Donitriptan
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Jump to: navigation, search
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | None |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | 170912-52-4 |
| PubChem (CID) | 197706 |
| ChemSpider | 171128 |
| UNII | 70968BVH2J |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1742428 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H25N5O2 |
| Molar mass | 403.477 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
|
|
|
|
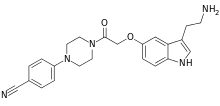
Donitriptan (INN) (code name F-11356) is a triptan drug which was investigated as an antimigraine agent but ultimately was never marketed.[1] It acts as a high-affinity, high-efficacy/near-full agonist of the 5-HT1B (pKi = 9.4–10.1; IA = 94%) and 5-HT1D receptors (pKi = 9.3–10.2; IA = 97%), and is among the most potent of the triptan series of drugs.[2][3][4] Donitriptan was being developed in France by bioMérieux-Pierre Fabre and made it to phase II clinical trials in Europe before development was discontinued.[5][6][7]
References[edit]
- ^ Dukat M (March 2001). "Donitriptan (Pierre Fabre)". Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2 (3): 415–8. PMID 11575714.
- ^ Perez M, Fourrier C, Sigogneau I, Pauwels PJ, Palmier C, Valentin JP, John GW, Halazy S (1995) Synthesis and serotonergic activity of arylpiperazide derivatives of serotonin: Potent agonists for 5-HT1D receptors. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 38:3602–3607.
- ^ Jes Olesen (2006). The Headaches. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 470–. ISBN 978-0-7817-5400-2.
- ^ John GW, Pauwels PJ, Perez M, et al. (July 1999). "F 11356, a novel 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) derivative with potent, selective, and unique high intrinsic activity at 5-HT1B/1D receptors in models relevant to migraine". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 290 (1): 83–95. PMID 10381763.
- ^ Chas Bountra; Rajesh Munglani; William K. Schmidt (28 May 2013). Pain: Current Understanding, Emerging Therapies, and Novel Approaches to Drug Discovery. CRC Press. pp. 402–. ISBN 978-0-203-91125-9.
- ^ W.W. Fleischhacker; D.J. Brooks (21 May 2003). Neuropsychopharmacology. Springer Vienna. pp. 38–. ISBN 978-3-211-83903-4.
- ^ Stewart J. Tepper (2004). Understanding Migraine and Other Headaches. Univ. Press of Mississippi. pp. 118–. ISBN 978-1-60473-048-7.
|
Antimigraine preparations (N02C)
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analgesic/abortive |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Prophylactic |
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Simple piperazines (no additional rings) |
|
|---|---|
| Phenylpiperazines |
|
| Benzylpiperazines | |
| Diphenylalkylpiperazines (benzhydrylalkylpiperazines) |
|
| Pyrimidinylpiperazines | |
| Pyridinylpiperazines | |
| Benzo(iso)thiazolylpiperazines | |
| Tricyclics (piperazine attached via side chain) |
|
| Others/Uncategorized | |
| This drug article relating to the nervous system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |