- published: 10 Feb 2016
- views: 23626
-
remove the playlistU.s. Presidential Primary
-
remove the playlistLatest Videos
-
remove the playlistLongest Videos
- remove the playlistU.s. Presidential Primary
- remove the playlistLatest Videos
- remove the playlistLongest Videos
- published: 13 Feb 2012
- views: 1371957
- published: 05 Nov 2012
- views: 331073
- published: 09 Nov 2015
- views: 2170445
- published: 11 Jun 2008
- views: 39141
- published: 09 Feb 2016
- views: 902
- published: 19 Apr 2016
- views: 1299
- published: 27 Apr 2016
- views: 198
- published: 10 Feb 2016
- views: 309

The series of presidential primary elections and caucuses held in each U.S. state and territory is part of the nominating process of United States presidential elections. This process was never included in the United States Constitution, and thus was created over time by the political parties. Some states only hold primary elections, some only hold caucuses, and others use a combination of both. These primaries and caucuses are staggered between January and June before the general election in November. The primary elections are run by state and local governments, while caucuses are private events that are directly run by the political parties themselves. A state's primary election or caucus usually is an indirect election: instead of voters directly selecting a particular person running for President, it determines how many delegates each party's national convention will receive from their respective state. These delegates then in turn select their party's presidential nominee.
Each party determines how many delegates are allocated to each state. Along with those delegates chosen during the primaries and caucuses, state delegations to both the Democratic and Republican conventions also include "unpledged" delegates, usually current and former elected officeholders and party leaders, who can vote for whomever they want.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 7:46
7:46Race to Washington: Trump & Sanders win first primary vote in US presidential race
Race to Washington: Trump & Sanders win first primary vote in US presidential raceRace to Washington: Trump & Sanders win first primary vote in US presidential race
Billionaire Donald Trump and Senator Bernie Sanders easily swept to victory in the New Hampshire primaries, buoyed by voters clamoring for change in American politics and politicians not backed by Wall Street contributors. READ MORE: http://on.rt.com/745a RT LIVE http://rt.com/on-air Subscribe to RT! http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=RussiaToday Like us on Facebook http://www.facebook.com/RTnews Follow us on Twitter http://twitter.com/RT_com Follow us on Instagram http://instagram.com/rt Follow us on Google+ http://plus.google.com/+RT Listen to us on Soundcloud: https://soundcloud.com/rttv RT (Russia Today) is a global news network broadcasting from Moscow and Washington studios. RT is the first news channel to break the 1 billion YouTube views benchmark. -
 5:20
5:20Primary Elections Explained
Primary Elections ExplainedPrimary Elections Explained
Help support videos like this: http://www.cgpgrey.com/subbable *T-Shirts now for sale!* Help support making videos: http://goo.gl/1Wlnd Grey's blog: http://www.cgpgrey.com/blog/ If you would like to help me make more videos please join the discussion on: Google+: http://plus.google.com/115415241633901418932/posts Twitter: http://twitter.com/#!/cgpgrey Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greys-Blog/193301110697381 Or suggest ideas and vote on other peoples' ideas on my channel: http://www.youtube.com/user/CGPGrey -
 5:39
5:39U.S. presidential elections 2012 easily explained (explainity® explainer video)
U.S. presidential elections 2012 easily explained (explainity® explainer video)U.S. presidential elections 2012 easily explained (explainity® explainer video)
This year the president of the United States will be elected. But how does the american election actually work? With this video explainity tries to explain the U.S. presidential election in a simple way. This explainer video was produced by explainity GmbH Homepage: www.explainity.com E-Mail: info@explainity.com If you are interested in an own explainity explainer video, visit our website www.explainity.com and contact us. We are looking forward to your inquiry. You are welcome to use this explainer video for your own purpose and website. Keep in mind that this explainer video must not be altered in regards to content and graphics. If you decide to use it, please credit explainity as the producer and refer to our website at www.explainity.com. -
 0:00
0:00LIVE News Stream Newsmax TV | News Stream Live | Election Coverage Live TV
LIVE News Stream Newsmax TV | News Stream Live | Election Coverage Live TVLIVE News Stream Newsmax TV | News Stream Live | Election Coverage Live TV
LIVE Super Tuesday and Election Coverage - 2016 Campaign and Primary Results coverage - Live news streaming from Newsmax TV, available nationwide on DirectTV 349 and Verizon FiOS 115. The Newsmax channel is also available online at NewsmaxTV.com and via Roku, Android and iPhone apps. More Related Videos & NewsmaxTV Live: http://www.newsmaxtv.com Subscribe to NewsmaxTV: Please click the Subscribe Button above. Subscribe to Newsmax Alerts: http://w3.newsmax.com/emails/nm_signu... Like us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/newsmax Follow us on Twitter: https://twitter.com/Newsmax Follow us on Google+: http://bit.ly/1bMbP4w Newsmax covers the latest developments in politics, national and world news, health, faith, personal finance, and technology with a unique American perspective and topics that the major media often ignore. #Campaign2016 #Election2016 #SuperTuesday #SuperTuesday2 #GOPconvention #republicanConvention -
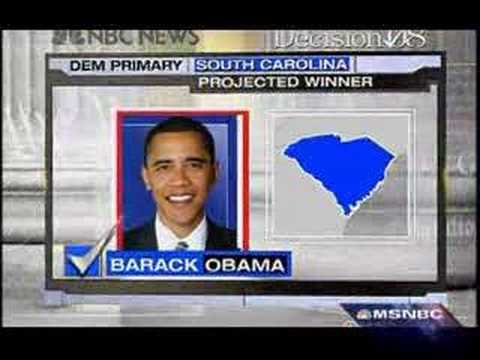 10:18
10:182008 US Presidential Election, Part 1: The Primary Season
2008 US Presidential Election, Part 1: The Primary Season2008 US Presidential Election, Part 1: The Primary Season
Countdown with Keith Olbermann, www.globaldiscussions.net Forum of discussions on international relations & institutions, international trade, Bretton Woods, unions, NGOs, governance, poverty, development studies, sciences & technologies, ethics & morality, religions, tribe, ethnic and identity issues, war, arms smuggling/proliferation, WMD, global affairs, politics & policies, technologies of communication, media, free speech, democracy, freedom, history & geography, commerce, global economy & globalization, health, arts, cultures & acculturation, race, immigration, women, gender & equality issues, sports. -
 6:16
6:16US presidential primary elections: Nick Harper
US presidential primary elections: Nick HarperUS presidential primary elections: Nick Harper
New Hampshire in the U.S. is holding a pivotal primary on Tuesday. There are 30 Republicans on the party's ballot and 28 on the Democratic ballot. For more News visit: http://www.sabc.co.za/news -
 2:20
2:20US presidential primary storm expected in New York
US presidential primary storm expected in New YorkUS presidential primary storm expected in New York
New Yorkers find themselves in the midst of the presidential primary storm today as the state becomes the latest to weigh in on who will become the nominees for the Democratic and Republican Parties. All polling data shows comfortable leads for both Hillary Clinton, who is the former Senator for New York, and local businessman Donald Trump. Democratic challenger Bernie Sanders continues to draw huge crowds to campaign events while Trump's main challenger believes he can prevent the tycoon from clinching enough delegates to secure the nomination before the Republican party's convention in July. For more News visit: http://www.sabc.co.za/news -
 6:39
6:39How Does the U.S. Presidential Election Process Work?
How Does the U.S. Presidential Election Process Work?How Does the U.S. Presidential Election Process Work?
Every four years in November, Americans head to the polls to elect a new President of the United States. Join http://www.WatchMojo.com as we explain how U.S. presidential elections work. Help us caption & translate this video! http://amara.org/v/BPOB/ -
 132:16
132:16Presidential Primary 2016 Results
Presidential Primary 2016 ResultsPresidential Primary 2016 Results
Help us spread the word about the liberty movement, we're reaching millions help us reach millions more. we all want liberty. Find the free live feed at http://www.infowars.com/watch-alex-jones-show/ Stay in the know - Follow Alex on Twitter https://twitter.com/RealAlexJones Like Alex on FACEBOOK - https://www.facebook.com/AlexanderEme... :Web: http://www.infowars.com/ http://www.prisonplanet.com/ http://www.infowars.net/ :Subscribe and share your login with 20 friends: http://www.prisonplanet.tv http://www.InfowarsNews.com ***Get the Best Patriot Made Firearms on the Market** http://www.HDfirearms.com *proud sponsor of Infowars.com **SAVE AMERICA UPSIDE DOWN FLAG T-SHIRT** [Limited Edition] Get yours today: http://bit.ly/SaveAmericaTshirt Visit http://www.InfowarsLife.com to get the products Alex Jones and his family trust, while supporting the growth of our expanding media operation. [http://bit.ly/1R5gsqk] Liver Shield™ [http://bit.ly/1cOwQix] ProstaGuard™ [http://bit.ly/1mnchEz3] Child Ease™ [http://bit.ly/1xs9F6t] WinterSunD3™ [http://bit.ly/1L3gDSO] Ancient Defense™ [http://bit.ly/1EHbA6E] Secret-12™ [http://bit.ly/1txsOge] Oxy Powder™ [http://bit.ly/1s6cphV] Occu Power™ [http://bit.ly/1rGOLsG] DNA Force™ [http://bit.ly/1nIngBb] X2 Survival Shield™ [http://bit.ly/1kaXxKL] Super Female Vitality™ [http://bit.ly/1mhAKCO] Lung Cleanse™ [http://bit.ly/1mGbikx] Silver-Bullet - Colloidal Silver™ [http://bit.ly/1rUsgkl] Fluoride Shield™ [http://bit.ly/1xcoUfo] Super Male Vitality™ [http://bit.ly/1z5BCP9] Survival Shield - Nascent Iodine™ [http://bit.ly/1o4sQtc] Patriot Blend 100% Organic Coffee™ [http://bit.ly/1iVL6HB] Immune Support 100% Organic Coffee™ All available at - http://www.infowarsshop.com/ INFOWARS HEALTH - START GETTING HEALTHY BEFORE IT'S TOO LATE - http://www.infowarshealth.com/ Newsletter Sign up / Infowars Underground Insider : http://www.infowars.com/newsletter -
 3:55
3:55US New Hampshire presidential primary vote has Americans on edge
US New Hampshire presidential primary vote has Americans on edgeUS New Hampshire presidential primary vote has Americans on edge
Many in the U.S. are speculating that the results of the first primary election in the race for U.S. president will reveal Donald Trump on the Republican side and Bernie Sanders on the Democratic side as the winners in this important step in becoming the nominee for U.S. president. As polls close Tuesday in the northeastern U.S. state of New Hampshire, the primary there seems to be just as contentious as last week’s Iowa caucuses. CCTV America’s Sean Callebs is in Manchester, New Hampshire.
- Arizona
- Ballot access
- Bandwagon effect
- Barack Obama
- Bill Brock
- Bill Clinton
- Blanket primary
- Bob Dole
- California
- Caucus
- Caucuses
- Closed primary
- Dark horse
- Delaware Plan
- Delegate
- District of Columbia
- Dwight Eisenhower
- Edmund Muskie
- Estes Kefauver
- Eugene McCarthy
- Florida
- Freedom of assembly
- Gary Hart
- George H. W. Bush
- George McGovern
- George W. Bush
- Gerald Ford
- Guam
- Harry S. Truman
- Howard Dean
- Hubert Humphrey
- Independent (voter)
- Indirect election
- Iowa caucus
- Iowa caucuses
- Iowa City, Iowa
- Jimmy Carter
- John Edwards
- John Kerry
- John McCain
- Larry J. Sabato
- Los Angeles Times
- Massachusetts
- Mitt Romney
- Montana
- National Primary
- New England
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New York
- Newt Gingrich
- Open primary
- Pat Buchanan
- Political boss
- Primary election
- Pro forma
- Progressive Era
- Puerto Rico
- Richard Gephardt
- Rick Santorum
- Robert A. Taft
- Ronald Reagan
- Seattle
- Straw poll
- Super Tuesday
- Superdelegate
- Ted Kennedy
- Texas Straw Poll
- Theodore Roosevelt
- Vermont
- Vietnam War
- Voter turnout
- Walter Mondale
- White (people)
- William Howard Taft
- Woodrow Wilson
- Barack Obama
- Bill Brock
- Bill Clinton
- Bob Dole
- Dark horse
- Edmund Muskie
- Estes Kefauver
- Eugene McCarthy
- Gary Hart
- George McGovern
- Gerald Ford
- Howard Dean
- Hubert Humphrey
- Jimmy Carter
- John Edwards
- John Kerry
- John McCain
- Mitt Romney
- Newt Gingrich
- Pat Buchanan
- Rick Santorum
- Ronald Reagan
- Ted Kennedy
- Theodore Roosevelt
- Walter Mondale
- William Howard Taft
- Woodrow Wilson
-

Race to Washington: Trump & Sanders win first primary vote in US presidential race
Billionaire Donald Trump and Senator Bernie Sanders easily swept to victory in the New Hampshire primaries, buoyed by voters clamoring for change in American politics and politicians not backed by Wall Street contributors. READ MORE: http://on.rt.com/745a RT LIVE http://rt.com/on-air Subscribe to RT! http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=RussiaToday Like us on Facebook http://www.facebook.com/RTnews Follow us on Twitter http://twitter.com/RT_com Follow us on Instagram http://instagram.com/rt Follow us on Google+ http://plus.google.com/+RT Listen to us on Soundcloud: https://soundcloud.com/rttv RT (Russia Today) is a global news network broadcasting from Moscow and Washington studios. RT is the first news channel to break the 1 billion YouTube views benchmark. -

Primary Elections Explained
Help support videos like this: http://www.cgpgrey.com/subbable *T-Shirts now for sale!* Help support making videos: http://goo.gl/1Wlnd Grey's blog: http://www.cgpgrey.com/blog/ If you would like to help me make more videos please join the discussion on: Google+: http://plus.google.com/115415241633901418932/posts Twitter: http://twitter.com/#!/cgpgrey Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greys-Blog/193301110697381 Or suggest ideas and vote on other peoples' ideas on my channel: http://www.youtube.com/user/CGPGrey -

U.S. presidential elections 2012 easily explained (explainity® explainer video)
This year the president of the United States will be elected. But how does the american election actually work? With this video explainity tries to explain the U.S. presidential election in a simple way. This explainer video was produced by explainity GmbH Homepage: www.explainity.com E-Mail: info@explainity.com If you are interested in an own explainity explainer video, visit our website www.explainity.com and contact us. We are looking forward to your inquiry. You are welcome to use this explainer video for your own purpose and website. Keep in mind that this explainer video must not be altered in regards to content and graphics. If you decide to use it, please credit explainity as the producer and refer to our website at www.explainity.com. -

LIVE News Stream Newsmax TV | News Stream Live | Election Coverage Live TV
LIVE Super Tuesday and Election Coverage - 2016 Campaign and Primary Results coverage - Live news streaming from Newsmax TV, available nationwide on DirectTV 349 and Verizon FiOS 115. The Newsmax channel is also available online at NewsmaxTV.com and via Roku, Android and iPhone apps. More Related Videos & NewsmaxTV Live: http://www.newsmaxtv.com Subscribe to NewsmaxTV: Please click the Subscribe Button above. Subscribe to Newsmax Alerts: http://w3.newsmax.com/emails/nm_signu... Like us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/newsmax Follow us on Twitter: https://twitter.com/Newsmax Follow us on Google+: http://bit.ly/1bMbP4w Newsmax covers the latest developments in politics, national and world news, health, faith, personal finance, and technology with a unique American perspective... -

2008 US Presidential Election, Part 1: The Primary Season
Countdown with Keith Olbermann, www.globaldiscussions.net Forum of discussions on international relations & institutions, international trade, Bretton Woods, unions, NGOs, governance, poverty, development studies, sciences & technologies, ethics & morality, religions, tribe, ethnic and identity issues, war, arms smuggling/proliferation, WMD, global affairs, politics & policies, technologies of communication, media, free speech, democracy, freedom, history & geography, commerce, global economy & globalization, health, arts, cultures & acculturation, race, immigration, women, gender & equality issues, sports. -

US presidential primary elections: Nick Harper
New Hampshire in the U.S. is holding a pivotal primary on Tuesday. There are 30 Republicans on the party's ballot and 28 on the Democratic ballot. For more News visit: http://www.sabc.co.za/news -

US presidential primary storm expected in New York
New Yorkers find themselves in the midst of the presidential primary storm today as the state becomes the latest to weigh in on who will become the nominees for the Democratic and Republican Parties. All polling data shows comfortable leads for both Hillary Clinton, who is the former Senator for New York, and local businessman Donald Trump. Democratic challenger Bernie Sanders continues to draw huge crowds to campaign events while Trump's main challenger believes he can prevent the tycoon from clinching enough delegates to secure the nomination before the Republican party's convention in July. For more News visit: http://www.sabc.co.za/news -

How Does the U.S. Presidential Election Process Work?
Every four years in November, Americans head to the polls to elect a new President of the United States. Join http://www.WatchMojo.com as we explain how U.S. presidential elections work. Help us caption & translate this video! http://amara.org/v/BPOB/ -

Presidential Primary 2016 Results
Help us spread the word about the liberty movement, we're reaching millions help us reach millions more. we all want liberty. Find the free live feed at http://www.infowars.com/watch-alex-jones-show/ Stay in the know - Follow Alex on Twitter https://twitter.com/RealAlexJones Like Alex on FACEBOOK - https://www.facebook.com/AlexanderEme... :Web: http://www.infowars.com/ http://www.prisonplanet.com/ http://www.infowars.net/ :Subscribe and share your login with 20 friends: http://www.prisonplanet.tv http://www.InfowarsNews.com ***Get the Best Patriot Made Firearms on the Market** http://www.HDfirearms.com *proud sponsor of Infowars.com **SAVE AMERICA UPSIDE DOWN FLAG T-SHIRT** [Limited Edition] Get yours today: http://bit.ly/SaveAmericaTshirt Visit http://www.InfowarsLife.com to get th... -

US New Hampshire presidential primary vote has Americans on edge
Many in the U.S. are speculating that the results of the first primary election in the race for U.S. president will reveal Donald Trump on the Republican side and Bernie Sanders on the Democratic side as the winners in this important step in becoming the nominee for U.S. president. As polls close Tuesday in the northeastern U.S. state of New Hampshire, the primary there seems to be just as contentious as last week’s Iowa caucuses. CCTV America’s Sean Callebs is in Manchester, New Hampshire.
Race to Washington: Trump & Sanders win first primary vote in US presidential race
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:46
- Updated: 10 Feb 2016
- views: 23626
- published: 10 Feb 2016
- views: 23626
Primary Elections Explained
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:20
- Updated: 13 Feb 2012
- views: 1371957
- published: 13 Feb 2012
- views: 1371957
U.S. presidential elections 2012 easily explained (explainity® explainer video)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:39
- Updated: 05 Nov 2012
- views: 331073
- published: 05 Nov 2012
- views: 331073
LIVE News Stream Newsmax TV | News Stream Live | Election Coverage Live TV
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:00
- Updated: 09 Nov 2015
- views: 2170445
- published: 09 Nov 2015
- views: 2170445
2008 US Presidential Election, Part 1: The Primary Season
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:18
- Updated: 11 Jun 2008
- views: 39141
- published: 11 Jun 2008
- views: 39141
US presidential primary elections: Nick Harper
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:16
- Updated: 09 Feb 2016
- views: 902
- published: 09 Feb 2016
- views: 902
US presidential primary storm expected in New York
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:20
- Updated: 19 Apr 2016
- views: 1299
- published: 19 Apr 2016
- views: 1299
How Does the U.S. Presidential Election Process Work?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:39
- Updated: 23 Oct 2012
- views: 48852
Presidential Primary 2016 Results
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 132:16
- Updated: 27 Apr 2016
- views: 198
- published: 27 Apr 2016
- views: 198
US New Hampshire presidential primary vote has Americans on edge
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:55
- Updated: 10 Feb 2016
- views: 309
- published: 10 Feb 2016
- views: 309
-

US Presidential Primary Election season is over - VOA Ashna
_روند انتخابات مقدماتی ریاست جمهوری ایالات متحدۀ امریکا دیروز، با پیروزی هیلری کلنتن کاندید حزب دیموکرات در برابر برنی سندرز رقیب هم حزبی اش، به پایان رسید. خانم کلنتن یک گام دیگر به نامزدی نهایی حزب خود نزدیکتر شد به چینل یوتیوب تلویزیون آشنا بپیوندید و در کنار خبرهای داغ روز، صدها ویدیوی جالب و دیدنی دیگر را تماشا کنید. خبرهای تلویزیون آشنا را از وبسایت، فیسبوک، تویتر و انستاگرام ما نیز دنبال کرده می توانید: VOA Afghanistan Ashna TV in Dari brings you top news from Afghanistan and around the world, and US features and interviews Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/voatvashna Twitter: https://twitter.com/ashnatv Instagram: https://instagram.com/voaashnatv -

-

William Kreml a Green Party Presidential Primary Candidate speaks to Green Party NY Convention
William P. Kreml talks about Cuomo and BDS, the basis for an ideology, the progress brain, Articles of the Constitution and the Bill of Rights. Citizens United via Skype to Green Party NY Convention Bill Kreml for President http://www.billkreml.org Green Party NY http://www.gpny.org Green Party US http://www.gp.org -

Donald Trump Breaks Record For Most Votes In A GOP Presidential Primary D
USA Presidential election Campaign 2016 Donald Trump Vs Hillary Clinton Debate 2016 Hillary Clinton Vs Donald Trump debate 2016 Donald Trump Vs Hillary Clinton New Polls Hillary Clinton Vs Donald Trump TV Show -

Locals react to California Presidential Primary Election results
KSBY wanted to get voters' reactions to Tuesday night's election results and spoke with locals who are Donald Trump, Hillary Clinton or Bernie Sanders supporters. Some say the general election in November will be the hardest yet in terms of decision-making. We talked to both Republicans and Democrats at Cal Poly, at Trader Joe's in San Luis Obispo and at Pismo Beach. -

N.J. presidential primary election results 2016: County by county
Click here for the full scoop on: N.J. presidential primary election results 2016: County by county.http://www.taansai.com/ Although Hillary Clinton had the backing of enough delegates to lock up the Democratic nomination for President before New Jersey voters cast ballots in Tuesday's primary election, her opponent, U.S. Sen. Bernie Sanders, maintained the race wasn't over.As it turned out, the Garden State helped push Clinton over the top, giving her an impressive margin of victory and more than enough votes to secure her party's nomination.The former Secretary of State will represent the Democratic Party and battle it out with the presumptive Republican presidential candidate, businessman Donald Trump, in the November general election that will determine who succeeds two-term Democratic... -

Donald Trump Breaks Record For Most Votes In A GOP Presidential Primary - Donald Trump Jr On Hannity
Donald Trump Breaks Record For Most Votes In A GOP Presidential Primary - Donald Trump Jr On Hannity =========================================== **Please Click Below to SUBSCRIBE for More "Wake Up America" Videos: http://goo.gl/0fC284 =========================================== -

Clinton wins the Democratic presidential primary in California, the Associated Press projects.
Hillary Clinton wins the Democratic presidential primary in California, the Associated Press projects. HILLARY CLINTON CLAIMS HISTORIC VICTORY, BERNIE SANDERS VOWS TO FIGHT ON Hillary Clinton declared victory Tuesday night in the Democratic presidential nomination, even as Sen. Bernie Sanders vowed to continue fighting until the party convention in July. Claiming her place in history, Hillary Clinton declared victory Tuesday night in her bruising battle for the Democratic presidential nomination, becoming the first woman to lead a major American political party and casting herself as the beneficiary of generations who fought for equality. "This campaign is about making sure there are no ceilings, no limits on any of us," Clinton said during an emotional rally in Brooklyn, eight years to t... -

Republican Primary Election Results 2016 | Presidential Primaries
Republican Primary Election Results The rally in Bethpage was Trump's first appearance in the state since losing the ... BETHPAGE - Republican Primary Election Results Donald J. Trump went early and often to his go-to refrain, ... on Wednesday that America would win again if he becomes president. ... USA TODAY: What each candidate needs to do ahead of New York's primary. Republican Primary Election Results to get update dont forget to subscribe -

Hillary Clinton Claims Victory in Democratic Presidential Primary
Former Secretary of State Hillary Clinton spoke to thousands at the Brooklyn Navy Yard and claimed victory in the nomination race for president. She hailed being the first woman to lead a major-party ticket as a milestone.
US Presidential Primary Election season is over - VOA Ashna
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:30
- Updated: 15 Jun 2016
- views: 20
- published: 15 Jun 2016
- views: 20
Donald Trump Breaks Record For Most Votes In A GOP Presidential Primary - Donald Trump Jr On
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:18
- Updated: 14 Jun 2016
- views: 9
William Kreml a Green Party Presidential Primary Candidate speaks to Green Party NY Convention
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 15:44
- Updated: 13 Jun 2016
- views: 4
- published: 13 Jun 2016
- views: 4
Donald Trump Breaks Record For Most Votes In A GOP Presidential Primary D
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:06
- Updated: 09 Jun 2016
- views: 20
- published: 09 Jun 2016
- views: 20
Locals react to California Presidential Primary Election results
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:02
- Updated: 09 Jun 2016
- views: 14
- published: 09 Jun 2016
- views: 14
N.J. presidential primary election results 2016: County by county
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:02
- Updated: 09 Jun 2016
- views: 3
- published: 09 Jun 2016
- views: 3
Donald Trump Breaks Record For Most Votes In A GOP Presidential Primary - Donald Trump Jr On Hannity
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:06
- Updated: 09 Jun 2016
- views: 3199
- published: 09 Jun 2016
- views: 3199
Clinton wins the Democratic presidential primary in California, the Associated Press projects.
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:22
- Updated: 08 Jun 2016
- views: 0
- published: 08 Jun 2016
- views: 0
Republican Primary Election Results 2016 | Presidential Primaries
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:58
- Updated: 08 Jun 2016
- views: 14
- published: 08 Jun 2016
- views: 14
Hillary Clinton Claims Victory in Democratic Presidential Primary
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 18:08
- Updated: 08 Jun 2016
- views: 417
- published: 08 Jun 2016
- views: 417
-

Ninth Democratic Primary Debate - April 14 2016 on CNN
PLEASE NOTE: HD Quality doesn't start until 8:42 because I couldn't find an HD video that included the candidates' opening statements. Democratic Debate #9 April 14, 2016 @ 9:00pm ET on CNN Brooklyn, New York - Brooklyn Navy Yard Debaters: Hillary Clinton, Bernie Sanders Moderators: Wolf Blitzer (Lead); Dana Bash, Errol Louis Debate Co-sponsor: NY1 -

Live Coverage: New York Presidential Primary
Help us spread the word about the liberty movement, we're reaching millions help us reach millions more. Share the free live video feed link with your friends & family: http://www.infowars.com/show Follow Alex on TWITTER - https://twitter.com/RealAlexJones Like Alex on FACEBOOK - https://www.facebook.com/AlexanderEmerickJones Infowars on G+ - https://plus.google.com/+infowars/ :Web: http://www.infowars.com/ http://www.prisonplanet.com/ http://www.infowars.net/ :Subscribe and share your login with 20 friends: http://www.prisonplanet.tv http://www.InfowarsNews.com Visit http://www.InfowarsLife.com to get the products Alex Jones and his family trust, while supporting the growth of our expanding media operation. [http://bit.ly/1WYw8jp] Vitamin Mineral Fusion™ [http://bit.ly/1QYBNBv] Joi... -

Twelfth Republican Primary Debate - March 10 2016 on CNN
The final Republican primary debate Republican Debate #12 March 10, 2016 @ 9:00pm ET on CNN Coral Gables, Florida - University of Miami Debaters: Ted Cruz, John Kasich, Marco Rubio, Donald Trump Moderators: Jake Tapper (Lead); Dana Bash, Stephen Dinan, Hugh Hewitt Debate Co-sponsors: Salem Radio Network, The Washington Times -

(2/11/2016) PBS Democratic Presidential Debate (FULL VIDEO)
w/ Closed Captioning (CC) Thursday, February 11, 2016 Hillary Clinton vs. Bernie Sanders Democratic Party Presidential Primary Debate Milwaukee, Wisconsin Courtesy: PBS NewsHour -------------------------------- OPINION: Bernie Sanders won the New Hampshire Primary, but he is still 100% unlikely to win the Democratic nomination. Hillary Clinton is glorified like the "Queen of the Party" among the Democrats. Obviously, she was preselected by the Democratic Party to succeed Barack Hussein Obama as the leading frontrunner since 2008. If Sanders is actually serious about becoming president, he would run as an independent. I think he has a much better chance beating both Hillary and the GOP as an independent candidate. -

(1/14/2016) 2016 Republican Presidential Debate (FULL VIDEO)
GOP Primary Debate for the Nomination From North Charleston, South Carolina Thursday, January 14, 2016 Courtesy: FOX Business Network Note: Some parts of the video were cut off due to error. I apologize for any inconvenience. ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- OPINION: Bernie Sanders is 100% unlikely to win the Democratic nomination. Hillary Clinton is glorified like the "Queen of the Party" among the Democrats. Obviously, she was preselected by the Democratic Party to succeed Barack Hussein Obama as the leading frontrunner since 2008. If Sanders is actually serious about becoming president, he would run as an independent. I think he has a much better chance beating both Hillary and the GOP as an independent cand... -

NBC News-YouTube Democratic Debate (Full)
Join NBC News' Lester Holt, Andrea Mitchell, Chuck Todd and YouTube creators Connor Franta, Marques Brownlee, MinuteEarth and Franchesca Ramsey as Hillary Clinton, Bernie Sanders and Martin O'Malley debate in Charleston, South Carolina. Pre-Debate coverage begins at 8pm ET. » Subscribe to NBC News: http://nbcnews.to/SubscribeToNBC » Watch more NBC video: http://bit.ly/MoreNBCNews NBC News is a leading source of global news and information. Here you will find clips from NBC Nightly News, Meet The Press, and our original series Debunker, Flashback, Nerdwatch, and Show Me. Subscribe to our channel for news stories, technology, politics, health, entertainment, science, business, and exclusive NBC investigations. Connect with NBC News Online! Visit NBCNews.Com: http://nbcnews.to/ReadNBC Find... -

United States presidential primary
The series of presidential primary elections and caucuses held in each U.S. state and territory is part of the nominating process of United States presidential elections. This process was never included in the United States Constitution, and thus was created over time by the political parties. Some states only hold primary elections, some only hold caucuses, and others use a combination of both. These primaries and caucuses are staggered generally between January and June before the general election in November. The primary elections are run by state and local governments, while caucuses are private events that are directly run by the political parties themselves. A state's primary election or caucus is usually an indirect election: instead of voters directly selecting a particular person ... -

World Panorama - Episode 219 | US Presidential Primaries 2016
This week on World Panorama we bring you the latest from the US Presidential Primaries with Donald Trump and Hillary Clinton scoring big victories. Also, a round-up of other significant international news of the week. Guest: K P Nayar, Consulting Editor, The Telegraph Anchor: Frank Pereira -

New York Presidential Primary Coverage
Help us spread the word about the liberty movement, we're reaching millions help us reach millions more. we all want liberty. Find the free live feed at http://www.infowars.com/watch-alex-jones-show/ Stay in the know - Follow Alex on Twitter https://twitter.com/RealAlexJones Like Alex on FACEBOOK - https://www.facebook.com/AlexanderEme... :Web: http://www.infowars.com/ http://www.prisonplanet.com/ http://www.infowars.net/ :Subscribe and share your login with 20 friends: http://www.prisonplanet.tv http://www.InfowarsNews.com ***Get the Best Patriot Made Firearms on the Market** http://www.HDfirearms.com *proud sponsor of Infowars.com **SAVE AMERICA UPSIDE DOWN FLAG T-SHIRT** [Limited Edition] Get yours today: http://bit.ly/SaveAmericaTshirt Visit http://www.InfowarsLife.com to get th...
Ninth Democratic Primary Debate - April 14 2016 on CNN
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 119:49
- Updated: 17 Apr 2016
- views: 46558
- published: 17 Apr 2016
- views: 46558
Live Coverage: New York Presidential Primary
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 63:49
- Updated: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 60739
- published: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 60739
Twelfth Republican Primary Debate - March 10 2016 on CNN
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 114:27
- Updated: 28 Mar 2016
- views: 31808
- published: 28 Mar 2016
- views: 31808
(2/11/2016) PBS Democratic Presidential Debate (FULL VIDEO)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 106:14
- Updated: 12 Feb 2016
- views: 158394
- published: 12 Feb 2016
- views: 158394
(1/14/2016) 2016 Republican Presidential Debate (FULL VIDEO)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 120:20
- Updated: 15 Jan 2016
- views: 321664
- published: 15 Jan 2016
- views: 321664
NBC News-YouTube Democratic Debate (Full)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 113:44
- Updated: 18 Jan 2016
- views: 3537234
- published: 18 Jan 2016
- views: 3537234
United States presidential primary
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 36:40
- Updated: 04 Jan 2016
- views: 110
- published: 04 Jan 2016
- views: 110
World Panorama - Episode 219 | US Presidential Primaries 2016
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 26:50
- Updated: 02 May 2016
- views: 345
- published: 02 May 2016
- views: 345
New York Presidential Primary Coverage
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 123:56
- Updated: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 706
- published: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 706
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

Race to Washington: Trump & Sanders win first primary vote in US presidential race
- Report rights infringement
- published: 10 Feb 2016
- views: 23626

Primary Elections Explained
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 Feb 2012
- views: 1371957

U.S. presidential elections 2012 easily explained (explainity® explainer video)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Nov 2012
- views: 331073

LIVE News Stream Newsmax TV | News Stream Live | Election Coverage Live TV
- Report rights infringement
- published: 09 Nov 2015
- views: 2170445

2008 US Presidential Election, Part 1: The Primary Season
- Report rights infringement
- published: 11 Jun 2008
- views: 39141

US presidential primary elections: Nick Harper
- Report rights infringement
- published: 09 Feb 2016
- views: 902

US presidential primary storm expected in New York
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Apr 2016
- views: 1299

How Does the U.S. Presidential Election Process Work?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Oct 2012
- views: 48852

Presidential Primary 2016 Results
- Report rights infringement
- published: 27 Apr 2016
- views: 198

US New Hampshire presidential primary vote has Americans on edge
- Report rights infringement
- published: 10 Feb 2016
- views: 309
- Playlist
- Chat

US Presidential Primary Election season is over - VOA Ashna
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Jun 2016
- views: 20

Donald Trump Breaks Record For Most Votes In A GOP Presidential Primary - Donald Trump Jr On
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Jun 2016
- views: 9

William Kreml a Green Party Presidential Primary Candidate speaks to Green Party NY Convention
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 Jun 2016
- views: 4

Donald Trump Breaks Record For Most Votes In A GOP Presidential Primary D
- Report rights infringement
- published: 09 Jun 2016
- views: 20

Locals react to California Presidential Primary Election results
- Report rights infringement
- published: 09 Jun 2016
- views: 14

N.J. presidential primary election results 2016: County by county
- Report rights infringement
- published: 09 Jun 2016
- views: 3

Donald Trump Breaks Record For Most Votes In A GOP Presidential Primary - Donald Trump Jr On Hannity
- Report rights infringement
- published: 09 Jun 2016
- views: 3199

Clinton wins the Democratic presidential primary in California, the Associated Press projects.
- Report rights infringement
- published: 08 Jun 2016
- views: 0

Republican Primary Election Results 2016 | Presidential Primaries
- Report rights infringement
- published: 08 Jun 2016
- views: 14

Hillary Clinton Claims Victory in Democratic Presidential Primary
- Report rights infringement
- published: 08 Jun 2016
- views: 417
- Playlist
- Chat

Ninth Democratic Primary Debate - April 14 2016 on CNN
- Report rights infringement
- published: 17 Apr 2016
- views: 46558

Live Coverage: New York Presidential Primary
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 60739

Twelfth Republican Primary Debate - March 10 2016 on CNN
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Mar 2016
- views: 31808

(2/11/2016) PBS Democratic Presidential Debate (FULL VIDEO)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 12 Feb 2016
- views: 158394

(1/14/2016) 2016 Republican Presidential Debate (FULL VIDEO)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Jan 2016
- views: 321664

NBC News-YouTube Democratic Debate (Full)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 18 Jan 2016
- views: 3537234

United States presidential primary
- Report rights infringement
- published: 04 Jan 2016
- views: 110

World Panorama - Episode 219 | US Presidential Primaries 2016
- Report rights infringement
- published: 02 May 2016
- views: 345

New York Presidential Primary Coverage
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 706
UK pound plunges as referendum results point to EU exit
Edit The Associated Press 24 Jun 2016High turnout reported as Britons cast vote in EU referendum
Edit The Guardian 24 Jun 2016[VIDEO]: Texas Woman Awakens From Surgery With British Accent
Edit WorldNews.com 23 Jun 2016As Polls Close, UKIP's Nigel Farage Concedes Defeat For Brexit Referendum
Edit WorldNews.com 23 Jun 2016Vote Count Update (California Secretary of State)
Edit Public Technologies 24 Jun 2016Presidential Primary Election Update – Ballot Count Updates to be Released on Friday, June 24 (Sacramento County Department of Voter Registration and Elections)
Edit Public Technologies 24 Jun 2016Tim Kaine Could Be Hillary Clinton's Safest VP Option Yet
Edit WPTV 24 Jun 2016Bernie Sanders revolution is 'just getting started'
Edit Belfast Telegraph 24 Jun 2016Bernie Sanders: Allow working Americans to run the country, not political elites
Edit Indian Express 24 Jun 2016Marco Rubio should have asked my advice
Edit The Miami Herald 24 Jun 2016Bernie Sanders says his revolution is 'just getting started'
Edit The Columbus Dispatch 24 Jun 2016The Latest: Sanders still says he's 'just getting started'
Edit The Oklahoman 24 Jun 2016Who needs Jesus when we have Marco Rubio?
Edit The Miami Herald 24 Jun 2016The Latest: Sanders supporters wait hours for his NYC speech
Edit Austin American Statesman 24 Jun 2016Education Ministry to undertake major infrastructural projects
Edit Jamaica Observer 24 Jun 2016'No point in learning pinyin before school' (Shanghai Municipal Government)
Edit Public Technologies 24 Jun 2016Obama expected to speak to Cameron later today on Brexit
Edit The Irish Times 24 Jun 2016- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »








