- published: 02 Apr 2014
- views: 111757
-
remove the playlistGroundwater
- remove the playlistGroundwater
- published: 23 Jan 2013
- views: 18201
- published: 09 May 2012
- views: 56926
- published: 03 May 2006
- views: 174115
- published: 30 May 2016
- views: 5919
- published: 08 Oct 2015
- views: 206103
- published: 02 Apr 2014
- views: 10040
- published: 24 Jun 2014
- views: 6027

Groundwater
Groundwater (or ground water) is the water present beneath Earth's surface in soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. A unit of rock or an unconsolidated deposit is called an aquifer when it can yield a usable quantity of water. The depth at which soil pore spaces or fractures and voids in rock become completely saturated with water is called the water table. Groundwater is recharged from, and eventually flows to, the surface naturally; natural discharge often occurs at springs and seeps, and can form oases or wetlands. Groundwater is also often withdrawn for agricultural, municipal, and industrial use by constructing and operating extraction wells. The study of the distribution and movement of groundwater is hydrogeology, also called groundwater hydrology.
Typically, groundwater is thought of as water flowing through shallow aquifers, but, in the technical sense, it can also contain soil moisture, permafrost (frozen soil), immobile water in very low permeability bedrock, and deep geothermal or oil formation water. Groundwater is hypothesized to provide lubrication that can possibly influence the movement of faults. It is likely that much of Earth's subsurface contains some water, which may be mixed with other fluids in some instances. Groundwater may not be confined only to Earth. The formation of some of the landforms observed on Mars may have been influenced by groundwater. There is also evidence that liquid water may also exist in the subsurface of Jupiter's moon Europa.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 5:11
5:11What Is Groundwater?
What Is Groundwater?What Is Groundwater?
This lighthearted animation tells the story of groundwater: where it is, where it comes from, and where it goes. Learn more about this video: http://ow.ly/vcFiU -
 10:30
10:30What is groundwater?
What is groundwater?What is groundwater?
What Is Groundwater? How does it affect our daily lives, and why is it so important? Where does it fit in within the Water Cycle? All this and more as this educational video explains many facets and concepts behind one of Western Australia's major water sources. 1:07 - Fresh Water Breakdown 1:35 - Where Does Groundwater Come From? 2:16 - Most Groundwater Comes from Rainfall 2:59 - Porosity Example 3:31 - Permeability 4:39 - Raindrop animation 4:54 - Aquifers 6:14 - call to action to Preserve water 6:30 - Confined Aquifer 8:03 - The Water table 8:46 - Summary For a better quality render check here: https://youtu.be/-4F4h6KLiK4 Subscribe: http://goo.gl/1TKSCX Facebook: http://www.watercorporation.com.au/ Twitter: https://twitter.com/watercorpwa Website: https://www.watercorporation.com.au/ -
 5:46
5:46Groundwater introduction
Groundwater introductionGroundwater introduction
A basic introduction to the groundwater of Adelaide -- with Russell Martin. Looks at the different aquifers under the Adelaide Plains, their geological history, and how groundwater is used in Adelaide. -
 3:44
3:44Groundwater Animation
Groundwater AnimationGroundwater Animation
Groundhogs sing us a song about Groundwater. Concepts cover the historical path of water, uses of water and dangers groundwater faces. Better quality version here 2013 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0duNtVQojTM 2006 Full Quality Flash https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0duNtVQojTM -
 26:59
26:59Groundwater - Hydrogeology, 3 Zones, Process & Factors, Aquifers, Aquiclude, Aquitard
Groundwater - Hydrogeology, 3 Zones, Process & Factors, Aquifers, Aquiclude, AquitardGroundwater - Hydrogeology, 3 Zones, Process & Factors, Aquifers, Aquiclude, Aquitard
Dr. Manishika Jain explains concept of groundwater, the three types of water viz., Meteoric Water Connate Water Magmatic/Juvenile Water Zones of Groundwater, Zone of aeration or vadose zone Zone of Saturation Zone of Intermittent Saturation Concept of Aquifer, Aquiclude & Aquitard Along with factors affecting groundwater Porosity Permeability Darcy's Law - Velocity & Discharge Join our fully evaluated UPSC Geography optional test series at - https://www.doorsteptutor.com/Exams/IAS/Mains/Optional/Geography/Test-Series/, Post evaluation get personalized feedback & improvement call for each test. IAS Mains Geography optional postal course visit - http://www.examrace.com/IAS/IAS-FlexiPrep-Program/Postal-Courses/Examrace-IAS-Geography-Series.htm For Maps and locations books click here - http://www.examrace.com/IAS/IAS-FlexiPrep-Program/Postal-Courses/Examrace-IAS-Geography-Maps-Series.htm CBSE NET Geography optional postal course visit - http://www.examrace.com/CBSE-UGC-NET/CBSE-UGC-NET-FlexiPrep-Program/Postal-Courses/Examrace-CBSE-UGC-NET-Geography-Series.htm Lectures organised in topics and subtopics: https://www.doorsteptutor.com/Exams/IAS/Mains/Optional/Geography/ For IAS Prelims visit https://www.doorsteptutor.com/Exams/IAS/Prelims/ For Lecure Handouts visit http://www.examrace.com/Study-Material/Geography/ or do google search "Youtube Lecture Handouts Examrace Groundwater" Have a doubt? No worries. We promptly respond to queries asked as comments. -
 3:49
3:49Groundwater Flow Demonstration Model
Groundwater Flow Demonstration ModelGroundwater Flow Demonstration Model
I was commissioned to build this model in support of a presentation about geotechnical engineering. The goal is to illustrate the flow paths that groundwater takes under an obstruction (e.g. a sheet pile or cutoff wall). So much of engineering is just theoretical work, so it was really cool to see such an elegant example of a geotechnical engineering concept borne out in real dirt and water. Thanks for watching and let me know what you think. -
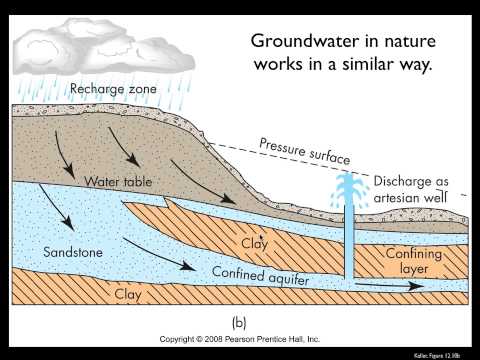 5:38
5:38Groundwater Flow - Part 1
Groundwater Flow - Part 1Groundwater Flow - Part 1
How does groundwater flow from one place to another? And how do we tell? -
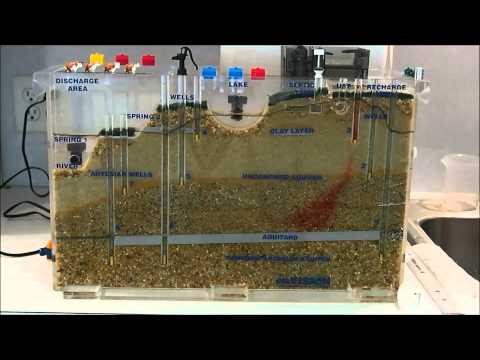 21:13
21:13Lab 5 Groundwater Model 1
Lab 5 Groundwater Model 1Lab 5 Groundwater Model 1
-
 1:49
1:49It's called groundwater!
It's called groundwater!It's called groundwater!
Groundwater is an important source of fresh water for industries, municipalities, farms, and rural homeowners in British Columbia. BC operates a network of over 180 observation wells to track groundwater levels in areas of high use. This information helps us to see how healthy aquifers are so we can make good decisions about groundwater use in BC. See trends in BC groundwater levels: http://www.env.gov.bc.ca/soe/indicators/water/wells/index.html Download BC groundwater data: http://www.env.gov.bc.ca/wsd/data_searches/obswell/index.html Learn more about freshwater in BC: http://www.gov.bc.ca/water -
 2:01
2:01GROUND WATER TESTING WITH COCONUT
GROUND WATER TESTING WITH COCONUTGROUND WATER TESTING WITH COCONUT
WHILE BUYING LAND OR AFTER BUYING WATER CHECK FOR BOREWELLS.
-

What Is Groundwater?
This lighthearted animation tells the story of groundwater: where it is, where it comes from, and where it goes. Learn more about this video: http://ow.ly/vcFiU
published: 02 Apr 2014 -

What is groundwater?
What Is Groundwater? How does it affect our daily lives, and why is it so important? Where does it fit in within the Water Cycle? All this and more as this educational video explains many facets and concepts behind one of Western Australia's major water sources. 1:07 - Fresh Water Breakdown 1:35 - Where Does Groundwater Come From? 2:16 - Most Groundwater Comes from Rainfall 2:59 - Porosity Example 3:31 - Permeability 4:39 - Raindrop animation 4:54 - Aquifers 6:14 - call to action to Preserve water 6:30 - Confined Aquifer 8:03 - The Water table 8:46 - Summary For a better quality render check here: https://youtu.be/-4F4h6KLiK4 Subscribe: http://goo.gl/1TKSCX Facebook: http://www.watercorporation.com.au/ Twitter: https://twitter.com/watercorpwa Website: https://www.watercorporation.com...
published: 23 Jan 2013 -

Groundwater introduction
A basic introduction to the groundwater of Adelaide -- with Russell Martin. Looks at the different aquifers under the Adelaide Plains, their geological history, and how groundwater is used in Adelaide.
published: 09 May 2012 -

Groundwater Animation
Groundhogs sing us a song about Groundwater. Concepts cover the historical path of water, uses of water and dangers groundwater faces. Better quality version here 2013 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0duNtVQojTM 2006 Full Quality Flash https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0duNtVQojTM
published: 03 May 2006 -

Groundwater - Hydrogeology, 3 Zones, Process & Factors, Aquifers, Aquiclude, Aquitard
Dr. Manishika Jain explains concept of groundwater, the three types of water viz., Meteoric Water Connate Water Magmatic/Juvenile Water Zones of Groundwater, Zone of aeration or vadose zone Zone of Saturation Zone of Intermittent Saturation Concept of Aquifer, Aquiclude & Aquitard Along with factors affecting groundwater Porosity Permeability Darcy's Law - Velocity & Discharge Join our fully evaluated UPSC Geography optional test series at - https://www.doorsteptutor.com/Exams/IAS/Mains/Optional/Geography/Test-Series/, Post evaluation get personalized feedback & improvement call for each test. IAS Mains Geography optional postal course visit - http://www.examrace.com/IAS/IAS-FlexiPrep-Program/Postal-Courses/Examrace-IAS-Geography-Series.htm For Maps and locations books click here -...
published: 30 May 2016 -

Groundwater Flow Demonstration Model
I was commissioned to build this model in support of a presentation about geotechnical engineering. The goal is to illustrate the flow paths that groundwater takes under an obstruction (e.g. a sheet pile or cutoff wall). So much of engineering is just theoretical work, so it was really cool to see such an elegant example of a geotechnical engineering concept borne out in real dirt and water. Thanks for watching and let me know what you think.
published: 08 Oct 2015 -

Groundwater Flow - Part 1
How does groundwater flow from one place to another? And how do we tell?
published: 02 Apr 2014 -

Lab 5 Groundwater Model 1
published: 24 Jun 2014 -

It's called groundwater!
Groundwater is an important source of fresh water for industries, municipalities, farms, and rural homeowners in British Columbia. BC operates a network of over 180 observation wells to track groundwater levels in areas of high use. This information helps us to see how healthy aquifers are so we can make good decisions about groundwater use in BC. See trends in BC groundwater levels: http://www.env.gov.bc.ca/soe/indicators/water/wells/index.html Download BC groundwater data: http://www.env.gov.bc.ca/wsd/data_searches/obswell/index.html Learn more about freshwater in BC: http://www.gov.bc.ca/water
published: 24 Jun 2014 -

GROUND WATER TESTING WITH COCONUT
WHILE BUYING LAND OR AFTER BUYING WATER CHECK FOR BOREWELLS.
published: 21 Dec 2012
What Is Groundwater?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:11
- Updated: 02 Apr 2014
- views: 111757
- published: 02 Apr 2014
- views: 111757
What is groundwater?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:30
- Updated: 23 Jan 2013
- views: 18201
- published: 23 Jan 2013
- views: 18201
Groundwater introduction
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:46
- Updated: 09 May 2012
- views: 56926
- published: 09 May 2012
- views: 56926
Groundwater Animation
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:44
- Updated: 03 May 2006
- views: 174115
- published: 03 May 2006
- views: 174115
Groundwater - Hydrogeology, 3 Zones, Process & Factors, Aquifers, Aquiclude, Aquitard
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 26:59
- Updated: 30 May 2016
- views: 5919
- published: 30 May 2016
- views: 5919
Groundwater Flow Demonstration Model
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:49
- Updated: 08 Oct 2015
- views: 206103
- published: 08 Oct 2015
- views: 206103
Groundwater Flow - Part 1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:38
- Updated: 02 Apr 2014
- views: 10040
- published: 02 Apr 2014
- views: 10040
Lab 5 Groundwater Model 1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 21:13
- Updated: 24 Jun 2014
- views: 64196
- published: 24 Jun 2014
- views: 64196
It's called groundwater!
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:49
- Updated: 24 Jun 2014
- views: 6027
- published: 24 Jun 2014
- views: 6027
GROUND WATER TESTING WITH COCONUT
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:01
- Updated: 21 Dec 2012
- views: 140527
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

What Is Groundwater?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 02 Apr 2014
- views: 111757

What is groundwater?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Jan 2013
- views: 18201

Groundwater introduction
- Report rights infringement
- published: 09 May 2012
- views: 56926

Groundwater Animation
- Report rights infringement
- published: 03 May 2006
- views: 174115

Groundwater - Hydrogeology, 3 Zones, Process & Factors, Aquifers, Aquiclude, Aquitard
- Report rights infringement
- published: 30 May 2016
- views: 5919

Groundwater Flow Demonstration Model
- Report rights infringement
- published: 08 Oct 2015
- views: 206103

Groundwater Flow - Part 1
- Report rights infringement
- published: 02 Apr 2014
- views: 10040

Lab 5 Groundwater Model 1
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 Jun 2014
- views: 64196

It's called groundwater!
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 Jun 2014
- views: 6027

GROUND WATER TESTING WITH COCONUT
- Report rights infringement
- published: 21 Dec 2012
- views: 140527
-
Lyrics list:lyrics
-
Quarantatre, Disco Drive
Quarantatre
I gotta be, you gotta be
happy now, happier then
you have not to look miserable
Teenagers Recreated A $750 Drug For Just $2 Per Dose
Edit WPTV 01 Dec 2016Victoria's Secret Fashion Show Sparks Controversy
Edit Opposing Views 01 Dec 2016U.S. May Have to Forgive More Than $100 Billion In Student Loans
Edit WorldNews.com 01 Dec 2016India’s Supreme Court Gives Cinemas 10-Day Deadline to Begin Playing National Anthem
Edit WorldNews.com 01 Dec 2016Trump Taps Retired Marine General James Mattis For Defense Secretary
Edit WorldNews.com 01 Dec 2016Quick Chat with Timor-Leste based Defence member (Engineers Australia)
Edit Public Technologies 02 Dec 2016Cyclone Nada passes peacefully over Karaikal coast, heavy rains expected
Edit Deccan Chronicle 02 Dec 2016Denmark selectmen approve Poland Spring water extraction permit
Edit Conway Daily Sun 02 Dec 2016December 1, 2016 Handmade holiday gifts at the Campbellsport Public Library (Town of Ashford, WI)
Edit Public Technologies 02 Dec 2016November 9, 2016 Notice of Town Election on April 4, 2017, Town of Ashford (Town of Ashford, WI)
Edit Public Technologies 02 Dec 2016Manager of WKU hydrology lab conducts groundwater training program in Brazil (Western Kentucky University)
Edit Public Technologies 01 Dec 2016DEP Awards $150,000 Grant for Midway Infrastructure Improvements - 12/01/16 (Florida Department of Environmental Protection)
Edit Public Technologies 01 Dec 2016Mortality 10 times more in gas victims: Study
Edit The Times of India 01 Dec 2016DEP Final Report of Tenmile Creek Shows No Radioactivity Danger (State of Pennsylvania)
Edit Public Technologies 01 Dec 2016DEP Final Report of Tenmile Creek Shows No Radioactivity Danger (Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection)
Edit Public Technologies 01 Dec 2016UNESCO Deems Belgium's Beer Culture A Treasure Of Humanity
Edit National Public Radio 01 Dec 2016Light industries improve to help protect Perth’s rivers (State Government of Western Australia)
Edit Public Technologies 01 Dec 2016DEP's Daily Update on Mosaic - New Wales Sinkhole - 12/01/16 (Florida Department of Environmental Protection)
Edit Public Technologies 01 Dec 2016- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »








