Leu-enkephalin
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
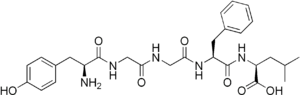
| IUPAC names
(2R)-2-[[(2R)-2-[[2-[[2-[[(2R)-2-amino-3-
(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoyl]amino]acetyl] amino]acetyl]amino]-3-phenylpropanoyl] amino]-4-methylpentanoic acid |
|
| Identifiers | |
| 58822-25-6 |
|
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL8234 |
| ChemSpider | 406229 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.055.852 |
| 1613 | |
| Jmol 3D model | Interactive image |
| PubChem | 461776 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C28H37N5O7 | |
| Molar mass | 555.62268 g/mol |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Leu-enkephalin is an endogenous opioid peptide neurotransmitter with the amino acid sequence Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Leu that is found naturally in the brains of many animals, including humans. It is one of the two forms of enkephalin; the other is met-enkephalin. The tyrosine residue at position 1 is thought to be analogous to the 3-hydroxyl group on morphine. Leu-enkephalin has agonistic actions at both the μ- and δ-opioid receptors, with significantly greater preference for the latter. It has little to no effect on the κ-opioid receptor.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
| This article does not cite any sources. (November 2011) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
| This biochemistry article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |