Bevantolol
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
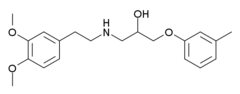 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| ATC code | C07AB06 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | 59170-23-9 |
| PubChem (CID) | 2372 |
| DrugBank | DB01295 |
| ChemSpider | 2282 |
| UNII | 34ZXW6ZV21 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:238698 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL314010 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H27NO4 |
| Molar mass | 345.43 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
|
|
|
|
| (verify) | |
Bevantolol (INN) was a drug candidate for angina and hypertension that acted as both a beta blocker and a calcium channel blocker.[1][2] It was discovered and developed by Warner-Lambert[3] but in January 1989 the company announced that it had withdrawn the New Drug Application; the company's chairman said: "Who needs the 30th beta blocker?"[4] As of 2016 it wasn't marketed in the US, UK, or Europe and the authors of a Cochrane review could find no product monograph for it.[5]
References[edit]
- ^ Frishman, WH; Goldberg, RJ; Benfield, P (January 1988). "Bevantolol. A preliminary review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic efficacy in hypertension and angina pectoris.". Drugs. 35 (1): 1–21. PMID 2894292.
- ^ Vaughan Williams, EM (July 1987). "Bevantolol: a beta-1 adrenoceptor antagonist with unique additional actions.". Journal of clinical pharmacology. 27 (7): 450–60. PMID 2888789.
- ^ McPherson, Edwin M. (2007). Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Encyclopedia. (3rd ed. ed.). Burlington: Elsevier. pp. 618–619. ISBN 9780815518563.
- ^ "Warner-Lambert Pipeline Narrowed to 40 Active Research Compounds". Pink Sheet. 30 January 1989.
- ^ Wong, GW; Boyda, HN; Wright, JM (10 March 2016). "Blood pressure lowering efficacy of beta-1 selective beta blockers for primary hypertension.". The Cochrane database of systematic reviews. 3: CD007451. PMID 26961574.
| This article about an amine is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
| This drug article relating to the cardiovascular system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |