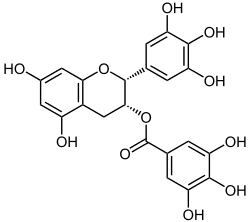
Epigallocatechin gallate
Names
IUPAC name
[(2R ,3R )-5,7-dihydroxy-2-(3,4,5-trihydroxyphenyl)chroman-3-yl] 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate
Preferred IUPAC name
(2R ,3R )-5,7-dihydroxy-2-(3,4,5-trihydroxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H -1-benzopyran-3-yl 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate
Other names
(-)-Epigallocatechin gallate
Identifiers
989-51-5 N
3D model (Jmol )
Interactive image
ChEBI CHEBI:4806 Y
ChEMBL ChEMBL297453 Y
ChemSpider 58575 Y
ECHA InfoCard 100.111.017
7002
MeSH Epigallocatechin+gallate
PubChem 65064
InChI=1S/C22H18O11/c23-10-5-12(24)11-7-18(33-22(31)9-3-15(27)20(30)16(28)4-9)21(32-17(11)6-10)8-1-13(25)19(29)14(26)2-8/h1-6,18,21,23-30H,7H2/t18-,21-/m1/s1
Y Key: WMBWREPUVVBILR-WIYYLYMNSA-N
Y
InChI=1/C22H18O11/c23-10-5-12(24)11-7-18(33-22(31)9-3-15(27)20(30)16(28)4-9)21(32-17(11)6-10)8-1-13(25)19(29)14(26)2-8/h1-6,18,21,23-30H,7H2/t18-,21-/m1/s1
Key: WMBWREPUVVBILR-WIYYLYMNBM
O=C(O[C@@H]2Cc3c(O[C@@H]2c1cc(O)c(O)c(O)c1)cc(O)cc3O)c4cc(O)c(O)c(O)c4
Properties
C 22 H 18 O 11
Molar mass 458.372 g/mol
Appearance
soluble (33.3-100 g/L)[vague [1]
Solubility soluble in ethanol, DMSO, dimethyl formamide[1] [2]
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their
standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
N verify what is Y N
Infobox references
Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG ), also known as epigallocatechin-3-gallate , is the ester of epigallocatechin and gallic acid , and is a type of catechin .
EGCG, the most abundant catechin in tea , is a polyphenol under basic research for its potential to affect human health and disease. EGCG is used in many dietary supplements .
Food sources [ edit ] It is found in high content in the dried leaves of white tea (4245 mg per 100 g), green tea (7380 mg per 100 g) and, in smaller quantities, black tea .[3] theaflavins and thearubigins .[4] polyphenol oxidases .[which?
Trace amounts are found in apple skin, plums , onions , hazelnuts , pecans and carob powder (at 109 mg per 100 g).[3]
Bioavailability [ edit ] When taken orally, EGCG has poor bioavailability even at such a high amount of daily intake equivalent to 8-16 cups of tea (800 mg), a dose causing mild adverse effects , such as nausea or heartburn .[5] urine over 3–15 hours.[6]
Research on potential therapeutic uses [ edit ] EGCG has been the subject of a number of basic and clinical research studies investigating its potential use as a therapeutic for a broad range of disorders.[7] [8] [9] [8] [9] Food and Drug Administration has issued warning letters against marketers of products claiming that EGCG provides anti-disease effects or overall health benefits.[10] [11]
See also [ edit ] References [ edit ]
^ a b "(-)-Epigallocatechin gallate" . Chemicalland21.com . ^ "Product Information: (-)-Epigallocatechin Gallate" (PDF) . Cayman Chemical. 4 September 2014. ^ a b Bhagwat, Seema; Haytowitz, David B.; Holden, Joanne M. (September 2011). USDA Database for the Flavonoid Content of Selected Foods, Release 3 (PDF) (Report). Agricultural Research Service, U.S. Department of Agriculture. Retrieved 18 May 2015 . ^ Lorenz, Mario; Urban, Janka; Engelhardt, Ulrich; Baumann, Gert; Stangl, Karl; Stangl, Verena (January 2009). "Green and Black Tea are Equally Potent Stimuli of NO Production and Vasodilation: New Insights into Tea Ingredients Involved". Basic Research in Cardiology . 104 (1): 100–110. doi :10.1007/s00395-008-0759-3 . PMID 19101751 . (subscription required (help )) . ^ Chow, H-H. Sherry; Cai, Yan; Hakim, Iman A.; Crowell, James A.; Shahi, Farah; Brooks, Chris A.; Dorr, Robert T.; Hara, Yukihiko; Alberts, David S. (15 August 2003). "Pharmacokinetics and safety of green tea polyphenols after multiple-dose administration of epigallocatechin gallate and polyphenon E in healthy individuals" . Clinical Cancer Research . 9 (9): 3312–3319. PMID 12960117 . ^ Lee, Mao-Jung; Maliakal, Pius; Chen, Laishun; Meng, Xiaofeng; Bondoc, Flordeliza Y.; Prabhu, Saileta; Lambert, George; Mohr, Sandra; Yang, Chung S. (October 2002). "Pharmacokinetics of tea catechins after ingestion of green tea and (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate by humans: formation of different metabolites and individual variability" . Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention . 11 (10 Pt 1): 1025–1032. PMID 12376503 . ^ Fürst, Robert; Zündorf, Ilse (May 2014). "Plant-derived anti-inflammatory compounds: hopes and disappointments regarding the translation of preclinical knowledge into clinical progress" (PDF) . Mediators of Inflammation . 2014 . doi :10.1155/2014/146832 . PMID 24987194 . 146832. ^ a b "Green tea" . National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health . U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, National Institutes of Health. 5 January 2016. ^ a b EFSA NDA Panel (EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies) (2011). "Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to Camellia sinensis (L.) Kuntze (tea), including catechins in green tea, and improvement of endothelium-dependent vasodilation (ID 1106, 1310), maintenance of normal blood pressure" . EFSA Journal . European Food Safety Authority. 9 (4). doi :10.2903/j.efsa.2011.2055 . ^ "Sharp Labs Inc: Warning Letter" . Inspections, Compliance, Enforcement, and Criminal Investigations . Food and Drug Administration. 9 July 2008. Retrieved 15 September 2015 . ^ "Fleminger Inc: Warning Letter" . Inspections, Compliance, Enforcement, and Criminal Investigations . Food and Drug Administration. 22 February 2010. Retrieved 6 January 2015 .
Food antioxidants
Fuel antioxidants
Measurements
Flavan-3-ols
O-methylated flavan-3ols
Glycosides
Acetylated
Misc.
ER
Agonists
Steroidal: 3α-Androstanediol 3β-Androstanediol 3α-Hydroxytibolone 3β-Hydroxytibolone 4-Androstenediol 4-Androstenedione 4-Hydroxyestradiol 4-Hydroxyestrone 5-Androstenediol 7-Oxo-DHEA 7α-Hydroxy-DHEA 7β-Hydroxyepiandrosterone 8,9-Dehydroestradiol 8,9-Dehydroestrone 8β-VE2 16α-Hydroxy-DHEA 16α-Hydroxyestrone 16α-Iodo-E2 16α-LE2 16β,17α-Epiestriol (16β-hydroxy-17α-estradiol) 17α-Dihydroequilenin 17α-Dihydroequilin 17α-Epiestriol (16α-hydroxy-17α-estradiol) 17β-Dihydroequilenin 17β-Dihydroequilin Abiraterone Abiraterone acetate 17α-Estradiol (alfatradiol) Alestramustine Almestrone Anabolic steroids (e.g., testosterone and esters , methyltestosterone , metandienone (methandrostenolone) , nandrolone and esters , many others; via estrogenic metabolites)Atrimustine Bolandiol Bolandiol dipropionate Butolame Clomestrone Cloxestradiol
DHEA DHEA-S Digitoxin (digitalis )Diosgenin Epiestriol (16β-epiestriol, 16β-hydroxy-17β-estradiol) Epimestrol Equilenin Equilin Estetrol Estradiol
Estramustine Estramustine phosphate Estrapronicate Estrazinol Estriol
Estrofurate Estromustine Estrone
Etamestrol (eptamestrol) Ethinyl estradiol
Ethinyl estriol Etynodiol diacetate Guggulsterone Hexolame Hydroxyestrone diacetate Mestranol Methylestradiol Moxestrol Mytatrienediol Nilestriol Noretynodrel Orestrate Pentolame Phytosterols (e.g., β-sitosterol , campesterol , stigmasterol )Polyestradiol phosphate Prodiame Prolame Promestriene Quinestradol Quinestrol
Non-steroidal: (R,R)-THC (S,S)-THC 1-Keto-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrophenanthrene 2,8-DHHHC Allenoic acid Alternariol Anethole Anol Benzestrol Bifluranol Biochanin A Bisdehydrodoisynolic acid Carbestrol Chalconoids (e.g., isoliquiritigenin , phloretin , phlorizin (phloridzin) , wedelolactone )Coumestans (e.g., coumestrol , psoralidin )Deoxymiroestrol Dianethole Dianol Diarylpropionitrile Dieldrin Dienestrol
Diethylstilbestrol
Dimestrol (dianisylhexene) Dimethylallenolic acid Doisynoestrol (fenocycline) Doisynolic acid Efavirenz Endosulfan ERB-196 (WAY-202196) Estrobin (DBE) Fenarimol Fenestrel FERb 033 Flavonoids (incl. 7,8-DHF , 8-prenylnaringenin , apigenin , baicalein , baicalin , calycosin , catechin , daidzein , daidzin , ECG , EGCG , epicatechin , equol , formononetin , glabrene , glabridin , genistein , genistin , glycitein , kaempferol , liquiritigenin , mirificin , myricetin , naringenin , pinocembrin , prunetin , puerarin , quercetin , tectoridin , tectorigenin )Fosfestrol (diethylstilbestrol diphosphate) Furostilbestrol (diethylstilbestrol difuroate) GTx-758 Hexestrol
ICI-85966 (Stilbostat) Lavender oil Lignans (e.g., enterodiol , enterolactone )Mestilbol Metalloestrogens (e.g., cadmium )Methallenestril Methestrol Methestrol dipropionate Methiocarb Methoxychlor Miroestrol Nyasol (cis -hinokiresinol) Paroxypropione Pentafluranol Phenestrol Photoanethole Prinaberel (ERB-041, WAY-202041) Propylpyrazoletriol Resorcylic acid lactones (e.g., zearalanone , zearalenol , zearalenone , zeranol (α-zearalanol) , taleranol (teranol, β-zearalanol) )Quadrosilan SC-4289 SKF-82,958 Stilbenoids (e.g., resveratrol )Synthetic xenoestrogens (e.g., alkylphenols , bisphenols (e.g., BPA , BPF , BPS ), DDT , parabens , PBBs , PHBA , phthalates , PCBs )Terfluranol WAY-166818 WAY-200070 Triphenylchlorethylene Triphenylmethylethylene WAY-214156
Antagonists
GPER
HMGCR
FPS
24-DHCR24
20,22-Desmolase
17α-Hydroxylase,
3α-HSD
3β-HSD
11β-HSD
21-Hydroxylase
11β-Hydroxylase
18-Hydroxylase
17β-HSD
5α-Reductase
Aromatase
Inhibitors: 4-AT 4-Cyclohexylaniline 4-Hydroxytestosterone 5α-DHNET 20α-Dihydroprogesterone Abyssinone II Aminoglutethimide Anastrozole Ascorbic acid (vitamin C )Atamestane ATD Bifonazole CGP-45,688 CGS-47,645 Chalconoids (e.g., isoliquiritigenin )Clotrimazole Corynesidone A Coumestrol DHT Difeconazole Econazole Ellagitannins Endosulfan Exemestane Fadrozole Fatty acids (e.g., conjugated linoleic acid , linoleic acid , linolenic acid , palmitic acid )Fenarimol Finrozole Flavonoids (e.g., 7-hydroxyflavone , 7-hydroxyflavanone , 7,8-DHF , acacetin , apigenin , baicalein , biochanin A , chrysin , EGCG , gossypetin , hesperetin , liquiritigenin , myricetin , naringenin , pinocembrin , rotenone , quercetin , sakuranetin , tectochrysin )Formestane Imazalil Isoconazole Ketoconazole Letrozole Liarozole Melatonin MEN-11066 Miconazole Minamestane Nimorazole NKS01 Norendoxifen ORG-33,201 Penconazole Phenytoin Prochloraz PGE2 (dinoprostone) Plomestane Prochloraz Propioconazole Pyridoglutethimide Quinolinoids (e.g., berberine , casimiroin , triptoquinone A , XHN22 , XHN26 , XHN27 )Resorcylic acid lactones (e.g., zearalenone )Rogletimide Stilbenoids (e.g., resveratrol )Talarozole Terpenoids (e.g., dehydroabietic acid , (–)-dehydrololiolide , retinol (vitamin A ), Δ9 -THC , tretinoin )Testolactone Tioconazole Triadimefon Triadimenol Troglitazone Valproic acid Vorozole Xanthones (e.g., garcinone D , garcinone E , α-mangostin , γ-mangostin , monodictyochrome A , monodictyochrome B )YM-511 Zinc
SST /EST
STS
27-Hydroxylase
Others
Inhibitors: Inhibit estradiol degradation: Cimetidine
Common
By country
Culture
Customs
Associated places
By country
History
Production and
Preparation
Tea and health
Sale
Tea-based
See also