- published: 14 Mar 2013
- views: 274783
-
remove the playlistDhcp Server
-
remove the playlistLatest Videos
-
remove the playlistLongest Videos
- remove the playlistDhcp Server
- remove the playlistLatest Videos
- remove the playlistLongest Videos
- published: 11 Mar 2013
- views: 134818
- published: 23 Oct 2013
- views: 165090
- published: 01 Aug 2011
- views: 111556
- published: 24 May 2014
- views: 17365
- published: 25 Mar 2013
- views: 46629
- published: 08 Dec 2010
- views: 84365
- published: 20 Jan 2012
- views: 24588
- published: 17 Apr 2012
- views: 45682
- published: 02 Jul 2013
- views: 13208

The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a network configuration protocol for hosts on Internet Protocol (IP) networks. Computers that are connected to IP networks must be configured before they can communicate with other hosts. The most essential information needed is an IP address, and a default route and routing prefix. DHCP eliminates the manual task by a network administrator. It also provides a central database of devices that are connected to the network and eliminates duplicate resource assignments.
In addition to IP addresses, DHCP also provides other configuration information, particularly the IP addresses of local Domain Name Server (DNS), network boot servers, or other service hosts.
DHCP is used for IPv4 as well as IPv6. While both versions serve much the same purpose, the details of the protocol for IPv4 and IPv6 are sufficiently different that they may be considered separate protocols.
Hosts that do not use DHCP for address configuration may still use it to obtain other configuration information. Alternatively, IPv6 hosts may use stateless address autoconfiguration. IPv4 hosts may use link-local addressing to achieve limited local connectivity.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 26:49
26:49Basic DHCP Setup on Windows Server 2012
Basic DHCP Setup on Windows Server 2012Basic DHCP Setup on Windows Server 2012
Info Level: Intermediate Presenter: Eli the Computer Guy Date Created: March 14, 2013 Length of Class: 26:49 Tracks Windows Server 2012 Prerequisites Building Your Own Network for a Computer Lab Introduction to Windows Server 2012 Installing Windows Server 2012 Navigation in Windows Server 2012 Introduction to Active Directory Directory Services Structure in Windows Server 2012 Introduction to Active Directory Infrastructure in Windows Server 2012 Introduction to DHCP TCP/IP and Subnet Masking Purpose of Class This class teaches students how to configure a basic DHCP Server on Windows Server 2012. You learn to create a DHCP Scope and set the appropriate TCP/IP Options. Class Notes Make sure that the Routers DHCP Service has been turned off Determine your TCP/IP Address Scheme before you setup DHCP Make sure the DHCP Server has a Static IP Address configured Resources -
 21:36
21:36Introduction to DHCP
Introduction to DHCPIntroduction to DHCP
Info Level: Beginner Presenter: Eli the Computer Guy Date Created: March 11, 2013 Length of Class: 21:35 Tracks Servers Networking Prerequisites Basic understanding of TCP /IP TCP/IP and Subnet Masking Purpose of Class This class teaches students what DCHP is and the core concepts of Dynamic Host Control Protocol. Class Notes DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol DHCP is a Server Service Separate from DNS Can be found in Windows Servers/ Linux/ Unix and Home or Small office Routers DHCP Servers Assign: Dynamic IP Addresses Static Subnet Mask Static Default gateway Static Primary and Secondary DNS Servers Scope is the pool of addresses that the DHCP server can assign from. Such as192.168.1.100 to 192.168.1.200 Lease is the length of time that the DHCP server will reserve the IP address for the client. Clients will try to renew the lease periodically Lease length can be manually configured on a per server basis Reservations are IP Addresses that are reserved for systems that need Static IP Addresses Steps for Getting an IP DHCPDiscover -- Client Requests an IP from Any Available DHCP Server DHCPOffer -- DHCP Servers offer IP Addresses DHCPRequest -- Client Acknowledges which IP Address it has accepted DHCPAck -- DHCP Server Acknowledges Client has accepted IP Address Resources http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc780760(v=ws.10).aspx -
 7:56
7:56Automatic IP Address Assignment: How DHCP Works
Automatic IP Address Assignment: How DHCP WorksAutomatic IP Address Assignment: How DHCP Works
Explains the concept of DHCP, an application-layer protocol that your own computer probably uses to get an IP address from your network. Here's a list of the sections in this video and their time codes: 00:14 - A world without DHCP 01:26 - DHCP to the rescue 02:15 - The four-step process My DHCP video was originally uploaded on September 7th 2013, but I made a new version after an attentive viewer pointed out some inaccuracies. == Further reading == Can I have multiple DHCP servers on one network? - http://serverfault.com/questions/368512/can-i-have-multiple-dhcp-servers-on-one-network How can IP conflicts be resolved? - http://support.microsoft.com/kb/133490/en The fine print: in some cases DHCP offer and ACK messages are unicast - https://stackoverflow.com/questions/10636699/why-are-dhcp-offer-and-ack-broadcasted -
 21:44
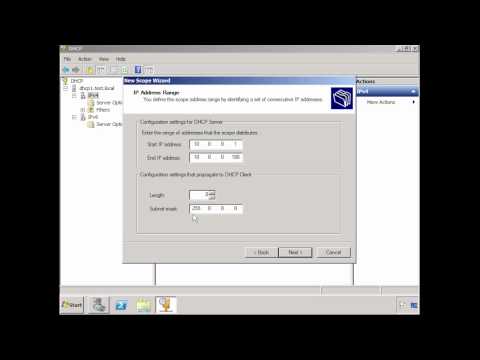
21:44DHCP for Windows Server 2008
DHCP for Windows Server 2008DHCP for Windows Server 2008
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) provides the network configuration for clients on a network. This video takes you through how to configure DHCP for Windows Server 2008 R2 and includes DHCP for IP version 6. -
 12:45
12:45How to Install and Configure DHCP Server on Windows Server 2012
How to Install and Configure DHCP Server on Windows Server 2012How to Install and Configure DHCP Server on Windows Server 2012
DHCP Sarver ( Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol ) is a client / server protocol. It automatically provides an IP address to a client when requested. -
 6:44
6:44What is DHCP in Hindi - DHCP Basics Video 1
What is DHCP in Hindi - DHCP Basics Video 1What is DHCP in Hindi - DHCP Basics Video 1
डीएचसीपी DHCP Tutorial in hindi Jagvinder Thind explains DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) Concepts in Hindi. DHCP Tutorial in Hindi -
 2:32
2:32Packet Tracer - Simple DHCP Server
Packet Tracer - Simple DHCP ServerPacket Tracer - Simple DHCP Server
In this video I show you how to setup a simple DHCP server on Cisco's Packet Tracer version 5.3.1 Best viewed in Full screen HD -
 8:36
8:36Basic DHCP Server configuration
Basic DHCP Server configurationBasic DHCP Server configuration
Step by step configuration of a DHCP server on Windows server 2008. And two clients (redhat 6 and win 7) -
 10:46
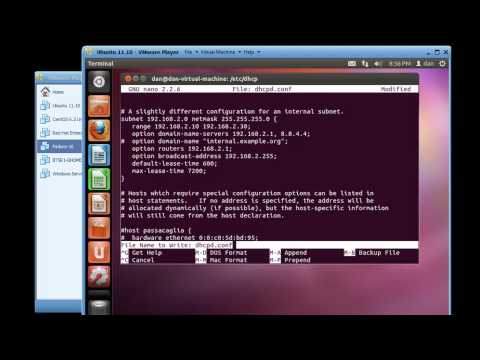
10:46Install and Configure a DHCP Server in Ubuntu 11.10
Install and Configure a DHCP Server in Ubuntu 11.10Install and Configure a DHCP Server in Ubuntu 11.10
How to install and configure a DHCP server in Ubuntu 11.10. The demonstration is done with Ubuntu and Fedora VMware virtual machines and shows a successful server configuration and the successful lease of an IP address to a network client. Subscribe! and visit me at http://danscourses.com for more information on Linux fundamentals -
 14:34
14:34Linux - DHCP Server Configuration
Linux - DHCP Server ConfigurationLinux - DHCP Server Configuration
-
 2:31
2:31Wie funktioniert DHCP?
Wie funktioniert DHCP?Wie funktioniert DHCP?
DHCP verwaltet IP-Adressen und arbeitet bei der Zuteilung von IP-Adressen nach dem Client-Server-Prinzip. Das bedeutet, wir haben einen DHCP-Client und einen DHCP-Server. Der DHCP-Server kann dabei auch als Dienst in einem Router integriert sein. Wenn man einen Computer mit einem aktivierten DHCP-Client startet, was der Normalzustand ist, dann wird ein funktional eingeschränkter Modus des TCP/IP-Protokolls gefahren. Der Modus hat keine gültige IP-Adresse, keine Subnetzmaske und keine IP-Adresse des Standard-Gateways. Damit der DHCP-Client an diese Daten kommt, verschickt er einen Broadcast (UDP-Datenpaket) mit der Ziel-Adresse 255.255.255.255 und der Absender-Adresse 0.0.0.0. Dieser Broadcast wird als DHCP-Discover bezeichnet und dient als Adressanforderung für alle verfügbaren DHCP-Server. Im Optimalfall gibt es nur einen DHCP-Server. Und der antwortet mit einer freien IP-Adresse und weiteren Parametern für die IP-Selbstkonfiguration (DHCP-Offer). Danach fordert der Client die Informationen mit einem DHCP-Request expliziert beim DHCP-Server an. Und der DHCP-Server bestätigt die Anforderung mit einem DHCP-ACK. Sobald der DHCP-Client die Bestätigung erhalten hat, speichert er die Daten lokal ab. Anschließend wird das TCP/IP-Protokoll vollständig in Betrieb genommen. http://www.elektronik.info/wie-funktioniert-dhcp/ powered by http://www.elektronik-kompendium.de/ -
 5:28
5:28Xbox One - Can't Connect To Your DHCP Server Error Troubleshooting Steps
Xbox One - Can't Connect To Your DHCP Server Error Troubleshooting StepsXbox One - Can't Connect To Your DHCP Server Error Troubleshooting Steps
If you have an error when testing your connection on your Xbox One Console saying "CAN'T CONNECT TO YOU DHCP SERVER" Follow this troubleshooting guide to get your connection up and running again so you can play online with friends. Links: https://support.xbox.com
- Booting
- BOOTP
- Bootstrap Protocol
- Cisco
- Data link layer
- DD-WRT
- Default gateway
- DHCP snooping
- DHCPv6
- Domain name
- Domain Name System
- Ethernet
- ICMPv6
- Internet layer
- Internet Protocol
- Internet Relay Chat
- IP address
- IPsec
- IPv4
- IPv6
- Link layer
- Linksys
- MAC address
- Media access control
- Name server
- NetBoot
- Peg DHCP
- Post Office Protocol
- Prefix delegation
- RARP
- Rogue DHCP
- SAMS Publishing
- Secure Shell
- Server (computing)
- SOCKS
- Static IP
- Subnet mask
- Telnet
- Template IPstack
- Time server
- Transport layer
- Tunneling protocol
- UDP Helper Address
- Unicast
- Wikipedia NOTHOWTO
- Zeroconf
-

Basic DHCP Setup on Windows Server 2012
Info Level: Intermediate Presenter: Eli the Computer Guy Date Created: March 14, 2013 Length of Class: 26:49 Tracks Windows Server 2012 Prerequisites Building Your Own Network for a Computer Lab Introduction to Windows Server 2012 Installing Windows Server 2012 Navigation in Windows Server 2012 Introduction to Active Directory Directory Services Structure in Windows Server 2012 Introduction to Active Directory Infrastructure in Windows Server 2012 Introduction to DHCP TCP/IP and Subnet Masking Purpose of Class This class teaches students how to configure a basic DHCP Server on Windows Server 2012. You learn to create a DHCP Scope and set the appropriate TCP/IP Options. Class Notes Make sure that the Routers DHCP Service has been turned off Determine your TCP/IP Address Scheme before you s... -

Introduction to DHCP
Info Level: Beginner Presenter: Eli the Computer Guy Date Created: March 11, 2013 Length of Class: 21:35 Tracks Servers Networking Prerequisites Basic understanding of TCP /IP TCP/IP and Subnet Masking Purpose of Class This class teaches students what DCHP is and the core concepts of Dynamic Host Control Protocol. Class Notes DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol DHCP is a Server Service Separate from DNS Can be found in Windows Servers/ Linux/ Unix and Home or Small office Routers DHCP Servers Assign: Dynamic IP Addresses Static Subnet Mask Static Default gateway Static Primary and Secondary DNS Servers Scope is the pool of addresses that the DHCP server can assign from. Such as192.168.1.100 to 192.168.1.200 Lease is the length of time that the DHCP server... -

Automatic IP Address Assignment: How DHCP Works
Explains the concept of DHCP, an application-layer protocol that your own computer probably uses to get an IP address from your network. Here's a list of the sections in this video and their time codes: 00:14 - A world without DHCP 01:26 - DHCP to the rescue 02:15 - The four-step process My DHCP video was originally uploaded on September 7th 2013, but I made a new version after an attentive viewer pointed out some inaccuracies. == Further reading == Can I have multiple DHCP servers on one network? - http://serverfault.com/questions/368512/can-i-have-multiple-dhcp-servers-on-one-network How can IP conflicts be resolved? - http://support.microsoft.com/kb/133490/en The fine print: in some cases DHCP offer and ACK messages are unicast - https://stackoverflow.com/questions/10636699/why-are... -

DHCP for Windows Server 2008
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) provides the network configuration for clients on a network. This video takes you through how to configure DHCP for Windows Server 2008 R2 and includes DHCP for IP version 6. -

How to Install and Configure DHCP Server on Windows Server 2012
DHCP Sarver ( Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol ) is a client / server protocol. It automatically provides an IP address to a client when requested. -

What is DHCP in Hindi - DHCP Basics Video 1
डीएचसीपी DHCP Tutorial in hindi Jagvinder Thind explains DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) Concepts in Hindi. DHCP Tutorial in Hindi -

Packet Tracer - Simple DHCP Server
In this video I show you how to setup a simple DHCP server on Cisco's Packet Tracer version 5.3.1 Best viewed in Full screen HD -

Basic DHCP Server configuration
Step by step configuration of a DHCP server on Windows server 2008. And two clients (redhat 6 and win 7) -

Install and Configure a DHCP Server in Ubuntu 11.10
How to install and configure a DHCP server in Ubuntu 11.10. The demonstration is done with Ubuntu and Fedora VMware virtual machines and shows a successful server configuration and the successful lease of an IP address to a network client. Subscribe! and visit me at http://danscourses.com for more information on Linux fundamentals -

Linux - DHCP Server Configuration
-

Wie funktioniert DHCP?
DHCP verwaltet IP-Adressen und arbeitet bei der Zuteilung von IP-Adressen nach dem Client-Server-Prinzip. Das bedeutet, wir haben einen DHCP-Client und einen DHCP-Server. Der DHCP-Server kann dabei auch als Dienst in einem Router integriert sein. Wenn man einen Computer mit einem aktivierten DHCP-Client startet, was der Normalzustand ist, dann wird ein funktional eingeschränkter Modus des TCP/IP-Protokolls gefahren. Der Modus hat keine gültige IP-Adresse, keine Subnetzmaske und keine IP-Adresse des Standard-Gateways. Damit der DHCP-Client an diese Daten kommt, verschickt er einen Broadcast (UDP-Datenpaket) mit der Ziel-Adresse 255.255.255.255 und der Absender-Adresse 0.0.0.0. Dieser Broadcast wird als DHCP-Discover bezeichnet und dient als Adressanforderung für alle verfügbaren DHCP-Ser... -

