- published: 22 Jun 2012
- views: 70578
-
remove the playlistCorporate Finance
-
remove the playlistLatest Videos
-
remove the playlistLongest Videos
- remove the playlistCorporate Finance
- remove the playlistLatest Videos
- remove the playlistLongest Videos
- published: 29 May 2015
- views: 9111
- published: 25 Jan 2015
- views: 8877
- published: 12 Oct 2012
- views: 20255
- published: 19 Aug 2012
- views: 133335
- published: 15 Jul 2014
- views: 3519
- published: 01 Feb 2016
- views: 11664

Corporate finance
Corporate finance is the area of finance dealing with the sources of funding and the capital structure of corporations and the actions that managers take to increase the value of the firm to the shareholders, as well as the tools and analysis used to allocate financial resources. The primary goal of corporate finance is to maximize or increase shareholder value. Although it is in principle different from managerial finance which studies the financial management of all firms, rather than corporations alone, the main concepts in the study of corporate finance are applicable to the financial problems of all kinds of firms.
Investment analysis (or capital budgeting) is concerned with the setting of criteria about which value-adding projects should receive investment funding, and whether to finance that investment with equity or debt capital. Working capital management is the management of the company's monetary funds that deal with the short-term operating balance of current assets and current liabilities; the focus here is on managing cash, inventories, and short-term borrowing and lending (such as the terms on credit extended to customers).
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
Aswath Damodaran
Aswath Damodaran is a Professor of Finance at the Stern School of Business at New York University (Kerschner Family Chair in Finance Education), where he teaches corporate finance and equity valuation. He is best known as author of several widely used academic and practitioner texts on Valuation, Corporate Finance and Investment Management. Damodaran is widely quoted on the subject of valuation, with "a great reputation as a teacher and authority". He has written several books on equity valuation, as well on corporate finance and investments. He is also widely published in leading journals of finance, including The Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis, The Journal of Finance, The Journal of Financial Economics and the Review of Financial Studies. He is also known as being a resource on valuation and analysis to investment banks on Wall Street.
Prior to joining NYU, he served as visiting lecturer at the University of California, Berkeley from 1984 to 1986. He was profiled in Business Week as one of the top 12 U.S. business school professors; he has also received awards for excellence in teaching from both universities. Damodaran also teaches on the TRIUM Global Executive MBA Program, an alliance of NYU Stern, the London School of Economics and HEC School of Management, and for the Master of Science in Global Finance (MSGF), which is a joint program between Stern and the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology. He also teaches the "Valuation" Open Enrollment program for Stern Executive Education.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 9:26
9:26Session 01: Objective 1 - What Is Corporate Finance?
Session 01: Objective 1 - What Is Corporate Finance?Session 01: Objective 1 - What Is Corporate Finance?
The Finance Coach: Introduction to Corporate Finance with Greg Pierce Textbook: Fundamentals of Corporate Finance Ross, Westerfield, Jordan Chapter 1: Introduction to Corporate Finance Objective 1 - Key Concepts: What is Corporate Finance? Capital Budgeting, Capital Structure, Working Capital Current Assets vs. Current Liabilities Financial Organizations More Information at: http://thefincoach.com/ -
 17:41
17:41Session 1: Corporate Finance: What is it?
Session 1: Corporate Finance: What is it? -
 21:23
21:23Session 2: The Objective in Corporate Finance
Session 2: The Objective in Corporate FinanceSession 2: The Objective in Corporate Finance
Sets up the objective in corporate finance decision making -
 6:14
6:141 Learn Corporate Finance in 1 Hour: Introduction
1 Learn Corporate Finance in 1 Hour: Introduction1 Learn Corporate Finance in 1 Hour: Introduction
In this course we are going to learn the principles of corporate finance. (video 1 of 8) To get CPD or CPE for this course, visit the Proformative Academy at www.proformative.com and use the COOK10 discount code to get a discount on your subscription. Learn more and become student at EF University for FREE - http://executivefinance.teachable.com/ Like us Facebook- https://www.facebook.com/exfinance/ Linkedin- https://www.linkedin.com/company/executive-finance Twitter- https://twitter.com/exfinance -
 21:54
21:54Introduction to Corporate Finance
Introduction to Corporate FinanceIntroduction to Corporate Finance
There are important differences between real assets that are used to make everything we buy in our economy. We buy goods and services. Financial services and securities are another group of assets. These are not tangible. They have no physical form. CAPX is a measure of capital expenditure. The amount of capital expenditure in a quarter or a year represents the capital budget. This is the dollar value of the actual decision upper management makes to invest in tangible and intangible assets. A group of investment and financing decisions illustrate this. Investments include locomotives for trains and advertising for consumer goods. These investments are tangible and intangible uses of cash. A car factory is another tangible investment example. Examples of financing decisions include reinvestment of profits. Share buy-backs are another. An important consideration is what a corporation in essence is. This legal entity is owned by shareholders who seek bottom line results. Modigliani & Miller showed that the only way managers can increase firm value is to increase bottom line profits. They also showed that fiddling with the pay-out policy or capital structure should not affect firm value. A corporation can act like a person. It is a legal entity that is owned by its shareholders but it acts like a person that moves and thinks like its managers. This also means that a corporation can sue and even be sued in a court of law. But liability stops with the corporation. Shareholders have limited liability. And anybody can form a corporation. Here’s how you can form your own corporation. You first go out and raise capital from investors. You invest the cash in your firm. If the company is profitable money will be pumped out of operations. This cash-flow can be reinvested to expand operations. Or it can be returned to shareholders. Warren Buffett is very critical of the decisions executives make regarding cash. He is such a big investor that he acts as a financial manager mediating cash flow between the financial markets and the companies he funds. In the United States the goal of management is to maximize profits. In Germany managers take into account the needs of stakeholders. This is a much more expansive concept that includes workers, suppliers, and bankers. American CEOs typically become frustrated when dealing with a stakeholder management mentality. Even so profit maximization is ephemeral with regard to timing. Profits can be generated in ways that are damaging to the company. Buffett finds this fraudulent. Cutting dividends to free up cash is harmful if the firm earns less than the opportunity cost of capital. This alludes to a trade-off that exists between the hurdle rate cost of capital and the opportunity cost of capital. Investing in a project locks cash in place and obviates other opportunities. At the end of a successful quarter the CFO has to decide whether to reinvest in a positive NPV project or to pay a fat dividend to shareholders. The shareholders can then invest for themselves however they wish. A kink in the process is introduced if there are agency problems in management. These can arise from stupidity or sloppiness in the form of misfeasance. Executives can also be outright dishonest in the form of malfeasance. Empire building is a grey area where CEOs seek massive bonuses from mergers & acquisitions that do improve or destroy shareholder wealth. This can be exacerbated by differences in information where executives know more about dividends, financing, and outstanding issues. Managers want to maximize bonuses and pay while stockholders want to retain as much profit as possible. Conflict can occur between executive and operational management groups. Stockholders can end up at odds with bankers and other lenders. This conflict has existed since the Dutch East Indies. Modern mechanisms to clean up executives includes tighter scrutiny of the board of directors over the CEO; more independent board members; prohibiting the CEO to be chair of the board and stock options to align upper management incentives with shareholders. In some markets executives who shirk are thrown out by more competent ones. Dr. Scott Brown is a researcher in finance who is nationally recognized by the Certified Financial Analyst Institute (CFA). He is an associate professor of finance at the AACSB Accredited Graduate School of Business at the University of Puerto Rico and author of his bestselling Udemy course on Value Investing. Discover More in this Udemy Course on Value Investing Here: https://www.udemy.com/how-to-build-your-million-dollar-stock-portfolio-from-zero/ Also sign up for special offers at http://drscottbrown.com -
 13:12
13:12What is Corporate Finance? (Corporate Finance Series)
What is Corporate Finance? (Corporate Finance Series)What is Corporate Finance? (Corporate Finance Series)
In this corporate finance presentation I go over our introduction to corporate finance/managerial finance. I talk about goals of corporate finance (liquidity, solvency and profitability) as well as going over the main points of corporate finance which is capital investments, capital structure and financing and of course working capital management. Learn about managerial finance through Dave's illustrations and learn about what we'll cover in the future! Subscribe: http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=ininjanotes ** Ninjanotes is privately owned and exclusive to ninjanotes.ca. Our products and services are not associated with any other "ninja" products or business tutorial/test prep material. ** Website: http://www.ninjanotes.ca Follow us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/pages/Ninja-Notes/334589563245679 Follow us on Twitter: http://twitter.com/ininjanotes We appreciate all of the support you guys have given us. Be apart of the mission to help us reach more students by subscribing, thumbs upping and adding the videos to your favorites! -
 79:20
79:20Corporate Finance by Aswath Damodaran Lecture 1
Corporate Finance by Aswath Damodaran Lecture 1Corporate Finance by Aswath Damodaran Lecture 1
http://www.symynd.com/ This video is a part of online course on Corporate Finance by Professor Aswath Damodaran of NYU. Course is available on the above website of Symynd ( symynd.com) -
 3:37
3:37Why Corporate Finance?
Why Corporate Finance?Why Corporate Finance?
Learn how corporate finance can help your business. -
 2:15
2:15Corporate Finance Essentials
Corporate Finance EssentialsCorporate Finance Essentials
For more information about the course: https://www.coursera.org/course/corpfinance This Coursera Corporate Finance course explores several issues related to companies, investors, and the interaction between them in the capital markets. By the end of this course you should be able to understand most of what you read in the financial press; understand and use the essential financial vocabulary used by companies and finance professionals; assess the required return on a company's debt and equity; estimate a company's cost of capital; evaluate the viability of an investment opportunity; and assess whether a company is creating or destroying value. Ultimately, this course will provide you with essential tools to both understand and make better financial decisions. -
 87:06
87:06Session 1 (MBA): The Foundations of Corporate Finance
Session 1 (MBA): The Foundations of Corporate FinanceSession 1 (MBA): The Foundations of Corporate Finance
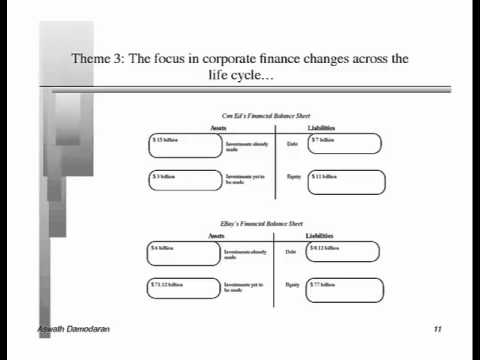
In this session, I laid out the structure for the class and an agenda of what I hope to accomplish during the next 15 weeks. In addition to describing the logistical details, I presented my view that corporate finance is the ultimate big picture class because everything falls under its purview. The “big picture” of corporate finance covers the three basic decisions that every business has to make: how to allocate scarce funds across competing uses (the investment decision), how to raise funds to finance these investments (the financing decision) and how much cash to take out of the business (the dividend decision). The singular objective in corporate finance is to maximize the value of the business to its owners. This big picture was then used to emphasize five themes,: that corporate finance is common sense, that it is focused, that the focus shifts over the life cycle and that you cannot break first principles with immunity. Syllabus (with slides for class): http://www.stern.nyu.edu/~adamodar/pdfiles/cfovhds/cfsyllspr16.pdf Project: http://www.stern.nyu.edu/~adamodar/pdfiles/cfovhds/cfproj.pdf Post class test: http://www.stern.nyu.edu/~adamodar/pdfiles/cfovhds/postclass/session1test.pdf Post class test solution: http://www.stern.nyu.edu/~adamodar/pdfiles/cfovhds/postclass/session1soln.pdf
-

Session 01: Objective 1 - What Is Corporate Finance?
The Finance Coach: Introduction to Corporate Finance with Greg Pierce Textbook: Fundamentals of Corporate Finance Ross, Westerfield, Jordan Chapter 1: Introduction to Corporate Finance Objective 1 - Key Concepts: What is Corporate Finance? Capital Budgeting, Capital Structure, Working Capital Current Assets vs. Current Liabilities Financial Organizations More Information at: http://thefincoach.com/
published: 22 Jun 2012 -

-

Session 2: The Objective in Corporate Finance
Sets up the objective in corporate finance decision making
published: 21 Aug 2014 -

1 Learn Corporate Finance in 1 Hour: Introduction
In this course we are going to learn the principles of corporate finance. (video 1 of 8) To get CPD or CPE for this course, visit the Proformative Academy at www.proformative.com and use the COOK10 discount code to get a discount on your subscription. Learn more and become student at EF University for FREE - http://executivefinance.teachable.com/ Like us Facebook- https://www.facebook.com/exfinance/ Linkedin- https://www.linkedin.com/company/executive-finance Twitter- https://twitter.com/exfinance
published: 29 May 2015 -

Introduction to Corporate Finance
There are important differences between real assets that are used to make everything we buy in our economy. We buy goods and services. Financial services and securities are another group of assets. These are not tangible. They have no physical form. CAPX is a measure of capital expenditure. The amount of capital expenditure in a quarter or a year represents the capital budget. This is the dollar value of the actual decision upper management makes to invest in tangible and intangible assets. A group of investment and financing decisions illustrate this. Investments include locomotives for trains and advertising for consumer goods. These investments are tangible and intangible uses of cash. A car factory is another tangible investment example. Examples of financing decisions in...
published: 25 Jan 2015 -

What is Corporate Finance? (Corporate Finance Series)
In this corporate finance presentation I go over our introduction to corporate finance/managerial finance. I talk about goals of corporate finance (liquidity, solvency and profitability) as well as going over the main points of corporate finance which is capital investments, capital structure and financing and of course working capital management. Learn about managerial finance through Dave's illustrations and learn about what we'll cover in the future! Subscribe: http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=ininjanotes ** Ninjanotes is privately owned and exclusive to ninjanotes.ca. Our products and services are not associated with any other "ninja" products or business tutorial/test prep material. ** Website: http://www.ninjanotes.ca Follow us on Facebook: https://www.faceb...
published: 12 Oct 2012 -

Corporate Finance by Aswath Damodaran Lecture 1
http://www.symynd.com/ This video is a part of online course on Corporate Finance by Professor Aswath Damodaran of NYU. Course is available on the above website of Symynd ( symynd.com)
published: 19 Aug 2012 -

Why Corporate Finance?
Learn how corporate finance can help your business.
published: 30 Oct 2014 -

Corporate Finance Essentials
For more information about the course: https://www.coursera.org/course/corpfinance This Coursera Corporate Finance course explores several issues related to companies, investors, and the interaction between them in the capital markets. By the end of this course you should be able to understand most of what you read in the financial press; understand and use the essential financial vocabulary used by companies and finance professionals; assess the required return on a company's debt and equity; estimate a company's cost of capital; evaluate the viability of an investment opportunity; and assess whether a company is creating or destroying value. Ultimately, this course will provide you with essential tools to both understand and make better financial decisions.
published: 15 Jul 2014 -

Session 1 (MBA): The Foundations of Corporate Finance
In this session, I laid out the structure for the class and an agenda of what I hope to accomplish during the next 15 weeks. In addition to describing the logistical details, I presented my view that corporate finance is the ultimate big picture class because everything falls under its purview. The “big picture” of corporate finance covers the three basic decisions that every business has to make: how to allocate scarce funds across competing uses (the investment decision), how to raise funds to finance these investments (the financing decision) and how much cash to take out of the business (the dividend decision). The singular objective in corporate finance is to maximize the value of the business to its owners. This big picture was then used to emphasize five themes,: that corporate fina...
published: 01 Feb 2016
Session 01: Objective 1 - What Is Corporate Finance?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:26
- Updated: 22 Jun 2012
- views: 70578
- published: 22 Jun 2012
- views: 70578
Session 1: Corporate Finance: What is it?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 17:41
- Updated: 19 Aug 2014
- views: 63644
Session 2: The Objective in Corporate Finance
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 21:23
- Updated: 21 Aug 2014
- views: 34011
- published: 21 Aug 2014
- views: 34011
1 Learn Corporate Finance in 1 Hour: Introduction
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:14
- Updated: 29 May 2015
- views: 9111
- published: 29 May 2015
- views: 9111
Introduction to Corporate Finance
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 21:54
- Updated: 25 Jan 2015
- views: 8877
- published: 25 Jan 2015
- views: 8877
What is Corporate Finance? (Corporate Finance Series)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 13:12
- Updated: 12 Oct 2012
- views: 20255
- published: 12 Oct 2012
- views: 20255
Corporate Finance by Aswath Damodaran Lecture 1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 79:20
- Updated: 19 Aug 2012
- views: 133335
- published: 19 Aug 2012
- views: 133335
Why Corporate Finance?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:37
- Updated: 30 Oct 2014
- views: 5709
- published: 30 Oct 2014
- views: 5709
Corporate Finance Essentials
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:15
- Updated: 15 Jul 2014
- views: 3519
- published: 15 Jul 2014
- views: 3519
Session 1 (MBA): The Foundations of Corporate Finance
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 87:06
- Updated: 01 Feb 2016
- views: 11664
- published: 01 Feb 2016
- views: 11664
-

Keiser Report 'Chattel' on Corporate Balance Sheets E988
Economic collapse and financial crisis is rising any moment. Getting informed about collapse and crisis may earn you, or prevent to lose money. Do you want to be informed with Max Keiser, Alex Jones, Gerald Celente, Peter Schiff, Marc Faber, Ron Paul,Jim Willie, V Economist, and many specialists about FINANCIAL CRISIS / OIL PRICE / GLOBAL ECONOMIC COLLAPSE / AGENDA 21 / DOLLAR COLLAPSE / GOLD / SILVER / BITCOIN / GLOBAL RESET / NEW WORLD ORDER / ECONOMİC COLLAPSE just follow us in this channel.. Please click above to subscribe to my channel.
published: 05 Nov 2016 -

Essentials Of Corporate Finance 7th Edition Test Bank Download
published: 05 Nov 2016 -

Fundemental Of Corporate Finance Second Edition
published: 05 Nov 2016 -

Essentials of Corporate Finance
http://erj-books.club/readonline/?item=0078034752&lan;=en
published: 05 Nov 2016 -

Corporate Finance 11e
http://erj-books.club/readonline/?item=1133947530&lan;=en
published: 05 Nov 2016 -

Fundamentals Of Corporate Finance 5th Edition
published: 05 Nov 2016 -

Fundamentals Of Corporate Finance 9th Edition
published: 05 Nov 2016 -

Fundamentals Of Corporate Finance 5th Canadian Edition
published: 05 Nov 2016 -

Fundamentals Of Corporate Finance 8th Edition Solution
published: 05 Nov 2016 -

Fundamentals Of Corporate Finance 9th Edition Solutions Manual Free Download
published: 05 Nov 2016
Keiser Report 'Chattel' on Corporate Balance Sheets E988
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 25:48
- Updated: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 15
- published: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 15
Essentials Of Corporate Finance 7th Edition Test Bank Download
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:35
- Updated: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 0
- published: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 0
Fundemental Of Corporate Finance Second Edition
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:35
- Updated: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 0
- published: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 0
Essentials of Corporate Finance
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:22
- Updated: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 0
Corporate Finance 11e
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:22
- Updated: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 0
Fundamentals Of Corporate Finance 5th Edition
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:37
- Updated: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 0
- published: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 0
Fundamentals Of Corporate Finance 9th Edition
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:38
- Updated: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 0
- published: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 0
Fundamentals Of Corporate Finance 5th Canadian Edition
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:35
- Updated: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 0
- published: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 0
Fundamentals Of Corporate Finance 8th Edition Solution
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:35
- Updated: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 1
- published: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 1
Fundamentals Of Corporate Finance 9th Edition Solutions Manual Free Download
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:35
- Updated: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 0
- published: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 0
-

Introduction to Corporate Finance, James Tompkins
This is the first lecture in my "Corporate Finance" series in which I both introduce myself as well as the structure of the class. The emphasis is on financial principles as it affect firm value with a specific focus on "asset investment" decisions. For example, the decision for Apple to get into the phone business.
published: 20 Feb 2014 -

Introduction to Corporate Finance, LSE Study Weekend 2012
Dr Jack Favilukis from the Department of Finance at LSE provides an introduction to Corporate Finance. He provides a general overview and also uses exam examples to illustrate the practical application of corporate finance concepts. To view all of the Finance courses on offer from the LSE through distance learning visit: http://www.londoninternational.ac.uk/lse
published: 15 Mar 2012 -

Applied Corporate Finance. Financial Distress & Corporate Restructuring
published: 03 Mar 2013 -

Session 2 (MBA): The Objective in Corporate Finance
In today's class, we started on what the objective in running a business should be. While corporate finance states it to be maximizing firm value, it is often practiced as maximizing stock price. To make the world safe for stock price maximization, we do have to make key assumptions: that managers act in the best interests of stockholders, that lenders are fully protected, that information flows to rational investors and that there are no social costs. We started on why one of these assumptions, that stockholders have power over managers, fails and we will continue ripping the Utopian world apart next class. Slides: http://www.stern.nyu.edu/~adamodar/podcasts/cfspr16/Session2.pdf Add on Slides: http://www.stern.nyu.edu/~adamodar/cfspr16/Session2addon.pdf Post class test: http://www.stern...
published: 03 Feb 2016 -

-

Applied Corporate Finance. M&A.; Mergers & Acquisitions
published: 03 Mar 2013
Introduction to Corporate Finance, James Tompkins
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 27:16
- Updated: 20 Feb 2014
- views: 8895
- published: 20 Feb 2014
- views: 8895
Introduction to Corporate Finance, LSE Study Weekend 2012
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 75:13
- Updated: 15 Mar 2012
- views: 59320
- published: 15 Mar 2012
- views: 59320
Applied Corporate Finance. Financial Distress & Corporate Restructuring
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 120:03
- Updated: 03 Mar 2013
- views: 5419
- published: 03 Mar 2013
- views: 5419
Session 2 (MBA): The Objective in Corporate Finance
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 87:06
- Updated: 03 Feb 2016
- views: 5090
- published: 03 Feb 2016
- views: 5090
Fundamentals of Corporate Finance: Chapter 7 Problems (2016)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 38:02
- Updated: 02 Dec 2015
- views: 1273
Applied Corporate Finance. M&A.; Mergers & Acquisitions
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 120:03
- Updated: 03 Mar 2013
- views: 46202
- published: 03 Mar 2013
- views: 46202
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

Session 01: Objective 1 - What Is Corporate Finance?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 Jun 2012
- views: 70578

Session 1: Corporate Finance: What is it?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Aug 2014
- views: 63644

Session 2: The Objective in Corporate Finance
- Report rights infringement
- published: 21 Aug 2014
- views: 34011

1 Learn Corporate Finance in 1 Hour: Introduction
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 May 2015
- views: 9111

Introduction to Corporate Finance
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 Jan 2015
- views: 8877

What is Corporate Finance? (Corporate Finance Series)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 12 Oct 2012
- views: 20255

Corporate Finance by Aswath Damodaran Lecture 1
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Aug 2012
- views: 133335

Why Corporate Finance?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 30 Oct 2014
- views: 5709

Corporate Finance Essentials
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Jul 2014
- views: 3519

Session 1 (MBA): The Foundations of Corporate Finance
- Report rights infringement
- published: 01 Feb 2016
- views: 11664
- Playlist
- Chat

Keiser Report 'Chattel' on Corporate Balance Sheets E988
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 15

Essentials Of Corporate Finance 7th Edition Test Bank Download
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 0

Fundemental Of Corporate Finance Second Edition
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 0

Essentials of Corporate Finance
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 0

Corporate Finance 11e
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 0

Fundamentals Of Corporate Finance 5th Edition
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 0

Fundamentals Of Corporate Finance 9th Edition
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 0

Fundamentals Of Corporate Finance 5th Canadian Edition
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 0

Fundamentals Of Corporate Finance 8th Edition Solution
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 1

Fundamentals Of Corporate Finance 9th Edition Solutions Manual Free Download
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 0
- Playlist
- Chat

Introduction to Corporate Finance, James Tompkins
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Feb 2014
- views: 8895

Introduction to Corporate Finance, LSE Study Weekend 2012
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Mar 2012
- views: 59320

Applied Corporate Finance. Financial Distress & Corporate Restructuring
- Report rights infringement
- published: 03 Mar 2013
- views: 5419

Session 2 (MBA): The Objective in Corporate Finance
- Report rights infringement
- published: 03 Feb 2016
- views: 5090

Fundamentals of Corporate Finance: Chapter 7 Problems (2016)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 02 Dec 2015
- views: 1273

Applied Corporate Finance. M&A.; Mergers & Acquisitions
- Report rights infringement
- published: 03 Mar 2013
- views: 46202
President-Elect Trump To Be Unelected On Dec. 19th If Democrats Have Their Way
Edit WorldNews.com 14 Nov 2016Horrific crash kills Yu Xu, 1st woman to fly China's J-10 fighter
Edit The Oklahoman 14 Nov 2016Trump wants to deport three million people
Edit Independent online (SA) 14 Nov 2016A Second Powerful Earthquake Has Hit New Zealand’s South Island
Edit Time Magazine 14 Nov 2016Why the supermoon on November 14 is special?
Edit The Times of India 14 Nov 2016Change - Announcement Of Appointment :: Appointment Of Chief Financial Officer (PACC Offshore Services Holdings Ltd)
Edit Public Technologies 14 Nov 2016The 5th meeting of the 16th Board of Directors of China Steel Corporation (CSC - China Steel Corporation)
Edit Public Technologies 14 Nov 2016Press Release - BDO Gets Best Bank Award From Global Finance (BDO Unibank Inc)
Edit Public Technologies 14 Nov 2016University System of New Hampshire, The College of New Jersey, and University of Wyoming Turn to Oracle Cloud to Drive Institutional Excellence (Oracle Corporation)
Edit Public Technologies 14 Nov 2016Grant Thornton takes top honours at regional corporate finance awards (Milton Keynes Chamber of Commerce Limited)
Edit Public Technologies 14 Nov 2016The 6th Council of State Financial Institutions Committee Meeting for 2016 (MOF - Ministry of Finance of the Kingdom of Thailand)
Edit Public Technologies 14 Nov 2016If cash crunch continues, street lights may go off, taps go dry
Edit The Hindu 14 Nov 2016Ambac to Participate in BTIG’s Bond Insurance Panel
Edit Nasdaq Globe Newswire 14 Nov 2016VIQ Solutions Strengthens Board of Directors with Appointment of former S&P;/TSX Top 100 CEO Joseph ...
Edit Stockhouse 14 Nov 2016Stornoway Announces FY 2016 Third Quarter Results (Stornoway Diamond Corporation)
Edit Public Technologies 14 Nov 2016Stornoway Announces FY 2016 Third Quarter Results
Edit Stockhouse 14 Nov 2016Mitsubishi Corp. Joint Euro MTN Prog.: R&I; Affirms AA- (R&I; - Rating and Investment Information Inc)
Edit Public Technologies 14 Nov 2016Ambac to Participate in BTIG's Bond Insurance Panel (Ambac Financial Group Inc)
Edit Public Technologies 14 Nov 2016- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »








