |
This (old) map shows Ancient Germania Antikes Germanien |
The Romans and the Germanic tribes
 |
Drusus campaigns in Germany from 12 B.C. to 9 B.C. |
 |
Tiberius campaigns (4-6 A.D.) and Domitius Aenobardus campaigns (3-1 B.C.) in Germany |
 |
Germania provincia in 9 A.D. |
 |
The battle of Teutoburgus (9 A.D.) |
 |
Germania Magna in 10 A.D. |
 |
Germanicus' campaign in Germany in 14 A.D. |
 |
Germanicus' campaign in Germany in 15 A.D. |
 |
Germanicus' campaign in Germany in 16 A.D. |
 |
The battle of Idistaviso between Germanicus and Arminius in 16 A.D.. |
 |
The battle of Angrivaran's Wall (16 A.D.) |
 |
Germanic peoples in Germany at the time of Augustus. |
 |
Around 68 BCE the ► Roman Empire conquers the south-west part of present-day Germany. The other parts remain under control of germanic tribes. Map showing the pre-Migration Age distribution of the Germanic tribes in Proto-Germanic times, and stages of their expansion up to 50 BC, AD 100 and AD 300. The extent of the Roman Empire in 68 BC and AD 117 is also shown. Proto-Germanische Völker |
 |
Rhaetian and Upper Germanic Limes Obergermanisch-raetischer Limes |
 |
The Roman Empire in CE 120 and Germania Das Römische Reich und Germanien im Jahre 120 |
 |
Alamanni Die Alamannen |
 |
Further expansion Territoriale Entwicklung der Alemannen |
 |
After the death of Theodosius I, the Roman Empire divides into the ► Western Roman Empire and the ► Eastern Roman Empire. Die Teilung des Römischen Reiches um 395. Das Weströmische Reich im Jahre 395 |
 |
After the division of the Western Roman Empire Germanic tribes enter the Empire and gradually take over control. This map shows invasions of the Roman Empire 100-500 |
 |
White Serbia in the 6th century (around 560), according to the book of Francis Dvornik |
 |
Dervan's Serbia, 7th century |
The Franks
| 481-843: Frankish Empire - independent monarchy including present-day Germany ► Frankish Empire |
 |
The Franks become the dominant tribe and establish their realm. The Frankish Realm includes large parts of present-day Germany, France, the Netherlands, Belgium and Switzerland. In 751 the Carolingian dynasty comes to power with Pepin the Short, but his succesor, Charlemagne reunites in 771 the Frankish domains. Charlemagne is crowned Emperor of the Romans, or Roman Emperor in the West, by Pope Leo III in 800. This map shows the rise of the Frankish Empire |
| 843-962: East Frankish Empire (Regnum Francorum Orientalis) - independent monarchy |
 |
The Treaty of Verdun, 843, confirms the division of the Empire in three. The East Frankish Kingdom develops with the coronation of the first German king in 919 into the Kingdom of Germany, a feudal country, divided in a growing number of more or less independent states. |
 |
This map shows the further division in the Treaty of Meerssen (870) |
The Holy Roman Empire
| 962-1806: Holy Roman Empire (Heiliges Römisches Reich) - independent country |
 |
King Otto I of Germany conquers Italy and is crowned Emperor of the Romans in 962, forming what would come to be known as the Holy Roman Empire and in the 15th century as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation (also referred to simply as Germany). This map shows Central Europe, i.e. the Kingdom of Germany, 919-1125. |
 |
The Duchy of Bavaria in the 10th century |
 |
The Holy Roman Empire during the reign of the Hohenstaufens (13th century) |
Hanseatic League
 |
Hanseatic trade routes |
 |
The Holy Roman Empire in the 14th century |
 |
The Holy Roman Empire and its circles in 1512 |
 |
The religious situation in central Europe about 1618 |
 |
Area controlled by the Holy Roman Empire around 1630. The most important countries inside the empire (and partially outside) are ► Austria and ► Brandenburg-Prussia. |
 |
The Holy Roman Empire in 1648, after the secession of the ► Netherlands and ► Switzerland. |
 |
The Holy Roman Empire in 1789, just before the French Revolution. |
Kleinstaaterei
 |
Under French pressure the Holy Roman Empire is dissolved in 1806. Germany fell apart in several countries from very small to rather big. In the period between 1806 en 1870 part of these states are member of several confederations. Between 1806 and 1870 the following states exist. In the following list the countries are listed with the membershops of the confederation. RB = Rhine Confederation (1806-1813), DB = German Confederation (1815-1866) and NB = North German Confederation (1866-1870). More information about these confederations can found in the next section.
|
The confederations
| 1806-1813: Rhine Confederation (Rheinbund) - confederation of French satellite states |
 |
As a result of the Napoleonic war the German Empire is replaced in 1806 by the Confederation of the Rhine. |
 |
At the same time and in the following years parts of Germany are annexed to the ► French Empire in 1811 |
 |
The Confederation of the Rhine in 1812 |
 |
1815-1867: German Confederation (Deutscher Bund) - confederation of German states, including Prussia and Austria |
 |
After the defeat of France in 1813, there is no central authority in Germany, but at the Vienna Congress in 1815, the German Confederation, a loose confederation of states in Germany including Prussia and Austria, is founded. |
 |
Borders of the German Confederation in 1820 |
 |
After a revolution in 1848 Germany is temporarily united in the German Empire, but the next year the German Confederation is restored. The confederation comes to an end after the Austro-Prussian War of 1866. This map shows the alliances of the member-states of the German Confederation in the Austro-Prussian War, 1866 |
 |
This map shows the aftermath of the Austro-Prussian War (1866). |
| 1867-1871: North German Confederation (Norddeutscher Bund) - confederation of North German states, led by Prussia |
 |
In 1867 the North German states form the North German Confederation, a loose confederation of states. Baden, Bavaria, Württemberg and the south part of Hesse remained outside the North German Confederation. In a way they were independent between 1867 and 1871, when they joined the German Empire. |
 |
This map shows the North German Confederation (1867-1871) |
German Empire
| 1871-1918: German Empire (Deutsches Reich) - independent monarchy, led by Prussia |
 |
In 1871 the German states, ► Austria not included, unite into the German Empire. |
 |
Map of the German Empire |
 |
Germany 1871-1914 |
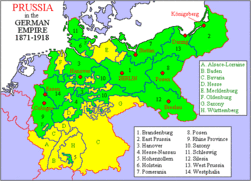 |
Prussia in the German Empire 1871-1918 |
 |
The distribution of Christian denominations in the German Empire, ca. 1895 |
 |
The distribution of Judaism in the German Empire, ca. 1895 |
 |
Emperor William II's dynamic expansion of military power contribute to tensions on the continent. The fragile European balance of power, which Bismarck had helped to create, breaks down in 1914. World War I is a fact. This map shows Germany's demands in 1915 |
 |
British propaganda publication "Germany's Future", allegedly according to an officially circulated pamphlet published in the beginning of 1917. |
German colonialism
 |
Map showing in blue the German colonies at the beginning of World War I |
Weimar Republic
| 1918-1933: German Empire (Deutsches Reich) - independent republic |
 |
The aftermath, including the Treaty of Versailles, leads to the end of the monarchy and to territorial losses, shown by this map. The ► Saar region is separated from Germany, as are eastern parts of Germany (to ► Poland), the ► Memel Territory and the ► Free City of Danzig. The German Empire becomes a republic. |
 |
Germany 1918-1937 |
 |
Übersichtskarte der Wahlen zur Nationalversammlung 1919 Map for the National Assembly in 1919 |
 |
Germany in 1925 |
Nazi Germany
| 1933–1945: (Greater) German Empire ((Gross)Deutsches Reich) - independent republic |
 |
Germany in 1939 |
 |
After the invasion of ► Poland World War II is a fact. Germany invades and occupies a lot of European countries and the NSDAP implements a program of genocide, at first through incarceration and forced labor and then by establishing death camps. This map shows the borders of Germany on August 31, 1939 Die deutsche Grenze, 31. August, 1939 |
 |
Administrative districts in territories under the control of Nazi Germany in 1941. Großdeutschland im Jahre 1941 |
 |
Eastern front of the Second World War circa 1941-1942. |
 |
Administrative units of the NSDAP 1944 |
 |
Greater Germany 1944 (German) |
 |
Greater Germany 1944 (English) |
 |
Main German Nazi concentration and extermination camps. Bordures from 1943. |
 |
Several plans, such as the Morgenthau Plan exist for the division and dismemberment of Germany after its defeat. Germany is to be divided into two separate states, while the Ruhr and its surrounding territories are to become an Internationally administered area. The Saar, East Prussia, and Upper Silesia are to be removed from Germany . |
 |
Another plan is the Roosevelt Plan |
 |
The Bakker Schut plan is a Dutch plan for the annexation of border regions. |
Germany after the Nazis
| 1945-1949: Occupied Germany - country under occupation of the allied powers |
 |
During the Yalta Conference in February 1945, and during the Potsdam Comference of August 1945 the Allies discussed the dismemberment and annexation of German territory. As context data in the discussions with their Allies the United States Department of State created a map roughly showing how many millions of German that they would have to deport as a consequence of the various proposals for a new German border in the east. |
 |
After Germany's unconditional surrender in 1945, the German Empire is dissolved and the United States, the United Kingdom, the USSR and, later, France occupy the country and assume responsibility for its administration. |
 |
In 1949, while the Industrial plans for Germany are being carried out, the country has been divided and dismembered. The Former eastern territories of Germany have been detached, as has an expanded Saarland. While not detached, the Ruhr area is under the control of the International Authority for the Ruhr and Berlin has been split in two. |
 |
Oder-neisse |
 |
Map of the occupation zones in Germany, 1945. It uses the German borders from 1937 since the Allies had decided to invalidate the 1938 German annexation of the German speaking Sudetenland and the Anschluss of Austria. It shows what would become the Inner German border in black and It also shows the area from which U.S. and British troops withdrew in the summer of 1945, including parts of the Sudetenland (which thereafter was ethnically cleansed). |
 |
Occupation Zones in Germany in 1947, using the 1937 external borders. It shows how the French have detached the Saar and turned it into a protectorate and the East German territories (east of the Oder-neisse line) that are under Polish and Soviet administration (de-facto annexation). In West German politics the annexation of the Eastern quarter of Germany remained for decades regarded as only temporary and the land was still considered German despite the 1944-1950 Expulsion of Germans after World War II, partly due to the political influence of this group of more than 12 million people, most of which now were in West Germany. |
 |
The commanders in chief exercised supreme authority in their respective zones and act in concert on questions affecting the whole country. ► Saarland becomes a separate polity aligned with France. Some Eastern parts are incorporated into Poland and the USSR. The German capital Berlin gets a separate status. Though the United States, the United Kingdom and the USSR agree in 1945 to treat Germany as a single economic unit with some central administrative departments in a decentralized framework, Soviet policy turns increasingly toward dominating that part of Europe where their armies are present, including eastern Germany. The United States and the United Kingdom move to establish a nucleus for a future German government by creating a central Economic Council for their two zones. The program later provides for a constituent assembly, an occupation statute governing relations between the Allies and the German authorities, and the political and economic merger of the French with the British and American zones. |
 |
1945-1946 |
 |
Soviet Sector of Germany (1945-1949), shown with pre-war German borders |
 |
In 1948 the Soviets, in an attempt to abrogate agreements for Four-Power control of the city, blockade Berlin. Until May 1949 the Allied-occupied part of Berlin is kept supplied only by an Allied airlift. The "Berlin airlift" succeeds in forcing the Soviets to accept, for the time being, the Allied role and the continuation of freedom in a portion of the city, West Berlin. This map shows the four sectors of the occupied Berlin[4] |
 |
The four sectors of Berlin |
Divided Germany
| 1949-present: Federal Republic of Germany (Bundesrepublik Deutschland) - independent federal republic |
 |
The United States and the United Kingdom move to establish a nucleus for a future German government by creating a central Economic Council for their two zones. The program later provides for a constituent assembly, an occupation statute governing relations between the Allies and the German authorities, and the political and economic merger of the French with the British and American zones. With the support of the United States, the United Kingdom and France the Federal Republic of Germany is constituted in 1949. At the same time in the USSR occupation zone the ► German Democratic Republic is established. |
 |
States in 1949 |
 |
Dismantling of "surplus" German heavy industry as reparations had the goal of lowering German standards of living to pre-defined minimum subsistence levels and thereby permanently removing the German industrial capacity to wage war. In West Germany the dismantling, which by then was occuring principaly in the Steel industry of the Ruhr area and had slowed down considerably, was ended in 1951 in connection with the German signing of the treaty for the European Coal and Steel Community. |
 |
States in 1952 |
 |
In 1957 Saar rejoined the Federal Republic of Germany. This map shows the states in 1957 |
 |
The Berlin Wall is the symbol of the controversy over Berlin. |
United Germany: Federal Republic of Germany
 |
After the collapse of the communist regime in 1990 the German Democratic Republic is incorporated into the Federal Republic of Germany. Berlin becomes a constituent part of Germany. |
 |
German federate states, the Länder, as created 1945-1947 after WWII. In red as of united Germany BRD in 1990. |
Linguistic maps
 |
German language througout the world |
 |
The development of the Germanic linguistic area |
 |
Map of German dialects |
 |
Dialectal ranges (not those of standard languages) of the Continental West Germanic languages |
 |
Green: High German Blue: Middle German Orange: Low German Light orange: Dutch Rose (light and intense): Frisian Light blue: Limburgish |
 |
German dialects |
 |
Low Saxon dialects since 1945 |
Religion maps
 |
Roman Catholic Ecclesiastical provinces |
 |
The member churches of the Evangelical Church in Germany |
 |
Church membership, 2011 |
 |
Membership in the Evangelical Church in Germany, 2011 |
 |
Membership in the Roman Catholic Church in Germany, 2011 |
 |
Membership in other religious groups as well as irreligion, 2011 |
Other maps
 |
Motorways (Autobahnen) in Germany |
 |
Motorways (Autobahnen) in Germany with borders of counties |
 |
German railways |
 |
Airports in Germany |
 |
Comparison of international airports in Germany |
 |
Public transport systems in Germany |
 |
Public transport associations in Germany |
 |
Nuclear energy in Germany |
 |
Research nuclear energy in Germany |
 |
Höchstspannungsnetz Deutschland |
 |
Windkraftanlagen in Deutschland (2011) |
 |
Sonnenstrahlung Karte – Deutschland |
 |
Centres of Deutsche Post AG for distribute letters |
 |
Map of the ARD member broadcasters |
 |
Map of German Green Belt |
 |
Wildlife parks in Germany |
 |
National parks in Germany |
 |
Biosphere Reserves in Germany |
 |
Wine regions |
 |
Show caves in Germany |
 |
Planetariums in Germany |
 |
World Heritage Sites in Germany |
 |
Car number plates |
 |
Kopftuchverbote im Schuldienst in Deutschland |
See also
Satellite maps
Notes and references
|
General remarks:
|
Entries available in the atlas
|
General pages The world and its continents and oceans (History, European Union) • Oceania • Oceans Themes Historical eras Entities with undisputed sovereign status Entities with disputed sovereign status Dependencies and other overseas territories Disputed subnational entities and territories Subnational autonomous entities Other regions Former sovereign nations Former dependencies and overseas territories |