Xbox One - Can't Connect To Your DHCP Server Error Troubleshooting Steps
If you have an error when testing your connection on your Xbox One Console saying "CAN'T CONNECT TO YOU DHCP SERVER" Follow this troubleshooting guide to get your connection up and running again so you can play online with friends. Links: https://support.xbox.com
Basic DHCP Setup on Windows Server 2012
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 26:49
- Updated: 14 Mar 2013
- views: 274783
- published: 14 Mar 2013
- views: 274783
Introduction to DHCP
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 21:36
- Updated: 11 Mar 2013
- views: 134818
- published: 11 Mar 2013
- views: 134818
Automatic IP Address Assignment: How DHCP Works
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:56
- Updated: 23 Oct 2013
- views: 165090
- published: 23 Oct 2013
- views: 165090
DHCP for Windows Server 2008
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 21:44
- Updated: 01 Aug 2011
- views: 111556
- published: 01 Aug 2011
- views: 111556
How to Install and Configure DHCP Server on Windows Server 2012
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 12:45
- Updated: 24 May 2014
- views: 17365
- published: 24 May 2014
- views: 17365
What is DHCP in Hindi - DHCP Basics Video 1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:44
- Updated: 25 Mar 2013
- views: 46629
- published: 25 Mar 2013
- views: 46629
Packet Tracer - Simple DHCP Server
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:32
- Updated: 08 Dec 2010
- views: 84365
- published: 08 Dec 2010
- views: 84365
Basic DHCP Server configuration
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:36
- Updated: 20 Jan 2012
- views: 24588
- published: 20 Jan 2012
- views: 24588
Install and Configure a DHCP Server in Ubuntu 11.10
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:46
- Updated: 17 Apr 2012
- views: 45682
- published: 17 Apr 2012
- views: 45682
Linux - DHCP Server Configuration
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 14:34
- Updated: 13 Aug 2011
- views: 31043
- published: 13 Aug 2011
- views: 31043
Wie funktioniert DHCP?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:31
- Updated: 02 Jul 2013
- views: 13208
- published: 02 Jul 2013
- views: 13208
Xbox One - Can't Connect To Your DHCP Server Error Troubleshooting Steps
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:28
- Updated: 07 Nov 2015
- views: 13370
-

Jaringan DHCP menggunakan router sebagai server
-

Instalación del servidor DHCP en win server 2008
Recorded with http://screencast-o-matic.com -

Windows Server 2012 R2 DHCP Kurulum Scope Oluşturma
-

Windows Server 2008 R2 - Instalacja usługi Active Directory DHCP DNS WINS
Windows Server 2008 R2 - Instalacja usługi Active Directory DHCP DNS konfiguracja kart siecowych ETH0 address IP 10.0.2.15 maska sieci 255.255.255.0 brama 10.0.2.2 DNS 172.16.0.254 ETH1 address IP 192.168.0.254 maska sieci 255.255.255.0 brama 192.168.0.254 DNS 172.16.0.254 -

Como configura o dhcp server no firewall endian
Como configura o dhcp server no firewall endian -

Part 1 Server Tuturial Video AD DHCP DNS extended to MDT server Installation Process
-

-

-

EnGenius Technologies Long Range
Get more info on Amazon-US: http://bit.ly/1WeJXNS This unit is worthless for home use, as you must manually assign an IP address for each user; there is no DHCP server in the I only learned this by the I have cancelled the order effective a few moments ago, and I hope and TigerDirect will Otherwise, this could become a MAJOR issue! The description says it be used as an access point, but they fail to mention this important item! -

How to create DHCP Server in Cisco Packet Tracer
commands to configure the router:- https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B7zK2PMh4S9lZTB6WTV4bl9IZEE Please like and subscribe for more videos -

how to configure DHCP in window server 2008 R2
-

Jaringan DHCP menggunakan router sebagai server
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:09
- Updated: 25 May 2016
- views: 0
- published: 25 May 2016
- views: 0
Instalación del servidor DHCP en win server 2008
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:31
- Updated: 25 May 2016
- views: 4
Windows Server 2012 R2 DHCP Kurulum Scope Oluşturma
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 18:10
- Updated: 25 May 2016
- views: 2
- published: 25 May 2016
- views: 2
Windows Server 2008 R2 - Instalacja usługi Active Directory DHCP DNS WINS
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 46:01
- Updated: 25 May 2016
- views: 17
- published: 25 May 2016
- views: 17
Como configura o dhcp server no firewall endian
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 13:33
- Updated: 24 May 2016
- views: 28
Part 1 Server Tuturial Video AD DHCP DNS extended to MDT server Installation Process
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 46:28
- Updated: 24 May 2016
- views: 0
- published: 24 May 2016
- views: 0
LAB-01: Master port, DHCP server, cấu hình Wi-Fi đơn giản, MAC Filter
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:00
- Updated: 24 May 2016
- views: 9
LAB-02: PPPoE client, DHCP server, 2 x SSID, QoS, Firewall, Channel, Isolation, Roaming
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:12
- Updated: 24 May 2016
- views: 2
EnGenius Technologies Long Range
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:21
- Updated: 24 May 2016
- views: 0
- published: 24 May 2016
- views: 0
How to create DHCP Server in Cisco Packet Tracer
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:02
- Updated: 24 May 2016
- views: 17
- published: 24 May 2016
- views: 17
how to configure DHCP in window server 2008 R2
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 18:51
- Updated: 24 May 2016
- views: 3
- published: 24 May 2016
- views: 3
-

DHCP server with many vlans HD
This Video show you How to configure DHCP server for many vlans. I hope it would be satisfying for everyone -

Installing and Configuring ADS, DNS and DHCP in Windows Server 2012 and Client Configuration
In this video you will see how to install Active Directory, DNS Server and DHCP Server installation and configuration in Windows Server 2012. And also you will find how to do the client configuration for all ADS, DNS and DHCP Servers. http://tech-answer.blogspot.in/ -

Video Tutorial DHCP Server, DNS Server, Web & Mail Server @ Ubuntu Server 14.04
How to Install and Configure DHCP Server, DNS Server, Web & Mail Server using Ubuntu Server 14.04 Created by : - Beryl Ramadhian (1103120118) - Satrio Kamaludin (1103120125) - Satrio Adi N (1103124316) - Putri Puspita (1103124320) -

09- Win Server 2012 Installing & Config (ARABIC) شرح عربي DHCP Server
DHCP Server IPv4 IPv6 -

Cisco Packet Tracer DNS+DHCP+HTTP Server & DHCP Service in Router
Cisco Packet Tracer DNS+DHCP+HTTP Server & DHCP Service in Router Project Download (3 files) -DHCP Service -DHCP Server -Just the topology Donate via PayPal - Secure https://www.paypal.com/us/cgi-bin/webscr?cmd=_s-xclick&hosted;_button_id=FBWZUE4CQU62Y Download the project : http://adf.ly/1Qhmr3 Hope this video Help you :) -

Installing and Configuring DHCP Server in Windows Server 2012 - Tutorial
Installing and Configuring DHCP Server in Windows Server 2012 -

Hướng dẫn cấu hình DHCP server và DNS server cơ bản trên windows server 2003
Đây là clip hướng dẫn cài đặt và cấu hình DHCP server, có chức năng cấp phát địa chỉ IP tự động và máy chủ phiên dịch DNS server cơ bản trên HĐH Windows Server 2003. Phần mềm sử dụng trong clip là VMware Workstation, dùng để tạo ra máy ảo, hỗ trợ việc cài đặt và kiểm tra chức năng của server. Người hướng dẫn: Phạm Thiên Thư Trường CĐ Kinh tế - Công nghệ TP.HCM -

Installing Active Directory, DNS and DHCP to Create a Windows Server 2012 Domain Controller
Schedule a Skype Meeting with Eli: https://silicondiscourse.com -

Dhcp Server Nasıl Kurulur - Server Dhcp Kurulumu - ademocut.com
Daha Geniş Bilgi için http://www.ademocut.com
DHCP server with many vlans HD
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 23:05
- Updated: 14 May 2015
- views: 2905
- published: 14 May 2015
- views: 2905
Installing and Configuring ADS, DNS and DHCP in Windows Server 2012 and Client Configuration
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 25:26
- Updated: 26 Sep 2013
- views: 192558
- published: 26 Sep 2013
- views: 192558
Video Tutorial DHCP Server, DNS Server, Web & Mail Server @ Ubuntu Server 14.04
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 26:10
- Updated: 09 Dec 2014
- views: 5293
- published: 09 Dec 2014
- views: 5293
09- Win Server 2012 Installing & Config (ARABIC) شرح عربي DHCP Server
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 40:10
- Updated: 03 Aug 2013
- views: 6250
Cisco Packet Tracer DNS+DHCP+HTTP Server & DHCP Service in Router
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 23:29
- Updated: 04 Jun 2013
- views: 93290
- published: 04 Jun 2013
- views: 93290
Installing and Configuring DHCP Server in Windows Server 2012 - Tutorial
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 23:36
- Updated: 24 Jan 2013
- views: 18720
Hướng dẫn cấu hình DHCP server và DNS server cơ bản trên windows server 2003
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 22:28
- Updated: 04 Mar 2014
- views: 15611
- published: 04 Mar 2014
- views: 15611
Installing Active Directory, DNS and DHCP to Create a Windows Server 2012 Domain Controller
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 27:45
- Updated: 01 Mar 2013
- views: 695371
- published: 01 Mar 2013
- views: 695371
Dhcp Server Nasıl Kurulur - Server Dhcp Kurulumu - ademocut.com
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 36:17
- Updated: 25 Aug 2013
- views: 2838
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

Basic DHCP Setup on Windows Server 2012
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Mar 2013
- views: 274783

Introduction to DHCP
- Report rights infringement
- published: 11 Mar 2013
- views: 134818

Automatic IP Address Assignment: How DHCP Works
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Oct 2013
- views: 165090

DHCP for Windows Server 2008
- Report rights infringement
- published: 01 Aug 2011
- views: 111556

How to Install and Configure DHCP Server on Windows Server 2012
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 May 2014
- views: 17365

What is DHCP in Hindi - DHCP Basics Video 1
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 Mar 2013
- views: 46629

Packet Tracer - Simple DHCP Server
- Report rights infringement
- published: 08 Dec 2010
- views: 84365

Basic DHCP Server configuration
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Jan 2012
- views: 24588

Install and Configure a DHCP Server in Ubuntu 11.10
- Report rights infringement
- published: 17 Apr 2012
- views: 45682

Linux - DHCP Server Configuration
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 Aug 2011
- views: 31043

Wie funktioniert DHCP?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 02 Jul 2013
- views: 13208

Xbox One - Can't Connect To Your DHCP Server Error Troubleshooting Steps
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Nov 2015
- views: 13370
- Playlist
- Chat

Jaringan DHCP menggunakan router sebagai server
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 May 2016
- views: 0

Instalación del servidor DHCP en win server 2008
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 May 2016
- views: 4

Windows Server 2012 R2 DHCP Kurulum Scope Oluşturma
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 May 2016
- views: 2

Windows Server 2008 R2 - Instalacja usługi Active Directory DHCP DNS WINS
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 May 2016
- views: 17

Como configura o dhcp server no firewall endian
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 May 2016
- views: 28

Part 1 Server Tuturial Video AD DHCP DNS extended to MDT server Installation Process
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 May 2016
- views: 0

LAB-01: Master port, DHCP server, cấu hình Wi-Fi đơn giản, MAC Filter
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 May 2016
- views: 9

LAB-02: PPPoE client, DHCP server, 2 x SSID, QoS, Firewall, Channel, Isolation, Roaming
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 May 2016
- views: 2

EnGenius Technologies Long Range
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 May 2016
- views: 0

How to create DHCP Server in Cisco Packet Tracer
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 May 2016
- views: 17

how to configure DHCP in window server 2008 R2
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 May 2016
- views: 3

Configuracion de DHCP en windows server 2012
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 May 2016
- views: 8
- Playlist
- Chat

DHCP server with many vlans HD
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 May 2015
- views: 2905

Installing and Configuring ADS, DNS and DHCP in Windows Server 2012 and Client Configuration
- Report rights infringement
- published: 26 Sep 2013
- views: 192558

Video Tutorial DHCP Server, DNS Server, Web & Mail Server @ Ubuntu Server 14.04
- Report rights infringement
- published: 09 Dec 2014
- views: 5293

09- Win Server 2012 Installing & Config (ARABIC) شرح عربي DHCP Server
- Report rights infringement
- published: 03 Aug 2013
- views: 6250

Cisco Packet Tracer DNS+DHCP+HTTP Server & DHCP Service in Router
- Report rights infringement
- published: 04 Jun 2013
- views: 93290

Installing and Configuring DHCP Server in Windows Server 2012 - Tutorial
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 Jan 2013
- views: 18720

Hướng dẫn cấu hình DHCP server và DNS server cơ bản trên windows server 2003
- Report rights infringement
- published: 04 Mar 2014
- views: 15611

Installing Active Directory, DNS and DHCP to Create a Windows Server 2012 Domain Controller
- Report rights infringement
- published: 01 Mar 2013
- views: 695371

Dhcp Server Nasıl Kurulur - Server Dhcp Kurulumu - ademocut.com
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 Aug 2013
- views: 2838
China to send nuclear-armed submarines into Pacific amid tensions with US
Edit The Guardian 26 May 2016China says its people will never allow Taiwan independence
Edit Asia Times 26 May 2016Obama Plans To Release Massive Cache Of UFO Files Prior To Leaving Office
Edit WorldNews.com 25 May 2016Sunny Leone, former porn star, turns erotic fiction writer
Edit BBC News 26 May 2016ISIS on Europe's doorstep
Edit CNN 26 May 2016State Dept. IT Staff Told To Keep Quiet About Clinton's Server
Edit Slashdot 26 May 2016Qualcomm says it's here to stay in China
Edit China Daily 26 May 2016Report traces arc of Hillary Clinton server, agency failures
Edit Austin American Statesman 26 May 2016Experts: Audit justifies FBI’s push for indictment
Edit Boston Herald 26 May 2016Experts: Audit justifies FBI’s push for Hillary Clinton indictment
Edit Boston Herald 26 May 2016Clinton draws fire for personal email use as ex-secy.
Edit Press TV 26 May 2016Pompeo Issues Statement on the State Department Inspector General Report on Hillary Clinton’s Usage of a Private Email Server (Mike Pompeo)
Edit Public Technologies 26 May 2016CNN Compares Hillary Past Email Statements to IG Investigation Results
Edit Breitbart 26 May 2016Hillary Clinton email use broke federal rules: police report
Edit Deccan Chronicle 26 May 2016Damning report on E-mailgate shows Hillary can’t be trusted
Edit New York Post 26 May 2016Telcoware acquires a patent (Telcoware Co Ltd)
Edit Public Technologies 26 May 2016US State Dept watchdog accuses Hillary of violating govt rules on emails
Edit China Daily 26 May 2016White House Countdown – God bless email
Edit Financial Times 26 May 2016- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »







