- published: 05 Apr 2016
- views: 21650
-
remove the playlistEducation In India
-
remove the playlistLatest Videos
-
remove the playlistLongest Videos
- remove the playlistEducation In India
- remove the playlistLatest Videos
- remove the playlistLongest Videos
Please tell us which country and city you'd like to see the weather in.
- published: 14 Jul 2014
- views: 4660991
- published: 20 May 2008
- views: 200752
- published: 18 May 2016
- views: 32437
- published: 19 May 2015
- views: 1947963
- published: 03 May 2012
- views: 8945
- published: 21 Feb 2014
- views: 21626
- published: 25 May 2016
- views: 4944
- published: 09 Mar 2015
- views: 2684

Education in India
Education in India is provided by the public sector as well as the private sector, with control and funding coming from three levels: central, state, and local. Under various articles of the Indian Constitution, free and compulsory education is provided as a fundamental right to children between the ages of 6 and 14. The ratio of public schools to private schools in India is 7:5.
India has made progress in terms of increasing the primary education attendance rate and expanding literacy to approximately three-quarters of the population in the 7-10 age group, by 2011. India's improved education system is often cited as one of the main contributors to its economic development. Much of the progress, especially in higher education and scientific research, has been credited to various public institutions. While enrollment in higher education has increased steadily over the past decade, reaching a Gross Enrollment Ratio of 24% in 2013, there still remains a significant distance to catch up with tertiary education enrollment levels of developed nations, a challenge that will be necessary to overcome in order to continue to reap a demographic dividend from India's comparatively young population.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

India
India, officially the Republic of India (Bhārat Gaṇarājya), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the south-west, and the Bay of Bengal on the south-east, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west;China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north-east; and Myanmar (Burma) and Bangladesh to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; in addition, India's Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand and Indonesia.
Home to the ancient Indus Valley Civilisation and a region of historic trade routes and vast empires, the Indian subcontinent was identified with its commercial and cultural wealth for much of its long history. Four religions—Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism—originated here, whereas Zoroastrianism, Judaism, Christianity, and Islam arrived in the 1st millennium CE and also shaped the region's diverse culture. Gradually annexed by and brought under the administration of the British East India Company from the early 18th century and administered directly by the United Kingdom after the Indian Rebellion of 1857, India became an independent nation in 1947 after a struggle for independence that was marked by non-violent resistance led by Mahatma Gandhi.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
Radio Stations - New Delhi
SEARCH FOR RADIOS
- Loading...

-
 11:22
11:22Education in India: Are students failing or the system?! | Sonam Wangchuk | TEDxGateway
Education in India: Are students failing or the system?! | Sonam Wangchuk | TEDxGatewayEducation in India: Are students failing or the system?! | Sonam Wangchuk | TEDxGateway
In this talk, Sonam Wangchuk shares his experience of bringing education reforms in the trans-Himalayan region of Ladakh, India. Sonam Wangchuk is the founder of Students' Educational & Cultural Movement of Ladakh (SECMOL). While he was doing his mechanical engineering at NIT Srinagar he understood the hardships faced by the Ladakhi students in the government schools; 95% of them were failing in their matric exams every year. Once he finished his graduation, he went back to Ladakh and started SECMOL together with some like-minded youth. After initially starting with coaching classes to help matric students, they soon realized that for a lasting solution they needed to bring reforms in the village primary schools. So they launched an education reform movement in collaboration with the government. Within seven years the results went up from 5% to 55%. Today it stands at 75%. For those who still failed, they set up a very special and innovative school which has produced many inspiring stories. This talk was given at a TEDx event using the TED conference format but independently organized by a local community. Learn more at http://ted.com/tedx -
 7:50
7:50EIC: Sex Education in India
EIC: Sex Education in IndiaEIC: Sex Education in India
The health ministry of India recently suggested that sex education be banned in the country. We look at India's attitude towards sex through a "government approved" sex education lecture. This video is a work of fiction that bears no resemblance to any human being living, dead, or abstaining from sex. Do subscribe, comment, and most importantly, share the video if you liked it! Follow us on - Facebook: www.facebook.com/EastIndiaComedy - Twitter: www.twitter.com/EastIndiaComedy - Website: www.eastindiacomedy.com Director: Sapan Verma. Director of Photography: Siddharth Vasani. Writer: Azeem Banatwalla and Sapan Verma. -
 3:55
3:55Education in India - BBC
Education in India - BBCEducation in India - BBC
Sanjeev visits some impressive young students taking time out of their school day to help teach street children the same syllabus. That's recycled learning, Indian style, and it makes a big impression on our presenter in this BBC Worldwide video clip. -
 10:37
10:37Real Truth of Education System in India by Abhishek Mishra
Real Truth of Education System in India by Abhishek MishraReal Truth of Education System in India by Abhishek Mishra
Indian education system needs a change now. India has now 35,000 colleges, and 700 universities but still these colleges only produces Degree holders not engineers. Just one out of nine children finishing school joins a college. India has one of the lowest higher education enrollment ratio of 11 per cent. In the US it is 83 per cent. My thinking is that we need to provide more practical knowledge rather than just theory -"Give a man a fish and you feed him one day, teach him how to catch fishes and you feed him for a lifetime" --------------------------------------------------------------------------------- About Abhishek, Abhishek Mishra is an Indian social activist, YouTuber. He makes videos in Hindi in order to spread awareness among people. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Stay Connected ⟶ Like Facebook page: http://www.fb.com/AbhishekMishraVideos ⟶ Follow on Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/Meamabhishek Thanks for watching. -
 6:20
6:20EIC: Education Then vs Now
EIC: Education Then vs NowEIC: Education Then vs Now
Education in the 90s was very different from what it is today. Our latest sketch looks at the differences between Education then and Education now. Get awesome discount coupons and offers from CouponDunia - India's #1 Coupon Website. http://www.coupondunia.in Director: Sapan Verma Writers: Sahil, Sapan, Sorabh, Kunal, Azeem, Angad, Atul DOP: Sid Editor: Rahul Lalchandani Music: Kaizad Gherda Production: Sonali Thakker & Manish Nihalani Additional Cast: Chaitanya Chinchlikar, Nida Chakraborty, Sanika More, Rashmi Chandani, Sonali Thakker, Manish Nihalani Sound: Maxim Mendonsa Location Courtesy: Whistling Woods Follow us on: Twitter: https://twitter.com/eastindiacomedy Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/EastIndiaComedy -
 2:12
2:12India's poor education system
India's poor education systemIndia's poor education system
Subscribe to our channel http://bit.ly/AJSubscribe Subscribe to our channel http://bit.ly/AJSubscribe In India, some of the country's poorest children benefit from a quota system which allows them to go to private school. But the vast majority are forced to rely on government-run schools, where resources are almost non-existant. Al Jazeera's Prerna Suri reports on the growing calls for the government to upgrade its own education facilities. At Al Jazeera English, we focus on people and events that affect people's lives. We bring topics to light that often go under-reported, listening to all sides of the story and giving a 'voice to the voiceless.' Reaching more than 270 million households in over 140 countries across the globe, our viewers trust Al Jazeera English to keep them informed, inspired, and entertained. Our impartial, fact-based reporting wins worldwide praise and respect. It is our unique brand of journalism that the world has come to rely on. We are reshaping global media and constantly working to strengthen our reputation as one of the world's most respected news and current affairs channels. Social Media links: Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/aljazeera Instagram: https://instagram.com/aljazeera/?ref=... Twitter: https://twitter.com/ajenglish Website: http://www.aljazeera.com/ google+: https://plus.google.com/+aljazeera/posts -
 4:39
4:39My New Life: Primary Education for All in India
My New Life: Primary Education for All in IndiaMy New Life: Primary Education for All in India
http://www.worldbank.org/india - In rural Rajasthan in Northern India, girls traditionally stayed at home and were sometimes married off when they are young. Things have started to change. For the first time in her life, Puja is going to school and has learned to read and write while having fun. She is making her dreams come true under the Sarva Shksha Abiyhan program which is changing the lives of girls across rural India through promoting universal primary education. Girls who have dropped out or have never been to school now have a second chance of getting an education. -
 10:03
10:03Pak Media On It's Education System Compared To India
Pak Media On It's Education System Compared To IndiaPak Media On It's Education System Compared To India
Are you interested in the current affairs and the happenings of India & Pakistan? Want to watch an unbiased view, with minute by minute updates of the current scenario? Vande Mataram India is the right place to be! Watch Latest News Headlines 2016, Geo News Headlines 2016, India Pakistan News Headlines 2016, Aaj tak News Headlines 2016, Express News Headlines 2016, AAJ News Headlines 2016, News Updates. Please subscribe for breaking News Headlines and Updates. Forum discussions, talk shows and much more. Stay tuned For More News Subscribe Now https://goo.gl/6w8tYQ -
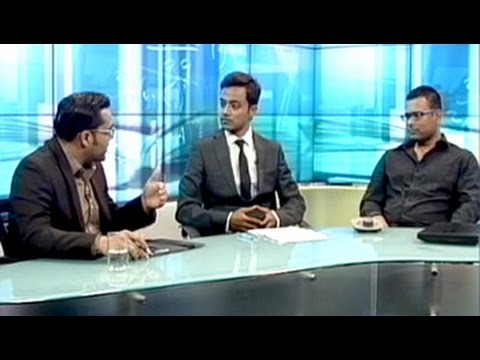 14:54
14:54The big debate: Education in India vs education in abroad
The big debate: Education in India vs education in abroadThe big debate: Education in India vs education in abroad
How and why do students choose a foreign university over one in India? Does one really score over another? Students debate the merits of both and how to make the big choice. Don't miss the big weekly debate, on this episode of Heads Up. Watch full video: http://www.ndtv.com/video/player/heads-up/the-big-debate-education-in-india-vs-education-in-abroad/359250?yt -
 32:23
32:23Indian Education System - an incomplete system
Indian Education System - an incomplete system
India
ALBUMS
- La Historia... Mis Exitos released: 2007
- Soy Diferente released: 2006
- Latin Songbird: Mi Alma y Corazón released: 2002
- Sola released: 1999
- Sobre el fuego released: 1997
- Dicen que soy released: 1994
- Llegó la India Via Eddie Palmieri released: 1992
- Breaking Night released: 1990
- Lo Mejor De India released:
La Historia... Mis Exitos
Released 2007- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Ese Hombre
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Si Tú Eres Mi Hombre
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Esa Mujer
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Nunca Voy a Olvidarte
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Costumbres
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Dicen Que Soy
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sobre el Fuego
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Que Te Pedí
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Mi Mayor Venganza
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Te Daré Dulzura
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sola
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Aun lo Amo
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Burlada Inocencia
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Déjame Volver Contigo
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen O Ella, O Yo
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen No Me lo Confiesas
Soy Diferente
Released 2006- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Soy Diferente (Versión Salsatón)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sólamente Una Noche (Versión Salsa)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Un Amor Obsesivo
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Cuando Hieres a Una Mujer
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen No Es Lo Mismo
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Lágrimas
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Tengo Que Dejarte Ir
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Soy Diferente (Versión Reggaetón)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Madre E Hija a.k.a. Madre
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sólamente Una Noche (Versión Reggaetón)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Bugarrón
Latin Songbird: Mi Alma y Corazón
Released 2002- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sedúceme
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Traición
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen El Anillo
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen El Hombre Perfecto (Bachata Balada)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Soy Mujer
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen La Gran Tirana
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Que Me Importa
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sedúceme (Pop Balada)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Enseñáme a Olvidar
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen El Hombre Perfecto (Merengue)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Razones Tengo
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Confiado En Ti
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Traición (Balada)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Navidad Sin Verte
Sola
Released 1999- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Hielo
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sola
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Déjame Volver Contigo
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Que Te Pedí
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Lo Siento Mi Amor
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Aun Lo Amo
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Esa Mujer
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Si Vuelves Tu
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sola (Balada)
Sobre el fuego
Released 1997- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Me cansé de ser la otra
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Costumbres
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Burlada inocencia
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen No me lo confiesas
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Si tú eres mi hombre
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Mi mayor venganza
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sobre el fuego
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Te daré dulzura
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen La voz de la experiencia (con Celia Cruz)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Si estuvieras aquí
Dicen que soy
Released 1994- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Nunca voy a olvidarte
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Que ganas de no verte nunca más
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Ese hombre
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Dicen que soy
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen O ella o yo
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Déjate amar
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen I just want to hang around you
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen No me conviene (con Tito Nieves)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Vivir lo nuestro (con Marc Anthony)
Llegó la India Via Eddie Palmieri
Released 1992- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Vivir Sin Ti
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Llegó la India
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Soledad
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Mi Primera Rumba
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Yemaya y Ochun (Prelude)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Yemaya y Ochun
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Merengue Internacional
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Solitude
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen I Wanna Dance
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Soledad (Bilingual version)
Breaking Night
Released 1990- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Right From the Start
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Dancing on the Fire
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Breaking Night
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Lover Who Rocks You (All Night)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Steppin' Out
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen I've Got a Plan
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen When You Were Mine
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen You Should Be Lovin' Me
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Send Yourself to Me
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen I'm Through With Love
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Dancing on the Fire (extended dance mix)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Right From the Start (12'' fly mix)
Lo Mejor De India
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Vivir Lo Nuestro
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Nunca Voy a Olvidarte
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Que Ganas De No Verte Más
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Ese Hombre
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Yemaya Y Ochun
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Mi Primera Rumba
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Llego La India
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Vivir Sin Tí
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Dicen Que Soy
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen O Ella O Yo
India
ALBUMS
- Unica released: 2010
- La Historia... Mis Exitos released: 2007
- Soy Diferente released: 2006
- Salsa divas released: 2004
- Latin Songbird: Mi Alma y Corazón released: 2002
- Sola released: 1999
- Sobre el fuego released: 1997
- Jazzin' released: 1996
- Dicen que soy released: 1994
- Llegó la India Via Eddie Palmieri released: 1992
- Breaking Night released: 1990
- Lo Mejor De India released:
Unica
Released 2010- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Smile
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Estupida (Salsa)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Si El Te Habla De Mi
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Te Vas Arrepentir
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Turn Off The Lights
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Si Estoy Loca
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Crying
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Ni Fines De Semana Ni Dias Festival
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Amor Secreto
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Triste
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Estupida (Balada)
La Historia... Mis Exitos
Released 2007- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Ese Hombre
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Si Tú Eres Mi Hombre
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Esa Mujer
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Nunca Voy a Olvidarte
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Costumbres
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Dicen Que Soy
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sobre el Fuego
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Que Te Pedí
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Mi Mayor Venganza
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Te Daré Dulzura
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sola
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Aun lo Amo
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Burlada Inocencia
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Déjame Volver Contigo
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen O Ella, O Yo
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen No Me lo Confiesas
Soy Diferente
Released 2006- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Soy Diferente (Versión Salsatón)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sólamente Una Noche (Versión Salsa)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Un Amor Obsesivo
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Cuando Hieres a Una Mujer
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen No Es Lo Mismo
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Lágrimas
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Tengo Que Dejarte Ir
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Soy Diferente (Versión Reggaetón)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Madre E Hija a.k.a. Madre
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sólamente Una Noche (Versión Reggaetón)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Bugarrón
Salsa divas
Released 2004- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Ríe y llora
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sedúceme
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Por si acaso no regreso
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Traición
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen La negra tiene tumbao
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Soy mujer
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Yo viviré
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Razones tengo
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Hay que emperar otra vez
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Que me importa
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Celia's oyo como va
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen El hombre perfecto
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen La negra tiene tumbao (DJ Fluid remix)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sedúceme (Obadam remix)
Latin Songbird: Mi Alma y Corazón
Released 2002- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sedúceme
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Traición
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen El Anillo
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen El Hombre Perfecto (Bachata Balada)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Soy Mujer
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen La Gran Tirana
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Que Me Importa
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sedúceme (Pop Balada)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Enseñáme a Olvidar
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen El Hombre Perfecto (Merengue)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Razones Tengo
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Confiado En Ti
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Traición (Balada)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Navidad Sin Verte
Sola
Released 1999- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Hielo
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sola
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Déjame Volver Contigo
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Que Te Pedí
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Lo Siento Mi Amor
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Aun Lo Amo
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Esa Mujer
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Si Vuelves Tu
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sola (Balada)
Sobre el fuego
Released 1997- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Me cansé de ser la otra
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Costumbres
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Burlada inocencia
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen No me lo confiesas
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Si tú eres mi hombre
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Mi mayor venganza
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sobre el fuego
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Te daré dulzura
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen La voz de la experiencia (con Celia Cruz)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Si estuvieras aquí
Jazzin'
Released 1996- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Jazzin'
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Fever
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Love for Sale
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Crazy He Calls Me
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen To Be in Love
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Take It or Lose It
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Wave
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Going Out of My Head
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Love Me
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen What a Difference a Day Makes
Dicen que soy
Released 1994- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Nunca voy a olvidarte
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Que ganas de no verte nunca más
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Ese hombre
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Dicen que soy
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen O ella o yo
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Déjate amar
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen I just want to hang around you
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen No me conviene (con Tito Nieves)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Vivir lo nuestro (con Marc Anthony)
Llegó la India Via Eddie Palmieri
Released 1992- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Vivir Sin Ti
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Llegó la India
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Soledad
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Mi Primera Rumba
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Yemaya y Ochun (Prelude)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Yemaya y Ochun
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Merengue Internacional
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Solitude
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen I Wanna Dance
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Soledad (Bilingual version)
Breaking Night
Released 1990- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Right From the Start
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Dancing on the Fire
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Breaking Night
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Lover Who Rocks You (All Night)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Steppin' Out
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen I've Got a Plan
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen When You Were Mine
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen You Should Be Lovin' Me
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Send Yourself to Me
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen I'm Through With Love
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Dancing on the Fire (extended dance mix)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Right From the Start (12'' fly mix)
Lo Mejor De India
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Vivir Lo Nuestro
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Nunca Voy a Olvidarte
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Que Ganas De No Verte Más
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Ese Hombre
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Yemaya Y Ochun
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Mi Primera Rumba
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Llego La India
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Vivir Sin Tí
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Dicen Que Soy
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen O Ella O Yo
-

Education in India: Are students failing or the system?! | Sonam Wangchuk | TEDxGateway
In this talk, Sonam Wangchuk shares his experience of bringing education reforms in the trans-Himalayan region of Ladakh, India. Sonam Wangchuk is the founder of Students' Educational & Cultural Movement of Ladakh (SECMOL). While he was doing his mechanical engineering at NIT Srinagar he understood the hardships faced by the Ladakhi students in the government schools; 95% of them were failing in their matric exams every year. Once he finished his graduation, he went back to Ladakh and started SECMOL together with some like-minded youth. After initially starting with coaching classes to help matric students, they soon realized that for a lasting solution they needed to bring reforms in the village primary schools. So they launched an education reform movement in collaboration with th... -

EIC: Sex Education in India
The health ministry of India recently suggested that sex education be banned in the country. We look at India's attitude towards sex through a "government approved" sex education lecture. This video is a work of fiction that bears no resemblance to any human being living, dead, or abstaining from sex. Do subscribe, comment, and most importantly, share the video if you liked it! Follow us on - Facebook: www.facebook.com/EastIndiaComedy - Twitter: www.twitter.com/EastIndiaComedy - Website: www.eastindiacomedy.com Director: Sapan Verma. Director of Photography: Siddharth Vasani. Writer: Azeem Banatwalla and Sapan Verma. -

Education in India - BBC
Sanjeev visits some impressive young students taking time out of their school day to help teach street children the same syllabus. That's recycled learning, Indian style, and it makes a big impression on our presenter in this BBC Worldwide video clip. -

Real Truth of Education System in India by Abhishek Mishra
Indian education system needs a change now. India has now 35,000 colleges, and 700 universities but still these colleges only produces Degree holders not engineers. Just one out of nine children finishing school joins a college. India has one of the lowest higher education enrollment ratio of 11 per cent. In the US it is 83 per cent. My thinking is that we need to provide more practical knowledge rather than just theory -"Give a man a fish and you feed him one day, teach him how to catch fishes and you feed him for a lifetime" --------------------------------------------------------------------------------- About Abhishek, Abhishek Mishra is an Indian social activist, YouTuber. He makes videos in Hindi in order to spread awareness among people. -------------------------------------... -

EIC: Education Then vs Now
Education in the 90s was very different from what it is today. Our latest sketch looks at the differences between Education then and Education now. Get awesome discount coupons and offers from CouponDunia - India's #1 Coupon Website. http://www.coupondunia.in Director: Sapan Verma Writers: Sahil, Sapan, Sorabh, Kunal, Azeem, Angad, Atul DOP: Sid Editor: Rahul Lalchandani Music: Kaizad Gherda Production: Sonali Thakker & Manish Nihalani Additional Cast: Chaitanya Chinchlikar, Nida Chakraborty, Sanika More, Rashmi Chandani, Sonali Thakker, Manish Nihalani Sound: Maxim Mendonsa Location Courtesy: Whistling Woods Follow us on: Twitter: https://twitter.com/eastindiacomedy Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/EastIndiaComedy -

India's poor education system
Subscribe to our channel http://bit.ly/AJSubscribe Subscribe to our channel http://bit.ly/AJSubscribe In India, some of the country's poorest children benefit from a quota system which allows them to go to private school. But the vast majority are forced to rely on government-run schools, where resources are almost non-existant. Al Jazeera's Prerna Suri reports on the growing calls for the government to upgrade its own education facilities. At Al Jazeera English, we focus on people and events that affect people's lives. We bring topics to light that often go under-reported, listening to all sides of the story and giving a 'voice to the voiceless.' Reaching more than 270 million households in over 140 countries across the globe, our viewers trust Al Jazeera English to keep them inform... -

My New Life: Primary Education for All in India
http://www.worldbank.org/india - In rural Rajasthan in Northern India, girls traditionally stayed at home and were sometimes married off when they are young. Things have started to change. For the first time in her life, Puja is going to school and has learned to read and write while having fun. She is making her dreams come true under the Sarva Shksha Abiyhan program which is changing the lives of girls across rural India through promoting universal primary education. Girls who have dropped out or have never been to school now have a second chance of getting an education. -

Pak Media On It's Education System Compared To India
Are you interested in the current affairs and the happenings of India & Pakistan? Want to watch an unbiased view, with minute by minute updates of the current scenario? Vande Mataram India is the right place to be! Watch Latest News Headlines 2016, Geo News Headlines 2016, India Pakistan News Headlines 2016, Aaj tak News Headlines 2016, Express News Headlines 2016, AAJ News Headlines 2016, News Updates. Please subscribe for breaking News Headlines and Updates. Forum discussions, talk shows and much more. Stay tuned For More News Subscribe Now https://goo.gl/6w8tYQ -

The big debate: Education in India vs education in abroad
How and why do students choose a foreign university over one in India? Does one really score over another? Students debate the merits of both and how to make the big choice. Don't miss the big weekly debate, on this episode of Heads Up. Watch full video: http://www.ndtv.com/video/player/heads-up/the-big-debate-education-in-india-vs-education-in-abroad/359250?yt -

Education in India: Are students failing or the system?! | Sonam Wangchuk | TEDxGateway
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 11:22
- Updated: 05 Apr 2016
- views: 21650
- published: 05 Apr 2016
- views: 21650
EIC: Sex Education in India
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:50
- Updated: 14 Jul 2014
- views: 4660991
- published: 14 Jul 2014
- views: 4660991
Education in India - BBC
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:55
- Updated: 20 May 2008
- views: 200752
- published: 20 May 2008
- views: 200752
Real Truth of Education System in India by Abhishek Mishra
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:37
- Updated: 18 May 2016
- views: 32437
- published: 18 May 2016
- views: 32437
EIC: Education Then vs Now
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:20
- Updated: 19 May 2015
- views: 1947963
- published: 19 May 2015
- views: 1947963
India's poor education system
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:12
- Updated: 03 May 2012
- views: 8945
- published: 03 May 2012
- views: 8945
My New Life: Primary Education for All in India
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:39
- Updated: 21 Feb 2014
- views: 21626
- published: 21 Feb 2014
- views: 21626
Pak Media On It's Education System Compared To India
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:03
- Updated: 25 May 2016
- views: 4944
- published: 25 May 2016
- views: 4944
The big debate: Education in India vs education in abroad
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 14:54
- Updated: 09 Mar 2015
- views: 2684
- published: 09 Mar 2015
- views: 2684
Indian Education System - an incomplete system
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 32:23
- Updated: 22 Feb 2015
- views: 13442
-

Start up India - Can our education ignite a million dreams? | C.P. Viswanath
Viswanath, portrayed the emergence of “ Karadi Path” and put forth a strong message to the august audience to give equal importance not only to foreign language but also to their native language and elaborated that understanding of the concepts is possible only through native language and innovations are extremely possible when there is strong conceptual knowledge. -

"Spaceman & Mammoth" Strives to Impact Higher Education System of India
"Spaceman & Mammoth" Strives to Impact Higher Education System of India ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ☛ Download ETV Android App: https://goo.gl/aub2D9 For Latest Updates on ETV Channels !! ☛ Visit our Official Website: http://www.etv.co.in ☛ Subscribe to Latest News -https://goo.gl/9Waw1K ☛ Subscribe to our YouTube Channel - http://bit.ly/JGOsxY ☛ Like us : https://www.facebook.com/ETVAndhraPradesh ☛ Follow us : https://twitter.com/etvandhraprades ☛ Circle us : https://goo.gl/H5cc6E ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- -

-

Education Loan : How to get an education loan in India?
An Education loan in India covers job oriented courses such as medicine, law, engineering, MBA, diploma/degree courses, CA, business management, aviation training, nursing, etc. http://www.avanse.com/education-loan -

Education is the Movement from Darkness to Light - Diya India
-

EIC Sex Education in India
-

DIGITAL INDIA WEEK - Online Education Workshop
-

-

TOP UNIVERSITY IN INDIA NEW LIFE EDUCATION ACADEMY RAICHUR
-

Start up India - Can our education ignite a million dreams? | C.P. Viswanath
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 18:25
- Updated: 14 Jul 2016
- views: 17
- published: 14 Jul 2016
- views: 17
"Spaceman & Mammoth" Strives to Impact Higher Education System of India
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:04
- Updated: 14 Jul 2016
- views: 81
- published: 14 Jul 2016
- views: 81
Sunny Leone $ex Education In India
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:16
- Updated: 13 Jul 2016
- views: 5
Education Loan : How to get an education loan in India?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:15
- Updated: 13 Jul 2016
- views: 2
- published: 13 Jul 2016
- views: 2
Education is the Movement from Darkness to Light - Diya India
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:16
- Updated: 13 Jul 2016
- views: 3
- published: 13 Jul 2016
- views: 3
EIC Sex Education in India
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:50
- Updated: 13 Jul 2016
- views: 0
- published: 13 Jul 2016
- views: 0
DIGITAL INDIA WEEK - Online Education Workshop
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:38
- Updated: 13 Jul 2016
- views: 14
- published: 13 Jul 2016
- views: 14
NDTV Dialogues: The Current State of Education in India
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 12:00
- Updated: 12 Jul 2016
- views: 6
TOP UNIVERSITY IN INDIA NEW LIFE EDUCATION ACADEMY RAICHUR
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:47
- Updated: 12 Jul 2016
- views: 0
- published: 12 Jul 2016
- views: 0
India vs Pakistan education | India gets 60K H1 visa while pak gets only 10-15 | Pak analyst
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:09
- Updated: 12 Jul 2016
- views: 90
-

Indian education system especially in Engineering has failed
I am not just complaining. I am going to see that the system changes. It may take time and more people but I believe that it will change. I appreciate and respect every teacher who is giving his 100% to help the students. Dear students, Instead of becoming intolerant towards a religion, try becoming intolerant to bad teaching in the colleges. Make sure that all the colleges do the justice to the fees that you are paying. Dear Faculty and the management of the colleges, If you really think that it is the student's responsibility to search for various resources to learn, then why should they be paying for colleges? Why should they attend the classes? I am not talking about the things that are not in the curriculum. If you still feel that students should read only the books to... -

Higher Education in India - Detailed Analysis of Past Papers CBSE NET 2016 & 2 Concepts - NEP & CBCS
Dr. Manishika Jain explains the ideas to be understood for higher education section of NET Paper 1 along with concept of CBCS and NEP. Get complete postal course at http://www.examrace.com/CBSE-UGC-NET/CBSE-UGC-NET-FlexiPrep-Program/Postal-Courses/Examrace-CBSE-UGC-NET-Paper-I-Series.htm Lectures organised in topics and subtopics: https://www.doorsteptutor.com/Exams/UGC/ For Lecure Handouts visit http://www.examrace.com/Study-Material/ or do google search "Youtube Lecture Handouts Examrace Higher Education" Have a doubt? No worries. We promptly respond to queries asked as comments. -

-

Sarokaar - Autonomy of Higher Education & Research Institutions in India
Nobel Prize winner and renowned Economist Prof. Amartya Sen recently wrote a soon to be published essay for a publication questioning the policies of the present government. Prof. Sen also accused the current dispensation for abolishing the autonomy of higher educational and research institutions. In this episode of Sarokaar we discuss the state of higher education in India in the context of Prof. Amartya Sen’s article. We try to explore whether the autonomy of higher educational institutions is in danger and whether it true that the government intervention in the autonomy of such institutions has increased; or is it a part of an older tradition of politics. It was also discussed whether the higher educational institution can be made free from government’s interference. Guests: Dr. Bakul... -

PoE - Philosophy of Education in Teacher Education Syllabi in India - Avinash Kumar
Event - International Seminar on Philosophy of Education, Bangalore Date - 25-Jan-2013 Speaker - Avinash Kumar, Student, M.A. Education, Azim Premji University, Bangalore, India Abstract - This paper investigates and attempts to answer three questions. First, what is the position of 'philosophy of education' in the syllabi of teacher education programmes in India? Second, is the way philosophy of education presently conceived and taught in teacher education programmes most conducive to the goal of developing teachers as required by National Curriculum Framework, 2005, and envisioned in National Curriculum Framework for Teacher Education, 2010? And third, can a re-conception of philosophy of education in teacher education, and a realignment of its contents and methods, assist in making t... -

-

-

Lok Sabha TV - Status of Education in India (featuring Kiran Bhatty)
-

The Crisis of Higher Education in India: How Can Public Policy and Governance Reforms Help?
(Visit: http://www.uctv.tv) The Indian higher education system is facing a crisis that is affecting its ability to build world class higher education institutions. Issues relating to quality, access and equity are some of the significant challenges .C. Raj Kumar, Vice Chancellor, O.P. Jindal Global University in India, examines these issues with a view to understanding as to how public policy, regulatory and governance reforms in higher education can help India build, nurture and develop institutions of global excellence. Recorded on 04/19/2016. Series: "Center for Studies in Higher Education" [Education] [Show ID: 30874]
Indian education system especially in Engineering has failed
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 24:09
- Updated: 07 Jan 2016
- views: 94941
- published: 07 Jan 2016
- views: 94941
Higher Education in India - Detailed Analysis of Past Papers CBSE NET 2016 & 2 Concepts - NEP & CBCS
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 27:04
- Updated: 15 Jun 2016
- views: 2936
- published: 15 Jun 2016
- views: 2936
INDIAN Education System (OLD VS TODAY) SUPERB Explanation By Rajiv Dixit
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 107:10
- Updated: 05 Sep 2012
- views: 98466
Sarokaar - Autonomy of Higher Education & Research Institutions in India
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 57:15
- Updated: 20 Jul 2015
- views: 6190
- published: 20 Jul 2015
- views: 6190
PoE - Philosophy of Education in Teacher Education Syllabi in India - Avinash Kumar
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 56:29
- Updated: 17 Oct 2013
- views: 1958
- published: 17 Oct 2013
- views: 1958
Talk: Poverty, Markets and Elementary Education in India by Prof Geetha Nambissan
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 50:08
- Updated: 17 Jun 2015
- views: 351
Social Work Education in India
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 32:25
- Updated: 05 Dec 2013
- views: 2005
Lok Sabha TV - Status of Education in India (featuring Kiran Bhatty)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 54:36
- Updated: 20 Apr 2015
- views: 459
- published: 20 Apr 2015
- views: 459
The Crisis of Higher Education in India: How Can Public Policy and Governance Reforms Help?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 61:47
- Updated: 26 May 2016
- views: 241
- published: 26 May 2016
- views: 241
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

Education in India: Are students failing or the system?! | Sonam Wangchuk | TEDxGateway
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Apr 2016
- views: 21650

EIC: Sex Education in India
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Jul 2014
- views: 4660991

Education in India - BBC
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 May 2008
- views: 200752

Real Truth of Education System in India by Abhishek Mishra
- Report rights infringement
- published: 18 May 2016
- views: 32437

EIC: Education Then vs Now
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 May 2015
- views: 1947963

India's poor education system
- Report rights infringement
- published: 03 May 2012
- views: 8945

My New Life: Primary Education for All in India
- Report rights infringement
- published: 21 Feb 2014
- views: 21626

Pak Media On It's Education System Compared To India
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 May 2016
- views: 4944

The big debate: Education in India vs education in abroad
- Report rights infringement
- published: 09 Mar 2015
- views: 2684

Indian Education System - an incomplete system
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 Feb 2015
- views: 13442
- Playlist
- Chat

Start up India - Can our education ignite a million dreams? | C.P. Viswanath
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Jul 2016
- views: 17

"Spaceman & Mammoth" Strives to Impact Higher Education System of India
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Jul 2016
- views: 81

Sunny Leone $ex Education In India
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 Jul 2016
- views: 5

Education Loan : How to get an education loan in India?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 Jul 2016
- views: 2

Education is the Movement from Darkness to Light - Diya India
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 Jul 2016
- views: 3

EIC Sex Education in India
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 Jul 2016
- views: 0

DIGITAL INDIA WEEK - Online Education Workshop
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 Jul 2016
- views: 14

NDTV Dialogues: The Current State of Education in India
- Report rights infringement
- published: 12 Jul 2016
- views: 6

TOP UNIVERSITY IN INDIA NEW LIFE EDUCATION ACADEMY RAICHUR
- Report rights infringement
- published: 12 Jul 2016
- views: 0

India vs Pakistan education | India gets 60K H1 visa while pak gets only 10-15 | Pak analyst
- Report rights infringement
- published: 12 Jul 2016
- views: 90
- Playlist
- Chat

Indian education system especially in Engineering has failed
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Jan 2016
- views: 94941

Higher Education in India - Detailed Analysis of Past Papers CBSE NET 2016 & 2 Concepts - NEP & CBCS
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Jun 2016
- views: 2936


Sarokaar - Autonomy of Higher Education & Research Institutions in India
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Jul 2015
- views: 6190

PoE - Philosophy of Education in Teacher Education Syllabi in India - Avinash Kumar
- Report rights infringement
- published: 17 Oct 2013
- views: 1958

Talk: Poverty, Markets and Elementary Education in India by Prof Geetha Nambissan
- Report rights infringement
- published: 17 Jun 2015
- views: 351

Social Work Education in India
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Dec 2013
- views: 2005

Lok Sabha TV - Status of Education in India (featuring Kiran Bhatty)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Apr 2015
- views: 459

The Crisis of Higher Education in India: How Can Public Policy and Governance Reforms Help?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 26 May 2016
- views: 241
Hillary and Jill – Jill Stein That Is – Went Up the Hill To…
Edit WorldNews.com 14 Jul 2016'Maybe the Brits are just having us on': the world reacts to Boris Johnson as foreign minister
Edit The Guardian 14 Jul 2016Are Obama and Clinton Counting on Republican Majorities to Pass TPP?
Edit CounterPunch 14 Jul 2016Trump Appears “Clueless” How He Could Win With This VP Pick
Edit WorldNews.com 13 Jul 2016Megachurch Pastor Says He'd Vote For Trump Over Jesus
Edit WorldNews.com 13 Jul 2016India vs West Indies: India coach Anil Kumble rolls his arm in the nets, watch video
Edit Indian Express 14 Jul 2016POWERGRID one of the India’s Best Companies to Work for 2016 (Power Grid Corporation of India Limited)
Edit Public Technologies 14 Jul 2016New India Investment Trust PLC - Net Asset Value(s) (New India Investment Trust plc)
Edit Public Technologies 14 Jul 2016New India Investment Trust PLC - Portfolio Disclosures (New India Investment Trust plc)
Edit Public Technologies 14 Jul 2016Smt Maneka Sanjay Gandhi meets Twitter India team to address the issue of harassment of women & children on social media platforms (Ministry of Women and Child Development of the Republic of India)
Edit Public Technologies 14 Jul 2016Max India down 5% as it trades post demerger
Edit The Times of India 14 Jul 2016Cabinet approves the facilities being extended to persons residing in India on Long Term Visa (Ministry of Home Affairs of the Republic of India)
Edit Public Technologies 14 Jul 2016India wants good ties with Pak, but 'importing' of terror big issue, says Nitin Gadkari
Edit DNA India 14 Jul 2016India Notebook Market,Mass Notebook Market,Paper Notebook Market,Stationary Market Report India
Edit Community news 14 Jul 2016India pledges $25 million in fresh aid to Afghanistan
Edit Khaama Press 14 Jul 2016Development of Multi–Modal Logistic Parks under Sagarmala Programme to benefit containerized cargo movement in India (Ministry of Shipping of the Republic of India)
Edit Public Technologies 14 Jul 2016India to take part in world football tournament for homeless
Edit The Times of India 14 Jul 2016- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »







