Zapotin
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
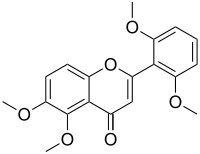 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-(2,6-Dimethoxyphenyl)-5,6-dimethoxy-4H-chromen-4-one
|
|
| Identifiers | |
| 14813-19-5 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 547068 |
| PubChem | 629965 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C19H18O6 | |
| Molar mass | 342.35 g·mol−1 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Zapotin is a natural chemical compound, classified as a flavone, isolated from White sapote (Casimiroa edulis).[1]
Several recent in vitro studies have shown that zapotin has potential anti-carcinogenic effects against isolated colon cancer cells.[2][3]
References[edit]
- ^ Sondheimer, F (1960). "Constituents of Casimiroa edulis Llave et Lex.—VI 2′,5,6-Trimethoxyflavone, 2′,5,6,7-tetramethoxyflavone (zapotin) and 5-hydroxy-2′,6,7-trimethoxyflavone (zapotinin)". Tetrahedron. 9 (3–4): 139–144. doi:10.1016/0040-4020(60)80001-4.
- ^ Murillo G, Hirschelman WH, Ito A, et al. (2007). "Zapotin, a phytochemical present in a Mexican fruit, prevents colon carcinogenesis". Nutrition and Cancer. 57 (1): 28–37. doi:10.1080/01635580701268097. PMID 17516860.
- ^ Maiti A, Cuendet M, Kondratyuk T, Croy VL, Pezzuto JM, Cushman M (Jan 2007). "Synthesis and cancer chemopreventive activity of zapotin, a natural product from Casimiroa edulis". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. American Chemical Society. 50 (2): 350–5. doi:10.1021/jm060915+. PMC 2523270
 . PMID 17228877.
. PMID 17228877.