- published: 29 Jan 2016
- views: 1587
-
remove the playlistBank Of Japan
-
remove the playlistLatest Videos
-
remove the playlistLongest Videos
- remove the playlistBank Of Japan
- remove the playlistLatest Videos
- remove the playlistLongest Videos
Please tell us which country and city you'd like to see the weather in.
- published: 31 Jan 2016
- views: 6354
- published: 25 Jan 2016
- views: 1152
- published: 15 Oct 2013
- views: 3047
- published: 14 Feb 2016
- views: 120
- published: 29 Jan 2016
- views: 2223
- published: 29 Jan 2016
- views: 1548
- published: 14 Mar 2016
- views: 216
- published: 30 Jan 2016
- views: 1372

Bank of Japan
The Bank of Japan (日本銀行, Nippon Ginkō, BOJ, JASDAQ: 8301) is the central bank of Japan. The Bank is often called Nichigin (日銀) for short. It has its headquarters in Chūō, Tokyo.
History
Like most modern Japanese institutions, the Bank of Japan was founded after the Meiji Restoration. Prior to the Restoration, Japan's feudal fiefs all issued their own money, hansatsu, in an array of incompatible denominations, but the New Currency Act of Meiji 4 (1871) did away with these and established the yen as the new decimal currency, which had parity with the Mexican silver dollar. The former han (fiefs) became prefectures and their mints became private chartered banks which, however, initially retained the right to print money. For a time both the central government and these so-called "national" banks issued money. A period of unanticipated consequences was ended when the Bank of Japan was founded in Meiji 15 (October 10, 1882), under the Bank of Japan Act 1882 (June 27, 1882), after a Belgian model. It has since been partly privately owned (its stock is traded over the counter, hence the stock number). A number of modifications based on other national banks were encompassed within the regulations under which the bank was founded. The institution was given a monopoly on controlling the money supply in 1884, but it would be another 20 years before the previously issued notes were retired.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Japan
Coordinates: 35°N 136°E / 35°N 136°E / 35; 136
Japan (![]() i/dʒəˈpæn/; Japanese: 日本 Nippon [nip̚põ̞ɴ] or Nihon [nihõ̞ɴ]; formally 日本国
i/dʒəˈpæn/; Japanese: 日本 Nippon [nip̚põ̞ɴ] or Nihon [nihõ̞ɴ]; formally 日本国 ![]() Nippon-koku or Nihon-koku, "State of Japan") is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, the East China Sea, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south. The kanji that make up Japan's name mean "sun origin", and Japan is often called the "Land of the Rising Sun".
Nippon-koku or Nihon-koku, "State of Japan") is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, the East China Sea, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south. The kanji that make up Japan's name mean "sun origin", and Japan is often called the "Land of the Rising Sun".
Japan is a stratovolcanic archipelago of 6,852 islands. The four largest are Honshu, Hokkaido, Kyushu, and Shikoku, which make up about ninety-seven percent of Japan's land area. Japan's population of 126 million is the world's tenth largest. Approximately 9.1 million people live in Tokyo, the capital city of Japan, which is the sixth largest city proper in the OECD. The Greater Tokyo Area, which includes Tokyo and several surrounding prefectures, is the world's largest metropolitan area with over 35 million residents and the world's largest urban agglomeration economy.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
Radio Stations - Tokyo
SEARCH FOR RADIOS
- Loading...

-
 6:02
6:02Business: why did Central Bank of Japan surprise markets with a move to negative interest?
Business: why did Central Bank of Japan surprise markets with a move to negative interest?Business: why did Central Bank of Japan surprise markets with a move to negative interest?
Subscribe to France 24 now: http://f24.my/youtubeEN FRANCE 24 live news stream: all the latest news 24/7 http://f24.my/YTliveEN Japan’s central bank has stunned markets by lowering interest rates to negative. The Bank of Japan’s new benchmark rate is -0.1%. It's seen as a dramatic step, and it means that commercial lenders will be charged when they make deposits at the Bank of Japan. Markus Karlsson spoke Richard Perry, analyst at Hantec Markets, about the pros and cons. Visit our website: http://www.france24.com Like us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/FRANCE24.English Follow us on Twitter: https://twitter.com/France24_en -
 1:37
1:37The Impact of Bank of Japan's Negative Rate Decision
The Impact of Bank of Japan's Negative Rate DecisionThe Impact of Bank of Japan's Negative Rate Decision
January 29 -- Bank of Japan Governor Haruhiko Kuroda sprung another surprise on investors Friday, adopting a negative interest-rate strategy to spur banks to lend in the face of a weakening economy. The move to penalize a portion of banks’ reserves complements the BOJ’s record asset-purchase program, including 80 trillion yen ($666 billion) a year in government-bond purchases, which was kept unchanged at the board meeting. -
 5:16
5:16Bank of Japan's dilemma I Authers Note
Bank of Japan's dilemma I Authers NoteBank of Japan's dilemma I Authers Note
► Subscribe to the Financial Times on YouTube: http://bit.ly/FTimeSubs Uncertain markets and a rising yen are putting pressure on Japan's central bank. The FT's John Authers talks to experts in Tokyo about whether the BoJ will act this month and if so, how. Filmed and edited by Tom Griggs. For more video content from the Financial Times, visit http://www.FT.com/video Twitter https://twitter.com/ftvideo Facebook https://www.facebook.com/financialtimes -
 71:06
71:06Overcoming Deflation: The Bank of Japan's Challenge
Overcoming Deflation: The Bank of Japan's ChallengeOvercoming Deflation: The Bank of Japan's Challenge
Haruhiko Kuroda, governor of the Bank of Japan, discusses the challenges of overcoming deflation and Japan's economic policy. SPEAKER: Haruhiko Kuroda PRESIDER: J. Tomilson Hill http://www.cfr.org/japan/overcoming-deflation-bank-japans-challenge/p31634 -
 9:59
9:59News Inside _ Bank of Japan goes negative Bank of Japan goes negative
News Inside _ Bank of Japan goes negative Bank of Japan goes negativeNews Inside _ Bank of Japan goes negative Bank of Japan goes negative
Bank of Japan goes negative Bank of Japan goes negative Japan's central bank has adopted a negative interest rate policy for the first time ever, as it works to prop up its flailing economy. Once considered extreme, negative rates have become much more prevalent with the European Central Bank (ECB) and central banks in other European nations inching into minus territory. We look at this new form of monetary stimulus, and what impact Japan's negative rate policy will have on Korea. Visit ‘Arirang Issue’ Official Pages Homepage: http://www.arirang.com Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/arirangtv Twitter: http://twitter.com/arirangworld Instagram: http://instagram.com/arirangworld -
 3:59
3:59Asia report: major move at the Bank of Japan
Asia report: major move at the Bank of JapanAsia report: major move at the Bank of Japan
29 January 2016: The Bank of Japan took economists by surprise by adopting a negative interest rate policy. The BOJ will apply a rate of –0.1% to excess reserves that financial institutional place at the bank. Unlike other monetary structures there is no deposit rate specifically in Japan, but what the Bank of Japan has done is to cut the rate that is closest to what the west knows as the deposit rate. -
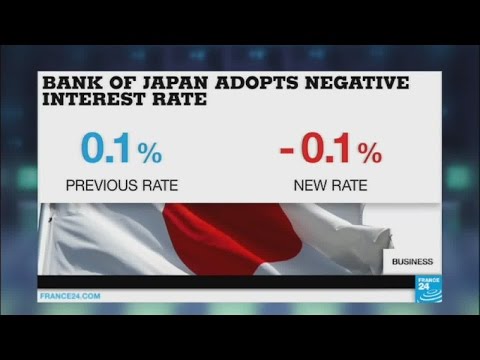 5:43
5:43Bank of Japan surprises markets with negative interest rate policy
Bank of Japan surprises markets with negative interest rate policyBank of Japan surprises markets with negative interest rate policy
Subscribe to France 24 now : http://f24.my/youtubeEN FRANCE 24 live news stream: all the latest news 24/7 http://f24.my/YTliveEN Take it as a lesson in how to turn a negative into a positive. Earlier this month, Japan ruled out negative interest rates, making it all the more of a surprise this Friday when the Bank of Japan lowered the benchmark from 0.1% to -0.1%. Now banks will be encouraged to lend more, and exporters could see relief as the yen should weaken. Plus, we find out the effects the Paris terror attacks had on the wider French economy's 2015 performance, and meet the man who is London's most popular landlord. Visit our website : http://www.france24.com Subscribe to our YouTube channel : http://f24.my/youtubeEN Like us on Facebook : https://www.facebook.com/FRANCE24.English Follow us on Twitter : https://twitter.com/France24_en -
 67:24
67:24Haruhiko Kuroda: Governor of the Bank of Japan
Haruhiko Kuroda: Governor of the Bank of Japan -
 3:06
3:06Bank Of Japan Monetary Policy Meeting - March 2016
Bank Of Japan Monetary Policy Meeting - March 2016Bank Of Japan Monetary Policy Meeting - March 2016
Welcome to the Investors Trading Academy event of the week. Each week our staff of analysts and educators tries to provide you a better understanding of a major market event scheduled soon and that have an effect on the global markets. With big central bank events ahead, we want to look at the one that is getting the least attention, but the one that could have the biggest punch, the Bank of Japan. After the ECB last week and the FOMC on Tuesday and Wednesday of this week, many traders are paying little attention to the BoJ. Even last week the move by the Reserve Bank of New Zealand barely made the headlines after the bank surprised and reduced their rate by 25 basis points. The Bank of Japan surprised markets on January 29 by cutting rates to negative. Prior to that move, we made the case that they needed to act. The market was ripe for it. They surprised many. But they haven’t gotten the desired effect. Since they cut their deposit rates below zero, the yield on the 10 year Japanese government bond has gone negative. And the 20, 30 and 40-year bond yield has collapsed too — indicating the market doesn’t believe Japan will ever emerge for the deflationary vortex. On that note, the move to negative rates hasn’t worked thus far. And when it comes to stocks and the yen, they’ve gotten the opposite of what they need and want. This monetary easing, which imposes a minus 0.1 percent interest rate on a portion of the new reserve accounts held by private financial institutions at the central bank, is the third major action conducted by the governor of the bank, Haruhiko Kuroda, who took the position in 2013. Kuroda’s first two major actions as governor were significant increases in government bond purchases. Ominously though, this is the first time his actions have failed to lead markets in the desired direction, one which is favorable for the Japanese economy. As a result of the negative interest rate, Japanese government bond yields decreased but the stock market declined, and despite a fleeting initial depreciation, the Japanese yen has sharply appreciated. Even though these market reactions were mainly caused by the rise in uncertainty regarding the outlook of the global economy, at the same time, it illustrates the simple fact that without desirable conditions in the global economy and markets, it’s difficult for Kuroda to make the bank’s monetary easing policy bring about the intended positive effects on the markets. Bank of Japan Governor Kuroda faces pressure to hold fire as a monetary policy meeting approaches this week, despite gloomy economic conditions. It is an unusual situation for a central bank chief who has talked gleefully of unleashing a monetary “bazooka” and vowed to do whatever it takes to put the nation’s economy back on a path to stable growth. But the BOJ’s latest move—negative interest rates—has created a backlash in Japan, leaving Mr. Kuroda and other BOJ officials scrambling in recent weeks. Pushing rates deeper into negative territory now could worsen the outcry and damage public confidence, and an expansion of its asset-purchase program might have little effect, people close to the central bank said. By Barry Norman, Investors Trading Academy - ITA -
 1:49
1:49Central Bank Of Japan Adopts Negative Interest Rates For The First Time Ever!
Central Bank Of Japan Adopts Negative Interest Rates For The First Time Ever!Central Bank Of Japan Adopts Negative Interest Rates For The First Time Ever!
January 29, 2016 Al Jazeera News http://MOXNews.com MOX NEWS NEEDS YOUR HELP TO CONTINUE! THANK YOU FOR ANY SUPPORT! ONE TIME ONLY DONATION https://www.paypal.com/cgi-bin/webscr?cmd=_s-xclick&hosted;_button_id=MHT8PM5BPSVC8 $1.00 ONE DOLLAR PER MONTH SUBSCRIPTION https://www.paypal.com/cgi-bin/webscr?cmd=_s-xclick&hosted;_button_id=DJ3ZYWM4TSD7L $3.00 THREE DOLLARS PER MONTH SUBSCRIPTION https://www.paypal.com/cgi-bin/webscr?cmd=_s-xclick&hosted;_button_id=HLTDW4G5UJH5L $5.00 FIVE DOLLARS PER MONTH SUBSCRIPTION https://www.paypal.com/cgi-bin/webscr?cmd=_s-xclick&hosted;_button_id=BNNGYSFS3XBW4 $10.00 TEN DOLLARS PER MONTH SUBSCRIPTION https://www.paypal.com/cgi-bin/webscr?cmd=_s-xclick&hosted;_button_id=WDLM8TUJ8459S $20.00 TWENTY DOLLARS PER MONTH SUBSCRIPTION https://www.paypal.com/cgi-bin/webscr?cmd=_s-xclick&hosted;_button_id=GNMQ7S22BPY5Q $50.00 FIFTY DOLLARS PER MONTH SUBSCRIPTION https://www.paypal.com/cgi-bin/webscr?cmd=_s-xclick&hosted;_button_id=ZY2M9PUG3U7UA $100.00 ONE HUNDRED DOLLARS PER MONTH SUBSCRIPTION https://www.paypal.com/cgi-bin/webscr?cmd=_s-xclick&hosted;_button_id=JATR49EVASLLQ
Rain Tree Crow
ALBUMS
- Rain Tree Crow released: 1992
Rain Tree Crow
Released 1992- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Big Wheels in Shanty Town
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Every Colour You Are
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Rain Tree Crow
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Red Earth (As Summertime Ends)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Pocket Full of Change
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Boat's for Burning
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen New Moon at Deer Wallow
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Blackwater
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen A Reassuringly Dull Sunday
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Blackcrow Hits Shoe Shine City
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Scratchings on the Bible Belt
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Cries and Whispers
Japan
ALBUMS
- The Collection released: 2009
- The Very Best Of released: 2006
- Assemblage released: 2006
- Adolescent Sex released: 2004
- The Best of Japan released: 2002
- The Masters released: 1997
- The Singles: Japan released: 1996
- In Vogue released: 1996
- Methods of Dance released: 1991
- The Other Side of Japan released: 1991
- Gentlemen Take Polaroids released: 1991
- Souvenir From Japan released: 1989
- Quiet Life released: 1986
- Exorcising Ghosts released: 1984
- Oil on Canvas released: 1983
- Leidenese Boy released: 1982
- Visions of China released: 1982
- Japan released: 1982
- Live at Hammersmith Odeon released: 1981
- Tin Drum released: 1981
- Obscure Alternatives released: 1978
- 1982-12-08: Budokan Hall, Tokyo, Japan released:
The Collection
Released 2009- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Quiet Life (7" version)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Visions of China
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Ghosts
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen I Second That Emotion
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Life in Tokyo
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen European Son
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen All Tomorrow's Parties (7" version)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Adolescent Sex
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Don't Rain on My Parade
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen In Vogue
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Unconventional
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Communist China
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Suburban Berlin
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Halloween
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Life in Tokyo (12" version)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen All Tomorrow's Parties (12" version)
The Very Best Of
Released 2006- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Ghosts (single version)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen I Second That Emotion (single mix)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Quiet Life (7" version)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Gentlemen Take Polaroids
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Art of Parties (single version)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Visions of China
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Taking Islands in Africa (Steve Nye remix)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen European Son (single mix)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Cantonese Boy
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Life in Tokyo, Part 1 (Special remix)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Nightporter
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Methods of Dance
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen All Tomorrow's Parties (7" version)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Canton (live)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Ghosts (album version)
Assemblage
Released 2006- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Adolescent Sex
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen State Line
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Communist China
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen ...Rhodesia
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Suburban Berlin
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Life in Tokyo
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen European Son
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen All Tomorrow's Parties
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Quiet Life
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen I Second That Emotion
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen European Son (John Punter 12" mix)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen I Second That Emotion (12" version)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Life in Tokyo, Part 2 (special remix)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Life in Tokyo (1982 version)
Adolescent Sex
Released 2004- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Transmission
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Unconventional
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Wish You Were Black
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Performance
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Lovers On Main Street
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Don't Rain On My Parade
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Suburban Love
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Adolescent Sex
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Communist China
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Television
The Best of Japan
Released 2002- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Adolescent Sex (Re-Recorded version)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Unconventional
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Communist China
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Automatic Gun
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen State Line
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen European Son
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen I Second That Emotion
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Life in Tokyo
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Quiet Life
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Fall in Love With Me
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Despair
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Other Side of Life
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen A Foreign Place
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Deviation (live)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Obscure Alternatives (live)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen In Vogue (live)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sometimes I Feel So Low (live)
The Masters
Released 1997- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Quiet Life
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen European Son
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen I Second That Emotion
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Life in Tokyo
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen All Tomorrow's Parties
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Deviation (Live)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Unconventional
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Halloween
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Love is Infectious
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Communist China
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Lovers on Main Street
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen In-Vogue
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Suburban Berlin
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Alien
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Obscure Alternatives
The Singles: Japan
Released 1996- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Life in Tokyo
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Life in Tokyo (Theme)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen All Tomorrow's Parties
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen In Vogue (live in Tokyo)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Life in Tokyo (12" extended version)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen European Son
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sometimes I Feel So Low
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Adolescent Sex (Re-Recorded version)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Life in Tokyo (extended remix)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Life in Tokyo (Theme)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen All Tomorrow's Parties (Steve Nye's 1983 remix)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen I Second That Emotion (extended remix)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Halloween
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen European Son (extended remix)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Quiet Life (extended version)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Fall in Love With Me
In Vogue
Released 1996- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Unconventional
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Lovers on Main Street
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Transmission
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen I Second That Emotion
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen All Tomorrow's Parties (12" version)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Alien
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Halloween
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Suburban Berlin
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Quiet Life
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Love Is Infectious
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Fall in Love With Me
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Adolescent Sex
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen European Son (12" version)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen In Vogue
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Life in Tokyo (12" version)
Methods of Dance
Released 1991- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Swing
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Gentlemen Take Polaroids
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Alien
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen ...Rhodesia
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Quiet Life
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen My New Career
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Taking Islands in Africa
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Methods of Dance
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Ain't That Peculiar
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Halloween
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen European Son
The Other Side of Japan
Released 1991- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Wish You Were Black
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Television
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Unconventional
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Transmission
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Automatic Gun
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Love Is Infectious
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sometimes I Feel So Low
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Tenant
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen In Vogue
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Halloween
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen A Foreign Place
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Don't Rain on My Parade
Gentlemen Take Polaroids
Released 1991- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Gentlemen Take Polaroids
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Swing
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Burning Bridges
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Experience of Swimming
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen My New Career
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Methods of Dance
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Ain't That Peculiar
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Nightporter
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Width of a Room
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Taking Islands in Africa
Souvenir From Japan
Released 1989- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen I Second That Emotion
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Life in Tokyo
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Deviation
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Suburban Berlin
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Adolescent Sex
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen European Son
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen All Tomorrow's Parties
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Communist China
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen State Line
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen .....Rhodesia
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Obscure Alternatives
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Quiet Life
Quiet Life
Released 1986- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Quiet Life
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Fall in Love With Me
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Despair
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen In Vogue
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Halloween
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen All Tomorrow's Parties
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Alien
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Other Side of Life
Exorcising Ghosts
Released 1984- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Methods of Dance
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Gentlemen Take Polaroids
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Quiet Life
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Night Porter
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen My New Career
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Other Side of Life
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Visions of China
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Ghosts
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Life Without Buildings
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Talking Drum
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Art of Parties
Oil on Canvas
Released 1983- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Oil on Canvas
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sons of Pioneers
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Gentlemen Take Polaroids
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Swing
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Cantonese Boy
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Visions of China
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Ghosts
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Voices Raised in Welcome, Hands Held in Prayer
Leidenese Boy
Released 1982- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Gentlemen Take Polaroids
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Swing
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Cantonese Boy
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Visions of China
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Nightporter
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Canton
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Ghosts
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Still Life in Mobile Homes
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Quiet Life
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen European Son
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Art of Parties
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Life in Tokyo
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Fall in Love With Me
Visions of China
Released 1982- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Intro (Burning Bridges)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sons of Pioneers
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Alien
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Gentlemen Take Polaroids
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Swing
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Cantonese Boy
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Visions of China
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Nightporter
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Ghosts
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Still Life in Mobile Homes
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Methods of Dance
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Quiet Life
Japan
Released 1982- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Art of Parties
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Talking Drum
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Ghosts
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Gentlemen Take Polaroids
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Still Life in Mobile Homes
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Visions of China
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Taking Islands in Africa (remix)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Swing
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Cantonese Boy
Live at Hammersmith Odeon
Released 1981- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Swing
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Gentlemen Take Polaroids
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Alien
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen ...Rhodesia
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Quiet Life
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen My New Career
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Taking Islands in Africa
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Methods of Dance
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Ain't That Peculiar
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Halloween
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen European Son
Tin Drum
Released 1981- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Art of Parties
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Talking Drum
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Ghosts
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Canton
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Still Life in Mobile Homes
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Visions of China
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sons of Pioneers
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Cantonese Boy
Obscure Alternatives
Released 1978- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Automatic Gun
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen ...Rhodesia
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Love Is Infectious
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sometimes I Feel So Low
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Obscure Alternatives
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Deviation
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Suburban Berlin
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Tenant
1982-12-08: Budokan Hall, Tokyo, Japan
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Burning Bridges
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sons of Pioneers
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Alien
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Gentlemen Take Polaroids
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Swing
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Cantonese Boy
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Visions of China
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Nightporter
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Ghosts
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Still Life in Mobile Homes
Died: 1982-12-16
-

Business: why did Central Bank of Japan surprise markets with a move to negative interest?
Subscribe to France 24 now: http://f24.my/youtubeEN FRANCE 24 live news stream: all the latest news 24/7 http://f24.my/YTliveEN Japan’s central bank has stunned markets by lowering interest rates to negative. The Bank of Japan’s new benchmark rate is -0.1%. It's seen as a dramatic step, and it means that commercial lenders will be charged when they make deposits at the Bank of Japan. Markus Karlsson spoke Richard Perry, analyst at Hantec Markets, about the pros and cons. Visit our website: http://www.france24.com Like us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/FRANCE24.English Follow us on Twitter: https://twitter.com/France24_en -

The Impact of Bank of Japan's Negative Rate Decision
January 29 -- Bank of Japan Governor Haruhiko Kuroda sprung another surprise on investors Friday, adopting a negative interest-rate strategy to spur banks to lend in the face of a weakening economy. The move to penalize a portion of banks’ reserves complements the BOJ’s record asset-purchase program, including 80 trillion yen ($666 billion) a year in government-bond purchases, which was kept unchanged at the board meeting. -

Bank of Japan's dilemma I Authers Note
► Subscribe to the Financial Times on YouTube: http://bit.ly/FTimeSubs Uncertain markets and a rising yen are putting pressure on Japan's central bank. The FT's John Authers talks to experts in Tokyo about whether the BoJ will act this month and if so, how. Filmed and edited by Tom Griggs. For more video content from the Financial Times, visit http://www.FT.com/video Twitter https://twitter.com/ftvideo Facebook https://www.facebook.com/financialtimes -

Overcoming Deflation: The Bank of Japan's Challenge
Haruhiko Kuroda, governor of the Bank of Japan, discusses the challenges of overcoming deflation and Japan's economic policy. SPEAKER: Haruhiko Kuroda PRESIDER: J. Tomilson Hill http://www.cfr.org/japan/overcoming-deflation-bank-japans-challenge/p31634 -

News Inside _ Bank of Japan goes negative Bank of Japan goes negative
Bank of Japan goes negative Bank of Japan goes negative Japan's central bank has adopted a negative interest rate policy for the first time ever, as it works to prop up its flailing economy. Once considered extreme, negative rates have become much more prevalent with the European Central Bank (ECB) and central banks in other European nations inching into minus territory. We look at this new form of monetary stimulus, and what impact Japan's negative rate policy will have on Korea. Visit ‘Arirang Issue’ Official Pages Homepage: http://www.arirang.com Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/arirangtv Twitter: http://twitter.com/arirangworld Instagram: http://instagram.com/arirangworld -

Asia report: major move at the Bank of Japan
29 January 2016: The Bank of Japan took economists by surprise by adopting a negative interest rate policy. The BOJ will apply a rate of –0.1% to excess reserves that financial institutional place at the bank. Unlike other monetary structures there is no deposit rate specifically in Japan, but what the Bank of Japan has done is to cut the rate that is closest to what the west knows as the deposit rate. -

Bank of Japan surprises markets with negative interest rate policy
Subscribe to France 24 now : http://f24.my/youtubeEN FRANCE 24 live news stream: all the latest news 24/7 http://f24.my/YTliveEN Take it as a lesson in how to turn a negative into a positive. Earlier this month, Japan ruled out negative interest rates, making it all the more of a surprise this Friday when the Bank of Japan lowered the benchmark from 0.1% to -0.1%. Now banks will be encouraged to lend more, and exporters could see relief as the yen should weaken. Plus, we find out the effects the Paris terror attacks had on the wider French economy's 2015 performance, and meet the man who is London's most popular landlord. Visit our website : http://www.france24.com Subscribe to our YouTube channel : http://f24.my/youtubeEN Like us on Facebook : https://www.facebook.com/FRANCE24.Englis... -

-

Bank Of Japan Monetary Policy Meeting - March 2016
Welcome to the Investors Trading Academy event of the week. Each week our staff of analysts and educators tries to provide you a better understanding of a major market event scheduled soon and that have an effect on the global markets. With big central bank events ahead, we want to look at the one that is getting the least attention, but the one that could have the biggest punch, the Bank of Japan. After the ECB last week and the FOMC on Tuesday and Wednesday of this week, many traders are paying little attention to the BoJ. Even last week the move by the Reserve Bank of New Zealand barely made the headlines after the bank surprised and reduced their rate by 25 basis points. The Bank of Japan surprised markets on January 29 by cutting rates to negative. Prior to that move, we made the ca... -

Central Bank Of Japan Adopts Negative Interest Rates For The First Time Ever!
January 29, 2016 Al Jazeera News http://MOXNews.com MOX NEWS NEEDS YOUR HELP TO CONTINUE! THANK YOU FOR ANY SUPPORT! ONE TIME ONLY DONATION https://www.paypal.com/cgi-bin/webscr?cmd=_s-xclick&hosted;_button_id=MHT8PM5BPSVC8 $1.00 ONE DOLLAR PER MONTH SUBSCRIPTION https://www.paypal.com/cgi-bin/webscr?cmd=_s-xclick&hosted;_button_id=DJ3ZYWM4TSD7L $3.00 THREE DOLLARS PER MONTH SUBSCRIPTION https://www.paypal.com/cgi-bin/webscr?cmd=_s-xclick&hosted;_button_id=HLTDW4G5UJH5L $5.00 FIVE DOLLARS PER MONTH SUBSCRIPTION https://www.paypal.com/cgi-bin/webscr?cmd=_s-xclick&hosted;_button_id=BNNGYSFS3XBW4 $10.00 TEN DOLLARS PER MONTH SUBSCRIPTION https://www.paypal.com/cgi-bin/webscr?cmd=_s-xclick&hosted;_button_id=WDLM8TUJ8459S $20.00 TWENTY DOLLARS PER MONTH SUBSCRIPTION https://www.paypal.com/cgi...
Business: why did Central Bank of Japan surprise markets with a move to negative interest?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:02
- Updated: 29 Jan 2016
- views: 1587
- published: 29 Jan 2016
- views: 1587
The Impact of Bank of Japan's Negative Rate Decision
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:37
- Updated: 31 Jan 2016
- views: 6354
- published: 31 Jan 2016
- views: 6354
Bank of Japan's dilemma I Authers Note
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:16
- Updated: 25 Jan 2016
- views: 1152
- published: 25 Jan 2016
- views: 1152
Overcoming Deflation: The Bank of Japan's Challenge
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 71:06
- Updated: 15 Oct 2013
- views: 3047
- published: 15 Oct 2013
- views: 3047
News Inside _ Bank of Japan goes negative Bank of Japan goes negative
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:59
- Updated: 14 Feb 2016
- views: 120
- published: 14 Feb 2016
- views: 120
Asia report: major move at the Bank of Japan
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:59
- Updated: 29 Jan 2016
- views: 2223
- published: 29 Jan 2016
- views: 2223
Bank of Japan surprises markets with negative interest rate policy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:43
- Updated: 29 Jan 2016
- views: 1548
- published: 29 Jan 2016
- views: 1548
Haruhiko Kuroda: Governor of the Bank of Japan
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 67:24
- Updated: 20 Mar 2015
- views: 1479
Bank Of Japan Monetary Policy Meeting - March 2016
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:06
- Updated: 14 Mar 2016
- views: 216
- published: 14 Mar 2016
- views: 216
Central Bank Of Japan Adopts Negative Interest Rates For The First Time Ever!
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:49
- Updated: 30 Jan 2016
- views: 1372
- published: 30 Jan 2016
- views: 1372
-

Is A BOJ Rate Cut On The Horizon - 26 Jul 16 | Gazunda
This video is selected and uploaded by Gazunda Services Ltd. It is not our property. -

Japan Aso: Expect BOJ to do utmost to meet price target
Japan Aso: Expect BOJ to do utmost to meet price target. Japanese Finance Minister Taro Aso said on Tuesday he expected the Bank of Japan to continue doing its utmost to meet its 2 percent inflation target. Aso, speaking at a news conference, said it was up to the BOJ to decide specific monetary policy steps. The BOJ will hold a two-day policy meeting through Friday, and there is lingering speculation that it will expand quantitative easing to encourage inflation. (Reporting by Stanley White; Editing by Chang-Ran Kim)........ ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ See more: https://goo.gl/wA4EUc ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Source: Reuters.com New... -

Here's What to Expect From the Federal Reserve and Bank of Japan Meetings This Week
U.S. stocks fluctuated on Monday, after the S&P; 500 reached a fresh record closing high on Friday, as investors awaited meetings from the Federal Reserve and Bank of Japan this week. Subscribe to TheStreetTV on YouTube: http://t.st/TheStreetTV For more content from TheStreet visit: http://thestreet.com Check out all our videos: http://youtube.com/user/TheStreetTV Follow TheStreet on Twitter: http://twitter.com/thestreet Like TheStreet on Facebook: http://facebook.com/TheStreet Follow TheStreet on LinkedIn: http://linkedin.com/company/theStreet Follow TheStreet on Google+: http://plus.google.com/+TheStreet -

-

The Bank of Japan doesn't buy securities from the Gov't. End of story.
The Bank of Japan does not buy government securities from the Japanese government. End of story. Here is the link: https://www.boj.or.jp/en/mopo/measures/term_cond/yoryo06.htm/ -

What Will Fed and BOJ Do This Week?
July 25, 2016 (Kuala Lumpur) -- Emerging markets stocks and currencies fall as investors await key monetary policy decisions by the Federal Open Market Committee and Bank of Japan. Bloomberg TV Malaysia's Cynthia Ng goes over markets' expectations from the central banks, including more stimulus. -

Expect Japan’s Fiscal Policy To Be Cooperative: JP Morgan
Hear out what Tai Hui, JP Morgan Asset Management expects from the FOMC and the Bank of Japan meetings this week. -

Is This The Right Time For The Bank Of Japan To Move - 25 Jul 16 | Gazunda
This video is selected and uploaded by Gazunda Services Ltd. It is not our property. -

FOREX : semaine majeure avec La FED et la Bank of Japan (BoJ)
Apprendre le trading en Bourse et sur le Forex avec nos guides de trading GRATUITS : http://bit.ly/1c6T8ao Rejoignez nos analystes chaque jour pour des sessions de trading en live sur www.DailyFX.fr, site de recherche de Forex Capital Markets (FXCM). Ouvrez un compte de démonstration gratuit : http://bit.ly/1g0jWxq -

Trading am Sonntag - Wochenvorschau - Fed und BOJ-Woche
Wir starten in die letzte Woche des Julis und da geht es dank FED und BOJ nochmal richtig zur Sache. Diesmal mit einem kleinen Schwerpunkt zu den Bollinger Bands
Is A BOJ Rate Cut On The Horizon - 26 Jul 16 | Gazunda
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:31
- Updated: 26 Jul 2016
- views: 1
- published: 26 Jul 2016
- views: 1
Japan Aso: Expect BOJ to do utmost to meet price target
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:44
- Updated: 26 Jul 2016
- views: 0
- published: 26 Jul 2016
- views: 0
Here's What to Expect From the Federal Reserve and Bank of Japan Meetings This Week
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:17
- Updated: 25 Jul 2016
- views: 51
- published: 25 Jul 2016
- views: 51
YouTrading Vidéo : La BoJ - Bank of Japan
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:32
- Updated: 25 Jul 2016
- views: 8
The Bank of Japan doesn't buy securities from the Gov't. End of story.
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:34
- Updated: 25 Jul 2016
- views: 245
- published: 25 Jul 2016
- views: 245
What Will Fed and BOJ Do This Week?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:08
- Updated: 25 Jul 2016
- views: 172
- published: 25 Jul 2016
- views: 172
Expect Japan’s Fiscal Policy To Be Cooperative: JP Morgan
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:54
- Updated: 25 Jul 2016
- views: 1
- published: 25 Jul 2016
- views: 1
Is This The Right Time For The Bank Of Japan To Move - 25 Jul 16 | Gazunda
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:28
- Updated: 25 Jul 2016
- views: 22
- published: 25 Jul 2016
- views: 22
FOREX : semaine majeure avec La FED et la Bank of Japan (BoJ)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 13:59
- Updated: 25 Jul 2016
- views: 136
- published: 25 Jul 2016
- views: 136
Trading am Sonntag - Wochenvorschau - Fed und BOJ-Woche
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 79:31
- Updated: 24 Jul 2016
- views: 141
- published: 24 Jul 2016
- views: 141
-

Governor Haruhiko Kuroda, The Bank of Japan
Mr. Haruhiko Kuroda was appointed the 31st Governor of the Bank of Japan on March 20, 2013. He started his career at the Ministry of Finance in Japan in 1967. In the early years, he was seconded to the International Monetary Fund as Advisor to the Executive Director. His responsibilities at the Ministry encompassed fields such as international finance and national and international tax as well as services in the finance minister's office including as secretary to the then Finance Minister Murayama. He represented the Ministry at a number of international monetary conferences as Vice Minister of Finance for International Affairs, including meetings of the Group of Seven Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors, International Monetary Fund/World Bank Joint Annual Meetings, and bilateral... -

-

Andy Hoffman: The Fed And Bank Of Japan Drop Further Credibility Destroying Bombs
Andy Hoffman: The Fed And Bank Of Japan Drop Further Credibility Destroying Bombs Economic collapse and financial crisis is rising any moment. Getting informed about collapse and crisis may earn you, or prevent to lose money. Do you want to be informed with Max Keiser, Alex Jones, Gerald Celente, Peter Schiff, Marc Faber, Ron Paul,Jim Willie, Steve Quayle, V Economist, and many specialists about FINANCIAL CRISIS / OIL PRICE / GLOBAL ECONOMIC COLLAPSE / AGENDA 21 / DOLLAR COLLAPSE / GOLD / SILVER / BITCOIN / GLOBAL RESET / NEW WORLD ORDER / ECONOMİC COLLAPSE just follow us in this channel.. Please click above to subscribe to my channel. -

Princes of the Yen: Central Bank Truth Documentary 『円の支配者』
“Princes of the Yen: Central Banks and the Transformation of the Economy” reveals how Japanese society was transformed to suit the agenda and desire of powerful interest groups, and how citizens were kept entirely in the dark about this. Based on a book by Professor Richard Werner, a visiting researcher at the Bank of Japan during the 90s crash, during which the stock market dropped by 80% and house prices by up to 84%. The film uncovers the real cause of this extraordinary period in recent Japanese history. Making extensive use of archival footage and TV appearances of Richard Werner from the time, the viewer is guided to a new understanding of what makes the world tick. And discovers that what happened in Japan almost 25 years ago is again repeating itself in Europe. To understand how,... -

Price Action Trading Report: Bank of Japan Humiliation & More Yen Longs
In this price action trading report, we look at the Bank of Japan's latest failed efforts to weaken the Yen, and show how I added another 3 short positions in USDJPY. Instruments analysed include the NIKKEI, SP500, EUR/JPY and USD/JPY. Photo credit: Yuya Shino / Reuters Resources Mentioned: Video report in which I analyse the yearly Yen charts: :https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KmRVkLowZqg Free PAST Price Action eBook: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KmRVkLowZqg How to Develop Big Winning Trades Video: http://forexuseful.com/new/members/21812-past-fast-track-video-course-and-scanner/ PAST Video Course: http://forexuseful.com/new/members/21812-past-fast-track-video-course-and-scanner/ Is Fundamental Analysis Fundamentally Useless? http://forexuseful.com/is-fundamental-analysis-fun... -

Forex Time - SORPRESA BANK OF JAPAN, COSA FARANNO LE ALTRE BANCHE CENTRALI?
Titolo: SORPRESA BANK OF JAPAN, COSA FARANNO LE ALTRE BANCHE CENTRALI? Argomenti: Cosa cambia sui mercati dopo la sorpresa della Bank of Japan. Come reagiranno Bce e Federal Reserve. Venerdì uscita dei dati sul mercato del lavoro Usa. La Federal Reserve ha fatto esplicito riferimento al mercato del lavoro come parametro per le decisioni di politica monetaria. Dollaro australiano: la Rba lo vorrebbe ancora più debole alla luce del calo dei prezzi delle materie prime Intanto la Bank of England sta a guardare. Non sono previste azioni nel breve periodo ma il rialzo dei tassi del quale si cominciava a parlare qualche mese fa dove è finito? -

FOMC and Bank of Japan preview - Analyst debates with Michael and Colin - CMC Markets 16 April 2015
Get the latest daily analysis on products such as US30, UK100, Japan225, USD/JPY, EUR/USD, GBP/USD, Crude oil and Gold via our CMC TV playlist. CMC Markets is a global leader in online trading, offering spread betting and Contracts for Difference (“CFDs”). Learn how to spread bet and how to trade CFDs with our variety of educational videos on trading strategies. Trade the financial markets such as currencies, commodities, indices, shares and treasuries. http://www.cmcmarkets.co.uk/ Riskwarning: This video is for general information only and is not intended to provide trading or investment advice or personal recommendations. Any information relating to past performance of an investment does not necessarily guarantee future performance. CMC shall not be responsible for any loss that you i... -

[522] Negative interest rates in Japan
The Bank of Japan introduced a negative interest rate on Friday and US GDP hit a soft patch for the fourth quarter. Ameera David weighs in. Then, Bianca Facchinei takes a look at the latest EU country to plan refugee deportations. Afterwards, RT correspondent Manuel Rapalo reports on Atlantic City’s economic woes from the resort city. After the break, Ameera sits down with Frances Coppola – Forbes contributor and blogger at “Coppola Comment” – to talk about Venezuela. And in The Big Deal, Ameera and Edward Harrison talk about the US and Japanese economies. Take a look! Check us out on Facebook -- and feel free to ask us questions: http://www.facebook.com/BoomBustRT https://www.facebook.com/harrison.writedowns https://www.facebook.com/erinade2020 https://www.facebook.com/biancafacch Fol...
Governor Haruhiko Kuroda, The Bank of Japan
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 43:43
- Updated: 24 May 2015
- views: 238
- published: 24 May 2015
- views: 238
Bank of Japan by Dr. Paul Cottrell
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 66:59
- Updated: 09 Feb 2016
- views: 65
Andy Hoffman: The Fed And Bank Of Japan Drop Further Credibility Destroying Bombs
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 25:39
- Updated: 30 Apr 2016
- views: 3547
- published: 30 Apr 2016
- views: 3547
Princes of the Yen: Central Bank Truth Documentary 『円の支配者』
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 92:40
- Updated: 04 Nov 2014
- views: 219598
- published: 04 Nov 2014
- views: 219598
Price Action Trading Report: Bank of Japan Humiliation & More Yen Longs
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 45:09
- Updated: 13 Feb 2016
- views: 236
- published: 13 Feb 2016
- views: 236
Forex Time - SORPRESA BANK OF JAPAN, COSA FARANNO LE ALTRE BANCHE CENTRALI?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 29:57
- Updated: 05 Nov 2014
- views: 2775
- published: 05 Nov 2014
- views: 2775
FOMC and Bank of Japan preview - Analyst debates with Michael and Colin - CMC Markets 16 April 2015
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 48:17
- Updated: 28 Apr 2016
- views: 101
- published: 28 Apr 2016
- views: 101
[522] Negative interest rates in Japan
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 27:48
- Updated: 30 Jan 2016
- views: 12299
- published: 30 Jan 2016
- views: 12299
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

Business: why did Central Bank of Japan surprise markets with a move to negative interest?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Jan 2016
- views: 1587

The Impact of Bank of Japan's Negative Rate Decision
- Report rights infringement
- published: 31 Jan 2016
- views: 6354

Bank of Japan's dilemma I Authers Note
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 Jan 2016
- views: 1152

Overcoming Deflation: The Bank of Japan's Challenge
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Oct 2013
- views: 3047

News Inside _ Bank of Japan goes negative Bank of Japan goes negative
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Feb 2016
- views: 120

Asia report: major move at the Bank of Japan
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Jan 2016
- views: 2223

Bank of Japan surprises markets with negative interest rate policy
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Jan 2016
- views: 1548

Haruhiko Kuroda: Governor of the Bank of Japan
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Mar 2015
- views: 1479

Bank Of Japan Monetary Policy Meeting - March 2016
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Mar 2016
- views: 216

Central Bank Of Japan Adopts Negative Interest Rates For The First Time Ever!
- Report rights infringement
- published: 30 Jan 2016
- views: 1372
- Playlist
- Chat

Is A BOJ Rate Cut On The Horizon - 26 Jul 16 | Gazunda
- Report rights infringement
- published: 26 Jul 2016
- views: 1

Japan Aso: Expect BOJ to do utmost to meet price target
- Report rights infringement
- published: 26 Jul 2016
- views: 0

Here's What to Expect From the Federal Reserve and Bank of Japan Meetings This Week
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 Jul 2016
- views: 51

YouTrading Vidéo : La BoJ - Bank of Japan
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 Jul 2016
- views: 8

The Bank of Japan doesn't buy securities from the Gov't. End of story.
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 Jul 2016
- views: 245

What Will Fed and BOJ Do This Week?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 Jul 2016
- views: 172

Expect Japan’s Fiscal Policy To Be Cooperative: JP Morgan
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 Jul 2016
- views: 1

Is This The Right Time For The Bank Of Japan To Move - 25 Jul 16 | Gazunda
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 Jul 2016
- views: 22

FOREX : semaine majeure avec La FED et la Bank of Japan (BoJ)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 Jul 2016
- views: 136

Trading am Sonntag - Wochenvorschau - Fed und BOJ-Woche
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 Jul 2016
- views: 141
- Playlist
- Chat

Governor Haruhiko Kuroda, The Bank of Japan
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 May 2015
- views: 238

Bank of Japan by Dr. Paul Cottrell
- Report rights infringement
- published: 09 Feb 2016
- views: 65

Andy Hoffman: The Fed And Bank Of Japan Drop Further Credibility Destroying Bombs
- Report rights infringement
- published: 30 Apr 2016
- views: 3547

Princes of the Yen: Central Bank Truth Documentary 『円の支配者』
- Report rights infringement
- published: 04 Nov 2014
- views: 219598

Price Action Trading Report: Bank of Japan Humiliation & More Yen Longs
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 Feb 2016
- views: 236

Forex Time - SORPRESA BANK OF JAPAN, COSA FARANNO LE ALTRE BANCHE CENTRALI?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Nov 2014
- views: 2775

FOMC and Bank of Japan preview - Analyst debates with Michael and Colin - CMC Markets 16 April 2015
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Apr 2016
- views: 101

[522] Negative interest rates in Japan
- Report rights infringement
- published: 30 Jan 2016
- views: 12299
Donald Trump rebuts criticism by slain Muslim-American soldier's father at Democratic convention
Edit DNA India 31 Jul 2016Hot air balloon carrying at least 16 people crashes in Texas
Edit San Francisco Chronicle 30 Jul 2016U.S.-backed forces now control 40 percent of IS-held city of Manbij: monitor
Edit Reuters 31 Jul 2016Officials: No apparent survivors in Texas balloon crash
Edit The Miami Herald 31 Jul 2016Polar bear at zoo plays with ice in Japan's scorching summer
Edit Kyodo 31 Jul 2016‘Helicopter money’ talk takes flight as Bank of Japan runs out of runway
Edit Japan Times 31 Jul 2016AP-Japan pact to pave the way for food parks, cold chains
Edit The Hindu 31 Jul 2016Japan beaten by Brazil in final Olympic warm-up (AFC - Asian Football Confederation)
Edit Public Technologies 31 Jul 2016Iran Urges Japan on $10 Billion Investment Plan (NIOC - National Iranian Oil Company)
Edit Public Technologies 31 Jul 2016Brazil beats Japan in final warmup ahead of Olympics
Edit Daily Herald 31 Jul 2016Japan's ANA completes purchase of Vietnam Airlines stake: report
Edit Topix 31 Jul 2016Ichiro Suzuki still a big hit in Japan as he closes in on No. 3,000
Edit The Morning Call 31 Jul 2016Brazil U23s 2-0 Japan U23s: Gabriel and Marquinhos score as Olympic hosts win their final ...
Edit The Daily Mail 31 Jul 2016Japan outclassed by Neymar's Brazil in final Rio tune-up
Edit Kyodo 31 Jul 2016- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »







