Parathion
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
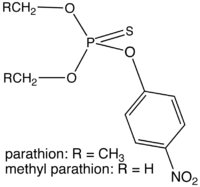
O,O-Diethyl O-(4-nitrophenyl) phosphorothioate
|
|
| Other names
E605
|
|
| Identifiers | |
| 56-38-2 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:27928 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL261919 |
| ChemSpider | 13844817 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.247 |
| KEGG | C06604 |
| UNII | 61G466064D |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C10H14NO5PS | |
| Molar mass | 291.26 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystals (pure form) |
| Melting point | 6 °C (43 °F; 279 K) |
| 24 mg/L | |
| Solubility in other solvents | high solubility |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | [1] |
|
EU classification (DSD)
|
|
| R-phrases | R24, R26/28, R48/25, R50/53 |
| S-phrases | S28, S36/37, S45, S60, S61 |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | 120 °C (248 °F; 393 K) |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
5 mg/kg (mouse, oral) 10 mg/kg (rabbit, oral) 3 mg/kg (dog, oral) 0.93 mg/kg (cat, oral) 5 mg/kg (horse, oral) 8 mg/kg (guinea pig, oral) 2 mg/kg (rat, oral)[3] |
|
LC50 (median concentration)
|
84 mg/m3 (rat, 4 hr)[3] |
|
LCLo (lowest published)
|
50 mg/m3 (rabbit, 2 hr) 14 mg/m3 (guinea pig, 2 hr) 15 mg/m3 (mouse)[3] |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
|
PEL (Permissible)
|
none (methyl parathion),[1] TWA 0.1 mg/m3 [skin] (ethyl parathion)[2] |
|
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 0.2 mg/m3 [skin] (methyl parathion)[1] TWA 0.05 mg/m3 [skin] (ethyl parathion)[2] |
|
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
N.D. (methyl parathion)[1] 10 mg/m3 (ethyl parathion)[2] |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Parathion, also called parathion-ethyl or diethyl parathion and locally known as "Folidol", is an organophosphate compound possessing a organothiophosphate group. It is a potent insecticide and acaricide. It was originally developed by IG Farben in the 1940s. It is highly toxic to non-target organisms, including humans. Its use is banned or restricted in many countries, and there are proposals to ban it from all use. The basic structure is shared by parathion methyl.
Contents
History[edit]
Parathion was developed by Gerhard Schrader for the German trust IG Farben in the 1940s. After the war and the collapse of IG Farben due to the war crime trials, the Western allies seized the patent, and parathion was marketed worldwide by different companies and under different brand names. The most common German brand was E605 (banned in Germany after 2002); this was not a food-additive "E number" as used in the EU today. "E" stands for Entwicklungsnummer (German for "development number"). It is an Irreversible Ach Inhibitor.
Safety concerns have later lead to the development of parathion methyl, which is somewhat less toxic.
Handling properties[edit]
When pure, parathion is a white crystalline solid. It is commonly distributed as a brown liquid that smells of rotting eggs or garlic. The insecticide is somewhat stable, although it darkens when exposed to sunlight.
Industrial synthesis[edit]
Parathion is synthesized from diethyl dithiophosphoric acid (C2H5O)2PS2H by chlorination to generate diethylthiophosphoryl chloride ((C2H5O)2P(S)Cl). In a salt metathesis reaction, the chloride treated with sodium 4-nitrophenolate (the sodium salt of 4-nitrophenol).[5]
- 2 (C2H5O)2P(S)SH + 3 Cl2 → 2 (C2H5O)2P(S)Cl + S2Cl2 + 2 HCl
- (C2H5O)2P(S)Cl + NaOC6H4NO2 → (C2H5O)2P(S)OC6H4NO2 + NaCl
Applications[edit]
As a pesticide, parathion is generally applied by spraying. It is often applied to cotton, rice and fruit trees. The usual concentrations of ready-to-use solutions are 0.05 to 0.1%. The chemical is banned for use on many food crops.
Insecticidal activity[edit]
Parathion acts on the enzyme acetylcholinesterase indirectly. After an insect (or a human) ingests parathion, an oxidase replaces the double bonded sulfur with oxygen to give paraoxon.[6]
- (C2H5O)2P(S)OC6H4NO2 + 1/2 O2 → (C2H5O)2P(O)OC6H4NO2 + S
The phosphate ester is more reactive in organisms than the phosphorothiolate ester, as the phosphorus atoms become much more electropositive.[6]
Degradation[edit]
Degradation of parathion leads to more water-soluble products. Hydrolysis, which deactivates the molecule, occurs at the aryl ester bond resulting in diethyl thiophosphate and 4-nitrophenol.[6]
- (C2H5O)2P(S)OC6H4NO2 + H2O → HOC6H4NO2 + (C2H5O)2P(S)OH
Degradation proceeds differently under anaerobic conditions: the nitro group on parathion is reduced to the amine.
- (C2H5O)2P(S)OC6H4NO2 + 6 H → (C2H5O)2P(S)OC6H4NH2 + 2 H2O
Safety[edit]
Parathion is a cholinesterase inhibitor. It generally disrupts the nervous system by inhibiting acetylcholinesterase. It is absorbed via skin, mucous membranes, and orally. Absorbed parathion is rapidly metabolized to paraoxon, as described in Insecticidal activity. Paraoxon exposure can result in headaches, convulsions, poor vision, vomiting, abdominal pain, severe diarrhea, unconsciousness, tremor, dyspnea, and finally lung-edema as well as respiratory arrest. Symptoms of poisoning are known to last for extended periods, sometimes months. The most common and very specific antidote is atropine, in doses of up to 100 mg daily. Because atropine may also be toxic, it is recommended that small frequently repeated doses be used in treatment. If human poisoning is detected early and the treatment is prompt (atropine and artificial respiration), fatalities are infrequent. Insufficient oxygen will lead to cerebral hypoxia and permanent brain damage. Peripheral neuropathy including paralysis is noticed as late sequelae after recovery from acute intoxication. Parathion and related organophosphorus pesticides are used in hundreds of thousands of poisonings annually, especially suicides.[7] It is known as "Schwiegermuttergift" (mother-in-law poison) in Germany. For this reason, most formulations contain a blue dye providing warning.
Parathion has been used as a chemical weapon, most notably by the Selous Scouts during the Rhodesian Bush War.[8]
Based on animal studies, parathion is considered by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency to be a possible human carcinogen.[9] Studies show that parathion is toxic to fetuses, but does not cause birth defects.[10]
It is classified as a UNEP Persistent Organic Pollutant and WHO Toxicity Class, "Ia, Extremely Hazardous".
Parathion is toxic to bees, fish, birds, and other forms of wildlife.[10]
Protection against poisoning[edit]
To provide the end user with a minimum standard of protection, suitable protective gloves, clothing, and a respirator with organic-vapour cartridges is normally worn. Industrial safety during the production process requires special ventilation and continuous measurement of air contamination in order not to exceed PEL levels, as well as careful attention to personal hygiene. Frequent analysis of workers' serum acetylcholinesterase activity is also helpful with regards to occupational safety, because the action of parathion is cumulative. Also, atropine has been used as a specific antidote.
Proposals to ban[edit]
According to the non-governmental organisation Pesticide Action Network or PAN, parathion is one of the most dangerous pesticides. This organization lists parathion also as a 'bad actor chemical'.[11] In the US alone more than 650 agricultural workers have been poisoned since 1966, of which 100 died. In underdeveloped countries many more people have suffered fatal and nonfatal intoxications. The World Health Organization, PAN and numerous environmental organisations propose a general and global ban. Its use is banned or restricted in 23 countries and its import is illegal in a total of 50 countries.[11]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0427". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ a b c "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0479". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ a b c "Parathion". Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ http://www.ehs.neu.edu/laboratory_safety/general_information/nfpa_hazard_rating/documents/NFPAratingJR.htm
- ^ Fee, D. C.; Gard, D. R.; Yang, C. (2005). "Phosphorus Compounds". Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. New York: John Wiley & Sons. doi:10.1002/0471238961.16081519060505.a01.pub2.
- ^ a b c Metcalf, R. L. (2002). "Insect Control". Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. New York: Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA. doi:10.1002/14356007.a14_263.
- ^ Litchfield, M.H. "Estimates of acute pesticide poisoning in agricultural workers in less developed countries" Toxicology Reviews 2005, volume 24, pp. 271-8. PMID 16499408
- ^ Moorcraft, Paul; McLaughlin, Peter (2008). The Rhodesian War: A Military History. Yorkshire: Pen & Sword. p. 106. ISBN 9781844156948.
- ^ "Parathion". Integrated Risk Information System. U. S. Environmental Protection Agency. 26 January 2007.
- ^ a b "Pesticide Information Profiles - Parathion". Extension Toxicology Network. Oregon State University. September 1993.
- ^ a b S. Kegley; B. Hill; S. Orme. "Parathion - Identification, toxicity, use, water pollution potential, ecological toxicity and regulatory information". Pesticide Action Network.
External links[edit]
- Parathion in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB)
- ATSDR - Methyl Parathion Expert Panel Report U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (public domain)
- CDC - NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (public domain)
- Ethyl parathion: International Chemical Safety Card 0006
- Methyl parathion: International Chemical Safety Card 0626

