- published: 14 Aug 2013
- views: 16722
-
remove the playlistBenghazi Travel Guides
-
remove the playlistLibya
-
remove the playlistLatest Videos
-
remove the playlistLongest Videos
- remove the playlistBenghazi Travel Guides
- remove the playlistLibya
- remove the playlistLatest Videos
- remove the playlistLongest Videos
Please tell us which country and city you'd like to see the weather in.
- published: 27 Jul 2012
- views: 1360374
- published: 16 Oct 2015
- views: 116102
- published: 24 Mar 2010
- views: 1513
- published: 03 Jul 2015
- views: 680
- published: 14 Jun 2013
- views: 2881
- published: 26 Jan 2011
- views: 8649
- published: 19 May 2014
- views: 791

Benghazi (/bɛnˈɡɑːzi/; Arabic: بنغازيBinġāzī, Libyan Arabic: [bənˈʁɑːzi] (![]() listen), Italian: Bengasi; Turkish: Bingazi; also: Bengasi,Benghasi,Banghāzī,Binghāzī,Bengazi,Βερενίκη Berenice and Hesperides) is the second largest city in Libya, the main city (or capital) of the Cyrenaica region (or ex-Province), and the former provisional capital of the National Transitional Council. The wider metropolitan area (which includes the southern towns of Gimeenis and Suluq) is also a district of Libya. The port city is located on the Mediterranean Sea.
listen), Italian: Bengasi; Turkish: Bingazi; also: Bengasi,Benghasi,Banghāzī,Binghāzī,Bengazi,Βερενίκη Berenice and Hesperides) is the second largest city in Libya, the main city (or capital) of the Cyrenaica region (or ex-Province), and the former provisional capital of the National Transitional Council. The wider metropolitan area (which includes the southern towns of Gimeenis and Suluq) is also a district of Libya. The port city is located on the Mediterranean Sea.
During the Kingdom era of Libya's history, Benghazi enjoyed a sort of joint-capital status (alongside Tripoli), possibly because the King used to reside in the nearby city of Bayda and the Senussis (royal family) in general were associated with Cyrenaica rather than Tripolitania. Benghazi continues to hold institutions and organizations normally associated with a national capital city. This creates a constant atmosphere of rivalry and sensitivities between Benghazi and Tripoli and by extension between the two regions (Cyrenaica and Tripolitania). The population of the entire district was 500,120 in 1995 (census) and has increased to 670,797 in the 2006 census.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Libya (Arabic: ليبيا Lībyā), Berber: ⵍⵉⴱⵢⴰ) is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Sudan to the southeast, Chad and Niger to the south, and Algeria and Tunisia to the west.
With an area of almost 1.8 million square kilometres (700,000 sq mi), Libya is the third largest country in Africa by area, and the 17th largest in the world. The largest city, Tripoli, is home to 1.7 million of Libya's 6.4 million people. The three traditional parts of the country are Tripolitania, Fezzan and Cyrenaica.
In 2009 Libya had the highest HDI in Africa and the fourth highest GDP (PPP) per capita in Africa, behind Seychelles, Equatorial Guinea and Gabon. Libya has the 10th-largest proven oil reserves of any country in the world and the 17th-highest petroleum production.
As a result of the Libyan civil war, the Libyan Arab Jamahiriya, which had at that time been in existence for 34 years, collapsed and Libya entered a period of governance by a transitional administration called the National Transitional Council. The NTC has stated its intention to oversee the first phase of a transition to constitutional democracy, after which it claims it will dissolve in favor of a representative legislature.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 51:34
51:34Libya Vacation Travel Video Guide
Libya Vacation Travel Video GuideLibya Vacation Travel Video Guide
Travel video about destination Libya. Libya is one of the most interesting desert countries and it is gradually opening its doors to the outside world. It is a veritable treasure trove of history. Ancient art and culture of various epochs as well as the fascinating exotic flair of the Orient make Libya a wonderful and fascinating holiday destination. The capital, Tripoli, awakes early in the morning as fishermen return from their nocturnal work at sea along with their catch which is fresh and tasty and ready for market. In antiquity Tripoli was called Oea and was one of the three cities of Tripolitania. Seventy kilometres west of Tripoli and also located on the Mediterranean coast are the remains of the ancient trading town of Sabratha. Its Theatre has been rebuilt and is an impressive structure that dates back to the second century A.D. It was originally built by the Romans who came here after the Phoenicians and gave the city a completely new appearance. It could accommodate up to five thousand onlookers. Just like the country’s former explorers we venture further and further into the desert and spend the night in Kirkiba Camp in circular straw huts at the foot of huge sand dunes. Next day we visit Garma, now in ruins, but whioch around two thousand years ago was the capital of the Garamantes Realm. From the Sahara we travel to the country’s eastern Mediterranean coast and to ancient Cyrenaika, the largest city in today’s Benghazi. Of the historic city of the Pentapolis, the Greek five-city alliance, nothing remains today as it is now covered by modern city buildings. Magnificent history, untouched coastlines and endless desert landscapes with oasis settlements, salt lakes, rock paintings and Berber towns: Libya, a little known land in amazing North Africa. -
 26:31
26:31Front Lines of the Libyan Revolution (Documentary)
Front Lines of the Libyan Revolution (Documentary)Front Lines of the Libyan Revolution (Documentary)
VICE Founder Shane Smith takes you into the heart of the Libyan revolution, where the stakes are simple: victory or death. We head into rebel-controlled eastern Libya, traveling from the Egyptian border to Benghazi and then onto the front lines in Misrata to document the violent revolution. Hosted by Shane Smith | Originally aired in 2011 on http://VICE.com More from Shane Smith: http://www.vice.com/author/shane-smith Follow Shane on Twitter: https://twitter.com/shanesmith30 Watch "Female Fighters of Kurdistan" here: http://bit.ly/Female-Fighters-1 Subscribe for videos that are actually good: http://bit.ly/Subscribe-to-VICE Check out our full video catalog: http://www.youtube.com/user/vice/videos Videos, daily editorial and more: http://vice.com Like VICE on Facebook: http://fb.com/vice Follow VICE on Twitter: http://twitter.com/vice Read our tumblr: http://vicemag.tumblr.com -
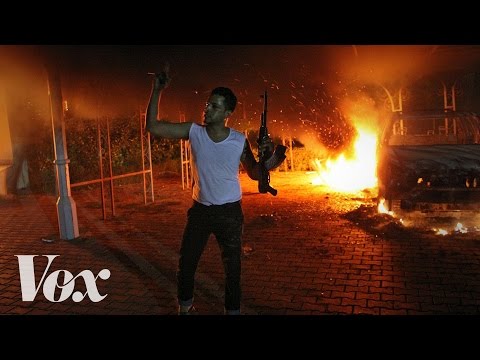 4:14
4:14Benghazi, the attack and the scandal, explained
Benghazi, the attack and the scandal, explainedBenghazi, the attack and the scandal, explained
Let's start with what actually happened on September 11, 2012. Subscribe to our channel! http://goo.gl/0bsAjO On September 11, 2012, a partially armed group of men stormed a US diplomatic outpost in the Libyan city of Benghazi. At the time, it was not clear who they were or why they'd attacked. But by the time the attack was over, four Americans, including US Ambassador to Libya Christopher Stevens, had been killed. The attack ended by the early hours of September 12. But it has echoed in Washington ever since. The controversy has centered on Republican accusations that the Obama administration did not take heed of intelligence warnings before the attack, that during the attack it refused to call in available military support, and that after the attack it deliberately covered up what had happened. Repeated independent investigations have disproven all of these allegations. But Republicans have continued to push them, insisting that these failures go all the way to the top, personally involving President Obama and then-Secretary of State Hillary Clinton. They've done so partly out political expediency — they think it's a great way to attack Clinton's presidential campaign — and partly out of a genuine belief that the administration is covering up the truth. But regardless of the motivation, it's kind of paid off for Republicans: The House Select Committee on Benghazi, created by Speaker of the House John Boehner in 2014, found the first documented evidence that Clinton used unauthorized private email servers for State Department business, which became a major scandal. Unless Clinton is defeated in the Democratic primary, Benghazi will be around for the rest of the 2016 election — and if she wins, you'll likely be hearing about it for much longer. Thumbnail: Getty Images Vox.com is a news website that helps you cut through the noise and understand what's really driving the events in the headlines. Check out http://www.vox.com to get up to speed on everything from Kurdistan to the Kim Kardashian app. Check out our full video catalog: http://goo.gl/IZONyE Follow Vox on Twitter: http://goo.gl/XFrZ5H Or on Facebook: http://goo.gl/U2g06o -
 0:59
0:59Libya Wikipedia travel guide video. Created by http://stupeflix.com
Libya Wikipedia travel guide video. Created by http://stupeflix.comLibya Wikipedia travel guide video. Created by http://stupeflix.com
Create your own video on http://studio.stupeflix.com/?w=1 ! Ruins of the theatre in the Roman city of Sabratha, west of Tripoli. Omar Mukhtar (18581931) was the leader of the Libyan uprising against Italian occupation. A wall carpet depicting Col. Gaddafi, in a hotel in Misratah. U.S. Secretary of State, Condoleezza Rice with her Libyan counterpart Foreign Minister Abd al-Rahman Shalgam. Libya is keen to shake off its pariah status and rejoin the international community. Desert landscape in Southern Libya; 90% of the country is desert. Libya's capital Tripoli has benefited greatly from the country's oil wealth. Tripoli's Old City - (El-Madina El-Kadima) - situated in the city centre, is one of the classical sites of the Mediterranean. The Benghazi campus of the former University of Libya (Al-Jami'a al-Libiya), Libya's first university. Mosque in Ghadames, close to the Tunisian and Algerian border. 97% of Libyans are followers of Islam. Coastline of Benghazi, Libya's second largest city. With the longest coastline among Mediterranean nations, Libya's mostly unspoilt beaches are a social gathering place. -
 2:40
2:40Libya Benghazi Destruction: Continued Fighting Leaves City in Ruins Displacing Thousands
Libya Benghazi Destruction: Continued Fighting Leaves City in Ruins Displacing ThousandsLibya Benghazi Destruction: Continued Fighting Leaves City in Ruins Displacing Thousands
The city of Benghazi in Libya has been at the centre of months of violence in the country. Benghazi now remains in ruins and is almost a ghost town, many people having left due to the conflict between two rival governments. Here is CCTV's Leslie Mirungu with more on this story -
 4:59
4:59Time Lapse Benghazi, Libya
Time Lapse Benghazi, LibyaTime Lapse Benghazi, Libya
Time Lapse Benghazi, Libya تايم لابس بنغازي ليبيا تصوير وتحرير...filmed and edited by محمد سعد ....mohamed saad انتاج ...Production 2013 طرابلس ليبيا..Tripoli, Libya Copyright © mohamed saad muntser -
 2:04
2:04Libya (12/2010) - Benghazi
Libya (12/2010) - BenghaziLibya (12/2010) - Benghazi
Benghazi or Bengasi (Arabic بنغازي,) transliterated as Binġāzī; Turkish: Bingazi) is the second largest city in Libya and the main city (or capital) of the Cyrenaica region (or ex-Province). The wider metropolitan area (which includes the southern towns of Gimeenis and Suluq) is also a district of Libya. During the Kingdom era of Libya's history, Benghazi enjoyed a sort of joint-capital status (alongside Tripoli), possibly because the King used to reside in the nearby city of Al Bayda' and the Senussis (royal family) in general were associated with Cyrenaica rather than Tripolitania. Benghazi continues to hold institutions and organizations normally associated with a national capital city. This creates a constant atmosphere of rivalry and sensitivities between Benghazi and Tripoli and by extension between the two regions (Cyrenaica and Tripolitania). The population of the entire district was 500,120 in 1995 (census) and has increased to 670,797 in the 2006 census. -
 4:23
4:23Libya On Edge: Fighting Sweeps Across Tripoli Following Violence In Benghazi
Libya On Edge: Fighting Sweeps Across Tripoli Following Violence In BenghaziLibya On Edge: Fighting Sweeps Across Tripoli Following Violence In Benghazi
Militiamen attacked Libya's interim Parliament, and the violence spread across Tripoli. CNN's Jomana Karadsheh reports. Would you like to know more? Turmoil in Libya: Fighting sweeps across Tripoli following violence in Benghazi (CNN, May 18, 2014) http://cnn.it/1kg91j7 "Fierce fighting swept across the Libyan capital of Tripoli on Sunday, a short time after armed men stormed the country's interim parliament. The violence appeared to be some of the worst since the 2011 revolution that ousted longtime leader Moammar Gadhafi. At least two people were killed and 66 were injured, according to the Health Ministry. Residents of Tripoli rushed home Sunday evening. One Libyan who spoke to CNN reported seeing shop owners quickly closing up. State media LANA reported that lawmakers had already left for the General National Congress when that attack happened as the session was over for the day. Armed men blocked the road that led to the parliament, LANA said, blocking members' access to their offices. Some lawmakers went on Libyan TV stations to talk about the attack, saying that fighting erupted in the area around the GNC. The attack involved members of powerful militias from the western mountain city of Zintan. But the al-Qaaqaa brigade, a Zintan militia based in Tripoli, issued a statement that it had "heeded the call of the homeland to save it from the abusing politicians ..." Two other militias from Zintan reportedly took part: al-Madani and al-Sawaeq. Libya is on "the brink of civil war," Col. Mukhtar Farnana, a prominent commander from Zintan, said in a televised statement, which he said was from the command of the self-declared Libyan National Army...." Libya Army In Benghazi Clashes With Ansar Al-Sharia https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CTwwGIJUOV4 Libyan Militia Fires On Protesters Killing At Least 43 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=V_cSYygcW8Y A Bitter Season Of Discontent https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2v0MHjUiJwM New Generation - Old Mantra https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oDEA65CLab0 -
 3:54
3:54Libyan Army clashes with Terrorists in Al-Laithi Benghazi
Libyan Army clashes with Terrorists in Al-Laithi BenghaziLibyan Army clashes with Terrorists in Al-Laithi Benghazi
-
 1:38
1:38College Students want to study abroad in BENGHAZI?!?
College Students want to study abroad in BENGHAZI?!?
- Africa
- Afrika Korps
- Ajdabiya
- Ajdabiya District
- Al Jawf, Libya
- Al Jazeera English
- Al Nasr Benghazi
- Al Wahat District
- Al-Ahly (Benghazi)
- Al-Berka
- Al-Funduq
- Al-Fuwayhat
- Al-Hadaa'iq
- Al-Hawari
- Al-Keesh
- Al-Khadhraa
- Al-Kwayfiya
- Al-Magroon
- Al-Magziha
- Al-Nawagiya
- Al-Quwarsha
- Al-Saahil al-Gharbi
- Al-Sabri
- Al-Salmani
- Al-Uruba
- Alahly Benghazi S.C.
- Alexandria
- Amphora
- Ancient Greece
- Apollonia, Cyrenaica
- Arab
- Arabic language
- Association football
- Australia
- Axis powers
- Bani Salim
- Bani Walid District
- Barca
- Barghathi
- Bayda, Libya
- BBC News
- Benetton Group
- Bengazi (film)
- Benghazi
- Benghazi al-Jadida
- Benghazi Cathedral
- Benina
- Benito Mussolini
- Berber people
- Berenice
- Berenice II
- Berenice II of Egypt
- Bernard Montgomery
- Bizerte
- Brak, Libya
- Bu Atni
- Bu-Fakhra
- Bubonic plague
- Business Insider
- Butnan District
- Canyon
- Cement
- Chalet
- Clay
- Condominium
- Construction
- Copt
- Crete
- Cyrenaica
- Cyrene, Libya
- Der Spiegel
- Derna District
- Derna, Libya
- Districts of Libya
- Dwight D. Eisenhower
- Egypt
- England
- Erwin Rommel
- Flag of Libya
- Free trade area
- French Air Force
- Gamal Abdel Nasser
- Garyounis
- Garyounis University
- Ghadames District
- Gharyan
- Gharyan District
- Ghat District
- Ghat, Libya
- Gimeenis
- Great Manmade River
- Greece
- Greek people
- Gulf of Sidra
- Gylippus
- H&M;
- Haaretz
- Hay al-Mukhtar
- Hesperides
- History of Benghazi
- Hizam Al Akhdar
- Huda Ben Amer
- Hun, Libya
- Idris I of Libya
- Idris of Libya
- Islam
- Italian language
- Italian people
- Italianate
- Italo Balbo
- Italy
- Jabal al Akhdar
- Jafara
- Jarrutha
- Jebel Akhdar, Libya
- Judo
- Jufra District
- Karamanli dynasty
- Karkoora
- Khoms, Libya
- Kingdom of Libya
- Kufra
- Kufra District
- Libya
- Libyan Arabic
- Libyan opposition
- London
- Lonely Planet
- Madinat Benghazi
- Magas of Cyrene
- Maghreb
- Maliki
- Maquis shrubland
- March 28 Stadium
- Marj
- Marj District
- Marsh
- Maydan al-Shajara
- Medina
- Medina quarter
- Mediterranean Sea
- Melbourne
- Microbus
- Misrata
- Misrata District
- Mizda District
- Modernist
- Moorish Revival
- Muammar Gaddafi
- Murqub District
- Murzuk
- Murzuq District
- Mustafa Abdul Jalil
- Nalut
- Nalut District
- Nike, Inc.
- Ninth grade
- Niqab
- Nuqat al Khams
- Oil industry
- Omar Mukhtar
- Operation Compass
- Operation Crusader
- Ottoman Empire
- Overpass
- Plateau
- Port of Benghazi
- Portal Geography
- Portal Libya
- Priest
- Processed food
- Ptolemy III of Egypt
- Pythian Games
- Quba District
- Raas Abayda
- Ring road
- Rovi Corporation
- Rugby sevens
- Russian Railways
- Sa'ada
- Sabha District
- Sabha, Libya
- Sadeq Naihoum
- Salafism
- Seattle
- Semi-arid climate
- Senussi
- Shabiyah
- Shuhadaa al-Salawi
- Sidi Abayd
- Sidi Hsayn
- Sidi Khalifa
- Silphium
- Sirocco
- Sirte
- Sirte District
- Skanska
- Souk
- Souq
- Steppe
- Suluq
- Sunni
- Taekwondo
- Talk Benghazi
- Textiles
- The Daily Telegraph
- The Economist
- The Guardian
- The Independent
- The Jerusalem Post
- The Kansas City Star
- The New York Times
- Thucydides
- Tibesti Hotel
- Time zone
- Tobruk
- Transport in Libya
- Tripoli
- Tripolitania
- Tunis
- Tunisia
- Tunisia Campaign
- Turkish language
- Ubari
- United Kingdom
- University of Libya
- Urban sprawl
- Victoria (Australia)
- Voice of Free Libya
- Washington (state)
- Wikipedia Cleanup
- Wikipedia Link rot
- Winnipeg Free Press
- World War II
- WP IPA for Arabic
- Yafran District
- Zawiya District
- Zawiya, Libya
- Zuwara
- ‘Aziziya
- Achaemenid Empire
- Ajdabiya
- Ajdabiya District
- Al Wahat District
- Alexandria
- Australia
- Bani Walid District
- Barca
- Benghazi
- Benghazi Cathedral
- Benina
- Bizerte
- Bu Atni
- Butnan District
- Crete
- Cyrenaica
- Derna District
- Egypt
- England
- Garyounis
- Ghadames District
- Gharyan
- Gharyan District
- Ghat District
- Gimeenis
- Great Manmade River
- Greece
- Gulf of Sidra
- Italy
- Jabal al Akhdar
- Jafara
- Jarrutha
- Jufra District
- Karkoora
- Kingdom of Libya
- Kufra
- Kufra District
- Libya
- London
- Madinat Benghazi
- March 28 Stadium
- Marj
- Marj District
- Medina
- Melbourne
- Misrata
- Misrata District
- Mizda District
- Murqub District
- Murzuk
- Murzuq District
- Nalut
- Nalut District
- Nuqat al Khams
- Port of Benghazi
- Pythian Games
- Quba District
- Raas Abayda
- Russian Railways
- Sabha District
- Seattle
- Sidi Abayd
- Sidi Hsayn
- Sidi Khalifa
- Sirte
- Sirte District
- Suluq
- The Kansas City Star
- Tibesti Hotel
- Tobruk
- Tripoli
- Tripolitania
- Tunis
- Tunisia
- Ubari
- United Kingdom
- Yafran District
- Zawiya District
- Zuwara
-

Libya Vacation Travel Video Guide
Travel video about destination Libya. Libya is one of the most interesting desert countries and it is gradually opening its doors to the outside world. It is a veritable treasure trove of history. Ancient art and culture of various epochs as well as the fascinating exotic flair of the Orient make Libya a wonderful and fascinating holiday destination. The capital, Tripoli, awakes early in the morning as fishermen return from their nocturnal work at sea along with their catch which is fresh and tasty and ready for market. In antiquity Tripoli was called Oea and was one of the three cities of Tripolitania. Seventy kilometres west of Tripoli and also located on the Mediterranean coast are the remains of the ancient trading town of Sabratha. Its Theatre has been rebuilt and is an impressive... -

Front Lines of the Libyan Revolution (Documentary)
VICE Founder Shane Smith takes you into the heart of the Libyan revolution, where the stakes are simple: victory or death. We head into rebel-controlled eastern Libya, traveling from the Egyptian border to Benghazi and then onto the front lines in Misrata to document the violent revolution. Hosted by Shane Smith | Originally aired in 2011 on http://VICE.com More from Shane Smith: http://www.vice.com/author/shane-smith Follow Shane on Twitter: https://twitter.com/shanesmith30 Watch "Female Fighters of Kurdistan" here: http://bit.ly/Female-Fighters-1 Subscribe for videos that are actually good: http://bit.ly/Subscribe-to-VICE Check out our full video catalog: http://www.youtube.com/user/vice/videos Videos, daily editorial and more: http://vice.com Like VICE on Facebook: http://fb.com/vic... -
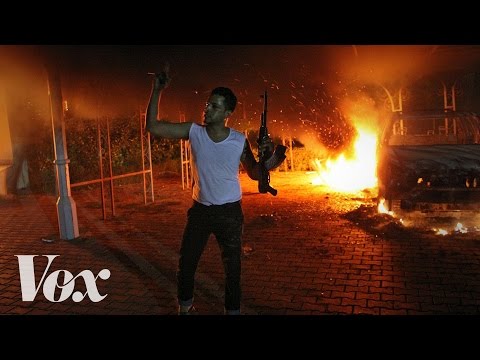
Benghazi, the attack and the scandal, explained
Let's start with what actually happened on September 11, 2012. Subscribe to our channel! http://goo.gl/0bsAjO On September 11, 2012, a partially armed group of men stormed a US diplomatic outpost in the Libyan city of Benghazi. At the time, it was not clear who they were or why they'd attacked. But by the time the attack was over, four Americans, including US Ambassador to Libya Christopher Stevens, had been killed. The attack ended by the early hours of September 12. But it has echoed in Washington ever since. The controversy has centered on Republican accusations that the Obama administration did not take heed of intelligence warnings before the attack, that during the attack it refused to call in available military support, and that after the attack it deliberately covered up what h... -

Libya Wikipedia travel guide video. Created by http://stupeflix.com
Create your own video on http://studio.stupeflix.com/?w=1 ! Ruins of the theatre in the Roman city of Sabratha, west of Tripoli. Omar Mukhtar (18581931) was the leader of the Libyan uprising against Italian occupation. A wall carpet depicting Col. Gaddafi, in a hotel in Misratah. U.S. Secretary of State, Condoleezza Rice with her Libyan counterpart Foreign Minister Abd al-Rahman Shalgam. Libya is keen to shake off its pariah status and rejoin the international community. Desert landscape in Southern Libya; 90% of the country is desert. Libya's capital Tripoli has benefited greatly from the country's oil wealth. Tripoli's Old City - (El-Madina El-Kadima) - situated in the city centre, is one of the classical sites of the Mediterranean. The Benghazi campus of the former University of Libya (... -

Libya Benghazi Destruction: Continued Fighting Leaves City in Ruins Displacing Thousands
The city of Benghazi in Libya has been at the centre of months of violence in the country. Benghazi now remains in ruins and is almost a ghost town, many people having left due to the conflict between two rival governments. Here is CCTV's Leslie Mirungu with more on this story -

Time Lapse Benghazi, Libya
Time Lapse Benghazi, Libya تايم لابس بنغازي ليبيا تصوير وتحرير...filmed and edited by محمد سعد ....mohamed saad انتاج ...Production 2013 طرابلس ليبيا..Tripoli, Libya Copyright © mohamed saad muntser -

Libya (12/2010) - Benghazi
Benghazi or Bengasi (Arabic بنغازي,) transliterated as Binġāzī; Turkish: Bingazi) is the second largest city in Libya and the main city (or capital) of the Cyrenaica region (or ex-Province). The wider metropolitan area (which includes the southern towns of Gimeenis and Suluq) is also a district of Libya. During the Kingdom era of Libya's history, Benghazi enjoyed a sort of joint-capital status (alongside Tripoli), possibly because the King used to reside in the nearby city of Al Bayda' and the Senussis (royal family) in general were associated with Cyrenaica rather than Tripolitania. Benghazi continues to hold institutions and organizations normally associated with a national capital city. This creates a constant atmosphere of rivalry and sensitivities between Benghazi and Tripoli and ... -

Libya On Edge: Fighting Sweeps Across Tripoli Following Violence In Benghazi
Militiamen attacked Libya's interim Parliament, and the violence spread across Tripoli. CNN's Jomana Karadsheh reports. Would you like to know more? Turmoil in Libya: Fighting sweeps across Tripoli following violence in Benghazi (CNN, May 18, 2014) http://cnn.it/1kg91j7 "Fierce fighting swept across the Libyan capital of Tripoli on Sunday, a short time after armed men stormed the country's interim parliament. The violence appeared to be some of the worst since the 2011 revolution that ousted longtime leader Moammar Gadhafi. At least two people were killed and 66 were injured, according to the Health Ministry. Residents of Tripoli rushed home Sunday evening. One Libyan who spoke to CNN reported seeing shop owners quickly closing up. State media LANA reported that lawmakers had already... -

Libyan Army clashes with Terrorists in Al-Laithi Benghazi
-

Libya Vacation Travel Video Guide
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 51:34
- Updated: 14 Aug 2013
- views: 16722
- published: 14 Aug 2013
- views: 16722
Front Lines of the Libyan Revolution (Documentary)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 26:31
- Updated: 27 Jul 2012
- views: 1360374
- published: 27 Jul 2012
- views: 1360374
Benghazi, the attack and the scandal, explained
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:14
- Updated: 16 Oct 2015
- views: 116102
- published: 16 Oct 2015
- views: 116102
Libya Wikipedia travel guide video. Created by http://stupeflix.com
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:59
- Updated: 24 Mar 2010
- views: 1513
- published: 24 Mar 2010
- views: 1513
Libya Benghazi Destruction: Continued Fighting Leaves City in Ruins Displacing Thousands
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:40
- Updated: 03 Jul 2015
- views: 680
- published: 03 Jul 2015
- views: 680
Time Lapse Benghazi, Libya
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:59
- Updated: 14 Jun 2013
- views: 2881
- published: 14 Jun 2013
- views: 2881
Libya (12/2010) - Benghazi
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:04
- Updated: 26 Jan 2011
- views: 8649
- published: 26 Jan 2011
- views: 8649
Libya On Edge: Fighting Sweeps Across Tripoli Following Violence In Benghazi
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:23
- Updated: 19 May 2014
- views: 791
- published: 19 May 2014
- views: 791
Libyan Army clashes with Terrorists in Al-Laithi Benghazi
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:54
- Updated: 22 Feb 2016
- views: 591
- published: 22 Feb 2016
- views: 591
College Students want to study abroad in BENGHAZI?!?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:38
- Updated: 30 Jan 2014
- views: 13546
-

Libya's Quiet War: The Tuareg of South Libya
In remote southwest Sahara, the indigenous Tuareg tribe — variously used and discriminated against by former strongman Muammar Qaddafi — fight for their place in a post-revolutionary Libya. Living deep in Libya’s desert near large oil fields and lucrative smuggling routes, hundreds of miles from Libya’s capital, the Tuareg find themselves impoverished and isolated on this prized land. Nowhere is this felt more than in the oasis town of Ubari. Here the Tuareg are pitted against former neighbors in a proxy battle for assets and power, backed by government and international interests. VICE News travels to meet the Tuareg on the front lines of Ubari and the border town of Ghat, to find out what is really happening in this rarely visited land. Read "In a Southern Libya Oasis, a Proxy War En... -

Life After Qaddafi — Libya: A Broken State
Subscribe to VICE News here: http://bit.ly/Subscribe-to-VICE-News Three years after the Libyan revolution and the subsequent downfall of its dictator Muammar Qaddafi, the country has descended further into chaos and insecurity. Rebel militias, radical Islamists and former Qaddafi commander Khalifa Haftar are among the different groups vying for power and oil wealth, creating a vacuum in which violence and militancy reign supreme. VICE News filmmaker Medyan Dairieh was in Libya in 2011 to witness the revolution. This year, he returned to follow members of the 17th February battalion, a rebel group fighting against Haftar’s forces. Dairieh witnessed first-hand how life after the Libyan revolution has devolved into lawlessness and Islamic State-linked extremism. Watch “VICE News Archives: ... -

Libya: State of Insecurity - Fault Lines
Fault Lines traveled to Libya to look deeper into the circumstances surrounding the Delta Force raid and to examine the US operation may have undermined the Libyan government, which is already struggling to gain control and authority over its country. We also examine human rights abuses committed by the very militias supported by NATO’s intervention. For more Fault Lines: http://america.aljazeera.com/watch/shows/fault-lines.html -

Gaddafi The Truth About Libya- Documentary
(LIKE to spread the message) http://bit.ly/CIickToSubscribe Gaddafi The Truth About Libya- Documentary Original here: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2HwfPYY2lRM Insight into the events that led up to NATO intervention in Libya, On 17 May 2011 the International Criminal Court issued a request for an arrest warrant against Gaddafi for crimes against humanity. Some believe it is about protecting civilians, others say it is about oil, but some are convinced intervention in Libya is all about Gaddafi's plan to introduce the gold dinar, a single African currency made from gold, a true sharing of the wealth. "It's one of these things that you have to plan almost in secret, because as soon as you say you're going to change over from the dollar to something else, you're going to be targeted," s... -

What Was Libya Like 20 Years Ago?
Gaddafi's 25 Years In Power (1994): An honest portrayal of life in Libya after 25 years under Gaddafi. For similar stories, see: Libya's Descent Into Immigration Chaos https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=U0vtLspGbmg Libya's Struggle To Cope With Surge In Migrant Smuggling https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JrM64lMEFfI On The Front Line Of Benghazi's Battle With ISIS https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MTSPCYRuUKs Subscribe to journeyman for daily uploads: http://www.youtube.com/journeymanpictures For downloads and more information visit: https://www.journeyman.tv/film/88/gaddafis-25-years-in-power Like us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/journeymanpictures Follow us on Twitter: https://twitter.com/JourneymanVOD https://twitter.com/JourneymanNews Follow us on Instagram: https://instagram.... -

Libya 5 years after NATO intervention: From one of richest nations in Africa to most troubled
On this day five years ago, a NATO-led coalition began its military intervention in Libya. French fighter jets were deployed over the African country on March 19th, 2011. The operation triggered a series of events that changed the face of Libya. RT LIVE http://rt.com/on-air Subscribe to RT! http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=RussiaToday Like us on Facebook http://www.facebook.com/RTnews Follow us on Twitter http://twitter.com/RT_com Follow us on Instagram http://instagram.com/rt Follow us on Google+ http://plus.google.com/+RT Listen to us on Soundcloud: https://soundcloud.com/rttv RT (Russia Today) is a global news network broadcasting from Moscow and Washington studios. RT is the first news channel to break the 1 billion YouTube views benchmark. -

Libya War: What They Don't Want You to Know
SUPPORT BFP: http://ur1.ca/ge4h7 TRANSCRIPT AND SOURCES: http://www.corbettreport.com/?p=8999 We are taught all our lives that our modern political systems are "by and for the people." In order to justify taking us to war, then, our misleaders have to convince us that war is not a racket, as General Smedley Butler revealed, and is not for the benefit of the industrialists who sell the munitions or the politicians in their back pocket or the financiers that own them both, but in the interest of the average man or woman. In other words, they lie through their teeth. Find out more about the lies that led us to Libya in 2011, and the cover up of what is taking place there today in this week's edition of The Eyeopener report. -

Drowning for Freedom: Libya’s Migrant Jails (Part 1)
Watch Part 2, “Trapped and Forgotten” - http://bit.ly/1Cwjv9k Watch Part 3, “Escaping Hell” - http://bit.ly/1xCZ5nP As Libya descends further into civil war and lawlessness, migrants from Africa and the Middle East continue to journey to the country’s coast in search of smugglers to take them across the Mediterranean Sea and into Europe. Search and rescue operations by Libya’s coast guard are restricted due to diminishing resources, and have to contend with dangerous gangs of armed traffickers. Those rescued at sea by the coast guard are brought to detention centers, where they face deplorable conditions and are forced to remain for long periods of time. In some instances, migrants are detained by militias in unofficial prisons outside of government control. In part one of a three part... -

The Libya Gamble: Inside Hillary Clinton’s Push for War & the Making of a Failed State
http://democracynow.org - The New York Times has published a major two-part exposé titled "The Libya Gamble" on how then Secretary of State Hillary Clinton pushed President Obama to begin bombing Libya five years ago this month. Today, Libya is a failed state and a haven for terrorists. How much should Hillary Clinton be blamed for the crisis? We speak to journalist Scott Shane of The New York Times. Democracy Now! is an independent global news hour that airs weekdays on nearly 1,400 TV and radio stations Monday through Friday. Watch our livestream 8-9AM ET: http://democracynow.org Please consider supporting independent media by making a donation to Democracy Now! today: http://democracynow.org/donate FOLLOW DEMOCRACY NOW! ONLINE: Facebook: http://facebook.com/democracynow Twitter: ht...
Libya's Quiet War: The Tuareg of South Libya
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 25:55
- Updated: 17 Feb 2016
- views: 361892
- published: 17 Feb 2016
- views: 361892
Life After Qaddafi — Libya: A Broken State
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 13:20
- Updated: 12 Nov 2014
- views: 322839
- published: 12 Nov 2014
- views: 322839
Libya: State of Insecurity - Fault Lines
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 25:26
- Updated: 22 Aug 2015
- views: 14888
- published: 22 Aug 2015
- views: 14888
Gaddafi The Truth About Libya- Documentary
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 60:27
- Updated: 08 Jun 2012
- views: 487506
- published: 08 Jun 2012
- views: 487506
What Was Libya Like 20 Years Ago?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:40
- Updated: 11 May 2016
- views: 12862
- published: 11 May 2016
- views: 12862
Libya 5 years after NATO intervention: From one of richest nations in Africa to most troubled
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:04
- Updated: 19 Mar 2016
- views: 32765
- published: 19 Mar 2016
- views: 32765
Libya War: What They Don't Want You to Know
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:23
- Updated: 08 Apr 2014
- views: 155141
- published: 08 Apr 2014
- views: 155141
Drowning for Freedom: Libya’s Migrant Jails (Part 1)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:57
- Updated: 17 Mar 2015
- views: 288963
- published: 17 Mar 2015
- views: 288963
The Libya Gamble: Inside Hillary Clinton’s Push for War & the Making of a Failed State
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 18:16
- Updated: 03 Mar 2016
- views: 16350
- published: 03 Mar 2016
- views: 16350
-

13 Hours: The Secret Soldiers of Benghazi Full "Movie English Streaming HD 2016
[[W4TCH 13 Hours: The Secret Soldiers of Benghazi Film COMPLETE In HD 1080p]] : http://cutt.us/CbU0u + ~ ~ ~ For More Visit: Like MTV: https://www.facebook.com/MTV Follow MTV: https://twitter.com/MTV Keep up with us on Instagram: http://instagr.am/Clevver Website: http://www.clevver.com Add us to your circles on Google+: http://google.com/+ClevverMovies Twitter: https://twitter.com/thewrap ~~Thanks & Enjoy To Watch~~?uniqueYO1N7846K7792U4EV7IVTXPNIunique -

13 Hours: The Secret Soldiers of Benghazi full "Movie"
"if you want to Watch And Download HD Movie :http://bit.ly/1ZYzlAV + Subscribe to Our Newsletter: http://bit.ly/1XBrgkc Twitter: https://twitter.com/thewrap Instagram: https://instagram.com/thewrap/ Find us at www.TheWrap.com Like MTV: https://www.facebook.com/MTV Follow MTV: https://twitter.com/MTV +-+-+-+-+ THANK YOU +-+-+-+-+ by : 0NY0NK+-+-+-+-+" -

13 Hours: The Secret Soldiers of Benghazi Full "Movie 2016
[[M4TU12 5UwUN]] : http://j.mp/1UOt6hI + ⇜ ⇜ ⇜ For More Clevver Visit: Like us on Facebook: http://Facebook.com/ClevverMovies Follow us on Twitter: http://Twitter.com/ClevverMovies Keep up with us on Instagram: http://instagr.am/Clevver Website: http://www.clevver.com Add us to your circles on Google+: http://google.com/+ClevverMovies Tweet Jovenshire: https://twitter.com/TheJovenshire ⇜⇜ ⇝⇝ Thanks & Enjoy To Watch ⇜⇜ uniqueX8QJMA5GQO90U88TVLXL0X3F8unique -

the best sense"'13 Hours The Secret Soldiers of Benghazi (2016)'"
the best sense"'13 Hours The Secret Soldiers of Benghazi (2016)'" -

benghazi YT
-

13 Hours: The Secret Soldiers of Benghazi (2016) - Movie Review
Here's my review of the newest Michael Bay movie that came out at the beginning of this year. DISCLAIMER: I do not own any of the music or photos that are used within this video. 13 Hours: The Secret Soldiers of Benghazi is owned by Paramount Pictures. Copyright Disclaimer Under Section 107 of the Copyright Act 1976, allowance is made for "fair use" for purpose such as criiticsm, comment, news reporting, teaching, scholarship and research. Fair use is a use permitted by copyright statue that might otherwise be infringing. Non-profit, educational or personal use tips the balance in favor of fair use. -

13 Hours: The Secret Soldiers of Benghazi
13 Hours: The Secret Soldiers of Benghazi Watch latest movies and wrestling shows on Aflami APP http://www.aflami.info https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=info.aflam.aflami.arab.movies -

Secret soldiers of Benghazi
There are three videos you can watch and it's where I got my information. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T8y1Q_4tDUU https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4E_Ts4Zr7tA https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zmMB5aftiV0 -

13 Hours The Secret Soldiers of Benghazi - 13 Saat Bingazi'nin Gizli Askerleri Türkçe Dublaj İndir
2016 13 Hours The Secret Soldiers of Benghazi - 13 Saat Bingazi'nin Gizli Askerleri Br m720p x265 TRD(İMDB 7.4): İndirme Linki : http://bc.vc/n0ay9C7 Rar Şifresi : hizlifilmindir Format : Matroska at 870 Kbps Length : 899 MiB for 2s 24dk 29s 536ms Video #0 : HEVC at 661 Kbps Aspect : 1280 x 534 (2.397) at 23.976 fps Audio #0 : AC-3 at 192 Kbps Infos : 2 kanal, 48.0 KHz Language : tr -

Watch 13 Hours: The Secret Soldiers of Benghazi Full Movie online free Streaming Eng Subtitle
» _ⓅⓛⓐⓨⓃⓞⓦ⚩ ►:][[ ( http://tinyurl.com/grsulw9 ) ]][:◄ '13 Hours: The Secret Soldiers of Benghazi FuLLMoviE #13HoursTheSecretSoldiersofBenghazi » ⓈⓊⒷⓈⒸⓇⒾⒷⒺ❃ⓁⒾⓀⒺ★ⒸⓄⓂⓂⒺⓃⓉ❀ⓈⒽⒶⓇⒺ » ✹ 13 Hours: The Secret Soldiers of Benghazi FULL MOVIE 2016 Online Stream HD DVD-RIP High Quality Free Streaming English Subtitle No Download Storyline #13HoursTheSecretSoldiersofBenghazi : During an attack on a U.S. compound in Libya, a security team struggles to make sense out of the chaos. In 2012, the threat level in Benghazi, Libya was deemed "critical". When everything went wrong, six men had the courage to do what was right. Starring by : ... Watch 13 Hours: The Secret Soldiers of Benghazi Full Movie online ... Ꮎ Year: 2016 Vote : 7.4 +13+Hours%3A+The+Secret+Soldiers+of+Benghazi watch-13HoursTheSe...
13 Hours: The Secret Soldiers of Benghazi Full "Movie English Streaming HD 2016
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 91:40
- Updated: 19 Jun 2016
- views: 0
- published: 19 Jun 2016
- views: 0
13 Hours: The Secret Soldiers of Benghazi full "Movie"
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:56
- Updated: 19 Jun 2016
- views: 0
- published: 19 Jun 2016
- views: 0
13 Hours: The Secret Soldiers of Benghazi Full "Movie 2016
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 103:52
- Updated: 19 Jun 2016
- views: 2
- published: 19 Jun 2016
- views: 2
the best sense"'13 Hours The Secret Soldiers of Benghazi (2016)'"
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:47
- Updated: 19 Jun 2016
- views: 4
benghazi YT
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:32
- Updated: 19 Jun 2016
- views: 35
- published: 19 Jun 2016
- views: 35
13 Hours: The Secret Soldiers of Benghazi (2016) - Movie Review
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:50
- Updated: 19 Jun 2016
- views: 15
- published: 19 Jun 2016
- views: 15
13 Hours: The Secret Soldiers of Benghazi
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:06
- Updated: 19 Jun 2016
- views: 1
- published: 19 Jun 2016
- views: 1
Secret soldiers of Benghazi
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 15:49
- Updated: 19 Jun 2016
- views: 3
- published: 19 Jun 2016
- views: 3
13 Hours The Secret Soldiers of Benghazi - 13 Saat Bingazi'nin Gizli Askerleri Türkçe Dublaj İndir
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:52
- Updated: 19 Jun 2016
- views: 31
- published: 19 Jun 2016
- views: 31
Watch 13 Hours: The Secret Soldiers of Benghazi Full Movie online free Streaming Eng Subtitle
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 112:47
- Updated: 18 Jun 2016
- views: 2
- published: 18 Jun 2016
- views: 2
-

Death and Deceit In Benghazi Libya - What Really Happened
What really happened before and during the terror attack against our US Consulate in Benghazi Libya? We may never know, but one thing is for sure we will try and get as much of this information out to the public as possible. This story is only being covered on FOX News in detail and yet we can't find this information on any other network. The more we learn the more suspicious it is. Stay tuned as more information gets uncovered. -

On The Front Line Of Benghazi's Battle With ISIS
The Battle Of Benghazi: Joining the men fighting ISIS on the front line, and the civilians caught in the crossfire For similar stories, see: Why Are Kurds Joining Up With ISIS? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q2X7eP6d0ME The Abandoned Front Line Of Europe's Refugee Crisis https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wQj1xvQth6Y Libya's Struggle To Cope With Surge In Migrant Smuggling https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JrM64lMEFfI Subscribe to journeyman for daily uploads: http://www.youtube.com/journeymanpictures For downloads and more information visit: http://www.journeyman.tv/?lid=69552 Like us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/journeymanpictures Follow us on Twitter: https://twitter.com/JourneymanVOD https://twitter.com/JourneymanNews Follow us on Instagram: https://instagram.com/journeyman... -

Ignoring U.S. Destabilization of Libya, GOP Benghazi Hearing Asks Clinton All the Wrong Questions
Former secretary of state and current Democratic hopeful Hillary Clinton underwent a marathon day of testimony Thursday before the House Select Committee probing the 2012 attack in Libya, which killed U.S. Ambassador Christopher Stevens and three other Americans. Throughout the hearing, Clinton defended her record on Benghazi in the face of Republican criticism. Republicans say Clinton ignored pre-attack warnings and mishandled its aftermath, even though seven previous congressional probes have found no wrongdoing. Clinton handled Republican questions with a calm demeanor, and afterward panel chair Trey Gowdy, Republican congressmember of South Carolina, admitted the hearing failed to turn up anything new. Melvin Goodman, former CIA and State Department analyst, says the Benghazi hearing h... -

Splinter Cell Blacklist: Perfectionist Walkthrough Part 2 - Benghazi Libya
We take you through the prologue mission Benghazi Libya in part 2 of our Perfectionist Walkthrough. We play through in Ghost style. -

The Truth About Benghazi
The shocking facts behind the September 11 2012 Al Qaeda attack on the American consulate in Benghazi, Libya. The Washington cover-up, the American arms sales to Islamic extremists, the deep history of the Arab Spring that turned to an American foreign policy winter of discontent and disaster. Sources: http://www.fdrurl.com/benghazi Freedomain Radio is 100% funded by viewers like you. Please support the show by signing up for a monthly subscription or making a one time donation at: http://www.fdrurl.com/donate Bitcoin Address: 1Fd8RuZqJNG4v56rPD1v6rgYptwnHeJRWs Litecoin Address: Lbxr3M8oezWaguEBc35MoyvQT88C85Sqpi Get more from Stefan Molyneux and Freedomain Radio including books, podcasts and other info at: http://www.freedomainradio.com Amazon US Affiliate Link: www.fdrurl.com/Amazon... -

13 hours Benghazi - Operators Full Interview
Full interview (45 minutes) with surviving security contractors from Benghazi, Libya attack. Final 15 minutes is Hillary Clinton lying under oath regarding the incident and finally Oliver North's take on the incident. Full credit for the interviews belongs to Fox News Channel. Security Contractors Interview: 0:00 - 46:07 Hillary Clinton Lying 46:07 - 57:17 Oliver North Comments 57:17 - 1:01:24 -

Safehouse: Benghazi, Libya - Perfectionist - Splinter Cell Blacklist Walkthrough
Game: Tom Clancy's Splinter Cell: Blacklist 2nd story mission: Safehouse - Benghazi, Libya Difficulty: Perfectionist Ghost only, undetected, no unnecessary ko's, no restarting checkpoints, clear savegame, all collectibles (dead drops, high value targets, blacklist laptops) -

Americans Killed in Benghazi, Libya Return to U.S.
President, secretary of state attend as bodies of four Americans arrive at Andrews Air Force Base. -

The Real Deal Ep # 147 HILLARY'S BENGHAZI... How the West Destroyed Libya
MBC Official Backup Channel https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCu9nEaYvp1ILUlM75D0b8lg Jim's New Facebook Archive Page https://www.facebook.com/The-Real-Deal-with-James-H-Fetzer…/ Live Shows https://livestream.com/accounts/4937810/events/3629901 MBC Website http://mediabroadcastingcenter.com/ HD Video Archives & Mp3's http://podcast.mediabroadcastingcenter.com/
Death and Deceit In Benghazi Libya - What Really Happened
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 38:57
- Updated: 21 Oct 2012
- views: 12840
- published: 21 Oct 2012
- views: 12840
On The Front Line Of Benghazi's Battle With ISIS
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 23:43
- Updated: 25 Feb 2016
- views: 43553
- published: 25 Feb 2016
- views: 43553
Ignoring U.S. Destabilization of Libya, GOP Benghazi Hearing Asks Clinton All the Wrong Questions
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 22:09
- Updated: 23 Oct 2015
- views: 7924
- published: 23 Oct 2015
- views: 7924
Splinter Cell Blacklist: Perfectionist Walkthrough Part 2 - Benghazi Libya
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 34:25
- Updated: 20 Aug 2013
- views: 12313
- published: 20 Aug 2013
- views: 12313
The Truth About Benghazi
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 58:56
- Updated: 03 May 2014
- views: 99766
- published: 03 May 2014
- views: 99766
13 hours Benghazi - Operators Full Interview
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 61:25
- Updated: 11 Jan 2016
- views: 3662
- published: 11 Jan 2016
- views: 3662
Safehouse: Benghazi, Libya - Perfectionist - Splinter Cell Blacklist Walkthrough
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 29:27
- Updated: 21 Sep 2013
- views: 1111
- published: 21 Sep 2013
- views: 1111
Americans Killed in Benghazi, Libya Return to U.S.
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 27:01
- Updated: 14 Sep 2012
- views: 15548
- published: 14 Sep 2012
- views: 15548
The Real Deal Ep # 147 HILLARY'S BENGHAZI... How the West Destroyed Libya
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 119:20
- Updated: 05 Jan 2016
- views: 3154
- published: 05 Jan 2016
- views: 3154
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

Libya Vacation Travel Video Guide
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Aug 2013
- views: 16722

Front Lines of the Libyan Revolution (Documentary)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 27 Jul 2012
- views: 1360374
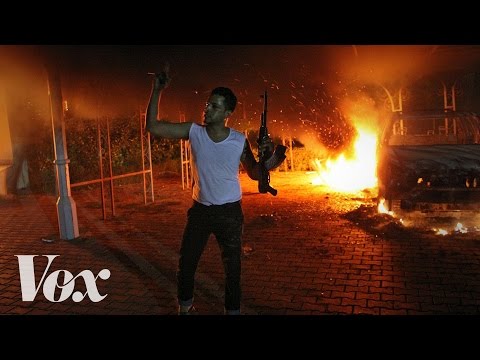
Benghazi, the attack and the scandal, explained
- Report rights infringement
- published: 16 Oct 2015
- views: 116102

Libya Wikipedia travel guide video. Created by http://stupeflix.com
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 Mar 2010
- views: 1513

Libya Benghazi Destruction: Continued Fighting Leaves City in Ruins Displacing Thousands
- Report rights infringement
- published: 03 Jul 2015
- views: 680

Time Lapse Benghazi, Libya
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Jun 2013
- views: 2881

Libya (12/2010) - Benghazi
- Report rights infringement
- published: 26 Jan 2011
- views: 8649

Libya On Edge: Fighting Sweeps Across Tripoli Following Violence In Benghazi
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 May 2014
- views: 791

Libyan Army clashes with Terrorists in Al-Laithi Benghazi
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 Feb 2016
- views: 591

College Students want to study abroad in BENGHAZI?!?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 30 Jan 2014
- views: 13546
- Playlist
- Chat

Libya's Quiet War: The Tuareg of South Libya
- Report rights infringement
- published: 17 Feb 2016
- views: 361892

Life After Qaddafi — Libya: A Broken State
- Report rights infringement
- published: 12 Nov 2014
- views: 322839

Libya: State of Insecurity - Fault Lines
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 Aug 2015
- views: 14888

Gaddafi The Truth About Libya- Documentary
- Report rights infringement
- published: 08 Jun 2012
- views: 487506

What Was Libya Like 20 Years Ago?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 11 May 2016
- views: 12862

Libya 5 years after NATO intervention: From one of richest nations in Africa to most troubled
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Mar 2016
- views: 32765

Libya War: What They Don't Want You to Know
- Report rights infringement
- published: 08 Apr 2014
- views: 155141

Drowning for Freedom: Libya’s Migrant Jails (Part 1)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 17 Mar 2015
- views: 288963

The Libya Gamble: Inside Hillary Clinton’s Push for War & the Making of a Failed State
- Report rights infringement
- published: 03 Mar 2016
- views: 16350
- Playlist
- Chat

13 Hours: The Secret Soldiers of Benghazi Full "Movie English Streaming HD 2016
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Jun 2016
- views: 0

13 Hours: The Secret Soldiers of Benghazi full "Movie"
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Jun 2016
- views: 0

13 Hours: The Secret Soldiers of Benghazi Full "Movie 2016
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Jun 2016
- views: 2

the best sense"'13 Hours The Secret Soldiers of Benghazi (2016)'"
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Jun 2016
- views: 4

benghazi YT
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Jun 2016
- views: 35

13 Hours: The Secret Soldiers of Benghazi (2016) - Movie Review
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Jun 2016
- views: 15

13 Hours: The Secret Soldiers of Benghazi
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Jun 2016
- views: 1

Secret soldiers of Benghazi
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Jun 2016
- views: 3

13 Hours The Secret Soldiers of Benghazi - 13 Saat Bingazi'nin Gizli Askerleri Türkçe Dublaj İndir
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Jun 2016
- views: 31

Watch 13 Hours: The Secret Soldiers of Benghazi Full Movie online free Streaming Eng Subtitle
- Report rights infringement
- published: 18 Jun 2016
- views: 2
- Playlist
- Chat

Death and Deceit In Benghazi Libya - What Really Happened
- Report rights infringement
- published: 21 Oct 2012
- views: 12840

On The Front Line Of Benghazi's Battle With ISIS
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 Feb 2016
- views: 43553

Ignoring U.S. Destabilization of Libya, GOP Benghazi Hearing Asks Clinton All the Wrong Questions
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Oct 2015
- views: 7924

Splinter Cell Blacklist: Perfectionist Walkthrough Part 2 - Benghazi Libya
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Aug 2013
- views: 12313

The Truth About Benghazi
- Report rights infringement
- published: 03 May 2014
- views: 99766

13 hours Benghazi - Operators Full Interview
- Report rights infringement
- published: 11 Jan 2016
- views: 3662

Safehouse: Benghazi, Libya - Perfectionist - Splinter Cell Blacklist Walkthrough
- Report rights infringement
- published: 21 Sep 2013
- views: 1111

Americans Killed in Benghazi, Libya Return to U.S.
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Sep 2012
- views: 15548

The Real Deal Ep # 147 HILLARY'S BENGHAZI... How the West Destroyed Libya
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Jan 2016
- views: 3154
Repaired Egyptair MS804 Black Box 'Confirms Smoke'
Edit WorldNews.com 29 Jun 2016Pyonghattan Skyscrapers Arise Out Of Crippling North Korean Sanctions
Edit WorldNews.com 29 Jun 2016Trump: 'What Do You Think Of Waterboarding? I Like It A Lot'
Edit WorldNews.com 29 Jun 2016Britain Is Not Going to Leave The EU Anytime Soon
Edit WorldNews.com 29 Jun 2016BENGHAZI REPORT House Benghazi report is a dud
Edit Richmond Times Dispatch 30 Jun 2016ISIS may be on the decline — but beware al Qaeda
Edit New York Post 30 Jun 2016Islamic terrorists still have ‘a lot of momentum,’ CIA chief says
Edit The Miami Herald 30 Jun 2016Congress must authorize force against ISIS — and set limits
Edit LA Daily News 30 Jun 2016Shouldn’t we first help the Christian victims of Mideast genocide?
Edit New York Post 30 Jun 2016Suspend Saudi Arabia from UN Human Rights Council (Amnesty International Australia)
Edit Public Technologies 30 Jun 2016US to reveal drones’ civilian toll
Edit Stars and Stripes 30 Jun 2016The unlikely godfather of the Islamic State
Edit CNN 30 Jun 2016Italy recovers refugee ship that sunk off Libya
Edit Al Jazeera 29 Jun 2016- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »







